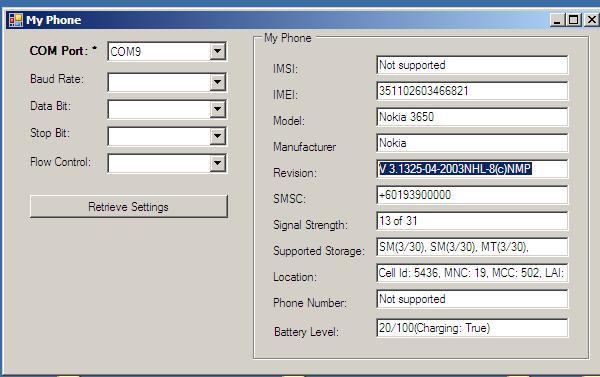
Introduction
This article describes a way of communicating with your mobile phone using AT commands. Normally, a GSM compatible mobile phone will have a built-in modem, which we can communicate using AT commands. The AT command set should be common among all the handphone manufacturers including Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Siemen, and Motorola, although slight differences exist.
In this article, I will use an open source .NET phone communication library to show you the various ways of communicating with your mobile phone. The library is available here.
Getting started
Before we can communicate with the GSM phone, a connection must be established first. The connection can be either serial, bluetooth, or irDA. As long as we can connect to the phone, it is fine.
In this article, I established a bluetooth connection with my mobile phone. Firstly, I create a partnership between my laptop and my Nokia mobile phone, and then select the Bluetooth Serial Port service on my mobile phone. The configuration may wary depending on the Bluetooth software and the driver for your modem. If everything is okay, you should be able to see a Bluetooth modem configured in your device manager. Successful configuration will have the following:

Take note that in my configuration, the COM port configured is COM9 and the baud rate is 115200. These settings will be used to connect to the mobile phone.
Test the configuration
After the Bluetooth connection is set up, we can use HyperTerminal to try to send AT commands to make sure the connection is okay.


As you can see, AT commands start with the word "AT". E.g., "ATE1" means echo the command typed locally, "AT+CGMM" displays the handphone model, and "AT+CSCA?" displays the SMSC configured in the mobile phone.
If everything is okay now, you can use the sample code attached in this article to retrieve various handphone settings. The results will be similiar to the screenshot displayed at the top of this article. Take note that different handsets may support different AT command sets. Certain AT commands may not be available in certain handsets.
The code in the solution is quite straightforward. It makes use of the open source library atSMS to retrieve various phone configurations by sending AT commands. You can read the list of the APIs available in the documentation and sample provided.
If cboComPort.Text = String.Empty Then
MsgBox("COM Port must be selected", MsgBoxStyle.Information)
Return
End If
Dim oGsmModem As New GSMModem
oGsmModem.Port = cboComPort.Text
If cboBaudRate.Text <> String.Empty Then
oGsmModem.BaudRate = Convert.ToInt32(cboBaudRate.Text)
End If
If cboDataBit.Text <> String.Empty Then
oGsmModem.DataBits = Convert.ToInt32(cboDataBit.Text)
End If
If cboStopBit.Text <> String.Empty Then
Select Case cboStopBit.Text
Case "1"
oGsmModem.StopBits = Common.EnumStopBits.One
Case "1.5"
oGsmModem.StopBits = Common.EnumStopBits.OnePointFive
Case "2"
oGsmModem.StopBits = Common.EnumStopBits.Two
End Select
End If
If cboFlowControl.Text <> String.Empty Then
Select Case cboFlowControl.Text
Case "None"
oGsmModem.FlowControl = Common.EnumFlowControl.None
Case "Hardware"
oGsmModem.FlowControl = Common.EnumFlowControl.RTS_CTS
Case "Xon/Xoff"
oGsmModem.FlowControl = Common.EnumFlowControl.Xon_Xoff
End Select
End If
Try
oGsmModem.Connect()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.Message, MsgBoxStyle.Critical)
Return
End Try
Try
txtRevision.Text = oGsmModem.Revision
Catch ex As Exception
txtRevision.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtIMSI.Text = oGsmModem.IMSI
Catch ex As Exception
txtIMSI.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtIMEI.Text = oGsmModem.IMEI
Catch ex As Exception
txtIMEI.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtModel.Text = oGsmModem.PhoneModel
Catch ex As Exception
txtModel.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtManufacturer.Text = oGsmModem.Manufacturer
Catch ex As Exception
txtManufacturer.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtSMSC.Text = oGsmModem.SMSC
Catch ex As Exception
txtSMSC.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
Dim rssi As Rssi = oGsmModem.GetRssi
txtSignal.Text = rssi.Current & " of " & rssi.Maximum
Catch ex As Exception
txtSignal.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
Dim storages() As Storage = oGsmModem.GetStorageSetting
Dim i As Integer
txtSupportedStorage.Text = String.Empty
For i = 0 To storages.Length - 1
Dim storage As Storage = storages(i)
txtSupportedStorage.Text += storage.Name & "(" &_
storage.Used & "/" & storage.Total & "), "
Next
Catch ex As Exception
txtSupportedStorage.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
Dim loc As Location = oGsmModem.GetLocation
txtLocation.Text = "Cell Id: " & loc.CellID & _
", MNC: " & loc.MNC & ", MCC: " & _
loc.MCC & ", LAI: " & loc.LAI
Catch ex As Exception
txtLocation.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
txtPhoneNumber.Text = oGsmModem.MSISDN
Catch ex As Exception
txtPhoneNumber.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
Try
Dim battery As Battery = oGsmModem.GetBatteryLevel
txtBattery.Text = battery.BatteryLevel & "/" & _
battery.MaximumLevel & "(Charging: " &_
battery.BatteryCharged & ")"
Catch ex As Exception
txtBattery.Text = "Not supported"
End Try
In future articles, I will show you how to send ASCII and Unicode SMS using AT commands and the open source library. So stay tuned...
