This article delves into the utilization of the HID protocol on Windows, allowing you to send and receive HID packets from any connected USB devices directly through an application, without the need for third-party DLLs
Warning
This USB sniffer, because of its user mode method access to hardware, cannot read HID packets with RID at 0, it's due to Windows protection level to prevent keyloggers/spying software.
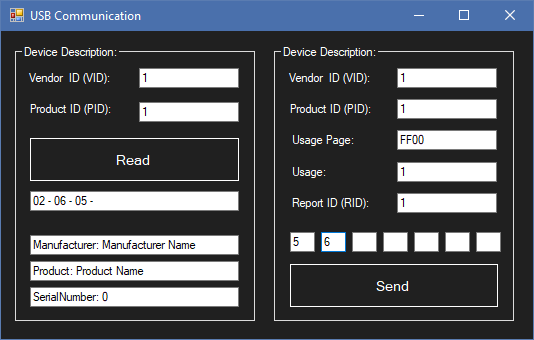
(Do not add 0x, else the application will crash since I haven't added 0x prefix support)
Background
This article was possible with this WDK sample:
Basically, it's just a rewrite of this sample, but in a simple form.
Using the Code
Main code:
void CheckHIDRead()
{
HIDReadInfo.Device = new HID_DEVICE[DeviceDiscovery.FindDeviceNumber()];
DeviceDiscovery.FindKnownHIDDevices(ref HIDReadInfo.Device);
for (var Index = 0; Index < HIDReadInfo.Device.Length; Index++)
{
if (HIDReadInfo.VendorID != 0)
{
var Count = 0;
if (HIDReadInfo.Device[Index].Attributes.VendorID == HIDReadInfo.VendorID)
{
Count++;
}
if (HIDReadInfo.Device[Index].Attributes.ProductID == HIDReadInfo.ProductID)
{
Count++;
}
if (Count == 2)
{
HIDReadInfo.iDevice = Index;
HIDReadInfo.Active = true;
return;
}
}
}
}
void CheckHIDWrite()
{
HIDWriteInfo.Device = new HID_DEVICE[DeviceDiscovery.FindDeviceNumber()];
DeviceDiscovery.FindKnownHIDDevices(ref HIDWriteInfo.Device);
for (var Index = 0; Index < HIDWriteInfo.Device.Length; Index++)
{
if (HIDWriteInfo.VendorID != 0)
{
var Count = 0;
if (HIDWriteInfo.Device[Index].Attributes.VendorID == HIDWriteInfo.VendorID)
{
Count++;
}
if (HIDWriteInfo.Device[Index].Attributes.ProductID == HIDWriteInfo.ProductID)
{
Count++;
}
if (HIDWriteInfo.Device[Index].Caps.UsagePage == HIDWriteInfo.UsagePage)
{
Count++;
}
if (HIDWriteInfo.Device[Index].Caps.Usage == HIDWriteInfo.Usage)
{
Count++;
}
if (Count == 4)
{
HIDWriteInfo.iDevice = Index;
HIDWriteInfo.Active = true;
return;
}
}
}
}
CheckHIDRead() and CheckHIDWrite() are used for checking if we have press Read or Send button and if entered data (VID-PID-Usa...) correspond to a connected USB device.
This function returns the number of USB HIDs in order to scan them.
Int32 FindDeviceNumber()
{
var hidGuid = new Guid();
var deviceInfoData = new SP_DEVICE_INTERFACE_DATA();
HidD_GetHidGuid(ref hidGuid);
SetupDiDestroyDeviceInfoList(hardwareDeviceInfo);
hardwareDeviceInfo = SetupDiGetClassDevs(ref hidGuid, IntPtr.Zero,
IntPtr.Zero, DIGCF_PRESENT | DIGCF_DEVICEINTERFACE);
deviceInfoData.cbSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(SP_DEVICE_INTERFACE_DATA));
var Index = 0;
while (SetupDiEnumDeviceInterfaces(hardwareDeviceInfo, IntPtr.Zero,
ref hidGuid, Index, ref deviceInfoData))
{
Index++;
}
return (Index);
}
This function returns a data structure of each USB device needed for HIDRead() and HIDWrite().
static public void FindKnownHIDDevices(ref HID_DEVICE[] HID_Devices)
{
var hidGuid = new Guid();
var deviceInfoData = new SP_DEVICE_INTERFACE_DATA();
var functionClassDeviceData = new SP_DEVICE_INTERFACE_DETAIL_DATA();
Hid.HidD_GetHidGuid(ref hidGuid);
SetupDiDestroyDeviceInfoList(hardwareDeviceInfo);
hardwareDeviceInfo = SetupDiGetClassDevs(ref hidGuid, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero,
DIGCF_PRESENT | DIGCF_DEVICEINTERFACE);
deviceInfoData.cbSize = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(SP_DEVICE_INTERFACE_DATA));
for (var iHIDD = 0; iHIDD < HID_Devices.Length; iHIDD++)
{
SetupDiEnumDeviceInterfaces(hardwareDeviceInfo, IntPtr.Zero, ref hidGuid, iHIDD, ref deviceInfoData);
var RequiredLength = 0;
SetupDiGetDeviceInterfaceDetail(hardwareDeviceInfo, ref deviceInfoData,
IntPtr.Zero, 0, ref RequiredLength, IntPtr.Zero);
if (IntPtr.Size == 8)
{
functionClassDeviceData.cbSize = 8;
}
else if (IntPtr.Size == 4)
{
functionClassDeviceData.cbSize = 5;
}
SetupDiGetDeviceInterfaceDetail(hardwareDeviceInfo, ref deviceInfoData,
ref functionClassDeviceData, RequiredLength,
ref RequiredLength, IntPtr.Zero);
OpenHIDDevice(functionClassDeviceData.DevicePath, ref HID_Devices, iHIDD);
}
}
This function extend FindKnownHIDDevices().
static void OpenHIDDevice(String DevicePath, ref HID_DEVICE[] HID_Device, Int32 iHIDD)
{
HID_Device[iHIDD].DevicePath = DevicePath;
CloseHandle(HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle);
HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle = CreateFile(HID_Device[iHIDD].DevicePath,
FileAccess.ReadWrite, FileShare.ReadWrite,
0, FileMode.Open, FileOptions.None,
IntPtr.Zero);
HID_Device[iHIDD].Caps = new HIDP_CAPS();
HID_Device[iHIDD].Attributes = new HIDD_ATTRIBUTES();
Hid.HidD_FreePreparsedData(ref HID_Device[iHIDD].Ppd);
HID_Device[iHIDD].Ppd = IntPtr.Zero;
Hid.HidD_GetPreparsedData(HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle, ref HID_Device[iHIDD].Ppd);
Hid.HidD_GetAttributes (HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle, ref HID_Device[iHIDD].Attributes);
Hid.HidP_GetCaps (HID_Device[iHIDD].Ppd , ref HID_Device[iHIDD].Caps);
var Buffer = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(126);
{
Hid.HidD_GetManufacturerString(HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle, Buffer, 126);
HID_Device[iHIDD].Manufacturer = Marshal.PtrToStringAuto(Buffer);
Hid.HidD_GetProductString(HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle, Buffer, 126);
HID_Device[iHIDD].Product = Marshal.PtrToStringAuto(Buffer);
Hid.HidD_GetSerialNumberString(HID_Device[iHIDD].Handle, Buffer, 126);
HID_Device[iHIDD].SerialNumber = Marshal.PtrToStructure<Int32>(Buffer);
}
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(Buffer);
}
Then come two important functions that will make you able to read or send HID packets between a USB HID and a PC.
static async public void BeginAsyncRead(object? state)
{
if (HIDReadInfo.Active == true)
{
var Device = HIDReadInfo.Device[HIDReadInfo.iDevice];
var ReportBuffer = new Byte[Device.Caps.InputReportByteLength];
if (ReportBuffer.Length > 0)
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
var NumberOfBytesRead = 0U;
Kernel32.ReadFile(Device.Handle, ReportBuffer, Device.Caps.InputReportByteLength, ref NumberOfBytesRead, IntPtr.Zero);
});
HIDReadInfo.ReportData = new List<Byte>(ReportBuffer);
}
}
}
static public void BeginSyncSend(object? state)
{
if (HIDWriteInfo.Done is false && HIDWriteInfo.Active is true)
{
var Device = HIDWriteInfo.Device[HIDWriteInfo.iDevice];
var ReportBuffer = new Byte[Device.Caps.OutputReportByteLength];
if (ReportBuffer.Length > 0)
{
ReportBuffer[0] = HIDWriteInfo.ReportID;
Array.Copy(HIDWriteInfo.ReportData, 0, ReportBuffer, 1, ReportBuffer.Length - 1);
var varA = 0U;
Kernel32.WriteFile(Device.Handle, ReportBuffer, Device.Caps.OutputReportByteLength, ref varA, IntPtr.Zero);
}
HIDWriteInfo.Done = true;
}
}
To be able to do that, you'd need to set the following data before:
VendorIDProductIDUsagePageUsageReportID
But be careful, you'd need to set the correct values for all those parameters, if one is false, you will not be able to send HID packets.
To read HID packets, you just need:
Also, you cannot read if the USB device cannot send data and you cannot write if the USB device cannot read data (defined inside its HID Report Descriptor).
A device is defined by its VendorID:ProductID but shrunk into several functions defined by its UsagePage, Usage and ReportID.
As an example, the first function of a mouse is to send coordinate data, so you can read data from PC and the second function is to receive mouse button customization data, so you can send data from PC.
And to set those variables, you need to read the HID Descriptor of the USB devices that you target, it can be retrieved with a USB sniffer as https://github.com/djpnewton/busdog or http://www.usblyzer.com/usb-analysis-features.htm
The HID Descriptor usually start with 0x05, 0x01.
And to learn to read HID Descriptor, use this tool: http://www.usb.org/developers/hidpage#HID Descriptor Tool and https://docs.kernel.org/hid/hidintro.html
Because this code is just a rewrite of an old C code from the 90s, it works on all Windows Versions.
History
- 2nd October, 2019: Initial version
- 10th September, 2023: Project upgrade from Windows Forms .NET framework to WPF .NET Core
