Introduction
A few months ago, I started learning React. Since React only implements the "V" in MVC, I soon started looking at Flux. There are many articles on Flux, however they fail to connect the dots (atleast for me).
This article will give an overview of using Flux with React along with a working example. You can download the full source code for the article from Github.
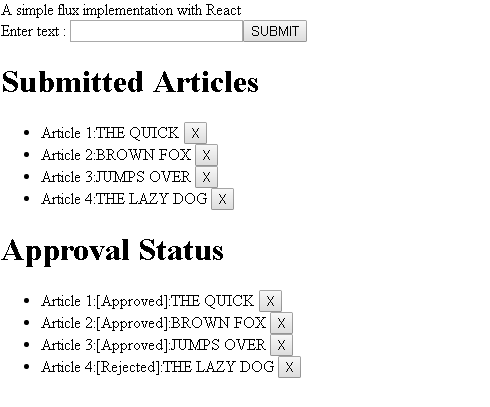
Let us say that the requirement is to create a fictitious Article Manager app, where a user can submit articles and a submission triggers an approval workflow. In the real world, this will involve calling APIs with a full blown UI. For the sake of simplicity, the UI for this app will be basic HTML with a text box input. If the article text is less than 10 characters, it will be approved, otherwise will be rejected outright (in the real world, you will might use APIs for plagiarism detection, spam checker and so on). At a maximum, the user will be able to submit 10 articles, there will also be an option to delete articles. User can either delete an article from the Approval Status List or Submitted articles, deleting an article will update both lists.
This article assumes that you already understand how to create React Components and use props/state effectively. You should also have NodeJS installed with the required packages for React/Flux. If you do not have this set up, Install NodeJS and download the hello world react app from github. Restore packages using "npm install" and run the app with "npm start" from the working directory command prompt where you have the sample code downloaded.
Getting Started with Flux
Flux is an architecture which is similar to the Publisher / Subscriber pattern. To understand it simply:
- A component publishes events using Action Creators
- Action Creator dispatches events to store using a Dispatcher
- Store registers for events which are dispatched
- Store updates its internal data structure with any changes required and emits a change event
- Components subscribe to change events emitted by the store to modify its internal state and re-render accordingly based on the data returned from the store.
Note that there can be multiple store's listening to Events dispatched from Action Creators and similarly multiple components can register for updates from the store and re-render accordingly.

Creating Components for the Article Manager App
Once you have a basic hello world react app running (please download the hello world react app from GitHub), let's start with identifying components for the Sample Article App.
- Content component (which will be a container for other components)
- A common Button component - which will be used for Submit and Remove buttons
- A List component - to display Submitted Articles and Approval status
- Finally an App Component which will mount the Content

Content Component
import React from 'react'
import Button from './Button.jsx';
import List from './List.jsx'
class Content extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { articles: [], articlesApproved: [], message: '' };
}
handleClick() {
}
render() {
var simpleContent =
<div>
{this.props.text}
<br />
Enter text : <input type="text"
name="simpletext" id="simpletext" />
<Button handleClick={this.handleClick}
text="SUBMIT" />
<br />
<List articles={this.state.articles}
listHeader="Submitted Articles" />
{this.state.message}
<List articles={this.state.articlesApproved}
listHeader="Approval Status" />
</div>;
return simpleContent;
}
}
export default Content;
Please note that the sample code uses es6 syntax, so every React component which uses state should be derived from React.Component and call the base constructor using super(props).
List and Button Component
import React from 'react'
const Button = (props) =>
<button onClick={props.handleClick} >{props.text}</button>
export default Button;
import React from 'react'
import Button from './Button.jsx'
class List extends React.Component {
handleClick(key) {
}
render() {
var articles = this.props.articles != undefined ?
this.props.articles.map((article,i) => {
return <li key={i}> Article {i+1}:{article}
<Button handleClick={()=>this.handleClick(i)}
text="X"/>
</li>
}) :[];
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.props.listHeader}</h1>
<ul>
{articles}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
}
export default List;
I've used a stateless function for the Button component since it is stateless and does not use any lifecylce methods (componentDidMount, componentWillUnmount, etc.). The list component is slightly complex and it requires referencing an internal click event using the this keyword so it requires es6 class derived from React.Component.
App.jsx component entry point to mount the container for the App:
import React from 'react'
import Content from './components/Content.jsx';
const App = () => <div>
<Content text="A simple flux implementation with React" /> </div>
export default App;
Implementing a ActionCreator to Dispatch Events
We've identified and created components required for the app. We now have to introduce a data structure to store data and a mechanism to dispatch events using the flux architecture.
To revisit the requirements, the user should be able to:
- Submit an article (maximum limit of 10 articles beyond which user will get an error message)
- Submitting an article should trigger an approval workflow (article text is less than 10 characters - it will be approved, otherwise rejected)
- Remove an article
Action creator exactly does this - it dispatches events 'SUBMIT_ARTICLE', 'APPROVE_ARTICLE' and 'REMOVE_ARTICLE' using AppDispatcher.dispatch({..}), once the events are dispatched, the Store picks up the events, updates/removes articles stored in an array and emits a change event.
import { Dispatcher } from 'flux';
export default new Dispatcher();
import AppDispatcher from './AppDispatcher';
class AppActions {
submitArticle(data) {
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
actionType: 'SUBMIT_ARTICLE',
value: data
});
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
actionType: 'APPROVE_ARTICLE',
value: data
});
}
removeArticle(key)
{
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
actionType: 'REMOVE_ARTICLE',
value: key
});
}
}
export default new AppActions()
Let's now modify the Content Component to address the requirements #1 and #2 as we have the Action Creator ready to dispatch events. Observe that AppActions.submitArticle(document.getElementById('simpletext').value) sends events to the ActionCreator eventually to be dispatched to the store.
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { articles: [], articlesApproved: [], message: '' };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
if (document.getElementById('simpletext').value.length >
0 && this.state.articles.length < 10) {
AppActions.submitArticle(document.getElementById('simpletext').value)
document.getElementById('simpletext').value = ''
}
}
Deleting articles will be handled from the List component. A unique index needs to be maintained in order to delete an item from an array. This is the reason li tag is rendered with a <li key={i}>.
handleClick(key) {
AppActions.removeArticle(key)
}
render() {
var articles = this.props.articles != undefined ?
this.props.articles.map((article,i) => {
return <li key={i}> Article {i+1}:{article}
<Button handleClick={()=>this.handleClick(i)}
text="X"/></li>
}) :[];
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.props.listHeader}</h1>
<ul>
{articles}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
Implementing a Store
A store is a datastructure to listen to events dispatched from ActionCreators and accordingly make changes to its internal state. In order for the store to emit events once the internal state is modified, it will need to derive from EventEmmiter.
AppDispatcher.register registers for events dispatched from Action creator and binds it to a callback method.
this.dispatchToken = AppDispatcher.register(this.dispatcherCallback.bind(this))
dispatcherCallback(action) {
switch (action.actionType) {
case 'SUBMIT_ARTICLE':
this.submitArticle(action.value);
break;
case 'APPROVE_ARTICLE':
this.approveArticle(action.value);
break;
case 'REMOVE_ARTICLE':
this.removeArticle(action.value);
}
this.emitChange(action.actionType);
return true;
}
Ok Events dispatched, updates made to the store based on the events dispatched and changes emitted using this.emitChange(action.actionType), so how will the Component know that the Store has made changes and needs to re-rendered. This is what addChangeListener does, using the code snippet below the component registers for changes in the store and re-renders accordingly.
Please note that the best practice is to have a store only emit one event, as a store should address a single domain in the App. I have made the store emit multiple events so as to demonstrate that a store can emit multiple events and a component can listen to multiple changes from the store.
class Content extends React.Component {
.
.
.
componentDidMount() {
AppStore.addChangeListener('SUBMIT_ARTICLE', this.onSubmit);
AppStore.addChangeListener('REMOVE_ARTICLE', this.onRemove);
}
Complete source for the Store
import AppDispatcher from './AppDispatcher';
import { EventEmitter } from 'events';
let _articles = [];
let _articlesApproved = []
class AppStore extends EventEmitter {
constructor() {
super();
this.dispatchToken = AppDispatcher.register(this.dispatcherCallback.bind(this))
}
emitChange(eventName) {
this.emit(eventName);
}
getAll() {
return _articles;
}
getApproved() {
return _articlesApproved;
}
submitArticle(article) {
_articles.push(article);
}
removeArticle(key)
{
_articles.splice(key,1);
_articlesApproved.splice(key,1)
}
approveArticle(article) {
if (article.length <= 10) {
_articlesApproved.push('[Approved]:' + article);
}
else {
_articlesApproved.push('[Rejected]:' + article);
}
}
addChangeListener(eventName, callback) {
this.on(eventName, callback);
}
removeChangeListener(eventName, callback) {
this.removeListener(eventName, callback);
}
dispatcherCallback(action) {
switch (action.actionType) {
case 'SUBMIT_ARTICLE':
this.submitArticle(action.value);
break;
case 'APPROVE_ARTICLE':
this.approveArticle(action.value);
break;
case 'REMOVE_ARTICLE':
this.removeArticle(action.value);
}
this.emitChange('STORE_' + action.actionType);
return true;
}
}
export default new AppStore();
Re-rendering Components Based on Events from the Store
A component needs to listen to changes from the store in order to re-render itself accordingly. This is the purpose of having an AppStore.addChangeListener in the componentDidMount method indicating that when a component is mounted, it should listen to any changes from the store. Any changes to the store should force a re-render of the component. This is done by updating the components' internal state using this.setState as in the code snippet below. Note that I have on purpose made the Content component listen to multiple events so as to demonstrate that this is something which is possible and to get a better understanding of store events, yes as a best practice, ideally, you will have only one event along the lines of a domain model.
componentDidMount() {
AppStore.addChangeListener('STORE_SUBMIT_ARTICLE', this.onSubmit);
AppStore.addChangeListener('STORE_REMOVE_ARTICLE', this.onRemove);
}
onRemove() {
this.listArticles()
}
onSubmit() {
this.listArticles()
}
listArticles()
{
let usermessage = ''
if (this.state.articles.length > 9) {
usermessage = 'You have exceeded the number of articles you can submit,You cannot add more articles'
}
this.setState({
articles: AppStore.getAll(),
articlesApproved: AppStore.getApproved(),
message: usermessage
})
}
Points of Interest
Flux architecture is easy to understand conceptually, but when it comes to implementation in a real world app, it is a bit tricky. The Sample App does not use APIs which ideally will be the case in the real world. In order to use APIs in ActionCreators, use a utility class to make an API call and then dispatch events to the store with the result returned from the APIs. Also this article uses Singleton classes for Store and ActionCreators using the export default new syntax. I will also try to write more articles to demonstrate the usage of Flux or Redux using easy to understand working examples along with API calls.
