Introduction
Serial port RS-232 is still used in industrial applications but has recently disappeared from most notebooks. There is a SerialPort class in the .NET Framework to handle all serial port communication, and you can use this class in your code simply by adding "using System.IO.Ports;". Also, for parallel port access, you must use Inpout32.dll from the following URL: http://logix4u.net/Legacy_Ports/Parallel_Port/Inpout32.dll_for_Windows_98/2000/NT/XP.html.
In this project, I use a real device to communicate by using the Hioki 3153 Hipot tester via serial port. Indication of a fail condition will be shown by the LED as told in this article: I/O Ports Uncensored - 1 - Controlling LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) with Parallel Port by Levent Saltuklaroglu.
At the end of this article, you can get information about the Hipot device. All the information was taken from the manual of the device. Thanks to Behlul Savaskan for typing these parts. I must also mention that Hioki may not have a customer support department. I asked some questions via e-mail, but I did not get any reply from them. Finally, I also added a setup project for copying inpout32.dll, which is needed for the parallel port to the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
The Namespace
I use two different namespaces: hipotinterface which includes the main program and the serial port code, and ParallelPort that handles the parallel port communication.
The Main Code
Here is the code for the serial port and the main window. When the main form is loaded with the FrmMain_Load event, all the parallel port pins are set to low and the device is set with the settings indicated in the HIOKI 3153 Automatic Insulation Resistance Withstanding Tester Settings section of this document. According to the user manual, after every command, a delimiter (Carriage Return and Line Feed) must be used. I used the Writeline method of the SerialPort class. Settings like "conf:with:kind AC50" were taken from the user manual. I use the FrmMain_Load event to force the device to be started with my initial settings when parameters are changed by the operator.
In the CommWith3153At9600 function, the Hipot device communicates with our PC. You can read the 3153 To PC Interface section for the details of the sent messages and queries.
The RunTest() function handles Red/Green label transformation, closing serial and parallel ports according to the result of the CommWith3153At9600 function.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Ports;
using System.Threading;
namespace hipotinterface
{
public partial class FrmMain : Form
{
public static SerialPort _serialPort =
new SerialPort("COM1", 9600, Parity.None, 8, StopBits.One);
public static string strTestResult = null;
static bool _ESR0CommandSent = false;
const string CRLF = "\r\n";
private void FrmMain_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ParallelPort.HipotParPort.HipotParPort1(false);
try
{
_serialPort.Open();
_serialPort.ReadTimeout = 5000;
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:with:kind AC50");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:with:volt 3.00");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("with:clow ON");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:with:cupp 5.5");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:with:clow 0.7");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("with:tim ON");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:with:tim 3.0");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("with:utim OFF");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("with:dtim OFF");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:ins:kind AC50");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:ins:volt 500");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("ins:rupp OFF");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:ins:rlow 4.0");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("ins:tim ON");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("conf:ins:tim 1.0");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("ins:del OFF");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine(":mode AWI");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.Close();
}
catch (Exception)
{
MessageBox.Show("Initialization Error.");
Application.Restart();
}
}
public FrmMain()
{
InitializeComponent();
AssemblyInfo ainfo = new AssemblyInfo();
this.Text = "Tuse HIPOT Operator Interface " + ainfo.Version;
}
public void CommWith3153At9600()
{
strTestResult = null;
try
{
_serialPort.Open();
_serialPort.ReadTimeout = 5000;
_serialPort.WriteLine("*cls");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("start");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_ESR0CommandSent = true;
while (_ESR0CommandSent == true)
{
char ch = ' ';
while ((ch == '0') || (ch == ' '))
{
_serialPort.WriteLine("ESR0?");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
string message = _serialPort.ReadLine();
if (message.StartsWith("9"))
{
ch = '9';
strTestResult = "Passed";
_ESR0CommandSent = false;
}
else if (message.StartsWith("10"))
{
ch = 'A';
strTestResult = "Above Failed";
_ESR0CommandSent = false;
}
else if (message.StartsWith("12"))
{
ch = 'C';
strTestResult = "Lower Failed";
_ESR0CommandSent = false;
}
}
}
if (strTestResult != "Passed")
{
_ESR0CommandSent = false;
}
statusBar1.Text = "Result: " + strTestResult;
}
catch (Exception)
{
MessageBox.Show("Cannot communicate with the device");
ParallelPort.HipotParPort.HipotParPort1(false);
System.Environment.Exit(-1);
}
}
public void RunTest()
{
button_Run.Enabled = false;
lblDut1.BackColor = SystemColors.Window;
lblDut1.Update();
statusBar1.Text = "";
lblDut1.Text = "";
strTestResult = null;
CommWith3153At9600();
if (strTestResult == "Passed")
{
lblDut1.BackColor = Color.GreenYellow;
}
else
{
lblDut1.BackColor = Color.Red;
lblDut1.Text = "Failed";
ParallelPort.HipotParPort.HipotParPort1(true);
statusBar1.Text = "HIPOT TEST FAILED";
MessageBox.Show("HIPOT TEST FAILED!!!",
"Hipot Test Failed",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
_serialPort.WriteLine("stop");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.WriteLine("*cls");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.Close();
ParallelPort.HipotParPort.HipotParPort1(false);
goto result1;
}
_serialPort.WriteLine("*cls");
_serialPort.WriteLine(CRLF);
_serialPort.Close();
strTestResult = null;
result1:
button_Run.Enabled = true;
button_Run.Text = "RUN";
button_Run.Update();
}
private void button_Run_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
RunTest();
}
}
}
The Parallel Port Code
The code in the Parallelport.cs file was modified from I/O Ports Uncensored - 1 - Controlling LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) with Parallel Port by Levent Saltuklaroglu; if you need line by line information, you should take a look at the article. The code assumes that LPT1 is the default parallel port and lights only the first pin (D0) when the test fails.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ParallelPort
{
public partial class HipotParPort : Form
{
public static int nAddress = 888;
public static Int32 onValue = 1;
public static Int32 offValue = 0;
public static int nDelay = 1000;
public class PortAccess
{
[DllImport("inpout32.dll", EntryPoint="Out32")]
public static extern void Output(int nAddress, int nDecimalValue);
}
public static void HipotParPort1(Boolean bBulbOn)
{
Application.DoEvents();
if (bBulbOn)
PortAccess.Output(nAddress, onValue);
else
PortAccess.Output(nAddress, offValue);
Thread.Sleep(nDelay);
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.SuspendLayout();
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(104, 47);
this.Name = "HipotParPort";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
}
}
How to Use the HIPOT Program
The Hipot Interface program is used for controlling HIOKI HIPOT test devices.
Attention: You must remove all external I/O cards, start/stop buttons etc., if there are any. Because, they will not work in remote mode. Besides that, the top cover must be closed for operator safety. I asked Hioki about the usage of this top cover in remote mode; unfortunately, I did not get any response. If you run the program, you will see the following screen:
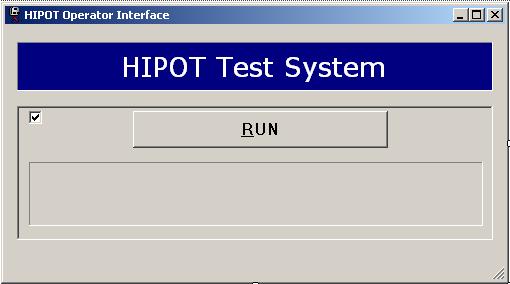
You must click the RUN button to start testing. If the DUT (Device Under Test) passes the testing, there will be a green bar on the form. Otherwise, you will see a red bar to indicate that the test has failed and also a pop-up message.
HIOKI 3153 Automatic Insulation Resistance Withstanding Tester Settings
- Default connection settings of the 3153 Hipot tester:
- Serial Port: "COM1"
- Bps: 9600
- Parity:1
- Databits:8
- StopBits:1
- Program arrange mode of the Hipot tester as in the following initial settings:
- Send any character to pass 3153 to Remote mode
- Set Withstand Test-voltage type to AC 50 Hz
- Set Withstand Test Voltage to 3.00kV
- Set Withstand Cutoff Current Upper Limit to 5.5 mA
- Set Withstand Cutoff Current Lower Limit to 0.7 mA
- Set Withstand Ramp Timer (Test Time) to 3.0 s
- Set Withstand Ramp-up Timer to OFF
- Set Withstand Ramp-down Timer to OFF
- Set Insulation Test-voltage Type to DC
- Set Insulation Test Voltage to 500V
- Set Insulation Resistance Upper Limit to OFF
- Set Insulation Resistance Lower Limit to 4.0 Mohm
- Set Insulation Test Time to 1.0 s
- Set Insulation Delay Time to OFF
- Set Test Mode: Withstand Voltage mode -> Insulation Resistance mode
Note that these settings were obtained by trying the device manually.
- If the result of the test is fail, then the D0 pin (#2) of the parallel port gets high. But you can also set other pins to be lit.
- If the result of the test is fail and to make the tester hear the beep sound, then stop command will not be sent to the Hipot tester. To stop it, the operator has to click the OK button.
3153 To PC Interface
The 3153 includes two 8 bit event registers. It is possible to determine the status of the unit by reading these registers.
The event registers are cleared in these situations:
- When a "*cls" command is executed
- When the event register is executed
- When the unit is powered on
- Standard Event Status Register (SESR) bit assignments
Bit 7
PON
| Power On flag
When the power is turned on or off recovery from a power cut, this bit is set to 1
|
| Bit 6 | Unused |
| Bit 5 CME | Command error
When a command which has been received contains a syntactic or semantic error, this bit is set to 1
- The command is not supported by the 3153
- There is a mistake in a program header
- The number of data parameters is wrong
- The format of parameters is wrong
|
| Bit 4 EXE | Execution error
When for some reason a command which has been received cannot be executed, this bit is set to 1
- The designated data value is outside the set range
- The designated data value is not acceptable
|
| Bit 3 DDE | Device dependent error
When a command cannot be executed due to some reason other than a command error, a query error, or an execution error, this bit is set to 1
|
| Bit 2 QYE | Query error
This bit is set to 1 when a query error is detected by the output queue control
- When the data overflows the output queue
- When data in the output queue has been lost
|
| Bit 1 | Unused |
| Bit 0 | Unused |
- Event Status Register 0 (ESR0) bit assignments
| Bit 7 | Unused |
| Bit 6 | Unused |
| Bit 5 | Unused |
| Bit 4 | Unused |
Bit 3
EOM | Test completed |
Bit 2
LFAIL
| Below lower limit of comparator |
Bit 1
UFAIL
| Above upper limit of comparator |
Bit 0
PASS
| Within limits of comparator |
- ESR0 = xxxx1100 = 0x0C = .12 ----> Test completed and below lower limit of comparator (FAIL)
- ESR0 = xxxx1010 = 0x0A = .10 ----> Test completed and above upper limit of comparator (FAIL)
- ESR0 = xxxx1001 = 0x09 = .9 -----> Test completed and within limits of comparator (PASS)
- RS 232 Command Reference
- CLS -----> Clears the status byte registers and the event registers
- ESR? -----> Returns the contents of the Standard Event Status Register (SESR) as a numerical value in NR1 format between 0 to 255 and then clears the SESR register
- ESR0? -----> Returns the value of the event status register 0 (ESR0) as a numerical value in NR1 format between 0 to 255 and then clears the ESR0 register
Final Note
I hope you have found my project very useful and can implement other devices. I try to avoid the classical way of putting all the available serial port options into a combo box. By examining the 3153 To PC interface section and my code, you can understand how things can be implemented. Also, please excuse me for my English.
