Introduction
This article will help you to understand designing a project with the help of repository pattern, Entity Framework, Web API, SQL Server 2012, Unit of Work Testing in ASP.NET MVC applications. We are developing a sample Book keeping solution project for a Book entity and Author enitity on which we can do Create, Read, Update and Delete operations.
This project will consist of five(5) interdependent sub projects once we complete.
Outcomes of this project as a summary
- This will helps you to develop/design a project in a multilayered approch
- How to define a Primary Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
- How to define a property with decimal datatype and insert values to it in Code First Approach
- How to define a Foriegn Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
- How to define an Unique Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
- How to install entity framework for a project
- Project Level example of OOP - Method Overloading
- Populate custom dropdown list and bind using Model
- Create customize URI for Web API method.
- How to return a decimal values as the response of Web API method.
- How to configure overloading Web API methods that can send multiple parameters.
- How to call a WebAPI Controller endpoint from MVC.
- How to bind dropdown values in different ways in controller
- How to bind dropdowns in Create/Edit View in Non StronglyType way and Strongly Type way
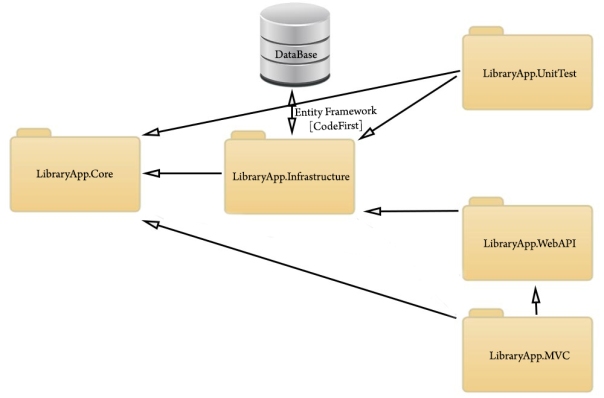
Architecture
This image contains the project listing in solution explorer after we complete the project.

1. LibraryApp.Core - Entities and Interfaces
Class Library - In this project we are including
- Entities
- Interface
Basically we may have two entities which are Book and Author. We can use this project for domain entities and interfaces for database operations. According to project requirements we can keep any upcoming Entity or Interface here.
2. LibraryApp.Infrastructure - Business Logics and Database Configurations
Class Library - In this project we are definning
- Database Configuarations
We can refer our connectionstring for database connection and other database configuarations
- Database Operations
Repositories - we're defining here database operations of Infromations/Entities/Objecs we're dealing with in Core Project. For each entity we can create seperate class file as a repository or we can include all operations in a single repository class.
- Libraries
What libraries we're going to use perform database operations. Such as Entity Framework Library or Dapper (Micro ORM) or any other technology.
3. LibraryApp.UnitTest - Unit of Work Test
Unit Test - In this project we are observing
Unit testing for infrastructure project repositories. We can verify that all the code which we wrote in the infrastructure project is behaving properly , if they work as we expected we can assure that infrastrcuture project will behave properly in Web Service Project.
4. LibraryApp.WebAPI - Web Service
Web API - In this project we are publishing
By instantiating and referencing our previous infrastructure project in this project, and with some configurations we can publish all the operations which are included in infrastructure project as web services. Here we are publishing those as HTTP methods. We identify those HTTP methods as APIController methods.
We're using this project as the bridge between Server and Client
Server Side
LibraryApp.Core
LibraryApp.Infrastructure
Bridge
LibraryApp.WebAPI
Client Side
LibraryApp.MVC
Once we publish these database operations, we can use those to create the frontend, as a web (ASP.NET MVC or WebForm) applicaton, mobile application or desktop application.
5. LibraryApp.MVC - Frond End
ASP.NET MVC 5 - In this project we are performing
As mentioned above, in this project, we are creating front end client application as a web application. Here we use ASP.NET MVC 5 and Bootstrap for our task.
Furthermore, following Image explains how each of above single projects interact with each other
Operations
- Books with Authors List Main Dashboard
- Authors List Dashboard
- Create a Book
- Edit a Book
- Delete a Book
- Create an Author
- Edit an Author
- Delete an Author
Operations in this project depict here
Main Dashboard - Booklist with Authors

Authors Dashboard - Authors List

Create a Book

Edit a Book

Create an Author

Edit an Author

Database
We develop this project using Enitiy Framwork Code First Approach, After project completion, database structure will look like following.
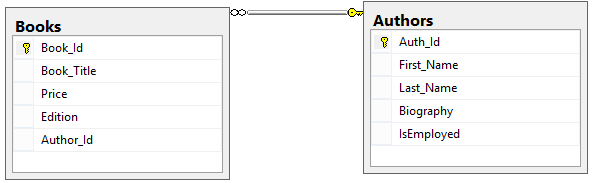
Specifications
In these tables IDs defined with Primary Key Constraint and INT datatype , here you will get the knowelege How to define a Primary Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
All the names and titles defined as NVARCHAR fields then any language and alphanumeric charachters will be able to be inserted here. Here I stored some data in Sinhala Language.
Implementation
From here on, I'll be explaining how to implement above project in code level, step by step.
Steps for LibraryApp.Core
1. Create Empty C# Class Library Project , Name it as "ProjectName.Core"
2. By right clicking that project solution, insert two(2) new folders as "Entities" and "Interfaces"
3. Now Create Class Files inside Entities folder for Entities/Object we want to be included
Book.cs
We are keeping Book table's Price here as a decimal value, then you will get the knowelege How to define a property with decimal datatype in Code First Approach
Book table's Author_Id will act as Foriegn Key to store Author Id. Follow this article to get to know more about How to Define a Foriegn Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
public class Book
{
public Book()
{
}
[Key]
public int Book_Id { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Book_Title { get; set; }
[DataType("decimal(16 ,3")]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public string Edition { get; set; }
[ForeignKey("Author")]
public int Author_Id { get; set; }
public Author Author { get; set; }
}
Author.cs
Author table's Last_Name column is built with Unique Key constraint. Follow this article to get to know more about How to Define an Unique Key for a property of a class in Code First Approach
public class Author
{
public Author()
{
}
[Key]
public int Auth_Id { get; set; }
[StringLength(50)]
public string First_Name { get; set; }
[Index("IX_FirstAndSecond", 1, IsUnique = true)]
[StringLength(50)]
public string Last_Name { get; set; }
public string Biography { get; set; }
[StringLength(1)]
[Column(TypeName = "char")]
public string IsEmployed { get; set; }
public ICollection<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
As you have already seen in the operations images, we may have few drop downs, hence in order to bind values to those drop downs we use another entity here as Basic
Basic.cs
public class Basic
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string NAME { get; set; }
}
In our Dashboard view we have some diffrent properties other than main entities, so for that, here we are using another entity as BookWithAuthor
BookWithAuthor.cs
public class BookWithAuthor
{
public int BookWithAuthor_Id { get; set; }
public string BookWithAuthor_Title { get; set; }
public string BookWithAuthor_AuthorName { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public string Edition { get; set; }
}
Now we are moving to create interfaces in Interfaces folder in Core project
IBookRepository.cs
public interface IBookRepository
{
void AddBook(Book book);
void EditBook(Book book);
void RemoveBook(int Book_Id);
IEnumerable<Book> GetBooks();
Book FindBookById(int Book_Id);
}
IAuthorRepository.cs
public interface IAuthorRepository
{
void AddAuthor(Author author);
void EditAuthor(Author author);
void RemoveAuthor(int Id);
IEnumerable<Author> GetAuthors();
Author FindAuthorById(int Id);
}
IBasic.cs
public interface IBasic
{
IEnumerable<Basic> GetAuthorsIdName();
IEnumerable<Basic> GetEditionIdName();
IEnumerable<Basic> GetEmplyeeStatusIdName(); }
IBooksWithAuthorsRepository.cs
public interface IBooksWithAuthorsRepository
{
IEnumerable<BookWithAuthor> GetBooksWithAuthors();
BookWithAuthor FindBooksWithAuthorsById(int BookWithAuthor_Id); }
After the end of this basement , solution will look like following

Steps for LibraryApp.Infrastructure
1. Create Empty C# Class Library Project , Name it as "ProjectName.Infrastructure"
2. By right clicking that project solution or using package manager console, Install Entity Framwork. Follow this article to get to know more about How to Install Entity Framwork
3. Give the System.Data.Entity Reference in References
4. Give the LibraryApp.Core Reference in References
5. Define connectionstring in App.Config
App.Config
Once we install Entity Framework, we can see App.Config file created in this project. After </configSections> tag we insert this connection string , Remember : we are using same connection string throughout rest of three(3) projects
<connectionStrings>
<add name="libraryappconnectionstring" connectionString="Data Source=.\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=LibraryAppDB;Integrated Security=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
6. Now Create Context Class File to define database configuarations
LibraryContext.cs
We refer connection string in web.config here, and the tables what need to be generated in database
public class LibraryContext : DbContext
{
public LibraryContext() : base("name=libraryappconnectionstring") {
}
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
public DbSet<Author> Authors { get; set; }
}
7. Implement the methods in repository classes, declared in interfaces
As I previously mentioned you can create separate repository for each entity or add every operation in single repository like this.
LibraryRepository.cs
This is the most important class in whole project since we operate Business Logic . Simply what details to be display and what/how operations goin to be performed.
In this repository class we inherit all the interfaces we included in Core project, then we can implement those methods we declared in the interfaces.
Here I used Linq to SQL approach with Entity Frameworks for perform our operations.
public class LibraryRepository : IBookRepository,
IAuthorRepository,
IBooksWithAuthorsRepository,
IBasic
{
LibraryContext context = new LibraryContext();
#region //-----------Books with Authors
public IEnumerable<BookWithAuthor> GetBooksWithAuthors()
{
var bookswithauthors = (
from book in context.Books
join author in context.Authors
on book.Author_Id equals author.Auth_Id
select new BookWithAuthor
{
BookWithAuthor_Id = book.Book_Id,
BookWithAuthor_Title = book.Book_Title,
BookWithAuthor_AuthorName = author.First_Name + " " + author.Last_Name,
Edition = book.Edition,
Price = book.Price
}).ToList();
return bookswithauthors;
}
public BookWithAuthor FindBooksWithAuthorsById(int BookWithAuthor_Id)
{
var bookwithauthor = (
from book in context.Books
join author in context.Authors
on book.Author_Id equals author.Auth_Id
where book.Book_Id == BookWithAuthor_Id
select new BookWithAuthor
{
BookWithAuthor_Id = book.Book_Id,
BookWithAuthor_Title = book.Book_Title,
BookWithAuthor_AuthorName = author.First_Name + " " + author.Last_Name,
Edition = book.Edition,
Price = book.Price
}).FirstOrDefault();
return bookwithauthor;
}
#endregion
#region //-----------Books
public void AddBook(Book book)
{
context.Books.Add(book);
context.SaveChanges();
}
public void EditBook(Book book)
{
context.Entry(book).State = System.Data.Entity.EntityState.Modified;
context.SaveChanges();
}
public Book FindBookById(int Book_Id)
{
var c = (from r in context.Books where r.Book_Id == Book_Id select r).FirstOrDefault();
return c;
}
public IEnumerable<Book> GetBooks()
{
return context.Books;
}
public void RemoveBook(int Book_Id)
{
Book book = context.Books.Find(Book_Id);
context.Books.Remove(book);
context.SaveChanges();
}
public decimal findBookPrice(int? book_id)
{
var bookprice = (
from r in context.Books
where r.Book_Id == book_id
select r.Price
).FirstOrDefault();
return bookprice;
}
public decimal findBookPrice(int? book_id, string bookname)
{
var bookprice = (
from book in context.Books
where book.Book_Id == book_id | book.Book_Title == bookname
select book.Price
).FirstOrDefault();
return bookprice;
}
#endregion
#region //-----------Authors
public void AddAuthor(Author author)
{
context.Authors.Add(author);
context.SaveChanges();
}
public void EditAuthor(Author author)
{
context.Entry(author).State = System.Data.Entity.EntityState.Modified;
context.SaveChanges();
}
public Author FindAuthorById(int Author_Id)
{
var c = (from r in context.Authors where r.Auth_Id == Author_Id select r).FirstOrDefault();
return c;
}
public IEnumerable<Author> GetAuthors()
{
return context.Authors;
}
public void RemoveAuthor(int Author_Id)
{
Author author = context.Authors.Find(Author_Id);
context.Authors.Remove(author);
context.SaveChanges();
}
#endregion
#region //-----------DropDowns
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetAuthorsIdName()
{
var authoridname = (
from author in context.Authors
select new Basic
{
ID = author.Auth_Id,
NAME = author.First_Name + " " + author.Last_Name
}).ToList();
return authoridname;
}
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEditionIdName()
{
return new List<Basic>(new[]
{
new Basic()
{
ID = 1,
NAME = "1st Edition"
},
new Basic()
{
ID = 2,
NAME = "2nd Edition"
}
});
}
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEmplyeeStatusIdName()
{
return new List<Basic>(new[]
{
new Basic()
{
ID = 1,
NAME = "Y"
},
new Basic()
{
ID = 2,
NAME = "N"
}
});
}
#endregion
}
8. Initiate database by inserting sample data from code first approach
LibraryDbInitalize.cs
public class LibraryDbInitalize : DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges<LibraryContext>
{
protected override void Seed(LibraryContext context)
{
context.Authors.Add
(
new Author
{
Auth_Id = 1,
First_Name = "Author FirstName 001",
Last_Name = "Author LastName 001",
Biography = "Author 1st Bio",
IsEmployed = "Y"
}
);
context.Books.Add
(
new Book
{
Book_Id = 1,
Book_Title = "Book Title 001",
Edition = "1st Edition",
Price = 40.0M, Author_Id = 1
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
base.Seed(context);
}
}
End of this LibraryApp.Infrastructure project, structure will look like below

Now we are going test our methods which are implemented in repository class
Steps for LibraryApp.UnitTest
1. Create Empty C# Unit Test Project , Name it as "ProjectName.UnitTest"
2. Add connectionstring in app.config file like above project
3. Give the LibraryApp.Core and LibraryApp.Infrastructure References in References
4. By right clicking that project solution, insert a class and name it as "ProjectNameRepositoryTest"
LibraryRepositoryTest.cs
public class LibraryRepositoryTest
{
LibraryRepository Repo;
[TestInitialize]
public void TestSetup()
{
LibraryDbInitalize db = new LibraryDbInitalize();
System.Data.Entity.Database.SetInitializer(db);
Repo = new LibraryRepository();
}
#region Author
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryInitalizeWithValidNumberOfData_Author()
{
var result = Repo.GetAuthors();
Assert.IsNotNull(result);
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(1, numberOfRecords);
}
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryAddsAuthor()
{
Author productToInsert = new Author
{
Auth_Id = 4,
First_Name = "Author FirstName 004",
Last_Name = "Author LastName 004",
Biography = "Author 4th Bio"
};
Repo.AddAuthor(productToInsert);
var result = Repo.GetAuthors();
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(2, numberOfRecords);
}
#endregion
#region Book
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryInitalizeWithValidNumberOfData_Book()
{
var result = Repo.GetBooksWithAuthors();
Assert.IsNotNull(result);
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(1, numberOfRecords);
}
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryAddsBook()
{
Book productToInsert = new Book
{
Book_Id = 4,
Book_Title = "Book Title 004",
Price = 9.00M,
Edition = "4th Edition",
Author_Id = 1
};
Repo.AddBook(productToInsert);
var result = Repo.GetBooks();
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(2, numberOfRecords);
}
#endregion
#region Books with Author
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryInitalizeWithValidNumberOfData_BooksWithAuthor()
{
var result = Repo.GetBooksWithAuthors();
Assert.IsNotNull(result);
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(1, numberOfRecords);
}
#endregion
#region DropDowns
[TestMethod]
public void IsRepositoryInitalizeWithValidNumberOfData_AuthorDropDown()
{
var result = Repo.GetAuthorsIdName();
Assert.IsNotNull(result);
var numberOfRecords = result.ToList().Count;
Assert.AreEqual(1, numberOfRecords);
}
#endregion
}
Here I wrote only few test cases, Like above, you can write test cases for all the methods you need to test before going to client side.
5. Then run the Test by going Test > Run > All Tests
If all tests passed, you will see screen like following in Test Explorer
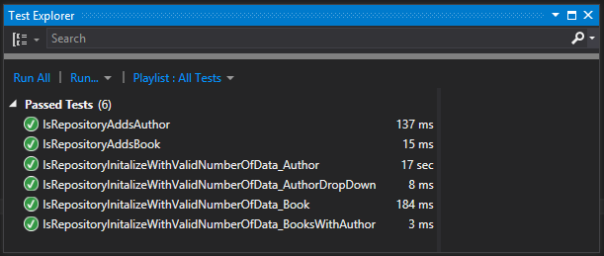
After end of this LibraryApp.UnitTest Project, structure will look like following

Now lets publish tested methods as HTTP methods in our LibraryApp.WebAPI project
Steps for LibraryApp.WebAPI
1. Create Empty C# Web API Project , Name it as "ProjectName.WebAPI"
2. By right clicking that project solution or using package manager console Install Entity Framwork.
3. Add connectionstring in web.config file like above project
4. Give the References to following libraries
System.Data.Entity
LibraryApp.Core
LibraryApp.Infrastructure
5. Add connectionstring in web.config file like above project
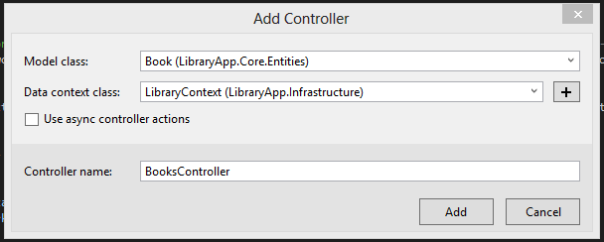
6. By right clicking controller folder of this project insert controllers
BooksController.cs
Select "Web API 2 Controller with actions, using Entity Framework"

Select the Data context class for now, we are selecting "LibraryContext" which we created in LibraryApp.Infrastructure. Later, we're going to change this.
Select the Model Class, that we created in LibraryApp.Core
As Controller name you can give any name here.
After above steps, Apicontroller automatically generates its methods like below , it is built with strongly coupled archiecture. Since it is initiating LibraryContext class.
BooksController.cs
public class BooksController : ApiController
{
private LibraryContext db = new LibraryContext();
public IQueryable<Book> GetBooks()
{
return db.Books;
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult GetBook(int id)
{
Book book = db.Books.Find(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(book);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public IHttpActionResult PutBook(int id, Book book)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (id != book.Book_Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
db.Entry(book).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
db.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!BookExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return StatusCode(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult PostBook(Book book)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.Books.Add(book);
db.SaveChanges();
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = book.Book_Id }, book);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult DeleteBook(int id)
{
Book book = db.Books.Find(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.Books.Remove(book);
db.SaveChanges();
return Ok(book);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
db.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private bool BookExists(int id)
{
return db.Books.Count(e => e.Book_Id == id) > 0;
}
}
Since we used scaffolding in visual studio, it is creating object of LibraryContext class to perform our operations, But we dont want LibraryContext class in Web API project , LibraryContext inherit from DbContext , it belongs to System.Data.Entity which is a component of Entity Framework
If we have anything of Entity Framework in our MVC(Client) project, then we are directly tightly couplling our UI and Database technolgoy.
But in our case, if we use LibraryContext then we're going to use component of Entity Framework on our Web API project, which is a partially tightly coupling scenario The reason been, we connect Web API project with MVC front end project.
We need to make our project completely away from tightly coupling, So to perform our operations, we already have Repository class in Infrastructure project, we can use it.
We need to change above strongly coupled architecture to loosly coupled architecture, so for that we are changing above code like below.
BooksController.cs
public class BooksController : ApiController
{
private LibraryRepository db = new LibraryRepository();
public IEnumerable<Book> GetBooks()
{
return db.GetBooks();
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult GetBook(int id)
{
Book book = db.FindBookById(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(book);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public IHttpActionResult PutBook(int id, Book book)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (id != book.Book_Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
db.EditBook(book);
return StatusCode(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult PostBook(Book book)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.AddBook(book);
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = book.Book_Id }, book);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
public IHttpActionResult DeleteBook(int id)
{
Book book = db.FindBookById(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.RemoveBook(id);
return Ok(book);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
[Route("api/Books/Editions")]
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEditionIdNameWebAPI()
{
return db.GetEditionIdName();
}
}
If we run above LibraryApp.WebAPI project and copy the following URIs in web browser we will getting XML files as following
GetBooks() HTTP method http://localhost:13793/api/Books

GetBook(int id) HTTP method http://localhost:13793/api/Books/{id}

Likewise above BooksController creation procedure we are generating AuthorsController class and BooksWithAuthorsController
AuthorsController.cs
public class AuthorsController : ApiController
{
private LibraryRepository db = new LibraryRepository();
public IEnumerable<Author> GetAuthors()
{
return db.GetAuthors();
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Author))]
public IHttpActionResult GetAuthor(int id)
{
Author author = db.FindAuthorById(id);
if (author == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(author);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public IHttpActionResult PutAuthor(int id, Author author)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (id != author.Auth_Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
db.EditAuthor(author);
return StatusCode(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Author))]
public IHttpActionResult PostAuthor(Author author)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.AddAuthor(author);
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = author.Auth_Id }, author);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(Author))]
public IHttpActionResult DeleteAuthor(int id)
{
Author author = db.FindAuthorById(id);
if (author == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.RemoveAuthor(id);
return Ok(author);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
[Route("api/Authors/all")]
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetAuthorsIdName()
{
return db.GetAuthorsIdName();
}
[Route("api/Authors/EmploymentStatus")]
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEmplyeeStatusIdNameWebAPI()
{
return db.GetEmplyeeStatusIdName();
}
}
with the help of [System.Web.Http.Route("api/ControllerName/AnyName")] we can create customized URI for our method as shown in above method.
BooksWithAuthorsController.cs
public class BooksWithAuthorsController : ApiController
{
private LibraryRepository db = new LibraryRepository();
public IEnumerable<BookWithAuthor> GetBookswithAuthors()
{
return db.GetBooksWithAuthors();
}
[ResponseType(typeof(BookWithAuthor))]
public IHttpActionResult GetBooksWithAuthorsById(int id)
{
BookWithAuthor bookwithauthor = db.FindBooksWithAuthorsById(id);
if (bookwithauthor == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(bookwithauthor);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(decimal))]
[System.Web.Http.Route("api/BooksWithAuthors/{id}/Price")]
public IHttpActionResult GetBooksPriceById(int? id)
{
decimal bookprice = db.findBookPrice(id);
return Ok(bookprice);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(decimal))]
[System.Web.Http.Route("api/BooksWithAuthors/{id}/{name}/Price")]
public IHttpActionResult GetBooksPriceById(int? id, string name = null)
{
decimal bookprice = db.findBookPrice(id,name);
return Ok(bookprice);
}
}
Specialities of above GetBooksPriceById() methods are, As the response of these overloading methods, we are returning decimal values.
Other thing you will learn from this is, how to configure overloading Web API methods that can send multiple parameters.
GetBooksPriceById(int? id) HTTP Method
http://localhost:13793/api/BooksWithAuthors/{id}/Price

Getbookspricebyid(int? Id, String Name =null) HTTP Method
http://localhost:13793/api/bookswithauthors/{id}/{book_title}/Price

End of this Web service project, each of these GET method, we can check oursleves by copying and pasting url on the browser whether correct data being fetched from DB.
Now we are moving to Last section of our project stack which is LibraryApp.MVC ASP.NET MVC 5 Client End
Steps for LibraryApp.MVC
1. Create Empty C# ASP.NET MVC 5 Project , Name it as "ProjectName.MVC"
2. Add connectionstring in web.config file like above project
3. Give the References to following libraries
System.Net.Http.Formatting
System.Net.Http.Headers
LibraryApp.Core
LibraryApp.Infrastructure
LibraryApp.WebAPI
4. Now Add new class in Model Folder as "LibraryClient.cs"
To Make MVC Controlllers we have to call the above API from our C# code. If you surf on internet about this you will see in most of example this scenario full filled with using jQuery via a simple AJAX call.
But we can use HttpClient. In this section you’ll look at how to call a WebAPI Controller endpoint from MVC. WebAPI Controller actions return JSON. So when you call them, you get a big string in return. You then parse this string into an object inside your MVC application and you're good to go.
So Lets handle our HTTP methods using LibraryClient file that can use in MVC Controllers.
LibraryClient.cs
public class LibraryClient
{
private string BOOKWITHAUTHOR_URI = "http://localhost:13793/api/BooksWithAuthors";
private string AUTHOR_URI = "http://localhost:13793/api/Authors";
private string BOOK_URI = "http://localhost:13793/api/Books";
#region //Books with Authors
public IEnumerable<BookWithAuthor> GetAllBookWithAuthors()
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOKWITHAUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("BooksWithAuthors").Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<BookWithAuthor>>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public BookWithAuthor GetBookwithAuthor(int id)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOKWITHAUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("BooksWithAuthors/" + id).Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<BookWithAuthor>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
#endregion
#region // Book
public Book GetBook(int id)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOK_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Books/" + id).Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<Book>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public bool CreateBook(Book book)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOK_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.PostAsJsonAsync("Books/", book).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
public bool EditBook(Book book)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOK_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.PutAsJsonAsync("Books/" + book.Book_Id, book).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
public bool DeleteBook(int id)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(BOOK_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.DeleteAsync("Books/" + id).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
#endregion
#region // Author
public IEnumerable<Author> GetAllAuthors()
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Authors").Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<Author>>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public Author GetAuthor(int id)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Authors/" + id).Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<Author>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public bool CreateAuthor(Author author)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.PostAsJsonAsync("Authors/", author).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
public bool EditAuthor(Author author)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.PutAsJsonAsync("Authors/" + author.Auth_Id, author).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
public bool DeleteAuthr(int id)
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.DeleteAsync("Authors/" + id).Result;
return response.IsSuccessStatusCode;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetAuthorsIdName()
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Authors/all").Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<Basic>>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEmplyeeStatusIdNameMVCModel()
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Authors/EmploymentStatus").Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<Basic>>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
public IEnumerable<Basic> GetEditionIdNameMVCModel()
{
try
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(AUTHOR_URI);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync("Books/Editions").Result;
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return response.Content.ReadAsAsync<IEnumerable<Basic>>().Result;
return null;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
#endregion
}
Now we can easily reuse above LibraryClient methods in our mvc controllers as following
BookWithAuthorController.cs
public class BookWithAuthorController : Controller
{
public ActionResult BookswithAuthors()
{
LibraryClient bwu = new LibraryClient();
ViewBag.listBookswithAuthors = bwu.GetAllBookWithAuthors();
return View();
}
}
BooksController.cs
public class BooksController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Create()
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
ViewBag.listAuthors = lc.GetAuthorsIdName().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.ID.ToString(),
Text = x.NAME
});
ViewBag.listEditions = lc.GetEditionIdNameMVCModel().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.NAME,
Text = x.NAME
});
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Create(Book book)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
lc.CreateBook(book);
return RedirectToAction("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor");
}
public ActionResult Delete(int id)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
lc.DeleteBook(id);
return RedirectToAction("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor");
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
Book book = new Book();
book = lc.GetBook(id);
ViewBag.listAuthors = lc.GetAuthorsIdName().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.ID.ToString(),
Text = x.NAME
});
ViewBag.listEditions = lc.GetEditionIdNameMVCModel().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.NAME,
Text = x.NAME
});
return View("Edit", book);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Edit(Book book)
{
LibraryClient pc = new LibraryClient();
pc.EditBook(book);
return RedirectToAction("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor");
}
}
To Bind dropdown with ViewBag property we can follow
1st Approach
ViewBag.listAuthers = new SelectList(lc.GetAuthersIdName(), "ID", "Name")
2nd Approach
ViewBag.listAuthers = lc.GetAuthersIdName().Select(x => new SelectListItem
{
Value = x.ID.ToString(),
Text = x.Name
});
AuthorsController.cs
public class AuthorsController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
ViewBag.listAuthors = lc.GetAllAuthors();
return View();
}
public ActionResult Create()
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
ViewBag.listEmploymentStatus = lc.GetEmplyeeStatusIdNameMVCModel().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.NAME,
Text = x.NAME
});
return View("Create");
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Create(Author author)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
lc.CreateAuthor(author);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Authors");
}
public ActionResult Delete(int id)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
lc.DeleteAuthr(id);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Authors");
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
LibraryClient lc = new LibraryClient();
Author author = new Author();
ViewBag.listEmploymentStatus = lc.GetEmplyeeStatusIdNameMVCModel().Select
(x => new SelectListItem
{ Value = x.NAME,
Text = x.NAME
});
author = lc.GetAuthor(id);
return View("Edit", author);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Edit(Author author)
{
LibraryClient pc = new LibraryClient();
pc.EditAuthor(author);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Authors");
}
}
Books with Authors List Main Dashboard
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Books with Authors";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4>Books with Authors</h4>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("Create","Books")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus"></span> Create New Book</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("Index", "Authors")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Authors List</button>
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
Book ID
</th>
<th>
Book Title
</th>
<th>
Author Name
</th>
<th>
Edition
</th>
<th>
Price
</th>
<th>
Actions
</th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in ViewBag.listBookswithAuthors)
{
<tr>
<td>
@item.BookWithAuthor_Id
</td>
<td>
@item.BookWithAuthor_Title
</td>
<td>
@item.BookWithAuthor_AuthorName
</td>
<td>
@item.Edition
</td>
<td>
@item.Price
</td>
<td>
<a class="btn btn-danger btn-xs" onclick="return confirm('Are you Sure ?')" href="@Url.Action("Delete","Books" , new { id = item.BookWithAuthor_Id })"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash"></span> Delete Book</a>
<a class="btn btn-warning btn-xs" href="@Url.Action("Edit","Books" , new { id = item.BookWithAuthor_Id })"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-scissors"></span> Edit Book</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
Create a Book
@model LibraryApp.Core.Entities.Book
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4>Create a Book</h4>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Book_Title, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Book_Title, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Book_Title, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Price, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Price, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Price, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Edition, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.DropDownList("Edition", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listEditions, "Select the Edition", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Edition, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Author_Id, "Author Name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@*Non Strongly Type*@
@Html.DropDownList("Author_Id", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listAuthors, "Select the author name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Author_Id, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-list-alt"></span> Book List</button>
</p>
</div>
If you notice here, above Create Book View class, It's binding its dropdown with Non strongly typed method
Non Strongly Type Method
@Html.DropDownList("Author_Id", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listAuthors, "Select the author name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
Strongly Type Method
@Html.DropDownList(m => m.Auther_Id, (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listAuthers, "Select the author name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
Edit a Book
@model LibraryApp.Core.Entities.Book
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4>Edit Book</h4>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Book_Id)
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Book_Title, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Book_Title, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Book_Title, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Price, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Price, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Price, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Edition, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@*@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Edition, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })*@
@Html.DropDownList("Edition", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listEditions, "Select the Edition", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Edition, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Author_Id, "Author Name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@*Non Strongly Type*@
@Html.DropDownList("Author_Id", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listAuthors, "Select the author name", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Author_Id, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-xs" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor")';">Back to List</button>
</p>
</div>
Authors List Dashboard
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Authors";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4> All Authors</h4>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("BookswithAuthors", "BookWithAuthor")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-list-alt"></span> Book List</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("Create", "Authors")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus"></span> Create an Author</button>
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
ID
</th>
<th>
First Name
</th>
<th>
Last Name
</th>
<th>
Biography
</th>
<th>
Employed
</th>
<th>
Action
</th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in ViewBag.listAuthors)
{
<tr>
<td>
@item.Auth_Id
</td>
<td>
@item.First_Name
</td>
<td>
@item.Last_Name
</td>
<td>
@item.Biography
</td>
<td>
@if (item.IsEmployed == "Y")
{
<p><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok" style="color:lime"></span></p>
}
@if (item.IsEmployed == "N")
{
<p><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-remove" style="color:deeppink"></span></p>
}
</td>
<td>
<a class="btn btn-danger btn-xs" onclick="return confirm('Are you Sure ?')" href="@Url.Action("Delete","Authors" , new { id = item.Auth_Id })"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash"></span> Delete Author</a>
<a class="btn btn-warning btn-xs" href="@Url.Action("Edit","Authors" , new { id = item.Auth_Id })"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-scissors"></span> Edit Author</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
Create an Author
@model LibraryApp.Core.Entities.Author
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4>Create an Author</h4>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.First_Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.First_Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.First_Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Last_Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Last_Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Last_Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Biography, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Biography, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Biography, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.IsEmployed, "Employed", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.DropDownList("IsEmployed", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listEmploymentStatus, "Select the Employment Status", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.IsEmployed, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("Index", "Authors")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Authors List</button>
</p>
</div>
Edit an Author
@model LibraryApp.Core.Entities.Author
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h4>Edit Author</h4>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.Auth_Id)
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.First_Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.First_Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.First_Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Last_Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Last_Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Last_Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Biography, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Biography, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Biography, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.IsEmployed,"Employed", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.DropDownList("IsEmployed", (IEnumerable<SelectListItem>)ViewBag.listEmploymentStatus, "Select the Employment Status", htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.IsEmployed, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
<p>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm" onclick="location.href='@Url.Action("Index", "Authors")';"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Authors List</button>
</p>
</div>
Following GitHub location contains the full source code for this sample book keeping solution application.SQL script no need to include since this built with code first approach.So you can try to develop this easily.
Feel free to post a comment on any mistakes/issue and questions that you find during the development of this application.Your advices/sugessions really important for me since I'm on infant stage of developments.
Orginal Post can be found Here
References
