Enhance your learning in MSBI & SQL Server by watching our step by step youtube videos:-
Some days back, I was installing SQL Server 2012 enterprise service pack 1. During installation, when I was running through the setup, it gave me two options (multi-dimensional and tabular) of how I want to install SQL Server analysis service. Below is the image captured while doing installation.

At the first glance, these options are clearly meant to specify how we want the model design for our analysis service.
Now the first option, i.e., “MultiDimensional” was pretty clear as I have been using them right from SQL Server 2005 till today, i.e., (Star schema or Snow flake).
After some Googling and hunting, I came to know about the second option. Let me throw some light on the same and then we will conclude what is BISM.
Now overall, we have two kinds of database systems, one is OLTP system where the database design thought process is in terms of tables and normalization rules (first normal form, second normal form and third normal form database design) are followed.
The second kinds of systems are OLAP systems where we mostly design in terms of fact tables and dimension tables. Cube which is a multi-dimensional view of data is created properly if you design your database as OLAP system.
So in simple words, we need to create a DB with OLAP design to ensure that proper cubes structure is created.

Now some times or I will say many times, it’s really not feasible to create different structures and then create cubes from them. It would be great if SSAS gives us some options where we can do analysis straight from normalized simple tables.
For instance, take simple end users who use “power pivot”. It’s very difficult for them to understand OLAP models like dimension and fact tables. But yes, they do understand tables with rows and columns. If you see Microsoft Excel, the format is in terms of tables which have rows and columns and these end users are comfortable with a tabular structure.
Below is a simple image of how simple end user visualizes data in Excel, i.e., tabular – rows and columns.

That’s where exactly the second option, i.e., the “Tabular” mode comes into the picture.
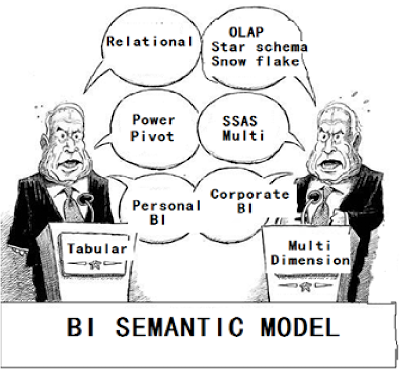
So if we put in simple words, BISM (Business intelligence semantic model) is a model which tries to serve simple users / programmers who are comfortable with tabular structure and also maintains professional OLAP models for corporate.

So BISM is a unifying name for both Multi-dimension and tabular models. So if you are a personal BI person who loves ADHOC analysis, you can use power pivot or SSAS tabular IDE to do analysis. And if you are a person who is working on a corporate project then Multi-dimension model is more scalable and worth looking into.

Just a last quick note: This is also a favorite SQL Server interview question which is making rounds now a days when SQL Server 2012 topic is discussed.
You can also see my video on Can views be updated (SQL Server interview questions)?
CodeProject
