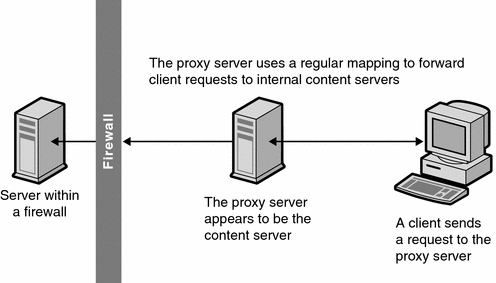
Introduction
This article illustrates how a reverse proxy server can be developed in C# .NET v2.0 using HTTP Handler in IIS. The idea is to intercept and manipulate incoming HTTP requests to the IIS web server. I've developed a simple server with a basic, HTTP Reverse Proxy functionality, but there is still a lot more to add.
Background
A reverse proxy differs from an ordinary forward proxy. A forward proxy is an intermediate server that accepts requests addressed to it. It then requests content from the origin server and returns it to the client. The client must be configured to use the forward proxy. The reverse proxy does not require any special configuration by the client. The client requests content from the reverse proxy. The reverse proxy then decides where to send those requests, and returns the content as if it was itself the origin. Reverse proxies can be used to bring several servers into the same URL space.
Using the code
The below code is the core of the Reverse Proxy Server. I've used a HTML parser written by Jeff Heaton for rewriting the URLs in the HTML page rendered by the Reverse Proxy Server.
Points to Ponder
IHttpHandler, the abstract HTTP Handler base class of .NET must be inherited to define custom HTTP Handler.
IRequiresSessionState must be inherited if we are required to manipulate session variables.
IsReusable is a read-only property which can be used to define where the application instance can be pooled/reused.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Web;
using System.Text;
using System.Web.Mail;
using System.Collections;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Web.SessionState;
using System.DirectoryServices;
namespace TryHTTPHandler
{
public class SyncHandler : IHttpHandler, IRequiresSessionState
{
public bool IsReusable { get { return true; } }
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext Context)
{
string ServerURL = "";
try
{
char[] URL_Separator = { '/' };
string[] URL_List = Context.Request.Url.AbsoluteUri.Remove(0,
7).Split(URL_Separator);
ServerURL = "http://" +
URL_List[2].Remove(URL_List[2].Length - 5, 5) + @"/";
string URLPrefix = @"/" + URL_List[1] + @"/" +
URL_List[2];
for ( int i = 3; i < URL_List.Length; i++ )
ServerURL += URL_List[i] + @"/";
ServerURL = ServerURL.Remove(ServerURL.Length -1, 1);
WriteLog(ServerURL + " (" +
Context.Request.Url.ToString() + ")");
Stream RequestStream = Context.Request.InputStream;
byte[] PostData = new byte[Context.Request.InputStream.Length];
RequestStream.Read(PostData, 0,
(int) Context.Request.InputStream.Length);
HttpWebRequest ProxyRequest = (
HttpWebRequest) WebRequest.Create(ServerURL);
if ( ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["UpchainProxy"] ==
"true" )
ProxyRequest.Proxy = new WebProxy(
ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Proxy"], true);
ProxyRequest.Method = Context.Request.HttpMethod;
ProxyRequest.UserAgent = Context.Request.UserAgent;
CookieContainer ProxyCookieContainer = new CookieContainer();
ProxyRequest.CookieContainer = new CookieContainer();
ProxyRequest.CookieContainer.Add(
ProxyCookieContainer.GetCookies(new Uri(ServerURL)));
ProxyRequest.KeepAlive = true;
if ( ProxyRequest.Method == "POST" )
{
ProxyRequest.ContentType =
"application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
ProxyRequest.ContentLength = PostData.Length;
Stream ProxyRequestStream = ProxyRequest.GetRequestStream();
ProxyRequestStream.Write(PostData, 0, PostData.Length);
ProxyRequestStream.Close();
}
HttpWebResponse ProxyResponse = (
HttpWebResponse) ProxyRequest.GetResponse();
if (ProxyRequest.HaveResponse)
{
foreach(Cookie ReturnCookie in ProxyResponse.Cookies)
{
bool CookieFound = false;
foreach(Cookie OldCookie in
ProxyCookieContainer.GetCookies(new Uri(ServerURL)))
{
if (ReturnCookie.Name.Equals(OldCookie.Name))
{
OldCookie.Value = ReturnCookie.Value;
CookieFound = true;
}
}
if (!CookieFound)
ProxyCookieContainer.Add(ReturnCookie);
}
}
Stream StreamResponse = ProxyResponse.GetResponseStream();
int ResponseReadBufferSize = 256;
byte[] ResponseReadBuffer = new byte[ResponseReadBufferSize];
MemoryStream MemoryStreamResponse = new MemoryStream();
int ResponseCount = StreamResponse.Read(ResponseReadBuffer, 0,
ResponseReadBufferSize);
while ( ResponseCount > 0 )
{
MemoryStreamResponse.Write(ResponseReadBuffer, 0,
ResponseCount);
ResponseCount = StreamResponse.Read(ResponseReadBuffer, 0,
ResponseReadBufferSize);
}
byte[] ResponseData = MemoryStreamResponse.ToArray();
string ResponseDataString = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(ResponseData);
if ( ProxyResponse.ContentType.StartsWith("text/html") )
{
HTML.ParseHTML Parser = new HTML.ParseHTML();
Parser.Source = ResponseDataString;
while( !Parser.Eof() )
{
char ch = Parser.Parse();
if ( ch == 0 )
{
HTML.AttributeList Tag = Parser.GetTag();
if ( Tag["href"] != null )
{
if ( Tag["href"].Value.StartsWith(
@"/") )
{
WriteLog("URL " +
Tag["href"].Value +
" modified to " + URLPrefix +
Tag["href"].Value);
ResponseDataString =
ResponseDataString.Replace(
"\"" +
Tag["href"].Value +
"\"", "\"" +
URLPrefix + Tag["href"].Value +
"\"");
}
}
if ( Tag["src"] != null )
{
if ( Tag["src"].Value.StartsWith(
@"/") )
{
WriteLog("URL " +
Tag["src"].Value +
" modified to " +
URLPrefix + Tag["src"].Value);
ResponseDataString =
ResponseDataString.Replace(
"\"" +
Tag["src"].Value +
"\"", "\"" +
URLPrefix + Tag["src"].Value +
"\"");
}
}
}
}
Context.Response.Write(ResponseDataString);
}
else
Context.Response.OutputStream.Write(ResponseData, 0,
ResponseData.Length);
MemoryStreamResponse.Close();
StreamResponse.Close();
ProxyResponse.Close();
}
catch ( Exception Ex )
{
Context.Response.Write(Ex.Message.ToString());
WriteLog("An error has occurred while requesting the URL
" + ServerURL + "(" +
Context.Request.Url.ToString() + ")\n" +
Ex.ToString());
}
}
private void WriteLog(string Message)
{
FileStream FS = new FileStream(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings[
"Log"], FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write);
string DateTimeString = DateTime.Now.ToString();
Message = "[" + DateTimeString + "] " + Message +
"\n";
byte[] FileBuffer = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(Message);
FS.Write(FileBuffer, 0, (int)FileBuffer.Length);
FS.Flush(); FS.Close();
}
}
}
Sample web.config Configuration File
<configuration>
<system.web>
<httpHandlers>
<add verb="*" path="*.sync" type="TryHTTPHandler.SyncHandler,
TryHTTPHandler" />
</httpHandlers>
<customErrors mode="Off" />
<appSettings>
<add key="UpchainProxy" value="true"/>
<add key="Proxy" value="proxy1:80"/>
<add key="Log" value="D:\\HTTPHandlerLog.rtf"/>
</appSettings>
</system.web>
</configuration>
Reverse Proxy Server Setup
In order to setup the Reverse Proxy Server in IIS, the following steps need to be performed.
- Compile the project to get .NET assemblies and create a web.config configuration file.
- Create a virtual directory in IIS, say "Handler" and copy the .NET assemblies into the "bin" folder of the virtual directory.
- Also copy the web.config configuration file to the virtual directory.
- Right-click the virtual directory just created and go to Properties>Directory>Configuration>Mappings>Add
- Specify the new application extension that will be handled by the Reverse Proxy Server, say ".sync" in the "Extension" field.
- In the "Add/Edit Applications Mapping" dialog box, browse and specify aspnet_isapi.dll in the "Executable" field. (For example: c:\windows\microsoft.net\framework\v2.0.50727\aspnet_isapi.dll)
- Set the "Verbs" to "All Verbs".
- Ensure that "Verify that files exist" is unchecked.
- Click "OK" until you close the "Properties" dialog box.
- Navigate to the reverse proxy URL in IE. (For example: http://localhost/handler/stg2web.sync)
- The filename with ".sync" extension will be taken as the back-end server name.
If you navigate to say, http://localhost/handler/stg2web.sync/tso5/logon.cfm, you will get the response from the back-end server, http://stg2web/tso5/logon.cfm
Specifications
Please note that these proxy features HTTP specifications and DO NOT support HTTPS. The following features are supported.
- HTTP GET
- HTTP POST
- HTTP Cookies
- URL Rewriting/Remapping
- Debug Logging
History
April 18, 2007 - Baseline (Version 1.0)
