Introduction
I decided to write this control after spending sometime browsing around without success. By this I didn't mean to say that existing lazy load controls out are bad,
but I just found them either too sophisticated or kind of difficult to use.
All I wanted to do was displaying my item list using an unsorted list <ul>
and the flexibility to modify the layout on each list item <li> without too much hassle. So the most sensible way I can think of is to make use of jQuery
AJAX functionality to call a Controller action that returns a PartialView, which then populates the content of the unsorted list. This article will go through
in more details how RustyLazyLoad control achieves this.
Below are some of the main advantages of RustyLazyLoad:
- Simple to use
- Clear separation between the use of jQuery and Razor
- Extensible - you can bind it to anything, not limited to unsorted list
- No jQuery programming needed
Because this control is intended to be simple, we should be aware of its limitations:
- It doesn't know if all your items have been loaded
- A PartialView is required as the item list template (or we can create one that serves all lazy loaded data)
- It is tightly bound to ASP.NET MVC and Razor
- Calling non-ASP.NET MVC actions has not been tested
- The service methods that serve the lazy load must have
limit and fromRowNumber as mandatory parameters to utilize LINQ query's
.Skip(fromRowNumber) and .Take(limit)
Using the code
RustyLazyLoad consists of six main components:
- rustylazyload.js
- rustylazyload.css
- RustyLazyLoadViewModel.cs
- _RustyLazyLoad.cshtml
- Your Controller lazy load action method and the corresponding ViewModel
- Your PartialView template
First, we'll quickly run through rustylazyload.js:
function LazyLoad(uniqueId) {
var _uniqueId = uniqueId;
var _containerId = "";
var _ajaxLoadContainerId = "";
var _ajaxActionUrl = "";
var _parameters = {};
this.init = function(option) {
_containerId = option.containerId;
_ajaxLoadContainerId = option.ajaxLoadContainerId;
_ajaxActionUrl = option.ajaxActionUrl;
_parameters = option.parameters;
bindScrollHandler();
load();
};
var bindScrollHandler = function() {
$(window).scroll(function() {
if ($(window).scrollTop() + $(window).height() > $(document).height() - 200) {
load();
}
});
};
var unbindScrollHandler = function() {
$(window).unbind("scroll");
};
var load = function() {
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: _ajaxActionUrl,
data: _parameters,
beforeSend: load_beforeSend,
success: load_success,
error: load_error
});
};
var load_beforeSend = function() {
unbindScrollHandler();
$(_ajaxLoadContainerId).toggleClass("lazyload-hidden").html("Loading..");
};
var load_success = function(result) {
setTimeout(function() {
if (result != null && result != "") {
$(_containerId).append(result, { duration: 500 });
$(_containerId).find(">:first-child").removeClass("ui-first-child");
$(_containerId).find(">:first-child").addClass("ui-first-child");
$(_containerId).find(">:nth-child(" + _parameters.fromRowNumber + ")").removeClass("ui-last-child");
$(_containerId).find(">:last-child").addClass("ui-last-child");
_parameters.fromRowNumber = $(_containerId).children().length;
}
if (_parameters.fromRowNumber == 0) {
$(_ajaxLoadContainerId).html("There is no data to display");
} else {
$(_ajaxLoadContainerId).toggleClass("lazyload-hidden").html("");
}
bindScrollHandler();
}, 500);
};
var load_error = function(result) {
var message = result.responseText.substring(1, result.responseText.length - 2);
$(_ajaxLoadContainerId).html("Error: " + message);
};
}
There are 4 mandatory fields that we need to specify when calling init():
_containerId - the Id of the data container object (<ul id="thisId"></ul>) _ajaxLoadContainerId - the Id of the "Loading" message container object (<div id="thisId">Loading..</div>)_ajaxActionUrl - The action Url which will be called using $.ajax() _parameters - a JSON object, which has 2 mandatory fields: limit (number of items to be loaded on demand) and fromRowNumber (marks the Nth loaded item to avoid repeated entries).
We won't go and discuss this code above line by line, instead we'll just highlight the important sections:
init() function does three things: maps the parameters, binds scroll event handler to the window, and calls load() to display the first batch bindScrollHandler() is quite trivial - it simply makes sure load() gets called when the window almost reaches the bottomload() calls _ajaxActionUrl using jQuery AJAX and passes all specified parameters in _parameters variable - ASP.NET MVC is smart enough
to map those parameters with the Controller action parameters- When the Controller action is performing,
load_beforeSend() temporarily disables the window scroll
event handler so we don't overload the server with AJAX requests, meanwhile displays the loading message HTML object which Id is stored in _ajaxLoadContainerId - On success,
load_success() should bind the result to _containerId HTML object, update the _parameters.fromRowNumber
with the number of items loaded (remember fromRowNumber is one of the mandatory items of _parameters), and re-enables the window scroll event handler - Any error will be handled in
load_error(), which will be displayed in _ajaxLoadContainerId HTML object - If you are using default ASP.NET MVC4 Mobile Application template, you shouldn't need to modify this file at all
Next is rustylazyload.css, which should be quite straight forward:
.lazyload-loading-container {
margin: 0;
padding: 15px;
text-align: center;
}
.lazyload-hidden {
display: none;
}
Now, the View Model RustyLazyLoadViewModel.cs:
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Models
{
public class RustyLazyLoadViewModel
{
public RustyLazyLoadViewModel()
{
Parameters = new Dictionary<string, object>();
}
public RustyLazyLoadViewModel(int limit, int fromRowNumber, string containerId,
string ajaxActionUrl, IDictionary<string, object> parameters = null)
{
Limit = limit;
FromRowNumber = fromRowNumber;
ContainerId = containerId;
AjaxActionUrl = ajaxActionUrl;
if (parameters != null)
Parameters = parameters;
}
public int Limit { get; set; }
public int FromRowNumber { get; set; }
public string ContainerId { get; set; }
public string AjaxActionUrl { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> Parameters { get; set; }
}
}
As you can see, this View Model captures pretty much the same parameters as rustylazyload.js' .init() function, except without
the _ajaxLoadContainerId. Why? Let's check out the View file.
_RustyLazyLoad.cshtml:
@using System.Text
@model RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Models.RustyLazyLoadViewModel
@{
var containerId = Model.ContainerId;
var ajaxLoadContainerId = string.Format("{0}Load", containerId);
var sbParameters = new StringBuilder();
if (Model.Parameters != null && Model.Parameters.Any())
{
foreach (var parameter in Model.Parameters)
{
sbParameters.AppendFormat("\"{0}\": \"{1}\", ", parameter.Key, parameter.Value);
}
}
var parameters = sbParameters.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(parameters))
{
parameters = parameters.Substring(0, parameters.Length - 2);
}
}
<ul id="@containerId" data-role="listview"
data-inset="true"></ul>
<div id="@ajaxLoadContainerId"
class="lazyload-loading-container lazyload-hidden
ui-listview ui-listview-inset
ui-corner-all ui-shadow ui-li-static
ui-btn-down-b ui-first-child ui-last-child"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function () {
var limit = @Model.Limit;
var fromRowNumber = @Model.FromRowNumber;
var containerId = '@string.Format("#{0}", containerId)';
var ajaxLoadContainerId = '@string.Format("#{0}", ajaxLoadContainerId)';
var ajaxActionUrl = '@Model.AjaxActionUrl';
var parameters = { limit: limit, fromRowNumber: fromRowNumber, @Html.Raw(parameters) };
var lazyLoad = new LazyLoad(containerId);
lazyLoad.init({
containerId: containerId,
ajaxLoadContainerId: ajaxLoadContainerId,
ajaxActionUrl: ajaxActionUrl,
parameters: parameters
});
});
</script>
For simplicity, _ajaxLoadContainerId is really just _containerId with a suffix, but it can be anything, really. Should we feel the need to specify
your AJAX loading message container Id manually, all we need to do is add AjaxLoadContainerId as a property in RustyLazyLoadViewModel.cs
and pass that on to variable ajaxLoadContainerId (line 5 in this page).
The lazy load item container is this:
<ul id="@containerId" data-role="listview" data-inset="true"></ul>
And the lazy load loading message container is this:
<div id="@ajaxLoadContainerId" ...></div>
Then using the Razor engine we convert the parameters into a JSON and pass it on to the lazy load control.
var parameters = { limit: limit, fromRowNumber: fromRowNumber, @Html.Raw(parameters) };
var lazyLoad = new LazyLoad(containerId);
lazyLoad.init({
containerId: containerId,
ajaxLoadContainerId: ajaxLoadContainerId,
ajaxActionUrl: ajaxActionUrl,
parameters: parameters
});
Lastly, the fifth and sixth component are best explained through an example.
Say there are 15 entries of User in the database with these
fields: Id, FirstName, LastName, Status and mapped to the model below. and we want to display the entries on the Home page in a progressive manner using
the lazy load control.
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services.Models
{
public class User
{
public User() { }
public User(long id, string firstName, string lastName, UserStatus status)
: this()
{
Id = id;
FirstName = firstName;
LastName = lastName;
Status = status;
}
public long Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public UserStatus Status { get; set; }
}
public enum UserStatus
{
[Description("All")]
All = 0,
[Description("Inactive")]
Inactive = 1,
[Description("Active")]
Active = 2,
[Description("Deactivated")]
Deactivated = 3
}
}
The first thing we need to do is create the service method:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services.Models;
namespace RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services
{
public interface IQueryService
{
IEnumerable<User> GetAllUsers(UserStatus status = UserStatus.All,
int limit = 0, int fromRowNumber = 0);
}
class QueryService : IQueryService
{
public IEnumerable<User> GetAllUsers(UserStatus status, int limit, int fromRowNumber)
{
var users = new List<User>();
for (var i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
var userFirstName = string.Format("firstName_{0}", i);
var userLastName = string.Format("lastName_{0}", i);
var userStatus = i % 2 == 0 ? UserStatus.Active : UserStatus.Inactive;
users.Add(new User(i, userFirstName, userLastName, userStatus));
}
if (limit <= 0)
{
users = users.Where(x => x.Status == status)
.Skip(fromRowNumber)
.ToList();
}
else
{
users = users.Where(x => x.Status == status)
.Skip(fromRowNumber)
.Take(limit)
.ToList();
}
return users;
}
}
}
In our HomeController, we will need to create the default [HttpGet] Controller action method Index() for our Index page
and the [HttpPost] Controller action method GetNextUsers() to serve the lazy loader:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services;
using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services.Models;
namespace RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IQueryService _query;
public HomeController()
{
_query = new QueryService();
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult GetNextUsers(UserStatus status, int limit, int fromRowNumber)
{
try
{
var users = _query.GetAllUsers(status, limit, fromRowNumber);
if (!users.Any())
return Json(string.Empty);
return PartialView("_UserList", users);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
return Json(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
In Index.cshtml (the View corresponding to the [HttpGet] Controller action method Index()) we will have something like this:
@using RustyLazyLoadTester
@using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Models
@using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services.Models
@{
ViewBag.PageTitle = "Home";
ViewBag.Title = string.Format("RustyLazyLoadTester - {0}", ViewBag.PageTitle);
var parameters = new Dictionary<string, object>();
parameters.Add("status", UserStatus.All);
}
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/lazyload") @* points to /Scripts/rustylazyload.js *@
@Html.Partial("_RustyLazyLoad", new RustyLazyLoadViewModel(
5, 0, "ulUsers", Url.Action("GetNextUsers", "Home"), parameters))
The two bolded lines there will activate the lazy load control and trigger the GetNextUsers() on demand.
If we look closely on the second bolded line:
@Html.Partial("_RustyLazyLoad", new RustyLazyLoadViewModel(
5, 0, "ulUsers", Url.Action("GetNextUsers", "Home"), parameters))
The value 5 is the limit. This dictates how the number of items to be retrieved on each load.
The value 0 is the fromRowNumber. This represents the N-th item in the result that needs to be ignored. As we load more data, this number will increase based
on the loaded items, so we don't have to worry about duplicates (unless our code involves some complex sorting which makes it possible to have a new item in the middle of the list).
When GetNextUsers() method is called, it simply renders PartialView _UserList.cshtml below:
@using Humanizer
@using RustyLazyLoadTester.Mobile.Services.Models
@model IEnumerable<User>
@foreach (var user in Model)
{
<li class="ui-li ui-li-static ui-btn-up-b">
<div>@string.Format("First name: {0}", user.FirstName)</div>
<div>@string.Format("Last name: {0}", user.LastName)</div>
<div>@string.Format("Status: {0}", user.Status.Humanize())</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
<div>---</div>
</li>
}
Note that the content is wrapped in an <li>. The reason for this is because the parent container (_containerId HTML object)
is a <ul>. But we can always change this implementation very easily, as long as we maintain the hierarchy as below:
<parentContainer>
<childContainer>
[Content]
</childContainer>
</parentContainer>
This is because RustyLazyLoad control uses the parent container's number of children to update the _fromRowNumber property, which ensures there is no duplicate entry in the next load.
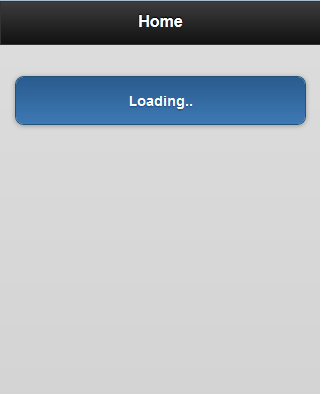
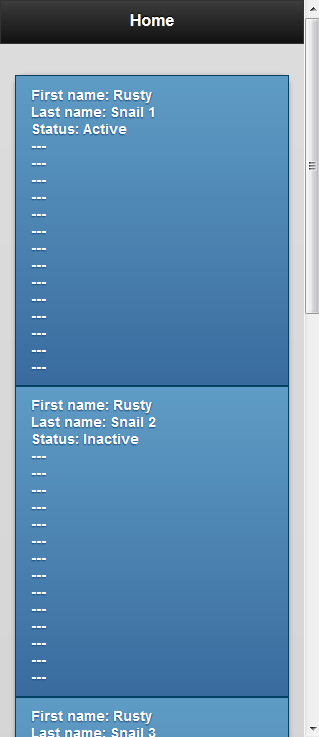
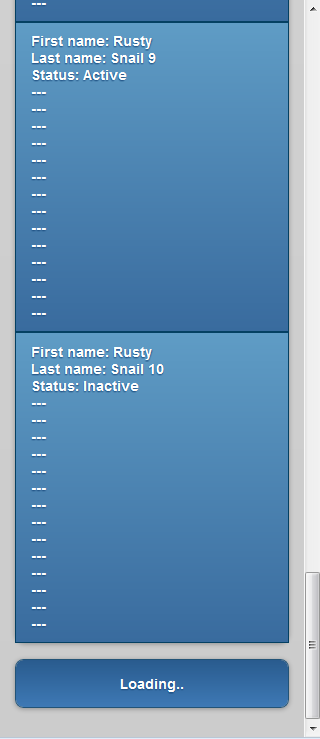
Below are the result: