Introduction
I have seen lot of beginners struggle with GridView and it is not working. To solve this to some extent, I have created an application
with most of the events and properties of GridView. This may be helpful for getting a clear idea about working with GridView. This application
also has a few JavaScript code snippets and stylesheets which may be useful to add some values to the GridView. Hope this article will be simple and sufficient.
What is a GridView?
The DataGrid or GridView control displays data in tabular form, and it also supports selecting, sorting, paging, and editing the data inside
the grid itself. The DataGrid or GridView generates a BoundColumn for each field in the data source (AutoGenerateColumns=true).
By directly assigning the data source to the GridView, the data can be rendered in separate columns, in the order it occurs in the data source.
By default, the field names appear in the grid's column headers, and values are rendered in text labels. A default format is applied to non-string values and it can be changed.
GridView Fields
| Column Name | Description |
BoundColumn | To control the order and rendering of columns. |
HyperLinkColumn | Presents the bound data in HyperLink controls |
ButtonColumn | Bubbles a user command from within a row to the grid event handler |
TemplateColumn | Controls which controls are rendered in the column |
CommandField | Displays Edit, Update, and Cancel links in response to changes in the DataGrid control's EditItemIndex property. |
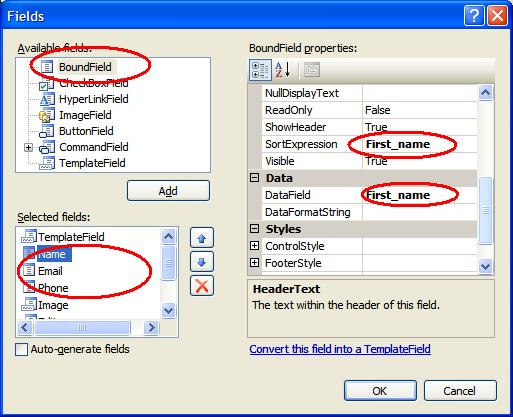
BoundColumn
By explicitly creating a BoundColumn in the grid's Columns collection, the order and rendering of each column can be controlled.
In the BoundField properties, when the DataField and the SortExpressions are given, sorting and rendering the data can be easily done.
HyperLinkColumn
A HyperLinkColumn presents the bound data in HyperLink controls. This is typically used to navigate from an item in the grid to a Details
view on another page by directly assigning the page URL in NavigationUrl or by rendering it from the database.

TemplateColumn
With a TemplateColumn, the controls which are rendered in the column and the data fields bound to the controls can be controlled. By using
the TemplateColumn, any type of data control can be inserted.

By clicking the Edit Templates option, it opens the Template field where we can see controls that can be added like Label, CheckBox,
and even a GridView.

CommandField
The EditCommandColumn is a special column type that supports in-place editing of the data in one row in the grid.
EditCommandColumn interacts with another property of the grid: EditItemIndex. By default, the value of EditItemIndex
is -1, meaning none of the rows (items) in the grid are being edited. If EditItemIndex is -1, an "edit" button is displayed
in the EditCommandColumn for each of the rows in the grid.
When the "edit" button is clicked, the grid's EditCommand event is thrown. It's up to the programmer to handle
this event in the code. The typical logic sets EditItemIndex to the selected row, and then rebinds the data to the grid.
When EditItemIndex is set to a particular row, the EditCommandColumn displays "update" and "cancel"
buttons for that row ("edit" is still displayed for the other rows). These buttons cause the
UpdateCommand and CancelCommand events to be thrown, respectively.

Different Types of Events
| Name | Description |
DataBinding | Occurs when the server control binds to a data source. (Inherited from Control.) |
DataBound | Occurs after the server control binds to a data source. (Inherited from BaseDataBoundControl.) |
Disposed | Occurs when a server control is released from memory, which is the last stage of the server control lifecycle when an ASP.NET page is requested. (Inherited from Control.) |
Init | Occurs when the server control is initialized, which is the first step in its lifecycle. (Inherited from Control.) |
Load | Occurs when the server control is loaded into the Page object. (Inherited from Control.) |
PageIndexChanged | Occurs when one of the pager buttons is clicked, but after the GridView control handles the paging operation. |
PageIndexChanging | Occurs when one of the pager buttons is clicked, but before the GridView control handles the paging operation. |
PreRender | Occurs after the Control object is loaded but prior to rendering. (Inherited from Control.) |
RowCancelingEdit | Occurs when the Cancel button of a row in edit mode is clicked, but before the row exits edit mode. |
RowCommand | Occurs when a button is clicked in a GridView control. |
RowCreated | Occurs when a row is created in a GridView control. |
RowDataBound | Occurs when a data row is bound to data in a GridView control. |
RowDeleted | Occurs when a row's Delete button is clicked, but after the GridView control deletes the row. |
RowDeleting | Occurs when a row's Delete button is clicked, but before the GridView control deletes the row. |
RowEditing | Occurs when a row's Edit button is clicked, but before the GridView control enters edit mode. |
RowUpdated | Occurs when a row's Update button is clicked, but after the GridView control updates the row. |
RowUpdating | Occurs when a row's Update button is clicked, but before the GridView control updates the row. |
SelectedIndexChanged | Occurs when a row's Select button is clicked, but after the GridView control handles the select operation. |
SelectedIndexChanging | Occurs when a row's Select button is clicked, but before the GridView control handles the select operation. |
Sorted | Occurs when the hyperlink to sort a column is clicked, but after the GridView control handles the sort operation. |
Sorting | Occurs when the hyperlink to sort a column is clicked, but before the GridView control handles the sort operation. |
Unload | Occurs when the server control is unloaded from memory. (Inherited from Control.) |
These events are all listed in the MSDN, and here I have given a few events which are frequently used in our day to day projects:
PageIndexChanging
This event occurs when the property of the grid AllowPaging is set to true, and in the code behind the PageIndexChanging event is fired.
Paging
The DataGrid provides the means to display a group of records from the data source (for example, the first 10), and then navigates
to the "page" containing the next 10 records, and so on through the data.
Paging in DataGrid is enabled by setting AllowPaging to true. When enabled, the grid will display page navigation buttons either
as "next/previous" buttons or as numeric buttons. When a page navigation button is clicked, the PageIndexChanged event is thrown.
It's up to the programmer to handle this event in the code.
GridView2.PageIndex = e.NewPageIndex;
TempTable();
RowCommand
The DataGrid fires the RowCommand event when any button is pressed. We can given any name as
command name, and based on that, the check will be done and the loop will be executed.
protected void GridView6_RowCommand(object sender, GridViewCommandEventArgs e)
{
if (e.CommandName == "view")
{
int row = int.Parse(e.CommandArgument.ToString());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.Append("<script language="'javascript'">\r\n");
sb.Append(" window.open('View.aspx?id=" + row + "',
null,'width=350,height=300,scrollbars=yes,left=350,top=200,right=5,bottom=5');");
sb.Append("</script>");
if (!this.IsClientScriptBlockRegistered("BindScript"))
{
RegisterClientScriptBlock("openScript", sb.ToString());
}
}
}
RowCreated
The DataGrid fires the RowCreate event when a new row is
created.
protected void GridView3_RowCreated(object sender, GridViewRowEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Row.RowType == DataControlRowType.DataRow && (e.Row.RowState ==
DataControlRowState.Normal || e.Row.RowState == DataControlRowState.Alternate))
{
CheckBox chkBxSelect = (CheckBox)e.Row.Cells[1].FindControl("chkselect");
CheckBox chkBxHeader = (CheckBox)this.GridView3.HeaderRow.FindControl("chkHeader");
chkBxSelect.Attributes["onclick"] = string.Format("javascript:ChildClick(
this,'{0}');", chkBxHeader.ClientID);
}
}
RowDeleting
The DataGrid fires the RowDeleting event when the command name is given as Delete.
protected void GridView3_RowDeleting(object sender, GridViewDeleteEventArgs e)
{
int row = e.RowIndex;
Temp.Rows[row].Delete();
GridView3.DataSource = Temp;
GridView3.DataBind();
}
RowUpdating
The DataGrid fires the RowUpdating event when the command name is given as Update.
CommandName="update"
protected void GridView3_RowUpdating(object sender, GridViewUpdateEventArgs e)
{
GridView3.EditIndex = e.RowIndex;
GridView3.DataSource = Temp;
GridView3.DataBind();
}
RowEditing
The DataGrid fires the RowEditing event when the command name is given as Edit.
/OnRowEditing="GridView3_RowEditing"
protected void GridView3_RowEditing(object sender, GridViewEditEventArgs e)
{
GridView3.EditIndex = e.NewEditIndex - 1;
int row = e.NewEditIndex;
Temp.Rows[row]["name"] = ((TextBox)GridView3.Rows[e.NewEditIndex].FindControl(
"txtname")).Text;
Temp.Rows[row]["gender"] = ((DropDownList)GridView3.Rows[e.NewEditIndex].FindControl(
"ddlgender")).Text;
Temp.Rows[row]["email"] = ((TextBox)GridView3.Rows[e.NewEditIndex].FindControl(
"txtemail")).Text;
Temp.Rows[row]["salary"] = ((TextBox)GridView3.Rows[e.NewEditIndex].FindControl(
"txtsalary")).Text;
Temp.AcceptChanges();
Total = decimal.Parse(Temp.Compute("sum(Salary)", "Salary>=0").ToString());
Session["Salary"] = Total;
GridView3.DataSource = Temp;
GridView3.DataBind();
}
RowDatabound
The DataGrid fires the RowDatabound event when a data row is bound to data in a GridView control.
protected void GridView4_RowDataBound(object sender, GridViewRowEventArgs e)
{
int index = e.Row.RowIndex;
if (e.Row.RowType == DataControlRowType.DataRow)
{
DataTable tempdt = new DataTable();
tempdt.Columns.Add("Id");
tempdt.Columns.Add("Language", typeof(String));
DataRow dr = tempdt.NewRow();
dr["Id"] = 1;
dr["Language"] = "C";
tempdt.Rows.Add(dr);
DataRow dr1 = tempdt.NewRow();
dr1["Id"] = 2;
dr1["Language"] = "C++";
tempdt.Rows.Add(dr1);
GridView gr = (GridView)(e.Row.FindControl("GridView5"));
if (gr != null)
{
gr.DataSource = tempdt;
gr.DataBind();
}
}
}
Sorting
Data in a grid is commonly sorted by clicking the header of the column to sort. Sorting in a DataGrid can be enabled by setting
AllowSorting to true. When enabled, the grid renders LinkButton controls in the header for each column. When the button is clicked,
the grid's SortCommand event is thrown. It's up to the programmer to handle this event in the code. Because DataGrid always displays
the data in the same order it occurs in the data source, the typical logic sorts the data source, and then rebinds the data to the grid.
protected void GridView2_Sorting(object sender, GridViewSortEventArgs e)
{
if (e.SortExpression.Trim() == this.SortField)
this.SortDirection = (this.SortDirection == "D" ? "A" : "D");
else
this.SortDirection = "A";
this.SortField = e.SortExpression;
TempTable();
}
Header and Footer of the Grid
This is a JavaScript to use when there is a necessity to check all the checkboxes in a column by checking a single checkbox in the grid header.
While we are checking the grid header, all the checkboxes inside the grid will be selected, and if any child column is unchecked, then the header will also be unchecked.
<script type="text/javascript">
var TotalChkBx;
var Counter;
window.onload = function()
{
TotalChkBx = parseInt('<%= this.GridView3.Rows.Count %>');
Counter = 0;
}
function SelectAll(CheckBox)
{
var TargetBaseControl = document.getElementById('<%= this.GridView3.ClientID %>');
var TargetChildControl = "chkselect";
var Inputs = TargetBaseControl.getElementsByTagName("input");
for(var n = 0; n < Inputs.length; ++n)
if(Inputs[n].type == 'checkbox' && Inputs[n].id.indexOf(TargetChildControl,0) >= 0)
Inputs[n].checked = CheckBox.checked;
Counter = CheckBox.checked ? TotalChkBx : 0;
}
function ChildClick(CheckBox, HCheckBox)
{
var HeaderCheckBox = document.getElementById(HCheckBox);
if(CheckBox.checked && Counter < TotalChkBx)
Counter++;
else if(Counter > 0)
Counter--;
if(Counter < TotalChkBx)
HeaderCheckBox.checked = false;
else if(Counter == TotalChkBx)
HeaderCheckBox.checked = true;
}
</script>
onclick="javascript:SelectAll(this);"
Maintaining the values in the footer is done by the following code:
protected void GridView3_RowDataBound(object sender, GridViewRowEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Row.RowType == DataControlRowType.Footer)
{
e.Row.Cells[4].Text = this.Total.ToString();
}
}
To maintain the grid header in a fixed state, a style sheet is used in the source code:
<style type="text/css">.DataGridFixedHeader {
BACKGROUND: url(Images/grid_header.jpg) repeat-x;
POSITION: relative; TOP: expression(this.offsetParent.scrollTop); HEIGHT: 27px }
</style>
<div style="width:80%; height:250px; overflow:auto;" >
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server"
Width="100%" AutoGenerateColumns="False"
CellPadding="4" DataKeyNames="id"
ForeColor="#333333" GridLines="None"
OnRowCreated="GridView1_RowCreated"
AllowPaging="True" AllowSorting="True"
OnPageIndexChanging="GridView1_PageIndexChanging" OnSorting="GridView1_Sorting"
PageSize="2" OnRowCommand="GridView1_RowCommand"
OnRowDeleting="GridView1_RowDeleting"
OnRowEditing="GridView1_RowEditing">
....
....
<HeaderStyle BackColor="#507CD1" Font-Bold="True" ForeColor="White"
CssClass="gridHeader DataGridFixedHeader" />
.....
.....
</asp:GridView>
</div>
Export GridView to Word, Excel, and PDF
Word
protected void btnword_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Response.AddHeader("content-disposition",
"attachment;filename=Information.doc");
Response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.NoCache);
Response.ContentType = "application/vnd.word";
System.IO.StringWriter stringWrite = new System.IO.StringWriter();
System.Web.UI.HtmlTextWriter htmlWrite = new HtmlTextWriter(stringWrite);
HtmlForm frm = new HtmlForm();
GridView1.Parent.Controls.Add(frm);
frm.Attributes["runat"] = "server";
frm.Controls.Add(GridView1);
frm.RenderControl(htmlWrite);
Response.Write(stringWrite.ToString());
Response.End();
}
Excel
protected void btnexcel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string attachment = "attachment; filename=Information.xls";
Response.ClearContent();
Response.AddHeader("content-disposition", attachment);
Response.ContentType = "application/ms-excel";
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
HtmlTextWriter htw = new HtmlTextWriter(sw);
HtmlForm frm = new HtmlForm();
GridView1.Parent.Controls.Add(frm);
frm.Attributes["runat"] = "server";
frm.Controls.Add(GridView1);
frm.RenderControl(htw);
Response.Write(sw.ToString());
Response.End();
}
PDF
protected void btnpdf_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Response.Clear();
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
HtmlTextWriter htw = new HtmlTextWriter(sw);
GridView1.RenderControl(htw);
Response.ContentType = "application/pdf";
Response.AddHeader("content-disposition",
"attachment; filename=Information.pdf");
Response.Write(sw.ToString());
Response.End();
}
Difference between DataGrid, DataList, and Repeater
A DataGrid, DataList, and Repeater are all ASP.NET data Web controls.
They have many things in common like the DataSource property, the DataBind method, and the ItemDataBound and ItemCreated events.
When you assign the DataSource property of a DataGrid to a DataSet, each DataRow present in the DataRow
collection of the DataTable is assigned to a corresponding DataGridItem, and this is the same for the rest of the two controls. But The HTML code
generated for a DataGrid has an HTML TABLE <ROW> element created for the particular DataRow and it is a table form representation
with columns and rows. For a DataList, it is an array of rows, and based on the template selected and the RepeatColumn property value, we can specify how many
DataSource records should appear per HTML <table> row. In short, in a DataGrid, we have one record per row,
but in a DataList, we can have five or six rows per row. For a Repeater control, the data records to be displayed depend upon the
templates specified, and the only HTML generated is the due to the templates.
In addition to these, DataGrid has in-built support for sorting, filtering, and paging the data, which is not possible when using
a DataList, and for a Repeater control, we would require to write explicit code to do paging.
Conclusion
This is my second article, and if you have any questions, you can refer to the project attached because all the code in the article is from
the project. Further questions or clarifications or mistakes are welcome.
