Introduction
This article shall describe an approach that may be used to upload any sort of a file through a Web service from a Windows Forms application. The approach demonstrated does not rely on the ASP.NET file uploader control and allows the developer the opportunity to upload files programmatically and without user intervention. Such an approach may be useful for doing something like processing out the contents of a local message queue when Internet service is available (if the user base were mobile and had only intermittent connectivity). The article also addresses the use of a file size check as a precursor to allowing a file to upload through the service.

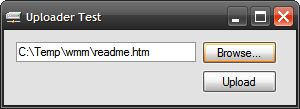
Figure 1: Test Application Shown Uploading a File.

Figure 2: Mixed bag of different file types in transient storage folder.
Getting Started
The solution contains two projects; one is a ASP.NET Web Service project (Uploader) and the other is a WinForms test application (TestUploader) used to demonstrate uploading files through the Web method provided in the Web service project.
The Web service project contains only a single Web service (FileUploader) which in turn contains only a single Web Method (UploadFile). The WinForms application contains only a single form which contains the controls (one textbox and two buttons used in conjunction with an OpenFileDialog control) and code necessary to select and upload files through the Web service.

Figure 3: Solution Explorer with both Projects Visible.
Code: Uploader Web Service Project
The Uploader Web service project is an ASP.NET Web service project containing a single Web service called, FileUploader; this Web service exposes a single Web method called, UploadFile.
The code for this Web service begins with the following:
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Web.Services
Imports System.Web.Services.Protocols
Imports System.IO
<WebService(Namespace:="http://tempuri.org/")> _
<WebServiceBinding(ConformsTo:=WsiProfiles.BasicProfile1_1)> _
<Global.Microsoft.VisualBasic.CompilerServices.DesignerGenerated()> _
Public Class FileUploader
Inherits System.Web.Services.WebService
The class starts out with the default imports; I added System.IO to the defaults to support the use of file and memory streams. The Web service namespace is left as the default http://tempuri.org/ which of course will have to be updated if the service were deployed.
The remainder of the code supplied in this class is used to define the Web method used to upload the file; the code is annotated. The essential process is that, files converted to byte arrays are passed along with the full name of the file (not the path) including the extension as arguments to the UploadFile Web method. The byte array is passed to a memory stream, and a file stream is opened pointing to a newly created file (named the name of the original file) within the target folder used to store the files. Once the file stream has been created, the memory stream is written into the file stream and then the memory stream and file stream are disposed of.
The Web method is set up to return a string; if all goes well, the string returned will read OK, if not, the error message encountered will be returned to the caller.
<WebMethod()> _
Public Function UploadFile(ByVal f As Byte(), ByVal fileName As String) As String
Try
Dim ms As New MemoryStream(f)
Dim fs As New FileStream(System.Web.Hosting.HostingEnvironment.
MapPath("~/TransientStorage/") & fileName, FileMode.Create)
ms.WriteTo(fs)
ms.Close()
fs.Close()
fs.Dispose()
Return "OK"
Catch ex As Exception
Return ex.Message.ToString()
End Try
End Function
Code: Test Uploader Win Forms Application
The test application contains a single Windows Form class; this form contains a text box used to display the name of the file selected for upload, a browse button used to launch an Open File dialog box which is used to navigate to and select a file for upload, and an upload button which is used to pass the file to the Web service so that the selected file may be stored on the server.
The code for this class begins with the following:
Imports System.IO
Public Class Form1
Aside from the default imports, I have added only System.IO to the list as this is necessary to support working with files. The namespace and class declarations are in the default configuration. In addition to System.IO, the project also adds in a web reference pointing to the File Uploader Web service, the reference is given the alias of Uploader.
The next bit of code in the class is a private method used to prepare the file for submittal to the Web service and to actually make that submittal. The code below is annotated to describe the activity but the essential parts of the operation are to check the file size to see if the Web service will accept the file (by default, the Web server will accept uploads smaller than 4 MB in size, the web.config file must be updated in order to support larger uploads), and to convert the file to a byte array. When everything is ready, the byte array and the name of the file including the extension is passed to an instance of the Web Service Web method.
Note that, when setting up the demo, you will have to remove and add the Web reference back into the project in order for it to work for you.
Public Sub UploadFile(ByVal filename As String)
Try
Dim strFile As String = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(filename)
Dim svc As New TestUploader.Uploader.FileUploader()
Dim fInfo As New FileInfo(filename)
Dim numBytes As Long = fInfo.Length
Dim dLen As Double = Convert.ToDouble(fInfo.Length / 1000000)
If (dLen < 5) Then
Dim fStream As New FileStream(filename, FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read)
Dim br As New BinaryReader(fStream)
Dim data As Byte() = br.ReadBytes(Convert.ToInt32(numBytes))
br.Close()
Dim sTmp As String = svc.UploadFile(data, strFile)
fStream.Close()
fStream.Dispose()
MessageBox.Show("File upload status: " & sTmp, "File Upload")
End If
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString(), "Upload Error")
End Try
End Sub
Following the UploadFile method, the next bit of code is used to handle the browse button’s click event. This code is used merely to display an Open File dialog to the user and to take the file selected through that dialog and display the file name in the form’s file name text box.
Private Sub btnBrowse_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As _
System.EventArgs) Handles btnBrowse.Click
OpenFileDialog1.Title = "Open File"
OpenFileDialog1.FileName = String.Empty
Try
OpenFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = "C:\Temp"
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString(), "Error")
End Try
OpenFileDialog1.ShowDialog()
If OpenFileDialog1.FileName = String.Empty Then
Return
Else
txtFileName.Text = OpenFileDialog1.FileName
End If
End Sub
The class wraps up with the button click event handler for the Upload button. This handler merely checks for text in the file name text box and, if something is there, it sends the value to the Upload method.
Private Sub btnUpload_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As _
System.EventArgs) Handles btnUpload.Click
If txtFileName.Text <> String.Empty Then
UploadFile(txtFileName.Text)
Else
MessageBox.Show("You must select a file first.", "No File Selected")
End If
End Sub
That wraps up all of the client and server side code necessary to upload any sort of file to a server from a WinForms application.
Summary
This article was intended to demonstrate an easy approach to uploading any sort of a file to a Web Server from a WinForms application. This example uses the default upload size of 4096 KB, if you need to upload larger files, you will need to alter this value by changing the httpRuntime maxRequestLength property to the desired value; at the same time you may need to increase the executionTimeout property to a greater value as well in order to support longer upload times. Take care when altering the values as Microsoft has established the default 4 MB limit to provide some safety against attempts to upload extremely large files that may hamper access to the server.
From the web.config file, increasing the upload file size is accomplished in this section of the file:
<configuration>
<appSettings/>
<connectionStrings/>
<system.web>
<httpRuntime
executionTimeout="110"
maxRequestLength="4096"
/>
