Introduction
I would be wrong in saying DART is new emerging phenomena in today's ever-changing programming world, as promised in this article, I would be letting you know more about DART language. For this article, I am taking liberty copying some common text from DART official website, as those information, that are constant like type of keywords or Build-in types. To make this article compliant with rules, I will make sure proper attributions are given.
This is the first article of this series. Hopefully, more would be coming within a few weeks.
Installation
You would require DART SDK and one code editing tool of your choice for writing the code, I prefer Visual Studio Code as it's lightweight and if you install Flutter and Dart extension, which has in built support for Dart (as Flutter base language for coding is Dart), it also provides feature like intellisense, etc.
For installing DART SDK, you can follow steps mentioned at [link], if you are concentrating only on DART; you just need to download Flutter SDK, Dart SDK in at this path bin\cache\dart-sdk.
For installing Flutter and Dart extension in Visual Studio Code, open command palette either by selecting View->Command Palette option or Ctrl+Shift+P, once searchbar appears, you need to write Extensions: Install Extensions. Search for Flutter & Dart separately and install it. Do this step, once you have already unzipped DART SDK in your PC.
In case you wouldn’t want to install anything, DART team come up with DartPad, where you could write small programs to check your logic. For this tutorial, you can easily write and compile your code with DartPad.
Basic Structure
Dart language has almost all features and programming constructs inbuilt to code interruptly, its fully Object Orient Programming language with syntax structure similar to C++, C#. The whole language specification is available here. From the PDF, I could extract more relevant definition of Dart.
Quote:
Dart is a class-based, single-inheritance, pure object-oriented programming language. Dart is optionally typed (19) and supports reified generics. The runtime type of every object is represented as an instance of class Type which can be obtained by calling the getter runtimeType declared in class Object, the root of the Dart class hierarchy
Before creating your first program, you should be aware of two things, first type of keyword available and inbuilt datatypes:
abstract | do | import | super |
as | dynamic | in | switch |
assert | else | interface | sync* |
async | enum | is | this |
async* | export | library | throw |
await | external | mixin | true |
break | extends | new | try |
case | factory | null | typedef |
catch | false | operator | var |
class | final | part | void |
const | finally | rethrow | while |
continue | for | return | with |
covariant | get | set | yield |
default | if | static | yield* |
deferred | implements | | |
Inbuild Datatypes
- numbers
- strings
- booleans
- lists (also known as arrays)
- maps
- runes (for expressing Unicode characters in a
string) - symbols
Tutorial Scope
Though DART is a complete language with lot of features and functionality, for this article, I am limiting my scope, and would be discussing these points only:
- TASK#1 Basic program creation
- TASK#2 Usage of basic datatypes which includes
numbers, strings and enums. List and Map would have their own article - TASK#3
IF ELSE and SWITCH - TASK#4 Looping using
for, while, do-while
Project Creation
Though if you installed IntelliJ Idea from JetBrain, it provides inbuilt template for creating Dart console application, otherwise creation of DART based project is very simple. Please follow these steps. I am using Visual Studio Code as my coding editor.
- Create a folder in your computer where you want to create your project, folder name would be name of the project.
- Create two folders inside your project folder by name bin and lib. (Please make sure name of folder is in lower case.)
- bin folder would contain your code files
- lib folder would contain files you want to use around the project, I would come back to this point further in the article
- Create a new file in root of project folder by name pubspec.yaml, and add the following code inside it:
name: darttutorial1
description: New Tutorial series for Dart
- here
name corresponds to name of project, for keeping it simple, you can use project folder name here - here
description corresponds to basic information about project
- Once you save pubspec.yaml file, Studio automatically creates pubspec.lock and .package file in root folder.
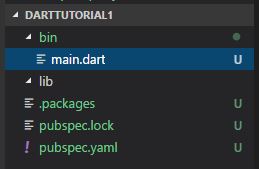
- Now you are ready to do Rock and Roll.
Using the Code
Task # 1 Basic Program Creation
- Like C++, entry point for Dart program is also
main() function - Now add main.dart file in bin folder by right clicking on folder and clicking on New File & name it as main.dart.
- Add the following code in file:
void main()
{
print ('Hello Dart');
}

print function used to print whatever is supplied into debug console terminal- If everything is setup correctly, if you Ctrl+F5, you can see 'Hello Dart' coming in output terminal, to open
DEBUG CONSOLE terminal in your VS Code, use CTRL + ` (Back Tick) - So we reached end of Task#1.
TASK#2 Usage of Basic datatypes which Includes numbers, strings and booleans
Note (From Dart website): Everything you can place in a variable is an object, and every object is an instance of a class. Even numbers, functions, and null are objects. All objects inherit from the Object class. Uninitialized variables have an initial value of null. Even variables with numeric types are initially null.
- Let's check basic datatypes, first being numbers, main constituent for same are
int (for integer value ranges from -263 to 263 - 1) and double (for floating values). They both are subtype of num object. - Let's do some stuff for
int and double, I will make sure that the code is self explanatory.
void main()
{
print ('testing integer functionality');
int myInt = 4;
myInt += 10;
assert(myInt == 14);
print ('testing double functionality');
double myDob = 4.2;
myDob += 10.2;
assert(myDob == 14.4);
print ('integer and double test passed');
}

- Now let's focus on
Enums, enums are similar to what we have in C++/C#, they are named const identifier, which automatically assigns Zero to first enum, then increment accordingly. - Let's do some programming with
enums:
enum NaturalNumbers { Zero,One,Two }
void main()
{
print(NaturalNumbers.Zero);
assert(NaturalNumbers.Zero.index == 0); print(NaturalNumbers.One);
assert(NaturalNumbers.One.index == 1); print(NaturalNumbers.Two);
assert(NaturalNumbers.Two.index == 2);}

- Last but most important
String, please note down, 'S' is capital in String, if you use lower case, Dart compiler would not recognize the syntax. String is used to manipulate and store text. We can use both single quote (') and double quote (") to store text. - Let's do some programming using
String:
void main()
{
String name = "Dart Language";
String usage = " Used in Mobile, Web and Virtual Machine";
print(name+usage);
assert(name+usage == 'Dart Language Used in Mobile, Web and Virtual Machine');
var name1 = "${name} is next emerging language";
print(name1);
assert(name1 == 'Dart Language is next emerging language'); }

- Converting between types, use
toString() to convert any number to String and use parse function to convert from String to number (example taken from Dart Site):
var one = int.parse('1');
assert(one == 1);
var onePointOne = double.parse('1.1');
assert(onePointOne == 1.1);
String oneAsString = 1.toString();
assert(oneAsString == '1');
String piAsString = 3.14159.toStringAsFixed(2);
assert(piAsString == '3.14');
- So we reached the end of Task#2.
TASK#3 IF ELSE and SWITCH
IF-ELSE statement is used where we need to choose one choice between two choices, i.e., outcome is either TRUE or FALSE. We use SWITCH in case we need to choose one choice from multiple choices, and all choices are generally known in advance. Let's write the program to check both functionalities:
enum NaturalNumbers { Zero,One,Two,Three }
void main()
{
bool DoYouLiveOnEarth = true;
if(DoYouLiveOnEarth)
print("Yes I live on Earth");
print('Moved to Mars by tesla ');
DoYouLiveOnEarth = false;
if(DoYouLiveOnEarth == false)
print("no Moved to Mars");
NaturalNumbers naturalNumbers = NaturalNumbers.Two;
switch (naturalNumbers) {
case NaturalNumbers.Zero: print("you are using ${naturalNumbers}"); break;
case NaturalNumbers.One: print("you are using ${naturalNumbers}"); break;
case NaturalNumbers.Two: print("you are using ${naturalNumbers}"); break;
case NaturalNumbers.Three: print("you are using ${naturalNumbers}"); break;
default: break;
}
}

So we reached end of Task#3.
TASK#4 Looping using for, while, do-while
For loop is executed where end conditions are generally known in advance, it provides readymade solution for incrementing and decrementing the variable on which For loop is running, and in case of while loop, we don't know the end result in advance, based on logic written inside the block. Let me write a small program to check their usage in Dart.
void main()
{
print("For loop");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
print("Hello ${i}");
}
print("WHILE loop");
int i=0;
bool breakCondition = false;
while(breakCondition== false)
{
print("Hello ${i}");
if(++i>=3) breakCondition = true;
}
}

So we reached the end of Task#4 and the end of this tutorial. Do let me know if you have any questions by posting in linked messageboard.
Though there is no download available for this article, you can still clone my github project for the same here.
Points of Interest
Flutter Tutorial
- Flutter Getting Started: Tutorial #1
- Flutter Getting Started: Tutorial 2 - StateFulWidget
DART Series
- DART2 Prima Plus - Tutorial 2 - LIST
History
- 05-July-2018 - First version
