Introduction
This article shall make use of API’s inside android.telephony and android.os.batterymanager packages present in the Android SDK to create a simple yet smart application to display the phone details, battery status and data connectivity status of an Android Smartphone.
Background
The Android framework gives you everything you need to build best-in-class app experiences. The core component of this is the Android Software Development Kit (Android SDK) that provides all necessary tools to build, test and deploy an application. In this article we mainly focus on the following packages / classes to display some of the very common information related to a cellular phone.
Service Provider Related
- Service state
- Cell Location
- Call State
- Connection State
- Signal Strength
- Data Exchange.
Phone Specific
- Device ID
- Phone number
- SW Version
- Operator Name
- SIM Country Code
- SIM Operator
- SIM Serial No
- Subscriber ID
- Network type
- Phone type
- Battery Related Information
In order to retrieve the above mentioned information from the Android system, we have to include the permissions in our android application in the AndroidManifest.xml file. The below mentioned list presents the user with appropriate permissions that are required to be included in AndroidManifest.xml file for a certain information request.
Permissions in Android manifest
| No | Information | Permission |
| 1 | Cell location | ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION |
| 2 | Call State | |
| 3 | Data Connection State | |
| 4 | Signal Strength | |
| 5 | Data Direction States | |
| 6 | Service State | |
| 7 | Device ID | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 8 | Phone Number | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 9 | Operator Name | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 10 | SIM Operator | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 11 | SIM Country Code | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 12 | SIM Serial No. | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 13 | Subscriber ID | READ_PHONE_STATE |
| 14 | Network Type | ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE |
| Phone Type | |
Designing the Android application layout
The next step is to design a layout file which shall display the information that we are interested in. For the sake of clarity i have included a tabbed layout in this sample. The first tab shall display the telephony related information while the second tab shall show the current battery status of the phone.
The main.xml
This layout shall host a tab widget. Depending on the selection shall display the Phone Status or Battery Status information
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@android:id/tabhost">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</TabWidget>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>phonestatus.xml
This layout shall display the telephony related information such as Call State,Cell location, Connection state, Signal level, Data activity, Phone number , IMEI code , Device SW version and so on.
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:scrollbarStyle="insideOverlay"
android:scrollbarAlwaysDrawVerticalTrack="false">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!--Service State-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/tvServiceState" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/serviceState_info" style="@style/textStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--cell location -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/tvCellLocation" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/cellLocation_info" style="@style/textStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--Call State-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/tvCallState" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/callState_info" style="@style/textStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--Data Connection State-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/tvConnState" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/connectionState_info" style="@style/textStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--Signal level -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/tvSignalLevel" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/signalLevel" style="@style/progressStyle"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/signalLevelInfo" style="@style/textSmallStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<!--Data Activity-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView android:text="@string/strData" style="@style/labelStyleRight"/>
<ImageView android:id="@+id/dataDirection" style="@style/imageStyle"/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView android:id="@+id/device_info" style="@style/labelStyleLeft"/>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
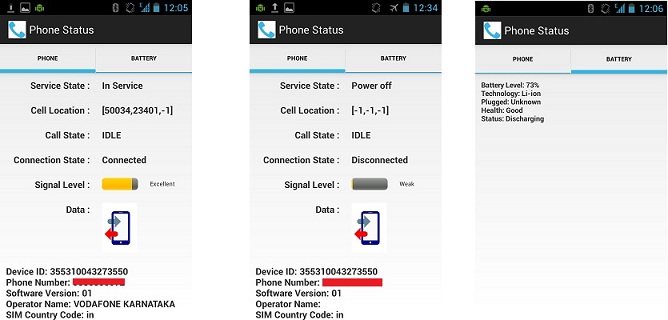
Once the data has been assigned inside the PhoneStatusActivity (described later). The layout file would produce a screen as below

The battery.xml
The layout shall serve as a placeholder to display the phone battery specific information. The layout file consists of a simple textview. The data source for this text view shall be set inside BatteryStatusActivity.java (described later)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/batterylevel" style="@style/textStyleCenter"/>
</LinearLayout>
The layout file shall output to something similar as shown below

Android Layout Styles
Styles in Android is analogous to cascading stylesheets (CSS) in web
design i.e they allow you to separate the design from the
content. For a consistent look and feel in the Battery Status and Phone Status layout we will include a styles.xml file inside the res/values folder which will specify properties such as height, padding, font color, font size,
background color,text alignment and much more.
To include a style.xml file inside Android project, let us create a new XML file under res/values folder and name it as styles.xml.
<resources xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<style name="AppTheme" parent="android:Theme.Light" />
<color name="blue">#0000FF</color>
<color name="white">#FFFFFF</color>
<color name="red">#FF0000</color>
<color name="yellow">#FFF200</color>
<color name="green">#00FF00</color>
<color name="black">#000000</color>
<style name="labelStyleRight">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:textSize">15dip</item>
<item name="android:textStyle">bold</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|right</item>
</style>
<style name="labelStyleLeft">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:textSize">15dip</item>
<item name="android:textStyle">bold</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|left</item>
</style>
<style name="textStyle">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:textSize">15dip</item>
<item name="android:textStyle">bold</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|left</item>
</style>
<style name="textStyleCenter">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:textSize">15dip</item>
<item name="android:textStyle">bold</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center</item>
</style>
<style name="textSmallStyle">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:textSize">10dip</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|left</item>
</style>
<style name="progressStyle">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:indeterminateOnly">false</item>
<item name="android:minHeight">20dip</item>
<item name="android:maxHeight">20dip</item>
<item name="android:progress">15</item>
<item name="android:max">100</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|left</item>
<item name="android:progressDrawable">@android:drawable/progress_horizontal</item>
<item name="android:indeterminateDrawable">@android:drawable/progress_indeterminate_horizontal</item>
</style>
<style name="imageStyle">
<item name="android:layout_width">fill_parent</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_weight">0.5</item>
<item name="android:src">@drawable/nodata</item>
<item name="android:scaleType">fitStart</item>
<item name="android:layout_margin">10dip</item>
<item name="android:gravity">center_vertical|left</item>
</style>
</resources> Using the code
1. Permissions in the AndroidManifest.xml file
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_UPDATES"/>
2. The android.telephony.TelephonyManager
Any information related to the telephony services on the device has to be accessed via TelephonyManager class. This class cannot be instantiated directly instead we retrieve a reference to an instance through
TelephonyManager tm = (TelephonyManager) getSystemService(TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
2.1 The PhoneStateListener object
The PhoneStateListener class is responsible for monitoring changes in specific telephony states
on the smartphone device. We shall override the methods for the state that we wish to receive updates for in the PhoneStateListener object and pass the PhoneStateListener instance, along with bitwise-or of the LISTEN_ flags to TelephonyManager.listen(). The application is now ready for updating any view based on the Telephony events
int events = PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_SIGNAL_STRENGTH |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_DATA_ACTIVITY |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CELL_LOCATION |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_STATE |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_FORWARDING_INDICATOR |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_DATA_CONNECTION_STATE |
PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_SERVICE_STATE;
tm.listen(phoneListener, events);
2.1.1 Listening to Phone States
Upon specifying the updates we wish to receive from TelephonyManager. The PhoneStateListener shall handle the callback methods for each change in the phone state. We shall record all such state changes in the corresponding handler methods provided by the PhoneStateListener class and update the status on the view.
NOTE: For demonstration purpose I've discussed only a handful of PhoneStateListener callback methods here in this article. Also the callback implementation methods are oversimplified for the sake of understanding. The methods do no more that updating a TextView or change of thumbnail image in some cases.
2.1.1.1. onCallStateChanged
Callback invoked when device call state changes. In this method we shall record whether the phone is OFFHOOK, RINGING or in the IDLE State based on the State.
| TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_IDLE | Device call state : No activity |
| TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_RINGING | Device call state : A new call arrived and is
ringing or waiting |
| TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_OFFHOOK | At least one call exists
that is dialing, active, or on hold, and no calls are ringing
or waiting |
public void onCallStateChanged(int state, String incomingNumber) {
String phoneState = "UNKNOWN";
switch(state){
case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_IDLE :
phoneState = "IDLE";
break;
case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_RINGING :
phoneState = "Ringing (" + incomingNumber + ") ";
break;
case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_OFFHOOK :
phoneState = "Offhook";
break;
}
setTextViewText(info_ids[INFO_CALL_STATE_INDEX], phoneState);
super.onCallStateChanged(state, incomingNumber);
}
2.1.1.2. onDataConnectionStateChanged
This callback method is invoked whenever there is a change in the data connection state. It can return any of the following 4 possibilities
| TelephonyManager.DATA_CONNECTED | Indicates IP traffic should be available |
| TelephonyManager.DATA_CONNECTING | Currently setting up a data connection |
| TelephonyManager.DATA_DISCONNECTED | Indicates IP Traffic is not available |
| TelephonyManager.DATA_SUSPENDED | The connection is up, but IP
traffic is temporarily unavailable. For example, in a 2G network,
data activity may be suspended when a voice call arrives |
public void onDataConnectionStateChanged(int state) {
String phoneState = "UNKNOWN";
switch(state){
case TelephonyManager.DATA_CONNECTED :
phoneState = "Connected";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_CONNECTING :
phoneState = "Connecting..";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_DISCONNECTED :
phoneState = "Disconnected";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_SUSPENDED :
phoneState = "Suspended";
break;
}
setTextViewText(info_ids[INFO_CONNECTION_STATE_INDEX], phoneState);
super.onDataConnectionStateChanged(state);
}
2.1.1.3. onDataActivity
This Callback is invoked when data activity state changes. The possible data activity states are as listed below
- TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_NONE - No IP Traffic.
- TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_IN - Receiving IP Traffic
- TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_OUT - Currently sending IP Traffic
- TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_INOUT - Currently sending and receiving IP Traffic
- TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_DORMANT - Data connection is active, but physical link is down
public void onDataActivity(int direction) {
String strDirection = "NONE";
switch(direction){
case TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_IN :
strDirection = "IN";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_INOUT:
strDirection = "IN-OUT";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_DORMANT:
strDirection = "Dormant";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_NONE:
strDirection="NONE";
break;
case TelephonyManager.DATA_ACTIVITY_OUT:
strDirection="OUT";
break;
}
setDataDirection(info_ids[INFO_DATA_DIRECTION_INDEX],direction);
super.onDataActivity(direction);
}
The setDataDirection is a user defined method updates a corresponding thumbnail image on a ImageView based on the status of DataActivity .
private void setDataDirection(int id, int direction){
int resid = getDataDirectionRes(direction);
((ImageView)findViewById(id)).setImageResource(resid);
}
2.1.2 End Listening to Phone States
For the application to stop listening to the updates from the TelephonyManager class. We now shall pass the PhoneStateListener instance along with LISTEN_NONE flag to TelephonyManager.listen() method
tm.listen(phoneListener, PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_NONE);
2.2 Querying the Basic Phone Information
The TelephonyManager readily exposes methods to access basic information related to phone such as subscriber information, IMEI Code, Phone no,Network type etc. The code related to this Phone status information is included in the PhoneStatusActivity.java
String deviceid = tm.getDeviceId();
String phonenumber = tm.getLine1Number();
String softwareversion = tm.getDeviceSoftwareVersion();
String operatorname = tm.getNetworkOperatorName();
String simcountrycode = tm.getSimCountryIso();
String simoperator = tm.getSimOperatorName();
String simserialno = tm.getSimSerialNumber();
String subscriberid = tm.getSubscriberId();
String networktype = getNetworkTypeString(tm.getNetworkType());
String phonetype = getPhoneTypeString(tm.getPhoneType());
The user defined utility methods returns the equivalent string
private String getNetworkTypeString(int type){
String typeString = "Unknown";
switch(type)
{
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EDGE:
typeString = "EDGE"; break;
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_GPRS:
typeString = "GPRS"; break;
case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_UMTS:
typeString = "UMTS"; break;
default:
typeString = "UNKNOWN"; break;
}
return typeString;
}
private String getPhoneTypeString(int type){
String typeString = "Unknown";
switch(type)
{
case TelephonyManager.PHONE_TYPE_GSM: typeString = "GSM"; break;
case TelephonyManager.PHONE_TYPE_NONE: typeString = "UNKNOWN"; break;
default:
typeString = "UNKNOWN"; break;
}
return typeString;
}
In this sample, Once we collect all the required information we shall display the same on a deviceInfo TextView
deviceinfo += ("Device ID: " + deviceid + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Phone Number: " + phonenumber + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Software Version: " + softwareversion + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Operator Name: " + operatorname + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("SIM Country Code: " + simcountrycode + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("SIM Operator: " + simoperator + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("SIM Serial No.: " + simserialno + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Subscriber ID: " + subscriberid + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Network Type: " + networktype + "\n");
deviceinfo += ("Phone Type: " + phonetype + "\n");
2.3 Phone Battery
The android.os.BatteryManager class provides information related to
the status of the phone battery in the form of strings and constants.
Ex:
Also we can extract both the current charging status and, if the device is being charged, whether
it's charging via USB or AC charger using
- BatteryManager.BATTERY_PLUGGED_AC - Battery is plugged to an AC source
- BatteryManager.BATTERY_PLUGGED_USB - Battery is plugged to a USB source
- BatteryManager.BATTERY_STATUS_CHARGING - Battery is connected to a power supply and is charging
- BatteryManager.BATTERY_STATUS_DISCHARGING - Battery is discharging
- BatteryManager.BATTERY_STATUS_FULL - Battery charge is complete
3. Activity class for Smartphone Status App
3.1 The StatusActivity class
This is the main activity that is called on the start of the application. This activity is responsible for creating a tab host for hosting PhoneStatusActivity and BatteryStatusActivity. By default PhoneStatusActivity shall be activated.
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TabHost host = getTabHost();
TabSpec statusspec = host.newTabSpec("Phone");
statusspec.setIndicator("Phone",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.nphone));
Intent phoneStatusIntent = new Intent(this, PhoneStatusActivity.class);
statusspec.setContent(phoneStatusIntent);
TabSpec batteryspec = host.newTabSpec("Battery");
batteryspec.setIndicator("Battery", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.nbattery));
Intent batteryIntent = new Intent(this, BatteryStatusActivity.class);
batteryspec.setContent(batteryIntent);
host.addTab(statusspec);
host.addTab(batteryspec);
}3.2 The PhoneStatusActivity class
The PhoneStatusActivity class is responsible for displaying the information received from TelephonyManager as described in the Section 2.1 and Section 2.2.
3.3 The BatteryStatusActivity class
The BatteryStatusActivity class is responsible for displaying the status of battery. The BatteryManager
broadcasts all battery and charging details in a sticky <a href="http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Intent.html">Intent</a>
that includes
the charging status. By hooking in to these intents we can continuosly
monitor the status of the phone battery. To achieve this, we register a
BroadcastReceiver to be run in the main activity thread
(BatteryStatusActivity).The
receiver will be called with any broadcast Intent that matches
filter (Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED), in the main application thread.
private void registerBatteryLevelReceiver() {
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED);
registerReceiver(battery_receiver, filter);
}
Once registered, whenever the BroadcastReceiver is receiving an Intent
broadcast (i.e. from BatteryManager), we shall update the status as below
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
boolean isPresent = intent.getBooleanExtra("present", false);
String technology = intent.getStringExtra("technology");
int plugged = intent.getIntExtra("plugged", -1);
int scale = intent.getIntExtra("scale", -1);
int health = intent.getIntExtra("health", 0);
int status = intent.getIntExtra("status", 0);
int rawlevel = intent.getIntExtra("level", -1);
int level = 0;
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
Log.i("BatteryLevel", bundle.toString());
if (isPresent) {
if (rawlevel >= 0 && scale > 0) {
level = (rawlevel * 100) / scale;
}
String info = "Battery Level: " + level + "%\n";
info += ("Technology: " + technology + "\n");
info += ("Plugged: " + getPlugTypeString(plugged) + "\n");
info += ("Health: " + getHealthString(health) + "\n");
info += ("Status: " + getStatusString(status) + "\n");
setBatteryLevelText(info);
} else {
setBatteryLevelText("Battery not present!!!");
}
}
More information on best practices for Monitoring the state of battery can be found here
We are done.!! Well almost. Run the application on your Android emulator or best deploy it on your smartphone to see the status of your phone. You can play around by querying different parameters and also by customizing the way the UI is updated as i did in this case for monitoring the Data activity and signal strength.
Happy Coding !!
History
Initial version - 22.03.2012
