Introduction
This article implements an algorithm to utilize plane normal vector and direction of point to plane distance vector to determine if a point is inside a 3D convex polygon for a given polygon vertices.
This is the original C++ version, I already ported the algorithm to C# version, Java version, JavaScript version, PHP version, Python version, Perl version and Fortran.
These versions cover different programming types, from compiled language to interpreted language, all support Object Oriented programming, which makes these series portings have a clear, stable and consistent common program architecture.
A MASM Assembly version is now available, although Assembly language has no OO feature, but with the help of its STRUCT and invoke mechanism, we can use a library based architecture to make the program to have same structure with all above advanced languages. This should be the last one for this series portings.
Background
I had a chance to get a glimpse for the point cloud process in laser scanning 3D field. One problem in the field is how to separate the points with a certain geometry boundary. For example, with a given 8 cube vertices, how to get all points inside the cube.
A few approaches can be found online to solve the problem. For example, Ray Tracing, which checks if the intersects number is odd to determine if the point is inside. Cartesian coordinate transform is also used in some special cases, for example, if the boundary is a perfect cube without any distortion.
I ended up this investigation with a simple way to solve it. The idea is mainly inspired by the reference article to discuss point-plane distance: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Point-PlaneDistance.html.
Here is the question and my solution.
Question
For a given 3D convex polygon with N vertices, determine if a 3D point (x, y, z) is inside the polygon.
Solution
A 3D convex polygon has many faces, a face has a face plane where the face lies in.
A face plane has an outward normal vector, which directs to outside of the polygon.
A point to face plane distance defines a geometry vector, if the distance vector has an opposite direction with the outward normal vector, then the point is in "inside half space" of the face plane, otherwise, it is in "outside half space" of the face plane.
A point is determined to be inside of the 3D polygon if the point is in "inside half space" for all faces of the 3D convex polygon.
That is the basic idea of this algorithm.
Algorithm geometry diagram:
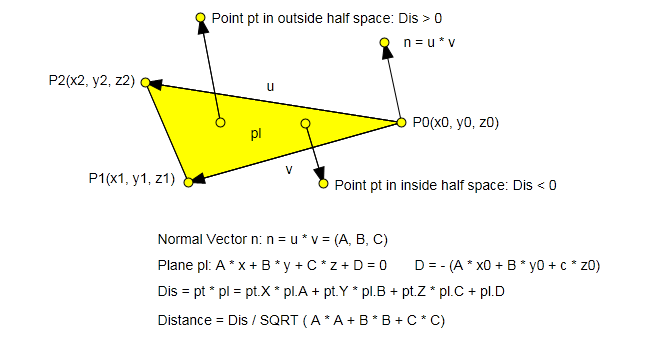
There is another question to be solved prior to utilizing the above method, we need to get face plane outward normal vectors for all faces of the polygon. Here are steps to accomplish this:
- Get any 3 vertices combinations from N vertices, which is prepared to construct a triangle plane.
- Get normal vector
n = (A, B, C) with the cross production of 2 edge vectors u and v from the 3 vertices P0, P1 and P2 triangle. The vertice P0(x0, y0, z0) is the common begin point of the 2 edge vectors. - Get the face plane with equation
A * x + B * y + C * z + D = 0. Here D = -(A * x0 + B * y0 + c * z0). - Determine if the triangle plane is a face plane with checking if all other vertices points are in the same half space of the triangle plane. This step requires the convex assumption. For a concave 3D polygon, it is not distinguished between a polygon real face and a polygon inner triangle with this rule.
- Get the face vertices with appending any other vertices that lie in the same triangle plane to these 3 vertices.
- After all, we find all faces with their outward normal vectors and their complete vertices.
Here is the essential formula:
For a point pt(X, Y, Z) and a plane pl(A, B, C, D), the sign of value (pt.X * pl.A + pt.Y * pl.B + pt.Z * pl.C + pl.D) is able to determine which half space the point is in.
Using the Code
The algorithm is wrapped into a VC++ DLL GeoProc. The main test program LASProc reads point cloud data from a LAS file, then writes all inside points into a new LAS file. A LAS file is able to be displayed with a freeware FugroViewer.
To consume the algorithm DLL, construct a polygon object first like this:
GeoPolygon polygonObj = GeoPolygon(verticesVector);
Then, construct the main process object:
GeoPolygonProc procObj = GeoPolygonProc(polygonObj);
Main procedure to check if a point (x, y, z) is inside the CubeVertices:
procObj.PointInside3DPolygon(x, y, z)
Here are the classes in the GeoProc DLL library:
The codes are almost self-evident with comments.
GeoPoint.h
#pragma once
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoPoint
{
public:
double x;
double y;
double z;
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPoint(void);
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoPoint(void);
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPoint(double x, double y, double z)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
this->z = z;
}
__declspec(dllexport) friend GeoPoint operator+(const GeoPoint& p0, const GeoPoint& p1)
{
return GeoPoint(p0.x + p1.x, p0.y + p1.y, p0.z + p1.z);
}
};
}
GeoVector.h
#pragma once
#include "GeoPoint.h"
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoVector
{
GeoPoint _p0; GeoPoint _p1;
double _x; double _y; double _z;
public:
__declspec(dllexport) GeoVector(void);
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoVector(void);
__declspec(dllexport) GeoVector(GeoPoint p0, GeoPoint p1)
{
this->_p0 = p0;
this->_p1 = p1;
this->_x = p1.x - p0.x;
this->_y = p1.y - p0.y;
this->_z = p1.z - p0.z;
}
__declspec(dllexport) friend GeoVector operator*(const GeoVector& u, const GeoVector& v)
{
double x = u._y * v._z - u._z * v._y;
double y = u._z * v._x - u._x * v._z;
double z = u._x * v._y - u._y * v._x;
GeoPoint p0 = v._p0;
GeoPoint p1 = p0 + GeoPoint(x, y, z);
return GeoVector(p0, p1);
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPoint GetP0(){return this->_p0;}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPoint GetP1(){return this->_p1;}
__declspec(dllexport) double GetX(){return this->_x;}
__declspec(dllexport) double GetY(){return this->_y;}
__declspec(dllexport) double GetZ(){return this->_z;}
};
}
GeoPlane.h
#pragma once
#include "GeoVector.h"
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoPlane
{
public:
double a;
double b;
double c;
double d;
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPlane(void);
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoPlane(void);
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPlane(double a, double b, double c, double d)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
this->c = c;
this->d = d;
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPlane(GeoPoint p0, GeoPoint p1, GeoPoint p2)
{
GeoVector v = GeoVector(p0, p1);
GeoVector u = GeoVector(p0, p2);
GeoVector n = u * v;
this->a = n.GetX();
this->b = n.GetY();
this->c = n.GetZ();
this->d = -(this->a * p0.x + this->b * p0.y + this->c * p0.z);
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPlane operator-()
{
return GeoPlane(-this->a, -this->b, -this->c, -this->d);
}
__declspec(dllexport) friend double operator*(const GeoPlane& pl, const GeoPoint& pt)
{
return (pt.x * pl.a + pt.y * pl.b + pt.z * pl.c + pl.d);
}
};
}
GeoFace.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include "GeoPoint.h"
#include "Utility.h"
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoFace
{
std::vector<GeoPoint> _pts;
std::vector<int> _idx;
int _n;
public:
__declspec(dllexport) GeoFace(void);
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoFace(void)
{
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(this->_pts);
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(this->_idx);
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoFace(std::vector<GeoPoint> pts, std::vector<int> idx)
{
this->_n = pts.size();
for(int i=0;i<_n;i++)
{
this->_pts.push_back(pts[i]);
this->_idx.push_back(idx[i]);
}
}
__declspec(dllexport) int GetN()
{
return this->_n;
}
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<int> GetI()
{
return this->_idx;
}
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<GeoPoint> GetV()
{
return this->_pts;
}
};
}
GeoPolygon.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include "GeoPoint.h"
#include "Utility.h"
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoPolygon
{
std::vector<GeoPoint> _pts;
std::vector<int> _idx;
int _n;
public:
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPolygon(void);
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoPolygon(void)
{
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(this->_pts);
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(this->_idx);
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPolygon(std::vector<GeoPoint> pts)
{
this->_n = pts.size();
for(int i=0;i<_n;i++)
{
this->_pts.push_back(pts[i]);
this->_idx.push_back(i);
}
}
__declspec(dllexport) int GetN()
{
return this->_n;
}
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<int> GetI()
{
return this->_idx;
}
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<GeoPoint> GetV()
{
return this->_pts;
}
};
}
GeoPolygonProc.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include "GeoPoint.h"
#include "GeoVector.h"
#include "GeoFace.h"
#include "GeoPlane.h"
#include "GeoPolygon.h"
#include "Utility.h"
namespace GeoProc
{
class GeoPolygonProc
{
GeoPolygon _polygon;
double _x0, _x1, _y0, _y1, _z0, _z1;
std::vector<GeoFace> _Faces;
std::vector<GeoPlane> _FacePlanes;
int _NumberOfFaces;
double _MaxDisError;
__declspec(dllexport) void GeoPolygonProc::Set3DPolygonBoundary();
__declspec(dllexport) void GeoPolygonProc::Set3DPolygonUnitError();
__declspec(dllexport) void GeoPolygonProc::SetConvex3DFaces();
public:
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPolygonProc(void) {}
__declspec(dllexport) ~GeoPolygonProc(void) {}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPolygonProc(GeoPolygon polygon)
{
this->_polygon = polygon;
Set3DPolygonBoundary();
Set3DPolygonUnitError();
SetConvex3DFaces();
}
__declspec(dllexport) GeoPolygon GetPolygon() { return _polygon; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetX0() { return this->_x0; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetX1() { return this->_x1; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetY0() { return this->_y0; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetY1() { return this->_y1; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetZ0() { return this->_z0; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetZ1() { return this->_z1; }
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<GeoFace> GetFaces() { return this->_Faces; }
__declspec(dllexport) std::vector<GeoPlane> GetFacePlanes()
{ return this->_FacePlanes; }
__declspec(dllexport) int GetNumberOfFaces() { return this->_NumberOfFaces; }
__declspec(dllexport) double GetMaxDisError() { return this->_MaxDisError; }
__declspec(dllexport) void SetMaxDisError(double value){this->_MaxDisError=value;}
__declspec(dllexport) bool GeoPolygonProc::PointInside3DPolygon(double x, double y,
double z);
};
}
Utility.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
class Utility
{
public:
Utility(void);
~Utility(void);
template<typename T>
static bool ContainsVector(std::vector<std::vector<T>>
vectorList, std::vector<T> vectorItem)
{
sort(vectorItem.begin(), vectorItem.end());
for (int i = 0; i < vectorList.size(); i++)
{
std::vector<T> temp = vectorList[i];
if (temp.size() == vectorItem.size())
{
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end());
if (equal(temp.begin(), temp.end(), vectorItem.begin()))
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
static void FreeVectorMemory(std::vector<T> &obj)
{
obj.clear();
std::vector<T>().swap(obj);
}
template<typename T>
static void FreeVectorListMemory(std::vector<std::vector<T>> &objList)
{
for(int i=0; i<objList.size(); i++)
{
objList[i].clear();
std::vector<T>().swap(objList[i]);
}
objList.clear();
std::vector<std::vector<T>>().swap(objList);
}
};
GeoPolygonProc.cpp
This is the main class for referencing the GeoProc library. It is capable of extending its functions to do more complex 3D polygon geometry processing based on the GeoProc library. The current GeoPolygonProc provides basic settings for 3D polygon boundary, face planes and faces. The particular public function PointInside3DPolygon is an example for adding other functions to solve 3D polygon problems.
SetConvex3DFaces is the essential method, it transforms the polygon presentation from a complete polygon vertice set to polygon faces and faces planes. The procedure is as given below:
- Declare a 1d
std::vector vertices to get all vertices from the given GeoPolygon object. - Declare a 2d
std::vector faceVerticeIndex, first dimension is face index, second dimension is face vertice index. - Declare a 1d
std:vector fpOutward for all face planes. - Go through all given vertices, construct a triangle plane
trianglePlane with any 3 vertices combination. - Determine if
trianglePlane is a face plane through checking if all other vertices are in the same half space. - Declare a 1d
std::vector verticeIndexInOneFace for a complete vertices indexes in one face. - Find other vertices in the same plane with the triangle plane, put them in 1d array
pointInSamePlaneIndex. - Add unique face to
faceVerticeIndex with adding the 3 triangle vertices and the other same plane vertices. - Add unique face plane to
fpOutward - Go through all faces and get all face planes and faces.
#include "math.h"
#include "GeoPolygonProc.h"
double MaxUnitMeasureError = 0.001;
namespace GeoProc
{
void GeoPolygonProc::Set3DPolygonBoundary()
{
std::vector<GeoPoint> vertices = _polygon.GetV();
int n = _polygon.GetN();
this->_x0 = vertices[0].x;
this->_x0 = vertices[0].x;
this->_y0 = vertices[0].y;
this->_y1 = vertices[0].y;
this->_z0 = vertices[0].z;
this->_z1 = vertices[0].z;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(vertices[i].x < _x0) this->_x0 = vertices[i].x;
if(vertices[i].y < _y0) this->_y0 = vertices[i].y;
if(vertices[i].z < _z0) this->_z0 = vertices[i].z;
if(vertices[i].x > _x1) this->_x1 = vertices[i].x;
if(vertices[i].y > _y1) this->_y1 = vertices[i].y;
if(vertices[i].z > _z1) this->_z1 = vertices[i].z;
}
}
void GeoPolygonProc::Set3DPolygonUnitError()
{
this->_MaxDisError = ( (fabs(_x0) + fabs(_x1) +
fabs(_y0) + fabs(_y1) +
fabs(_z0) + fabs(_z1) ) / 6 * MaxUnitMeasureError);
}
void GeoPolygonProc::SetConvex3DFaces()
{
std::vector<GeoPoint> vertices = this->_polygon.GetV();
int n = this->_polygon.GetN();
std::vector<GeoPlane> fpOutward;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> faceVerticeIndex;
for(int i=0; i< n; i++)
{
GeoPoint p0 = vertices[i];
for(int j= i+1; j< n; j++)
{
GeoPoint p1 = vertices[j];
for(int k = j + 1; k<n; k++)
{
GeoPoint p2 = vertices[k];
GeoPlane trianglePlane = GeoPlane(p0, p1, p2);
int onLeftCount = 0;
int onRightCount = 0;
int m = 0;
std::vector<int> pointInSamePlaneIndex;
for(int l = 0; l < n ; l ++)
{
if(l != i && l != j && l != k)
{
GeoPoint pt = vertices[l];
double dis = trianglePlane * pt;
if(fabs(dis) < this->_MaxDisError)
{
pointInSamePlaneIndex.push_back(l);
}
else
{
if(dis < 0)
{
onLeftCount ++;
}
else
{
onRightCount ++;
}
}
}
}
if(onLeftCount == 0 || onRightCount == 0)
{
std::vector<int> faceVerticeIndexInOneFace;
faceVerticeIndexInOneFace.push_back(i);
faceVerticeIndexInOneFace.push_back(j);
faceVerticeIndexInOneFace.push_back(k);
for(int p = 0; p < pointInSamePlaneIndex.size(); p ++)
{
faceVerticeIndexInOneFace.push_back(pointInSamePlaneIndex[p]);
}
if(!Utility::ContainsVector
(faceVerticeIndex, faceVerticeIndexInOneFace))
{
faceVerticeIndex.push_back(faceVerticeIndexInOneFace);
if(onRightCount == 0)
{
fpOutward.push_back(trianglePlane);
}
else if (onLeftCount == 0)
{
fpOutward.push_back(-trianglePlane);
}
}
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(faceVerticeIndexInOneFace);
}
else
{
}
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(pointInSamePlaneIndex);
} } }
this->_NumberOfFaces = faceVerticeIndex.size();
for(int i = 0; i<this->_NumberOfFaces; i++)
{
this->_FacePlanes.push_back(GeoPlane(fpOutward[i].a, fpOutward[i].b,
fpOutward[i].c, fpOutward[i].d));
std::vector<GeoPoint> v;
std::vector<int> idx;
int count = faceVerticeIndex[i].size();
for(int j = 0; j< count; j++)
{
idx.push_back(faceVerticeIndex[i][j]);
v.push_back(GeoPoint(vertices[ idx[j] ].x,
vertices[ idx[j] ].y,
vertices[ idx[j] ].z));
}
this->_Faces.push_back(GeoFace(v, idx));
}
Utility::FreeVectorMemory(fpOutward);
Utility::FreeVectorListMemory<int>(faceVerticeIndex);
}
bool GeoPolygonProc::PointInside3DPolygon(double x, double y, double z)
{
GeoPoint pt = GeoPoint(x, y, z);
for (int i=0; i < this->GetNumberOfFaces(); i++)
{
double dis = this->GetFacePlanes()[i] * pt;
if(dis > 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Here is the LAS Process program with using GeoProc DLL library:
LASProc.cpp
#include <tchar.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "GeoPolygonProc.h"
using namespace GeoProc;
GeoPolygonProc GetProcObj()
{
GeoPoint CubeVerticesArray[8] =
{
GeoPoint(-27.28046, 37.11775, -39.03485),
GeoPoint(-44.40014, 38.50727, -28.78860),
GeoPoint(-49.63065, 20.24757, -35.05160),
GeoPoint(-32.51096, 18.85805, -45.29785),
GeoPoint(-23.59142, 10.81737, -29.30445),
GeoPoint(-18.36091, 29.07707, -23.04144),
GeoPoint(-35.48060, 30.46659, -12.79519),
GeoPoint(-40.71110, 12.20689, -19.05819)
};
std::vector<GeoPoint> verticesVector( CubeVerticesArray,
CubeVerticesArray + sizeof(CubeVerticesArray) / sizeof(GeoPoint) );
GeoPolygon polygonObj = GeoPolygon(verticesVector);
GeoPolygonProc procObj = GeoPolygonProc(polygonObj);
return procObj;
}
void ProcLAS(GeoPolygonProc procObj)
{
std::ifstream rbFile;
rbFile.open("..\\LASInput\\cube.las",std::ios::binary|std::ios::in);
std::fstream wbFile;
wbFile.open("..\\LASOutput\\cube_inside.las",std::ios::binary|std::ios::out);
std::ofstream wtFile;
wtFile.open("..\\LASOutput\\cube_inside.txt",std::ios::out);
wtFile.precision(4);
unsigned long offset_to_point_data_value;
unsigned long variable_len_num;
unsigned char record_type_c;
unsigned short record_len;
unsigned long record_num;
double x_scale, y_scale, z_scale;
double x_offset, y_offset, z_offset;
rbFile.seekg(96);
rbFile.read ((char *)&offset_to_point_data_value, 4);
rbFile.read ((char *)&variable_len_num, 4);
rbFile.read ((char *)&record_type_c, 1);
rbFile.read ((char *)&record_len, 2);
rbFile.read ((char *)&record_num, 4);
rbFile.seekg(131);
rbFile.read ((char *)&x_scale, 8);
rbFile.read ((char *)&y_scale, 8);
rbFile.read ((char *)&z_scale, 8);
rbFile.read ((char *)&x_offset, 8);
rbFile.read ((char *)&y_offset, 8);
rbFile.read ((char *)&z_offset, 8);
char *bufHeader = (char *)malloc(offset_to_point_data_value);
rbFile.seekg(0);
rbFile.read(bufHeader, offset_to_point_data_value);
wbFile.write(bufHeader, offset_to_point_data_value);
double x, y, z; long xi, yi, zi;
int insideCount = 0;
char *bufRecord = (char *)malloc(record_len);
for(unsigned int i=0;i<record_num;i++)
{
int record_loc = offset_to_point_data_value + record_len * i;
rbFile.seekg(record_loc);
rbFile.read ((char *)&xi, 4);
rbFile.read ((char *)&yi, 4);
rbFile.read ((char *)&zi, 4);
x = (xi * x_scale) + x_offset;
y = (yi * y_scale) + y_offset;
z = (zi * z_scale) + z_offset;
if( x>procObj.GetX0() && x<procObj.GetX1() &&
y>procObj.GetY0() && y<procObj.GetY1() &&
z>procObj.GetZ0() && z<procObj.GetZ1())
{
if(procObj.PointInside3DPolygon(x, y, z))
{
wtFile << std::fixed << x << " " <<
std::fixed << y << " " << std::fixed
<< z << std::endl;
rbFile.seekg(record_loc);
rbFile.read(bufRecord, record_len);
wbFile.write(bufRecord, record_len);
insideCount++;
}
}
}
wbFile.seekp(107);
wbFile.write((char *)&insideCount, 4);
rbFile.close();
wbFile.close();
wtFile.close();
free(bufHeader);
free(bufRecord);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
GeoPolygonProc procObj = GetProcObj();
ProcLAS(procObj);
return 0;
}
GeoProcTest.cpp
The test project is to ensure all functions in GeoProc DLL library works.
#include <tchar.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "GeoPolygonProc.h"
using namespace GeoProc;
GeoPoint p1 = GeoPoint( - 27.28046, 37.11775, - 39.03485);
GeoPoint p2 = GeoPoint( - 44.40014, 38.50727, - 28.78860);
GeoPoint p3 = GeoPoint( - 49.63065, 20.24757, - 35.05160);
GeoPoint p4 = GeoPoint( - 32.51096, 18.85805, - 45.29785);
GeoPoint p5 = GeoPoint( - 23.59142, 10.81737, - 29.30445);
GeoPoint p6 = GeoPoint( - 18.36091, 29.07707, - 23.04144);
GeoPoint p7 = GeoPoint( - 35.48060, 30.46659, - 12.79519);
GeoPoint p8 = GeoPoint( - 40.71110, 12.20689, - 19.05819);
GeoPoint verticesArray[8] = { p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8 };
std::vector<GeoPoint> verticesVector( verticesArray,
verticesArray + sizeof(verticesArray) / sizeof(GeoPoint) );
GeoPolygon polygon = GeoPolygon(verticesVector);
void GeoPoint_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoPoint Test:" << std::endl;
GeoPoint pt = p1 + p2;
std::cout << pt.x << ", " <<
pt.y << ", " << pt.z << std::endl;
}
void GeoVector_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoVector Test:" << std::endl;
GeoVector v1 = GeoVector(p1, p2);
GeoVector v2 = GeoVector(p1, p3);
GeoVector v3 = v2 * v1;
std::cout << v3.GetX() << ", " <<
v3.GetY() << ", " << v3.GetZ() << std::endl;
}
void GeoPlane_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoPlane Test:" << std::endl;
GeoPlane pl = GeoPlane(p1, p2, p3);
std::cout << pl.a << ", " << pl.b << ",
" << pl.c << ", " << pl.d << std::endl;
pl = GeoPlane(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0);
std::cout << pl.a << ", " << pl.b << ",
" << pl.c << ", " << pl.d << std::endl;
pl = -pl;
std::cout << pl.a << ", " << pl.b << ",
" << pl.c << ", " << pl.d << std::endl;
double dis = pl * GeoPoint(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
std::cout << dis << std::endl;
}
void GeoPolygon_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoPolygon Test:" << std::endl;
std::vector<int> idx = polygon.GetI();
std::vector<GeoPoint> v = polygon.GetV();
for(int i=0; i<polygon.GetN(); i++)
{
std::cout << idx[i] << ": (" << v[i].x << ",
" << v[i].y << ", "
<< v[i].z << ")" << std::endl;
}
}
void GeoFace_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoFace Test:" << std::endl;
GeoPoint faceVerticesArray[4] = { p1, p2, p3, p4 };
std::vector<GeoPoint> faceVerticesVector( faceVerticesArray,
faceVerticesArray + sizeof(faceVerticesArray) / sizeof(GeoPoint) );
int faceVerticeIndexArray[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
std::vector<int> faceVerticeIndexVector( faceVerticeIndexArray,
faceVerticeIndexArray + sizeof(faceVerticeIndexArray) / sizeof(int) );
GeoFace face = GeoFace(faceVerticesVector, faceVerticeIndexVector);
std::vector<int> idx = face.GetI();
std::vector<GeoPoint> v = face.GetV();
for(int i=0; i<face.GetN(); i++)
{
std::cout << idx[i] << ": (" << v[i].x << ",
" << v[i].y << ", "
<< v[i].z << ")" << std::endl;
}
}
void Utility_Test()
{
std::cout << "Utility Test:" << std::endl;
int arr1[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
std::vector<int> arr1Vector( arr1, arr1 + sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(int) );
int arr2[4] = { 4, 5, 6, 7 };
std::vector<int> arr2Vector( arr2, arr2 + sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(int) );
std::vector<std::vector<int>> vector_2d;
vector_2d.push_back(arr1Vector);
vector_2d.push_back(arr2Vector);
int arr3[4] = { 2, 3, 1, 4 };
std::vector<int> arr3Vector( arr3, arr3 + sizeof(arr3) / sizeof(int) );
int arr4[4] = { 2, 3, 1, 5 };
std::vector<int> arr4Vector( arr4, arr4 + sizeof(arr4) / sizeof(int) );
bool b1 = Utility::ContainsVector(vector_2d, arr3Vector);
bool b2 = Utility::ContainsVector(vector_2d, arr4Vector);
std::cout << b1 << ", " << b2 << std::endl;
std::cout << arr1Vector.size() << std::endl;
Utility::FreeVectorMemory<int>(arr1Vector);
std::cout << arr1Vector.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << vector_2d.size() << std::endl;
Utility::FreeVectorListMemory<int>(vector_2d);
std::cout << vector_2d.size() << std::endl;
}
void GeoPolygonProc_Test()
{
std::cout << "GeoPolygonProc Test:" << std::endl;
GeoPolygonProc procObj = GeoPolygonProc(polygon);
std::cout << procObj.GetX0() << ", " <<
procObj.GetX1() << ", " <<
procObj.GetY0() << ", " <<
procObj.GetY1() << ", " <<
procObj.GetZ0() << ", " <<
procObj.GetZ1() << ", " << std::endl;
std::cout << procObj.GetMaxDisError() << std::endl;
procObj.SetMaxDisError(0.0125);
std::cout << procObj.GetMaxDisError() << std::endl;
int count = procObj.GetNumberOfFaces();
std::vector<GeoPlane> facePlanes = procObj.GetFacePlanes();
std::vector<GeoFace> faces = procObj.GetFaces();
std::cout << count << std::endl;
std::cout << "Face Planes:" << std::endl;
for(int i=0; i<count; i++)
{
std::cout << facePlanes[i].a << ", " <<
facePlanes[i].b << ", " <<
facePlanes[i].a << ", " <<
facePlanes[i].d << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "Faces:" << std::endl;
for(int i=0; i<count; i++)
{
std::cout << "Face #" << i + 1 << " :" <<std::endl;
GeoFace face = faces[i];
std::vector<int> idx = face.GetI();
std::vector<GeoPoint> v = face.GetV();
for(int i=0; i<face.GetN(); i++)
{
std::cout << idx[i] << ": (" << v[i].x << ",
" << v[i].y << ", "
<< v[i].z << ")" << std::endl;
}
}
GeoPoint insidePoint = GeoPoint( - 28.411750, 25.794500, - 37.969000);
GeoPoint outsidePoint = GeoPoint( - 28.411750, 25.794500, - 50.969000);
bool b1 = procObj.PointInside3DPolygon(insidePoint.x, insidePoint.y, insidePoint.z);
bool b2 = procObj.PointInside3DPolygon(outsidePoint.x, outsidePoint.y, outsidePoint.z);
std::cout << b1 << ", " << b2 << std::endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
GeoPoint_Test();
GeoVector_Test();
GeoPlane_Test();
GeoPolygon_Test();
GeoFace_Test();
Utility_Test();
GeoPolygonProc_Test();
}
Here is the test project output:
GeoPoint Test:
-71.6806, 75.625, -67.8234
GeoVector Test:
-178.391, 160.814, -319.868
GeoPlane Test:
-178.391, 160.814, -319.868, -23321.6
1, 2, 3, 4
-1, -2, -3, -4
-18
GeoPolygon Test:
0: (-27.2805, 37.1178, -39.0348)
1: (-44.4001, 38.5073, -28.7886)
2: (-49.6307, 20.2476, -35.0516)
3: (-32.511, 18.858, -45.2978)
4: (-23.5914, 10.8174, -29.3044)
5: (-18.3609, 29.0771, -23.0414)
6: (-35.4806, 30.4666, -12.7952)
7: (-40.7111, 12.2069, -19.0582)
GeoFace Test:
1: (-27.2805, 37.1178, -39.0348)
2: (-44.4001, 38.5073, -28.7886)
3: (-49.6307, 20.2476, -35.0516)
4: (-32.511, 18.858, -45.2978)
Utility Test:
1, 0
4
0
2
0
GeoPolygonProc Test:
-49.6307, -18.3609, 10.8174, 38.5073, -45.2978, -12.7952,
0.0292349
0.0125
6
Face Planes:
-178.391, 160.814, -178.391, -23321.6
104.61, 365.194, 104.61, -5811.87
342.393, -27.7904, 342.393, 2372.96
-342.394, 27.7906, -342.394, -10373
-104.61, -365.194, -104.61, -2188.14
178.391, -160.814, 178.391, 15321.6
Faces:
Face #1 :
0: (-27.2805, 37.1178, -39.0348)
1: (-44.4001, 38.5073, -28.7886)
2: (-49.6307, 20.2476, -35.0516)
3: (-32.511, 18.858, -45.2978)
Face #2 :
0: (-27.2805, 37.1178, -39.0348)
1: (-44.4001, 38.5073, -28.7886)
5: (-18.3609, 29.0771, -23.0414)
6: (-35.4806, 30.4666, -12.7952)
Face #3 :
0: (-27.2805, 37.1178, -39.0348)
3: (-32.511, 18.858, -45.2978)
4: (-23.5914, 10.8174, -29.3044)
5: (-18.3609, 29.0771, -23.0414)
Face #4 :
1: (-44.4001, 38.5073, -28.7886)
2: (-49.6307, 20.2476, -35.0516)
6: (-35.4806, 30.4666, -12.7952)
7: (-40.7111, 12.2069, -19.0582)
Face #5 :
2: (-49.6307, 20.2476, -35.0516)
3: (-32.511, 18.858, -45.2978)
4: (-23.5914, 10.8174, -29.3044)
7: (-40.7111, 12.2069, -19.0582)
Face #6 :
4: (-23.5914, 10.8174, -29.3044)
5: (-18.3609, 29.0771, -23.0414)
6: (-35.4806, 30.4666, -12.7952)
7: (-40.7111, 12.2069, -19.0582)
1, 0
Points of Interest
The algorithm does not need time consuming math computing, i.e., triangle function, square root, etc. Its performance is good. Although the algorithm is not suitable for a 3D concave polygon in a whole way, but if you can provide all face outward normal vector for a 3D concave polygon in some way, i.e., manually, then the algorithm is still feasible in a half way.
History
January 21st, 2016: Third version date
- Added a new project
GeoProcTest to test all functions in GeoProc DLL library - Prefixed all vector with
std:: and removed all using namespace std - Fixed a bug in function
FreeVectorMemory and FreeVectorListMemory with passing reference as argument to modify them inside the functions
January 19th, 2016: Second version date
- Used STL
std::vector to replace the new operator for dynamic array allocation. std::vector has a few advantages regarding how to manipulate array. It does not need a size to allocate array, while new operator does; It is capable of accessing array by index, while std::list cannot. - Removed the VC++ Precompiled Header to minimize the Windows dependency
- Used STL file stream functions, i.e.,
ifstream, seekg, read, etc. to replace C library functions, i.e., FILE, fread, fwrite, etc. in the LAS file read-write process
December 19th, 2015: Initial version date
Reference
