Watch windows is one of most commonly used debugging tools with Visual Studio. We generally used to explore the objects, values, properties and other nested objects as a tree structure. Most of the time, we used watch window to only view the values or change the current object properties values to see the effects of changed object during debugging. But we can use watch windows for many different purposes. In this blog post, I am going to list 10 tips that may help you while dealing with Watch Window.
Tips 1: Calling Methods from Watch Window
As I said earlier, most of the time, we used watch window to explore the objects and its properties, but we can call methods from watch window as well. If you are exploring some objects inside watch window, you can simply call any of the methods for that object inside watch window.
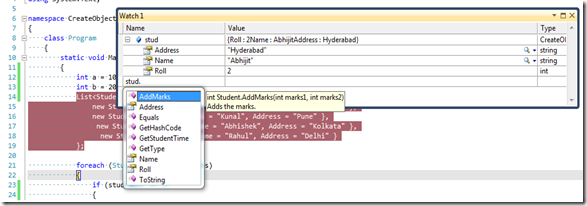
As you can see from the above image, when you have typed stud object, you are able to access all the properties and methods that are accessible by the original object.
As for example, you can pass the proper marks inside AddMarks() methods to get the result details as shown in below image.

Here is another trick, you can use some “temp” variable to store those data. But you have to declare the variable at “Immediate Window”. [Please read Tips 3 to know more about using Immediate window with Watch Window. ]
So, just declare a variable in “immediate window” and use it inside watch window as shown in below images:

As addition, you can use the same variable to do some additional operation as well.

While calling some methods from watch window, please make sure the execution time for the methods should be less enough (approximately less than 10 seconds). Otherwise, you will get exception on evaluation time out.
Tips 2: Drag-Drop & Copy-Paste Code inside Watch Window
While debugging, we generally right click on the code block and select “Add to Watch” to explore the result. But you can drag and drop code expression from VS Editor to watch window. Or, you can Copy and Paste a code expression to see the result. Below images show uses of the same.

Similarly, you can drag and drop object values inside a watch window too.

Similar, Drag and Drop, you can copy the code expression from Visual Studio editor and paste it inside watch window or within Watch window.

When you copy the source code and paste it, watch window will automatic show you the result. You can do the copy paste within watch window as well.

This has many advantages while you are dealing with large objects and working with multiple watch window (See Tips 4).
Tips 3: Use Runtime Object With Help of Immediate Window
This is a very interesting tip. You always debug with the context of current object, but what if you need to change the object instead of object value. You can instantiate a new object by just typing a new ClassName() which will generate the new instance of your class as shown in the below picture.

But, you need to take the help of Immediate window if you want to declare an object to use it further.

As shown in the above image, you can create a new object and use it in the immediate window.
Now you may think why I used Immediate window to declare the object, because Immediate window does not allow you declaration statements.

Tips 4: Using Multiple Watch Window
Ok, till now, what I have discussed is all about a single watch window. But Visual Studio provides us 4 different watch windows. They are Watch 1, Watch 2, Watch 3, Watch 4.

These watch windows are really helpful when you are dealing with a large object or want to see some data based on different classification. Maybe, you can use different watch window for different objects as well. This will make debugging very simple.

As per the above image, you can see that we can use multiple watch window to watch different objects. This use is very handy when you are working with a slightly complex application where you have many objects to view at the same time.
Tips 5: Moving Values between Multiple Watch Window
This is a continuation of Tip 4, as I have discussed about working with multiple watch windows, you can also pass values among them either by Copy Paste or Drag and Drop. Yes, this looks very simple but it is very helpful !

As the above image shows, we can drag and drop items between watch windows. Similarly, we can do copy paste values among watch windows.

You have a large set of properties in a single object, which is very difficult to watch in a single window and you don’t even want to check them all. Now you can move only the required members to different watch window to make your life simple.
Tips 6: Create Object ID
By using “Make Object ID” option, we are informing Visual Studio Debugger to keep track of that object no matter it’s within scope or out of scope for the current context. We can create “Object ID” either from Locals, Autos or from Watch Windows. Object ID is an integer number followed by a pound (#) sign. When we create Object ID for an particular object, Visual Studio Debugger (CLR Debugging Services) uses an integer value to uniquely identify the object. This “Object ID” allows you to get the object details even if it is out of scope.

I have published one complete article on the same, please read it from:
Tips 7: Different Type of Display Format
Watch window allows you to view the variables values in Hex Mode. This is a very simple feature, just right click on Watch window and select Hexadecimal Display.

Once you select “Hexadecimal Display”, you will get a screen similar like below:

But you have noticed that all values have changed to hexadecimal format, but what if you want to do it for particular values, not for all. Let’s say, you want to get hex value for variable “b”. Here is the trick, you can use some comma (,) separated format “d” for Integer and “h” hex with in watch window to get the list of values.

From the above image, you can see when we have “Hexadecimal display” on, we can still see integer value using “d” with the variable name. Similarly, we can get the hex value of any variables without changing the display mode of watch window.

Tips 8: Get Object Generation
If you are dealing with any objects in Watch window and you want to check the current generation for that Object, you can easily get that by calling GC.getGeneration(objectName).


Note: This is also applicable for newly created object Ids as described in Tips 6.
Tips 9: View Pseudo Variable
You can view pseudo variable within Watch window.

Here is a nice article on MSDN which describes about Debugging With Pseudo Variables And Format Specifiers.
Tips 10: Use XML/HTML/Text Visualizer from Watch Window
Like normal visualize objects, variable in VS code editor, you can view XML, HTML and Text Visualizer from watch window itself.

Summary
In this post, I have described 10 useful tips that are related to watch window. We use a few of them frequently.
Hope this will helps you.
Thanks for reading!
Filed under: Debugging, Tips and Tricks, Visual Studio
