Powershell is an advanced scripting framework, typically script is run in console host, most often remotely, but the Powershell scripts are still relatively frequently used interactively on a Windows computer. When a generic script executes, it is likely to need more than one option to be selected. Multiple options need to offered to the user in a cascading manner, with complex selection scenarios often desirable. For certain data selections, GUI in more intuitive and faster than CLI - in the console, even basic choice does not look very pretty.
For many situations, plain old Windows Forms is still a convenient means of prompting the user. This is the main focus of this article. We examine few elementary examples from http://www.java2s.com/ and convert those to Powershell. Later, we use the earlier samples as building blocks for something more complex. The fact all code of these examples in available in a one single file and no separate designer code needs to be merged, greatly simplifies the conversion. The focus is to keep the emerging Powershell code to a minimum required for processing various data selection scenarios for prompt, password, checkbox, radio, checked list, grid, treeview, tabbed dialogs and combination of those. In addition, it will be demonstrated that form element-specific event handlers will execute PowerShell code. Finally, controls like TreeView visualize the data very well on its own and potentially make few rounds of prompts unnecessary.
On the other hand, the Windows Presentation Foundation might feel somewhat heavy to embark and/or debug but entirely doable - examples are provided at the middle of this article. Interacting with WPF requires multithreading and this technique is also valuable for asynchronous status reporting of long running scripts.
A pleasant note is that all scripts continue to function in Minimal Server Interface and even in Server Core Windows Server 2012 GUI levels. The reason is: even after both "Server Graphical Shell" and "Server Graphical Management Tools & Infrastructure" Windows Features are "removed", full Microsoft .Net Framework is still present. The ultimate goal of the examples of offering a familiar user interface to complex custom data - can still be met on Windows Server Core. Note that since mouse is available even in Server Core, adding keyboard shortcuts to form elements isn't required.
In further examples, it is shown how to construct Powershell Selenium scripts from C# equivalents manually or record in Selenium IDE automatically; definite benefits of using Powershell to run Selenium recordings are illustrated.
Finally, the step-by-step conversion exercise is covered in detail.
One will recognize the Powershell version of the code to be practically identical to the C# version with only semantic differences. All sources available on the author's github repo and new code are being developed daily.
We currently need to construct the helper class responsible for passing information to the Powershell script caller in plain C# and make its properties available to Windows Form in the event handlers, though all dialogs will be drawn modally. Without such tight link, some hard-to- debug race condition errors might be possible. The analysis of these assumptions is deferred to the future article.
The samples provided in the article are hopefully easily tailored to any purpose the reader finds them fit.
The class that will be used to share information from the form to Powershell is quite basic. All it needs is to implement IWin32Window interface; it will also have various private data members with getters and setters and methods - to be used in the form in some examples below.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private int _data;
public int Data
{
get { return _data; }
set { _data = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
The Powershell stores its own Window Handle in the class:
if ($process_window -eq $null ){
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
The entries selection and the overall status is read from $caller.Message and $caller.Data:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
if($process_window.Data -ne $RESULT_CANCEL) {
write-debug ('Selection is : {0}' -f , $process_window.Message )
} else {
write-debug ('Result is : {0} ({1})' -f
$Readable.Item($process_window.Data) , $process_window.Data )
}
Alternative syntax can be
$guid = [guid]::NewGuid()
$helper_namespace = ("Util_{0}" -f ($guid -replace '-',''))
$helper_name = 'Helper'
Add-Type -UsingNamespace @(
'System.Drawing',
'System.IO',
'System.Windows.Forms',
'System.Drawing.Imaging',
'System.Collections.Generic',
'System.Text' `
) `
-MemberDefinition @"
// inline C# code without class decoration
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies @( 'System.Windows.Forms.dll',`
'System.Drawing.dll',`
'System.Data.dll',`
'System.Xml.dll') `
-Namespace $helper_namespace -Name $helper_name -ErrorAction Stop
$helper = New-Object -TypeName ('{0}.{1}' -f $helper_namespace,$helper_type)
This way one does not worry about seeing the annoying warning every time the inline C# code is modified:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. The type name 'Win32Window' already exists.
At C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\treeview_c.ps1:21 char:1
+ Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
NOTE, that few namespaces are already included by default and should not be provided explicitly in the invocation agument to avid
Warning as Error:
The using directive for 'System' appeared previously in this namespace
The using directive for 'System.Runtime.InteropServices' appeared previously in this namespace
Multiple Choice Prompt
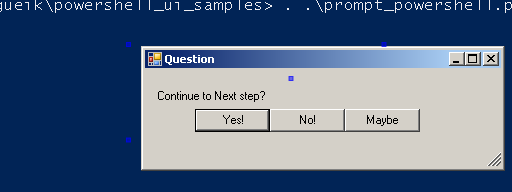
The multiple choice decision prompt is the simplest example that requires no communication between form elements - the form sets the $caller.Data independently in each button Click event handlers.
function PromptAuto(
[String] $title,
[String] $message,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(650,120)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Y') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_POSITIVE }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'N') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_NEGATIVE }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(50,40)
$b1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b1.Text = 'Yes!'
$b1.Add_Click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_POSITIVE; $f.Close(); })
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(125,40)
$b2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b2.Text = 'No!'
$b2.Add_Click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_NEGATIVE; $f.Close(); })
$b3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(200,40)
$b3.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b3.Text = 'Maybe'
$b3.Add_Click({$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL ; $f.Close()})
$l = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,20)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(280,20)
$l.Text = $message
$f.Controls.Add($b1)
$f.Controls.Add($b3)
$f.Controls.Add($b2)
$f.Controls.Add($l)
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
The options text and definitions are hard coded in the function.
$RESULT_POSITIVE = 0
$RESULT_NEGATIVE = 1
$RESULT_CANCEL = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_NEGATIVE = 'NO!';
$RESULT_POSITIVE = 'YES!' ;
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'MAYBE...'
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$title = 'Question'
$message = "Continue to Next step?"
$result = PromptAuto -title $title -message $message -caller $process_window
write-debug ("Result is : {0} ({1})" -f $Readable.Item($process_window.Data) , $process_window.Data )
One popular feature of closing the idle input box after some timeout can be provided by e.g. adding to the script a System.Windows.Forms.Panel subclass which houses a System.Timers.Timer :
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class TimerPanel : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private System.Timers.Timer _timer;
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public System.Timers.Timer Timer
{
get
{
return _timer;
}
set { _timer = value; }
}
public TimerPanel()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
_timer.Stop();
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this._timer = new System.Timers.Timer();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this._timer)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
this._timer.Interval = 1000;
this._timer.Start();
this._timer.Enabled = true;
this._timer.SynchronizingObject = this;
this._timer.Elapsed += new System.Timers.ElapsedEventHandler(this.OnTimerElapsed);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this._timer)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
private void OnTimerElapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
}
}
then placing all inputs on the panel.
$p = New-Object TimerPanel
$p.Size = $f.Size
$end = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$end = ([int]$end + 60)
$p.Timer.Stop()
$p.Timer.Interval = 5000;
$p.Timer.Start()
$p.Timer.add_Elapsed({
$start = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($start - $end)
$l.Text = ('Remaining time {0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds,($end - $start))
if ($end - $start -lt 0) {
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Close()
}
})
The properties and methods of Timer being public, therefore the script provides the event handler(s) - in the example above the one minute interval in seconds is harf coded

The full example is shown below and is available in the source zip file.
$RESULT_OK = 0
$RESULT_CANCEL = 1
$RESULT_TIMEOUT = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_OK = 'OK';
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'CANCEL';
$RESULT_TIMEOUT = 'TIMEOUT';
}
function PromptTimedAutoClose {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message,
[object]$caller
)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (240,110)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'O') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_OK }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (50,40)
$b1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$b1.Text = 'OK'
$b1.add_click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_OK; $f.Close(); })
$p = New-Object TimerPanel
$p.Size = $f.Size
$p.Controls.Add($b1)
$end = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$end = ([int]$end + 60)
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (130,40)
$b2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$b2.Text = 'Cancel'
$b2.add_click({
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Close();
})
$p.Controls.Add($b2)
$l = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (10,20)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (280,20)
$l.Text = $message
$p.Controls.Add($l)
$p.Timer.Stop()
$p.Timer.Interval = 5000;
$p.Timer.Start()
$p.Timer.add_Elapsed({
$start = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($start - $end)
$l.Text = ('Remaining time {0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds,($end - $start))
if ($end - $start -lt 0) {
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window ]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
}
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$title = 'Prompt w/timeout'
$message = "Continue ?"
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptTimedAutoClose -Title $title -Message $message -caller $caller
$result = $caller.Data
Write-Debug ("Result is : {0} ({1})" -f $Readable.Item($result),$result)

This example code is more interesting because the script will collect the state from several grouped element. Managing the individual checkbox and radiobutton behavior is left intact and only implements button Click handler where the Form draws the selected elements summary and stores it into the $caller - for simplicity, both $shapes and $color are placed into one $caller.Message.
function PromptWithCheckboxesAndRadionbuttons(
[String] $title,
[String] $message,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$checkBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$checkBox2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$checkBox3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$radioButton1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$radioButton2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$radioButton3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$button1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$color = ''
$shapes = @()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange(
@(
$radioButton1,
$radioButton2,
$radioButton3
))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 120)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(120, 144)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'Color'
$checkBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 8)
$checkBox1.Name = 'checkBox1'
$checkBox1.TabIndex = 1
$checkBox1.Text = 'Circle'
$checkBox2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 40)
$checkBox2.Name = 'checkBox2'
$checkBox2.TabIndex = 2
$checkBox2.Text = 'Rectangle'
$checkBox3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 72)
$checkBox3.Name = 'checkBox3'
$checkBox3.TabIndex = 3
$checkBox3.Text = 'Triangle'
$radioButton1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 32)
$radioButton1.Name = 'radioButton1'
$radioButton1.TabIndex = 4
$radioButton1.Text = 'Red'
$radioButton1.Add_CheckedChanged({ })
$radioButton2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 64)
$radioButton2.Name = 'radioButton2'
$radioButton2.TabIndex = 5
$radioButton2.Text = 'Green'
$radioButton3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 96)
$radioButton3.Name = 'radioButton3'
$radioButton3.TabIndex = 6
$radioButton3.Text = 'Blue'
$button1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 280)
$button1.Name = 'button1'
$button1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(112, 32)
$button1.TabIndex = 4
$button1.Text = 'Draw'
$button1.Add_Click({
$color = ''
$shapes = @()
foreach ($o in @($radioButton1, $radioButton2, $radioButton3)){
if ($o.Checked){
$color = $o.Text}
}
foreach ($o in @($checkBox1, $checkBox2, $checkBox3)){
if ($o.Checked){
$shapes += $o.Text}
}
$g = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromHwnd($f.Handle)
$rc = New-Object System.Drawing.Rectangle(150, 50, 250, 250)
$brush = New-Object System.Drawing.SolidBrush([System.Drawing.Color]::White)
$g.FillRectangle($brush, $rc)
$font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Verdana', 12)
$col = New-Object System.Drawing.SolidBrush([System.Drawing.Color]::Black)
$str = [String]::Join(';', $shapes )
$pos1 = New-Object System.Drawing.PointF(160, 60)
$pos2 = New-Object System.Drawing.PointF(160, 80)
$g.DrawString($color, $font, $col , $pos1)
$g.DrawString($str, $font, $col , $pos2)
start-sleep 1
$caller.Message = ('color:{0} shapes:{1}' -f $color , $str)
$f.Close()
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(408, 317)
$f.Controls.AddRange( @(
$button1,
$checkBox3,
$checkBox2,
$checkBox1,
$groupBox1))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'CheckBox and RadioButton Sample'
$groupBox1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { }
$f.Close()
})
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$F.Dispose()
return $caller.Data
}

The next iteration is to let the form receive a string of text from Powershell and display individual words as checked listbox items, waiting for the user to select individual words by clicking the checkbox next to word.
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$result = PromptCheckedList '' 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit'
write-debug ('Selection is : {0}' -f , $result )
The listbox on the right provides a visual cue to the user. When the 'Done' button is pressed, the selections are saved in the $caller object and form is closed and disposed.
This time, we return the $caller.Message explicitly, though it not really required. Note the event handler code highlighted in bold.
function PromptCheckedList
{
Param(
[String] $title,
[String] $message)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections.Generic')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Text')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$i = new-object System.Windows.Forms.CheckedListBox
$d = new-object System.Windows.Forms.ListBox
$d.SuspendLayout()
$i.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$i.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 11,
[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$i.FormattingEnabled = $true;
$i.Items.AddRange(( $message -split '[ ,]+' ));
$i.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(17, 12)
$i.Name = 'inputCheckedListBox'
$i.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(202, 188)
$i.TabIndex = 0
$i.TabStop = $false
$event_handler = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.ItemCheckEventArgs ] $eventargs
)
$item = $i.SelectedItem
if ( $eventargs.NewValue -eq [System.Windows.Forms.CheckState]::Checked ) {
$d.Items.Add( $item );
} else {
$d.Items.Remove( $item );
}
}
$i.Add_ItemCheck($event_handler)
$d.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Verdana', 11)
$d.FormattingEnabled = $true
$d.ItemHeight = 20;
$d.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(236, 12);
$d.Name = 'displayListBox';
$d.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(190, 184);
$d.TabIndex = 1;
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 280)
$b.Name = 'button1'
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(112, 32)
$b.TabIndex = 4
$b.Text = 'Done'
$b.Add_Click({
$shapes = @()
foreach ($o in $d.Items){
$shapes += $o
}
$caller.Message = [String]::Join(';', $shapes )
$f.Close()
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(408, 317)
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.Controls.AddRange( @( $i, $d, $b))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'CheckListBox Sample'
$i.ResumeLayout($false)
$d.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
$result = $caller.Message
$caller = $null
return $result
}
Here, the event handler in written in PowerShell but it operates the standard event arguments therefore the Powershell function is called from Form elements essentially connection them to one another. It is virtually indistinguishable from the class method it have been converted from.
this.inputCheckedListBox.ItemCheck +=
new System.Windows.Forms.ItemCheckEventHandler(this.inputCheckedListBox_ItemCheck);
...
private void inputCheckedListBox_ItemCheck(object sender, ItemCheckEventArgs e )
{
string item = inputCheckedListBox.SelectedItem.ToString();
if ( e.NewValue == CheckState.Checked )
displayListBox.Items.Add( item );
else
displayListBox.Items.Remove( item );
}
Next example comes from conversion Accordion Collapsible Panel from C# to Powershell. Naturally, the code is extremely redundant. Only portion is shown. Full script is in the source zip.

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$f.Text = $title
$f.SuspendLayout()
$p = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$m = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$p_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_3_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_3_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_3_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_2_4 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_1_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_1_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$lblMenu = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$m.SuspendLayout()
$p_3.SuspendLayout()
$p_2.SuspendLayout()
$p_1.SuspendLayout()
$p.SuspendLayout()
..
$p_1.Controls.AddRange(@($b_1_2, $b_1_1, $g_1) )
$p_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$p_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,23)
$p_1.Name = "p_1"
$p_1.TabIndex = 1
$b_1_1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$b_1_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$b_1_1.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$b_1_1.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$b_1_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * 2))
$b_1_1.Name = "b_1_1"
$b_1_1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$b_1_1.TabIndex = 2
$b_1_1.Text = "Group 1 Sub Menu 1"
$b_1_1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$b_1_1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$b_1_1_click = $b_1_1.add_Click
$b_1_1_click.Invoke({
param([object]$sender,[string]$message)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('{0} clicked!' -f $sender.Text) )
})
$b_1_2.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$b_1_2.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$b_1_2.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$b_1_2.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$b_1_2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * 3))
$b_1_2.Name = "$b_1_2"
$b_1_2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$b_1_2.TabIndex = 3
$b_1_2.Text = "Group 1 Sub Menu 2"
$b_1_2.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$b_1_2.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$g_1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gray
$g_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$g_1.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gray
$g_1.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$g_1.ImageAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleRight
$g_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$g_1.Name = "g_1"
$g_1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$g_1.TabIndex = 0
$g_1.Text = "Menu Group 1"
$g_1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$g_1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$g_1_click = $g_1.add_click
$g_1_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$ref_panel = ([ref]$p_1)
$ref_button_menu_group = ([ref]$g_1)
$num_buttons = 3
if ($ref_panel.Value.Height -eq $global:button_panel_height)
{
$ref_panel.Value.Height = ($global:button_panel_height * $num_buttons) + 2
$ref_button_menu_group.Value.Image = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap ("C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\unfinished\up.png")
}
else
{
$ref_panel.Value.Height = $global:button_panel_height
$ref_button_menu_group.Value.Image = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap ("C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\unfinished\down.png")
}
})
$m.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_3.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_2.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_1.ResumeLayout($false)
$p.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (210,280)
$f.Controls.Add($c1)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.Controls.Add($b1)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = "ProgressCircle"
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()

To fight redundancy one may introduce utility functions e.g.
function add_button {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$button_data_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$button_ref
)
$button_data = $button_data_ref.Value
$local:b = $button_ref.Value
$local:b.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$local:b.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$local:b.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$local:b.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$local:b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * $button_data['cnt']))
$local:b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$local:b.TabIndex = 3
$local:b.Name = $button_data['name']
$local:b.Text = $button_data['text']
$local:b.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$local:b.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$local:click_handler = $local:b.add_Click
if ($button_data.ContainsKey('callback')) {
$local:click_handler.Invoke($button_data['callback'])
}
else {
$local:click_handler.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('{0} default click handler!' -f $sender.Text))
})
}
$button_ref.Value = $local:b
}
and refactor the code to pack together code references, menu text, etc.:
[scriptblock]$b3_3_callback_ref = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = 'something'
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('This is custom callback for {0} click!' -f $sender.Text))
}
add_button -button_ref ([ref]$b3_3) `
-button_data_ref ([ref]@{
'cnt' = 3;
'text' = 'Menu 3 Sub Menu 3';
'name' = 'b3_3';
'callback' = $b3_3_callback_ref;
})
The eventual layout of button data objects and callback action code is of course highly domain-specific
Next example uses the code from ComboBox with a CheckedListBox as a Dropdown article. Unlike most of examples in this article, this script does not use $caller object - the CheckedComboBox class has plenty of proprties on its own - to return the selection data as text - but rather passes the hash of objects by reference to the form:
$albums = @{
'Ring Ring (1973)' = $false;
'Waterloo (1974)' = $false;
'ABBA (1975)' = $true;
'Arrival (1976)' = $false;
'The Album (1977)' = $true;
'Voulez-Vous (1979)' = $false;
'Super Trouper (1980)' = $false;
'The Visitors (1981)' = $false;
}
PromptCheckedCombo -Title 'Checked ComboBox Sample Project' -data_ref ([ref]$albums)
Write-Output ('Result is: {0}' -f $caller.Message)
$albums
Here the signature of the function is:
function PromptCheckedCombo {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$data_ref
)
...
$ccb = New-Object -TypeName 'CheckComboBoxTest.CheckedComboBox'
$data = $data_ref.Value
$cnt = 0
$data.Keys | ForEach-Object { $display_item = $_;
[CheckComboBoxTest.CCBoxItem]$item = New-Object CheckComboBoxTest.CCBoxItem ($display_item,$cnt)
$ccb.Items.Add($item) | Out-Null
if ($data[$display_item]) {
$ccb.SetItemChecked($cnt,$true)
}
$cnt++
}

In the Form delegate, one iterates of the referenced data keys and clears / sets the hash values
$eventMethod_ccb = $ccb.add_DropDownClosed
$eventMethod_ccb.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$data = $data_ref.Value
$data.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$display_item = $_;
$data_ref.Value[$display_item] = $false
}
foreach ($item in $ccb.CheckedItems) {
$data_ref.Value[$item.Name] = $true
}
$data_ref.Value = $data
})

Next example shows custom-drawn Bar Chart which has no third-party charting library dependencies. The VB.NET example code from Drawing a Bar Chart article is used, with few minor refactoring and modifications:
Add-Type -Language 'VisualBasic' -TypeDefinition @"
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
Imports System
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Drawing.Drawing2D
Imports System.Collections
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Public Class BarChart
Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Protected Overloads Overrides Sub Dispose(ByVal disposing As Boolean)
If disposing Then
If Not (components Is Nothing) Then
components.Dispose()
End If
End If
MyBase.Dispose(disposing)
End Sub
Private components As System.ComponentModel.IContainer
<System.Diagnostics.DebuggerStepThrough()> Private Sub InitializeComponent()
Me.AutoScaleBaseSize = New System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
Me.ClientSize = New System.Drawing.Size(344, 302)
Me.FormBorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle.Sizable
Me.Name = "BarChart"
Me.Text = "BarChart"
Me.components = New System.ComponentModel.Container
Me.ttHint = New System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip(Me.components)
End Sub
Dim blnFormLoaded As Boolean = False
Dim objHashTableG As New Hashtable(100)
Dim objColorArray(150) As Brush
Private Sub BarChart_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
End Sub
Public Sub LoadData(ByVal objCallerHashTable As Hashtable )
objHashTableG = objCallerHashTable.Clone()
End Sub
Public Sub RenderData
Me.BarChart_Paint(Nothing, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs( _
CreateGraphics(), _
New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height) _
))
End Sub
Private Sub BarChart_Paint(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs _
) Handles MyBase.Paint
Try
Dim intMaxWidth As Integer
Dim intMaxHeight As Integer
Dim intXaxis As Integer
Dim intYaxis As Integer
Me.SuspendLayout()
Me.LoadColorArray()
intMaxHeight = CType((Me.Height / 2) - (Me.Height / 12), Integer)
intMaxWidth = CType(Me.Width - (Me.Width / 4), Integer)
intXaxis = CType(Me.Width / 12, Integer)
intYaxis = CType(Me.Height / 2, Integer)
drawBarChart(objHashTableG.GetEnumerator , _
objHashTableG.Count, _
"Graph 1", _
intXaxis, _
intYaxis, _
intMaxWidth, _
intMaxHeight, _
True, _
False)
blnFormLoaded = True
Me.ResumeLayout(False)
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ex
End Try
End Sub
Public Sub drawBarChart(ByVal objEnum As IDictionaryEnumerator, _
ByVal intItemCount As Integer, _
ByVal strGraphTitle As String, _
ByVal Xaxis As Integer, _
ByVal Yaxis As Integer, _
ByVal MaxWidth As Int16, _
ByVal MaxHt As Int16, _
ByVal clearForm As Boolean, _
Optional ByVal SpaceRequired As Boolean = False)
Dim intGraphXaxis As Integer = Xaxis
Dim intGraphYaxis As Integer = Yaxis
Dim intWidthMax As Integer = MaxWidth
Dim intHeightMax As Integer = MaxHt
Dim intSpaceHeight As Integer
Dim intMaxValue As Integer = 0
Dim intCounter As Integer
Dim intBarWidthMax
Dim intBarHeight
Dim strText As String
Try
Dim grfx As Graphics = CreateGraphics()
If clearForm = True Then
grfx.Clear(BackColor)
End If
grfx.DrawString(strGraphTitle, New Font("Verdana", 12.0, FontStyle.Bold, GraphicsUnit.Point), Brushes.DeepPink, intGraphXaxis + (intWidthMax / 4), (intGraphYaxis - intHeightMax) - 40)
intBarHeight = CInt(intHeightMax / intItemCount)
intSpaceHeight = CInt((intHeightMax / (intItemCount - 1)) - intBarHeight)
If Not objEnum Is Nothing Then
While objEnum.MoveNext = True
If objEnum.Value > intMaxValue Then
intMaxValue = objEnum.Value
End If
End While
End If
intBarWidthMax = CInt(intWidthMax / intMaxValue)
If Not objEnum Is Nothing Then
intCounter = 1
objEnum.Reset()
While objEnum.MoveNext = True
intGraphYaxis = intGraphYaxis - intBarHeight
Dim objRec as Rectangle
objRec = New System.Drawing.Rectangle(intGraphXaxis, intGraphYaxis, intBarWidthMax * objEnum.Value, intBarHeight)
grfx.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, objRec)
grfx.FillRectangle(objColorArray(intCounter), objRec )
strText = objEnum.Key & "=" & objEnum.Value
Dim objLabelFont as Font
objLabelFont = New Font("Verdana", 7.2, FontStyle.Regular, GraphicsUnit.Point)
Dim textLabelArea As SizeF : textLabelArea = grfx.MeasureString(strText, objLabelFont)
Dim linePen As Pen: linePen = New Pen(Color.Gray, 1)
linePen.DashStyle = Drawing2D.DashStyle.Dash
Dim fontRatio As Single
fontRatio = objLabelFont.Height / objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetLineSpacing(FontStyle.Regular)
Dim ascentSize As Single
ascentSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetCellAscent(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim descentSize As Single
descentSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetCellDescent(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim emSize As Single
emSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetEmHeight(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim cellHeight As Single
cellHeight = ascentSize + descentSize
Dim internalLeading As Single
internalLeading = cellHeight - emSize
Dim externalLeading As Single
externalLeading = (objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetLineSpacing(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio) - cellHeight
Dim labelLeft As Single : labelLeft = intGraphXaxis + (intBarWidthMax * objEnum.Value)
labelLeft = intGraphXaxis
Dim labelBottom As Single: labelBottom = intGraphYaxis
Dim labelRight As Single : labelRight = labelLeft + textLabelArea.Width
Dim labelTop As Single : labelTop = textLabelArea.Height + labelBottom
Dim objLabelRec as Rectangle
objLabelRec = New System.Drawing.Rectangle(labelLeft, labelBottom, textLabelArea.Width , textLabelArea.Height )
grfx.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, objLabelRec)
grfx.FillRectangle(Brushes.White, objLabelRec )
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelTop, labelLeft , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelRight, labelTop, labelRight , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelTop, labelRight , labelTop)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelBottom, labelRight , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawString(strText, objLabelFont, Brushes.Black, labelLeft, labelBottom)
intCounter += 1
If SpaceRequired = True Then
intGraphYaxis = intGraphYaxis - intSpaceHeight
End If
If intCounter > objColorArray.GetUpperBound(0) Then
intCounter = 1
End If
End While
If clearForm = True Then
grfx.Dispose()
End If
End If
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ex
End Try
End Sub
Public Sub LoadColorArray()
objColorArray(1) = Brushes.Blue
objColorArray(2) = Brushes.Pink
objColorArray(3) = Brushes.Brown
objColorArray(4) = Brushes.BurlyWood
objColorArray(5) = Brushes.CadetBlue
objColorArray(6) = Brushes.Chartreuse
objColorArray(7) = Brushes.Chocolate
objColorArray(8) = Brushes.Coral
objColorArray(9) = Brushes.CornflowerBlue
objColorArray(10) = Brushes.Cornsilk
objColorArray(11) = Brushes.Crimson
objColorArray(12) = Brushes.Cyan
objColorArray(13) = Brushes.DarkBlue
objColorArray(14) = Brushes.DarkCyan
objColorArray(15) = Brushes.DarkGoldenrod
objColorArray(16) = Brushes.DarkGray
objColorArray(17) = Brushes.DarkGreen
objColorArray(18) = Brushes.DarkKhaki
objColorArray(19) = Brushes.DarkMagenta
objColorArray(20) = Brushes.DarkOliveGreen
objColorArray(21) = Brushes.DarkOrange
objColorArray(22) = Brushes.DarkOrchid
objColorArray(23) = Brushes.DarkRed
objColorArray(24) = Brushes.DarkSalmon
objColorArray(25) = Brushes.DarkSeaGreen
objColorArray(26) = Brushes.DarkSlateBlue
objColorArray(27) = Brushes.DarkSlateGray
objColorArray(28) = Brushes.DarkTurquoise
objColorArray(29) = Brushes.DarkViolet
objColorArray(30) = Brushes.DeepPink
objColorArray(31) = Brushes.DeepSkyBlue
objColorArray(32) = Brushes.DimGray
objColorArray(33) = Brushes.DodgerBlue
objColorArray(34) = Brushes.Firebrick
objColorArray(35) = Brushes.FloralWhite
objColorArray(36) = Brushes.ForestGreen
objColorArray(37) = Brushes.Fuchsia
objColorArray(38) = Brushes.Gainsboro
objColorArray(39) = Brushes.GhostWhite
objColorArray(40) = Brushes.Gold
objColorArray(41) = Brushes.Goldenrod
objColorArray(42) = Brushes.Gray
objColorArray(43) = Brushes.Green
objColorArray(44) = Brushes.GreenYellow
objColorArray(45) = Brushes.Honeydew
objColorArray(46) = Brushes.HotPink
objColorArray(47) = Brushes.IndianRed
objColorArray(48) = Brushes.Indigo
objColorArray(49) = Brushes.Ivory
objColorArray(50) = Brushes.Khaki
objColorArray(51) = Brushes.Lavender
objColorArray(52) = Brushes.LavenderBlush
objColorArray(53) = Brushes.LawnGreen
objColorArray(54) = Brushes.LemonChiffon
objColorArray(55) = Brushes.LightBlue
objColorArray(56) = Brushes.LightCoral
objColorArray(57) = Brushes.LightCyan
objColorArray(58) = Brushes.LightGoldenrodYellow
objColorArray(59) = Brushes.LightGray
objColorArray(60) = Brushes.LightGreen
objColorArray(61) = Brushes.LightPink
objColorArray(62) = Brushes.LightSalmon
objColorArray(63) = Brushes.LightSeaGreen
objColorArray(64) = Brushes.LightSkyBlue
objColorArray(65) = Brushes.LightSlateGray
objColorArray(66) = Brushes.LightSteelBlue
objColorArray(67) = Brushes.LightYellow
objColorArray(68) = Brushes.Lime
objColorArray(69) = Brushes.LimeGreen
objColorArray(70) = Brushes.Linen
objColorArray(71) = Brushes.Magenta
objColorArray(72) = Brushes.Maroon
objColorArray(73) = Brushes.MediumAquamarine
objColorArray(74) = Brushes.MediumBlue
objColorArray(75) = Brushes.MediumOrchid
objColorArray(76) = Brushes.MediumPurple
objColorArray(77) = Brushes.MediumSeaGreen
objColorArray(78) = Brushes.MediumSlateBlue
objColorArray(79) = Brushes.MediumSpringGreen
objColorArray(80) = Brushes.MediumTurquoise
objColorArray(81) = Brushes.MediumVioletRed
objColorArray(82) = Brushes.MidnightBlue
objColorArray(83) = Brushes.MintCream
objColorArray(84) = Brushes.MistyRose
objColorArray(85) = Brushes.Moccasin
objColorArray(86) = Brushes.NavajoWhite
objColorArray(87) = Brushes.Navy
objColorArray(88) = Brushes.OldLace
objColorArray(89) = Brushes.Olive
objColorArray(90) = Brushes.OliveDrab
objColorArray(91) = Brushes.Orange
objColorArray(92) = Brushes.OrangeRed
objColorArray(93) = Brushes.Orchid
objColorArray(94) = Brushes.PaleGoldenrod
objColorArray(95) = Brushes.PaleGreen
objColorArray(96) = Brushes.PaleTurquoise
objColorArray(97) = Brushes.PaleVioletRed
objColorArray(98) = Brushes.PapayaWhip
objColorArray(99) = Brushes.PeachPuff
objColorArray(100) = Brushes.Peru
objColorArray(101) = Brushes.Pink
objColorArray(102) = Brushes.Plum
objColorArray(103) = Brushes.PowderBlue
objColorArray(104) = Brushes.Purple
objColorArray(105) = Brushes.Red
objColorArray(106) = Brushes.RosyBrown
objColorArray(107) = Brushes.RoyalBlue
objColorArray(108) = Brushes.SaddleBrown
objColorArray(109) = Brushes.Salmon
objColorArray(110) = Brushes.SandyBrown
objColorArray(111) = Brushes.SeaGreen
objColorArray(112) = Brushes.SeaShell
objColorArray(113) = Brushes.Sienna
objColorArray(114) = Brushes.Silver
objColorArray(115) = Brushes.SkyBlue
objColorArray(116) = Brushes.SlateBlue
objColorArray(117) = Brushes.SlateGray
objColorArray(118) = Brushes.Snow
objColorArray(119) = Brushes.SpringGreen
objColorArray(120) = Brushes.SteelBlue
objColorArray(121) = Brushes.Tan
objColorArray(122) = Brushes.Teal
objColorArray(123) = Brushes.Thistle
objColorArray(124) = Brushes.Tomato
objColorArray(125) = Brushes.Transparent
objColorArray(126) = Brushes.Turquoise
objColorArray(127) = Brushes.Violet
objColorArray(128) = Brushes.Wheat
objColorArray(129) = Brushes.White
objColorArray(130) = Brushes.WhiteSmoke
objColorArray(131) = Brushes.Yellow
objColorArray(132) = Brushes.YellowGreen
End Sub
Private Sub BarChart_Resize(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Resize
If blnFormLoaded = True Then
BarChart_Paint(Me, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs(CreateGraphics(), New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height)))
End If
End Sub
Friend WithEvents ttHint As System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip
End Class
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll'
In this demo, Powershell opens the Form and sends two data samples to it, waiting for few seconds after each sample is rendered, then closes the Form.

$object = New-Object -TypeName 'BarChart'
$data1 = New-Object System.Collections.Hashtable(10)
$data1.Add("Product1", 25)
$data1.Add("Product2", 15)
$data1.Add("Product3", 35)
$object.LoadData([System.Collections.Hashtable] $data1)
[void]$object.Show()
start-sleep -seconds 5
$data2 = New-Object System.Collections.Hashtable(100)
$data2.Add("Item1", 50)
$data2.Add("Item2", 150)
$data2.Add("Item3", 250)
$data2.Add("Item4", 20)
$data2.Add("Item5", 100)
$data2.Add("Item6", 125)
$data2.Add("Item7", 148)
$data2.Add("Item8", 199)
$data2.Add("Item9", 267)
$object.LoadData([System.Collections.Hashtable] $data2)
$object.RenderData()
start-sleep -seconds 5
$object.Close()
$object.Dispose()
Two public methods LoadData and RenderData have been added to allow controlling the form from the script. To prevent modifying the original example, the first method clones the data from the caller, while the latter creates a dummy event Args and calls the handler:

Public Sub LoadData(ByVal objCallerHashTable As Hashtable )
objHashTableG = objCallerHashTable.Clone()
End Sub
Public Sub RenderData
Me.BarChart_Paint(Nothing, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs( _
CreateGraphics(), _
New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height) _
))
End Sub
No communication back from Form to the script is present, thus no separate object implementing IWin32Window is needed. For the sake of the example, a VB.Net version is still provided below:
Add-Type -Language 'VisualBasic' -TypeDefinition @"
Public Class MyWin32Window
Implements System.Windows.Forms.IWin32Window
Dim _hWnd As System.IntPtr
Public Sub New(ByVal handle As System.IntPtr)
_hWnd = handle
End Sub
Public ReadOnly Property Handle() As System.IntPtr Implements System.Windows.Forms.IWin32Window.Handle
Get
Handle = _hWnd
End Get
End Property
End Class
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'MyWin32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
To provide real world data samples for the Bar (or Gantt) Chart to render one would like to capture the Web Site Page element load times for some performance meaurement scenario. This is easily done with the help of FiddlerCore assembly, as shown below. The c# part of the script contains a modified fiddlercore-demo example, with the focus on subset of metrics provided by Fiddler:
Add-Type @"
using System;
using Fiddler;
namespace WebTester
{
public class Monitor
{
public Monitor()
{
#region AttachEventListeners
FiddlerApplication.OnNotification += delegate(object sender, NotificationEventArgs oNEA) { Console.WriteLine("** NotifyUser: " + oNEA.NotifyString); };
FiddlerApplication.Log.OnLogString += delegate(object sender, LogEventArgs oLEA) { Console.WriteLine("** LogString: " + oLEA.LogString); };
FiddlerApplication.BeforeRequest += (s) =>
{
s.bBufferResponse = true;
};
FiddlerApplication.BeforeResponse += (s) =>
{
};
FiddlerApplication.AfterSessionComplete += (fiddler_session) =>
{
if (fiddler_session.RequestMethod == "CONNECT")
return;
if (fiddler_session == null || fiddler_session.oRequest == null || fiddler_session.oRequest.headers == null)
return;
var full_url = fiddler_session.fullUrl;
Console.WriteLine("URL: " + full_url);
HTTPResponseHeaders response_headers = fiddler_session.ResponseHeaders;
Console.WriteLine("HTTP Response: " + response_headers.HTTPResponseCode.ToString());
var timers = fiddler_session.Timers;
var duration = timers.ClientDoneResponse - timers.ClientBeginRequest;
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Duration: {0:F10}", duration.Milliseconds));
};
#endregion AttachEventListeners
}
public void Start()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting FiddlerCore...");
CONFIG.IgnoreServerCertErrors = false;
FiddlerApplication.Startup(8877, true, true);
Console.WriteLine("Hit CTRL+C to end session.");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Shutdown.");
FiddlerApplication.Shutdown();
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1);
}
public static Monitor m;
static void Console_CancelKeyPress(object sender, ConsoleCancelEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Stop.");
m.Stop();
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1);
}
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.dll','System.Data.dll',"${shared_assemblies_path}\FiddlerCore4.dll"
Modifications mostly made to AfterSessionComplete delegate. This class is embedded in Powershell, and sets to listen to the traffic roughly for the duration of the $selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url) call:
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'WebTester.Monitor'
$o.Start()
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$o.Stop()
[bool]$fullstop = [bool]$PSBoundParameters['pause'].IsPresent
The alternative way to collect durations is to simply invoke Javascript in the Chrome browser through Selenium:
using System;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Remote;
namespace WebTester
{
public static class Extensions
{
static int cnt = 0;
public static T Execute<t>(this IWebDriver driver, string script)
{
return (T)((IJavaScriptExecutor)driver).ExecuteScript(script);
}
public static List<dictionary<string, string="">> Performance(this IWebDriver driver)
{
string performance_script = @"
var ua = window.navigator.userAgent;
if (ua.match(/PhantomJS/)) {
return 'Cannot measure on ' + ua;
} else {
var performance =
window.performance ||
window.mozPerformance ||
window.msPerformance ||
window.webkitPerformance || {};
// var timings = performance.timing || {};
// return timings;
var network = performance.getEntries() || {};
return network;
}
";
List<dictionary<string, string="">> result = new List<dictionary<string, string="">>();
IEnumerable<Object> raw_data = driver.Execute<ienumerable<object>>(performance_script);
foreach (var element in (IEnumerable<Object>)raw_data)
{
Dictionary<string, string=""> row = new Dictionary<string, string="">();
Dictionary<string, object=""> dic = (Dictionary<string, object="">)element;
foreach (object key in dic.Keys)
{
Object val = null;
if (!dic.TryGetValue(key.ToString(), out val)) { val = ""; }
row.Add(key.ToString(), val.ToString());
}
result.Add(row);
}
return result;
}
public static void WaitDocumentReadyState(
IWebDriver driver, string expected_state, int max_cnt = 10)
{
cnt = 0;
var wait = new OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait(driver, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30.00));
wait.PollingInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.50);
wait.Until(dummy =>
{
string result = driver.Execute<string>("return document.readyState").ToString();
Console.Error.WriteLine(String.Format("result = {0}", result));
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("cnt = {0}", cnt));
cnt++;
return ((result.Equals(expected_state) || cnt > max_cnt));
});
}
}
}
</string></string,></string,></string,></string,></ienumerable<object></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,></t>
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$expected_states = @( "interactive", "complete" );
[WebTester.Extensions]::WaitDocumentReadyState($selenium, $expected_states[1])
$script = @"
var ua = window.navigator.userAgent;
if (ua.match(/PhantomJS/)) {
return 'Cannot measure on '+ ua;
}
else{
var performance =
window.performance ||
window.mozPerformance ||
window.msPerformance ||
window.webkitPerformance || {};
// var timings = performance.timing || {};
// return timings;
// NOTE: performance.timing will not return anything with Chrome
// timing is returned by FF
// timing is returned by Phantom
var network = performance.getEntries() || {};
return network;
}
"@
$savedata = $true
if ($headless) {
$result = ([OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver]$selenium).ExecutePhantomJS($script,[System.Object[]]@())
$result | Format-List
return
} else {
$result = ([OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium).executeScript($script)
$result | ForEach-Object {
$element_result = $_
Write-Output $element_result.Name
Write-Output $element_result.duration
$o = New-Object PSObject
$caption = 'test'
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'url' $element_result.Name
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'caption' $caption
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'load_time' $element_result.duration
$o | Format-List
if ($savedata) {
insert_database3 -data $o -database "$script_directory\timings.db"
}
$o = $null
The full script is available in the attached zip file.
Next example shows another custom-drawn Line, Bar and Pie Chart library which also is implemented in a single C# class:

Add-Type @"
// "
/*
*********************************************************************************************
* FILE NAME : DrawGraph.cs *
* DESCRIPTION : Generates Bar, Line & Pie graph for a set of values [maximum limit= 10] *
* AUTHOR : Anoop Unnikrishnan (AUK)
// ... currently we use unmodified code ...
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll','System.Xml.dll'
The form is limited to selection of the graph shape. Note there are few more shapes available in library (not shown here)
function DrawGraph {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$data_ref,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,385)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.SuspendLayout()
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Anoop.Graph.DrawGraph' -ArgumentList @( [string[]]$data_ref.Value.Keys,
[float[]]$data_ref.Value.Values,
$null,
$null,
'Arial',
200
)
[System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox]$b = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox'
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (40,20)
$b.Name = 'p5'
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width - 20),($f.Size.Height - 100))
$b.SizeMode = [System.Windows.Forms.PictureBoxSizeMode]::AutoSize
$b.TabIndex = 1
$b.TabStop = $false
$m = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.MenuStrip'
$file_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m2 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m3 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$exit_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$m.SuspendLayout()
$m.Items.AddRange(@( $file_m1,$exit_m1))
$m.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$m.Name = "m0"
$m.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width),24)
$m.TabIndex = 0
$m.Text = "m0"
$shape_m1.Name = "LineGraphToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m1.Text = "Line Graph"
$eventMethod_shape_m1 = $shape_m1.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m1.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.DrawLineGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$shape_m2.Name = "BarGraphToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m2.Text = "Bar Graph"
$eventMethod_shape_m2 = $shape_m2.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m2.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.DrawBarGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$shape_m3.Name = "3dPieChartToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m3.Text = "3d Pie Chart"
$eventMethod_shape_m3 = $shape_m3.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m3.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.Draw3DPieGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$dash = New-Object -TypeName System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripSeparator
$exit_m1.Name = "exitToolStripMenuItem"
$exit_m1.Text = "Exit"
$eventMethod_exit_m1 = $exit_m1.add_click
$eventMethod_exit_m1.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
$f.Close()
})
$file_m1.DropDownItems.AddRange(@( $shape_m1, $shape_m2, $dash, $shape_m3))
$file_m1.Name = "DrawToolStripMenuItem1"
$file_m1.Text = "Draw"
$m.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (1,1)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $m,$b))
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
}

The caller passes the data by reference
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$data = @{
"USA" = 10;
"UK" = 30;
"Japan" = 60;
"China" = 40;
"Bhutan" = 5;
"India" = 60;
}
[void](DrawGraph -Title $title -caller $caller -data_ref ([ref]$data))

The grid is notably the most complex object to offer to the user to manipulate.
function PromptGrid(
[System.Collections.IList] $data,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartiaName('System.Windows.Forms') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | out-null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = 'how do we open these stones? '
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid
$grid.PreferredColumnWidth = 100
$System_Drawing_Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.HeaderForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::FromArgb(255,0,0,0)
$grid.Name = "dataGrid1"
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$System_Drawing_Point = New-Object System.Drawing.Point
$System_Drawing_Point.X = 13;
$System_Drawing_Point.Y = 48 ;
$grid.Location = $System_Drawing_Point
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Open'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add( $button )
$f.Controls.Add( $grid )
$button.add_Click({
if ($grid.IsSelected(0)){
$caller.Data = 42;
}
$f.Close()
})
$grid.DataSource = $data
$f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller)) | out-null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.refresh()
$f.Dispose()
}
function display_result{
param ([Object] $result)
$array = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($key in $result.keys){
$value = $result[$key]
$o = New-Object PSObject
$o | add-member Noteproperty 'Substance' $value[0]
$o | add-member Noteproperty 'Action' $value[1]
$array.Add($o)
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$ret = (PromptGrid $array $process_window)
}
$data = @{ 1 = @('wind', 'blows...');
2 = @('fire', 'burns...');
3 = @('water', 'falls...')
}
display_result $data
Here, the event handler is temporarily left as an exercise to the reader - it can be quite domain specific. Please visit the author's github repository for the updates to this script.
For example, one can use GridListView to prompt the user for missing parameters. If the script parameters are
[CmdletBinding()]param ( [string] $string_param1 = '' ,
[string] $string_param2 = '' ,
[string] $string_param3 = '' ,
[boolean] $boolean_param = $false,
[int] $int_param
)
and the invocation only passes some but not all, one can discover the parameters state with the help of the following code snippet:
[CmdletBinding()]
$CommandName = $PSCmdlet.MyInvocation.InvocationName
$ParameterList = (Get-Command -Name $CommandName).Parameters
$parameters = @{}
foreach ($Parameter in $ParameterList) {
$value = Get-Variable -Name $Parameter.Values.Name -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
Then fill the $parameters Hashtable and pass it to the Form:
$parameters = @{ }
$value | foreach-object {$parameters[$_.Name] = $_.Value }
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
Edit_Parameters -parameters ($parameters) -caller $caller -title 'Provide parameters: '
that is defined like that:
function Edit_Parameters {
Param(
[Hashtable] $parameters,
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller= $null
)
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | out-null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.SuspendLayout();
$f.Text = $title
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView
$grid.Autosize = $true
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.Name = 'dataGrid1'
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$grid.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13,50)
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$grid.ColumnCount = 2
$grid.Columns[0].Name = 'Parameter Name'
$grid.Columns[1].Name = 'Value'
$parameters.Keys | foreach-object {
$row1 = @( $_, $parameters[$_].ToString())
$grid.Rows.Add($row1)
}
$grid.Columns[0].ReadOnly = $true;
foreach ($row in $grid.Rows){
$row.cells[0].Style.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightGray
$row.cells[0].Style.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::White
$row.cells[1].Style.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Lucida Console', 9)
}
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Run'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add( $button)
$f.Controls.Add( $grid )
$grid.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$button.add_Click({
foreach ($row in $grid.Rows){
if (($row.cells[0].Value -ne $null -and $row.cells[0].Value -ne '' ) -and ($row.cells[1].Value -eq $null -or $row.cells[1].Value -eq '')) {
$row.cells[0].Style.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Red
$grid.CurrentCell = $row.cells[1]
return;
}
}
$f.Close()
})
$f.ShowDialog($caller) | out-null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.refresh()
$f.Dispose()
}
In the button handler, we prevent closing the form until there are blank parameters. The input focus it brought to the cell where the input is expected. For simplicity, we accept text input for all parameters regardless of the type here.

Now suppose one runs a series of loose (e.g. Selenium) tests utilizing Excel file for test parameters and results:

To read the settings
$data_name = 'Servers.xls'
[string]$filename = ('{0}\{1}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),$data_name)
$sheet_name = 'ServerList$'
[string]$oledb_provider = 'Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0'
$data_source = "Data Source = $filename"
$ext_arg = "Extended Properties=Excel 8.0"
# TODO: hard coded id
[string]$query = "Select * from [${sheet_name}] where [id] <> 0"
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection]$connection = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection ("$oledb_provider;$data_source;$ext_arg")
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand]$command = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand ($query)
[System.Data.DataTable]$data_table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter]$ole_db_adapter = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter
$ole_db_adapter.SelectCommand = $command
$command.Connection = $connection
($rows = $ole_db_adapter.Fill($data_table)) | Out-Null
$connection.open()
$data_reader = $command.ExecuteReader()
$plain_data = @()
$row_num = 1
[System.Data.DataRow]$data_record = $null
if ($data_table -eq $null) {}
else {
foreach ($data_record in $data_table) {
$data_record | Out-Null
# Reading the columns of the current row
$row_data = @{
'id' = $null;
'baseUrl' = $null;
'status' = $null;
'date' = $null;
'result' = $null;
'guid' = $null;
'environment' = $null ;
'testName' = $null;
}
[string[]]($row_data.Keys) | ForEach-Object {
# An error occurred while enumerating through a collection: Collection was
# modified; enumeration operation may not execute..
$cell_name = $_
$cell_value = $data_record."${cell_name}"
$row_data[$cell_name] = $cell_value
}
Write-Output ("row[{0}]" -f $row_num)
$row_data
Write-Output "`n"
# format needs to be different
$plain_data += $row_data
$row_num++
}
}
$data_reader.Close()
$command.Dispose()
$connection.Close()
and write the results
function update_single_field {
param(
[string]$sql,
# [ref]$connection does not seem to work here
# [System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$connection_ref,
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection]$connection,
[string]$where_column_name,
[object]$where_column_value,
[string]$update_column_name,
[object]$update_column_value,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$update_column_type_ref = ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::VarChar),
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$where_column_type_ref = ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::Numeric)
)
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand]$local:command = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand
$local:command.Connection = $connection
$local:command.Parameters.Add($update_column_name,$update_column_type_ref.Value).Value = $update_column_value
$local:command.Parameters.Add($where_column_name,$where_column_type_ref.Value).Value = $where_column_value
$local:command.CommandText = $sql
# TODO: Exception calling "Prepare" with "0" argument(s): "OleDbCommand.Prepare method requires all variable length parameters to have an explicitly set non-zero Size."
# $command.Prepare()
$local:result = $local:command.ExecuteNonQuery()
Write-Output ('Update query: {0}' -f (($sql -replace $update_column_name,$update_column_value) -replace $where_column_name,$where_column_value))
Write-Output ('Update result: {0}' -f $local:result)
$local:command.Dispose()
return $local:result
}
update_single_field `
-connection $connection `
-sql "UPDATE [${sheet_name}] SET [status] = @status WHERE [id] = @id" `
-update_column_name "@status" `
-update_column_value $false `
-update_column_type_ref ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::Boolean) `
-where_column_name '@id' `
-where_column_value 2
some home-brewed functions are written. There may be no Excel installed on the test box (e.g. Spoon.Net) and when the number of tests grows, it will not be handy to select certain tests to rerun. A gridview comes to rescue (arguably this is just an initial solution, better ones may exist):
$RESULT_OK = 0
$RESULT_CANCEL = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_OK = 'OK'
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'CANCEL'
}
# http:
# for singlee column spreadsheets see also
# http:
function PromptGrid (
[System.Collections.IList]$data,
[object]$caller = $null
) {
if ($caller -eq $null) {
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | Out-Null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = 'Test suite'
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid
$grid.PreferredColumnWidth = 100
$System_Drawing_Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.HeaderForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::FromArgb(255,0,0,0)
$grid.Name = 'dataGrid1'
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$System_Drawing_Point = New-Object System.Drawing.Point
$System_Drawing_Point.X = 13;
$System_Drawing_Point.Y = 48;
$grid.Location = $System_Drawing_Point
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Open'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add($button)
$f.Controls.Add($grid)
$button.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
# http:
# TODO:
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewSelectedRowCollection]$rows = $grid.SelectedRows
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewRow]$row = $null
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewSelectedCellCollection] $selected_cells = $grid.SelectedCells;
$script:Data = 0
$script:Status = $RESULT_CANCEL
# $last_row = ($grid.Rows.Count)
$last_row = $data.Count
for ($counter = 0; $counter -lt $last_row;$counter++) {
if ($grid.IsSelected($counter)) {
$row = $data[$counter]
$script:Data = $row.Guid
$script:Status = $RESULT_OK
}
}
$f.Close()
})
$grid.DataSource = $data
$f.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Refresh()
}
function display_result {
param([object[]]$result)
$script:Data = 0
$array = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($row_data in $result) {
$o = New-Object PSObject
foreach ($row_data_key in $row_data.Keys) {
$row_data_value = $row_data[$row_data_key]
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty $row_data_key $row_data_value
}
[void]$array.Add($o)
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$ret = (PromptGrid $array $process_window)
if ($script:Status -eq $RESULT_OK ) {
Write-Output @( 'Rerun ->', $script:Data )
}
}

The full script source is available in the source zip file.
The pure ListView container is rendered like:
function PromptListView
{
param(
[System.Collections.IList]$data_rows,
[string[]]$column_names = $null,
[string[]]$column_tags,
[bool]$debug
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$numCols = $column_names.Count
$width = $numCols * 120
$title = 'Select process'
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,400)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $true
$select_button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$select_button.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (10,10)
$select_button.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,23)
$select_button.Text = 'Select'
$select_button.add_click({
})
$button_panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$button_panel.Height = 40
$button_panel.Dock = 'Bottom'
$button_panel.Controls.AddRange(@( $select_button))
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel.Dock = 'Fill'
$f.Controls.Add($panel)
$list_view = New-Object windows.forms.ListView
$panel.Controls.AddRange(@( $list_view,$button_panel))
$list_view.View = [System.Windows.Forms.View]'Details'
$list_view.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,350)
$list_view.FullRowSelect = $true
$list_view.GridLines = $true
$list_view.Dock = 'Fill'
foreach ($col in $column_names) {
[void]$list_view.Columns.Add($col,100)
}
foreach ($data_row in $data_rows) {
$cell = (Invoke-Expression (('$data_row.{0}' -f $column_names[0]))).ToString()
$item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem ($cell)
for ($i = 1; $i -lt $column_names.Count; $i++) {
$cell = (Invoke-Expression ('$data_row.{0}' -f $column_names[$i]))
if ($cell -eq $null) {
$cell = ''
}
[void]$item.SubItems.Add($cell.ToString())
}
$item.Tag = $data_row
[void]$list_view.Items.Add($item)
}
$list_view.add_ItemSelectionChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItemSelectionChangedEventArgs]$e)
[System.Windows.Forms.ListView]$lw = [System.Windows.Forms.ListView]$sender
[int]$process_id = 0
[int32]::TryParse(($e.Item.SubItems[0]).Text,([ref]$process_id))
$script:Item = $process_id
})
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $column_tags.Count; $i++) {
$list_view.Columns[$i].Tag = $column_tags[$i]
}
$list_view.Add_ColumnClick({
$list_view.ListViewItemSorter = New-Object ListViewItemComparer ($_.Column,$script:IsAscending)
$script:IsAscending = !$script:IsAscending
})
$script:Item = 0
$script:IsAscending = $false
$f.Topmost = $True
$script:IsAscending = $false
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
$x = $f.ShowDialog()
}
with sort
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
public class ListViewItemComparer : System.Collections.IComparer
{
public int col = 0;
public System.Windows.Forms.SortOrder Order;
public ListViewItemComparer()
{
col = 0;
}
public ListViewItemComparer(int column, bool asc)
{
col = column;
if (asc)
{ Order = SortOrder.Ascending; }
else
{ Order = SortOrder.Descending; }
}
public int Compare(object x, object y)
{
if (!(x is ListViewItem)) return (0);
if (!(y is ListViewItem)) return (0);
ListViewItem l1 = (ListViewItem)x;
ListViewItem l2 = (ListViewItem)y;
if (l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag == null)
{
l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag = "Text";
}
if (l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag.ToString() == "Numeric")
{
float fl1 = float.Parse(l1.SubItems[col].Text);
float fl2 = float.Parse(l2.SubItems[col].Text);
return (Order == SortOrder.Ascending) ? fl1.CompareTo(fl2) : fl2.CompareTo(fl1);
}
else
{
string str1 = l1.SubItems[col].Text;
string str2 = l2.SubItems[col].Text;
return (Order == SortOrder.Ascending) ? str1.CompareTo(str2) : str2.CompareTo(str1);
}
}
}

function display_result {
param([object[]]$result)
$column_names = @(
'id',
'dest',
'port',
'state',
'title',
'link'
)
$column_tags = @(
'Numeric',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text'
)
$data_rows = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($row_data in $result) {
$o = New-Object PSObject
foreach ($row_data_key in $column_names) {
$row_data_value = $row_data[$row_data_key]
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty $row_data_key $row_data_value
}
[void]$data_rows.Add($o)
}
[void](PromptListView -data_rows $data_rows -column_names $column_names -column_tags $column_tags)
}
Loading data into the grid or listview one entry at a time may not be the desired interface. Generic list of dictionaries seems to not work, as a workaround one may store it inside a suitable class:
public class DictionaryContainer
{
private List<Dictionary<string, object>> _data = new List<Dictionary<string, object>> { };
public List<Dictionary<string, object>> Data
{
get { return _data; }
}
public void add_row(Dictionary<string, object> row)
{
_data.Add(row);
}
public DictionaryContainer()
{
}
}
in this example, the DataGridView with a Togggle All States class was used for rendering the data :
function SelectAllGrid {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,235)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$urls = @( 'http://www.travelocity.com/','http://www.bcdtravel.com/','http://www.airbnb.com','http://www.priceline.com','http://www.tripadvisor.com')
# https:
$array_of_dictionaries_container = New-Object -Type 'Custom.DictionaryContainer'
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne 5; $cnt++) {
$item = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]'
$item.Add('RandomNo',(Get-Random -Minimum 1 -Maximum 10001))
$item.Add('date',(Date))
$item.Add('url',$urls[$cnt])
$array_of_dictionaries_container.add_row($item)
}
$r = New-Object -TypeName 'Custom.SelectAllGrid' -ArgumentList $array_of_dictionaries_container
$r.Size = $f.Size
$f.Controls.Add($r)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
}
$script:Data = $null
SelectAllGrid -Title 'Selection Grid Sample Project'
It had been modified to become a Panel rather than Form and to accept:
private System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView dgvSelectAll;
public SelectAllGrid(DictionaryContainer userDataContainer = null)
{
this.dgvSelectAll = new System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView();
dgvSelectAll.DataSource = GetDataSource(userDataContainer);
}
public DataTable GetDataSource(DictionaryContainer userDataContainer = null)
{
DataTable dTable = new DataTable();
DataRow dRow = null;
List<dictionary<string, object="">> sampleData;
if (userDataContainer == null)
{
Random rnd = new Random();
sampleData = new List<dictionary<string, object="">> {
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.facebook.com"}} ,
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.linkedin.com"}} ,
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.odesk.com"}}
};
}
else
{
sampleData = userDataContainer.Data;
}
Dictionary<string, object=""> openWith = sampleData[0];
Dictionary<string, object="">.KeyCollection keyColl = openWith.Keys;
dTable.Columns.Add("IsChecked", System.Type.GetType("System.Boolean"));
foreach (string s in keyColl)
{
dTable.Columns.Add(s);
}
foreach (Dictionary<string, object=""> objitem in sampleData)
{
dRow = dTable.NewRow();
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object=""> kvp in objitem)
{
dRow[kvp.Key] = kvp.Value.ToString();
}
dTable.Rows.Add(dRow);
dTable.AcceptChanges();
}
return dTable;
}
</string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,>

Note that modifying the SelectAllGridto take List<Dictionary<string, object>> directly and passing the data via
$array_of_dictionaries = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.List[System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]]'
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne 5; $cnt++) {
$item = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]'
$item.Add('RandomNo',(Get-Random -Minimum 1 -Maximum 10001))
$item.Add('date',(Date))
$item.Add('url',$urls[$cnt])
$array_of_dictionaries.Add($item)
}
$array_of_dictionaries | ForEach-Object { $row = $_
$row | Format-List
}
$r = New-Object -TypeName 'Custom.SelectAllGrid' -ArgumentList $array_of_dictionaries
fails with the error:
New-Object : Cannot find an overload for "SelectAllGrid" and the argument count: "5".
and that one had to add System.Data.dll to the list of referenced assemblies of Custom.SelectAllGrid to prevent the error:
Add-Type : c:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Local Settings\Temp\ypffadcb.0.cs(90) :
The type 'System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable' is defined in an assembly that is not referenced.
You must add a reference to assembly
'System.Xml, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089'.
Next example uses Collapsible Groups Control to offer to the user the aggregated configration information:
function GroupedListBox
{
param(
[string]$title,
[bool]$show_buttons)
@('System.Drawing','System.Collections', 'System.Collections.Generic' , 'System.Drawing', 'System.ComponentModel', 'System.Windows.Forms', 'System.Data') | foreach-object { [void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$width = 500
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,400)
$glc = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.GroupListControl'
$glc.SuspendLayout()
$glc.AutoScroll = $true
$glc.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$glc.FlowDirection = [System.Windows.Forms.FlowDirection]::TopDown
$glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion = $false
$glc.WrapContents = $false
$glc.Anchor = ([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles](0 `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right `
))
$f.SuspendLayout()
if ($show_buttons) {
[System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox]$cb1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox'
$cb1.AutoSize = $true
$cb1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 52)
$cb1.Name = "chkSingleItemOnlyMode"
$cb1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(224, 17)
$cb1.Text = 'Single-Group toggle'
$cb1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $true
function chkSingleItemOnlyMode_CheckedChanged
{
param([Object] $sender, [EventArgs] $e)
$glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion = $cb1.Checked
if ($glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion) {
$glc.CollapseAll()
} else {
$glc.ExpandAll()
}
}
$cb1.Add_CheckedChanged({ chkSingleItemOnlyMode_CheckedChanged } )
[System.Windows.Forms.Label]$label1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Label'
$label1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 13)
$label1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(230, 18)
$label1.Text = 'Grouped List Control Demo'
[System.Windows.Forms.Button]$button1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Button'
$button1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(303, 46)
$button1.Name = "button1"
$button1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(166, 23)
$button1.TabIndex = 3
$button1.Text = 'Add Data Items (disconnected)'
$button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
$button1.Add_Click( { write-host $glc.GetType()
$x = $glc | get-member
write-host ($x -join "`n")
})
$f.Controls.Add($cb1)
$f.Controls.Add($button1)
$f.Controls.Add($label1)
$glc.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(0, 75)
$glc.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size($f.size.Width, ($f.size.Height - 75))
} else {
$glc.Size = $f.Size
}
for ($group = 1; $group -le 5; $group++)
{
[GroupedListControl.ListGroup]$lg = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.ListGroup'
$lg.Columns.Add("List Group " + $group.ToString(), 120 )
$lg.Columns.Add("Group " + $group + " SubItem 1", 150 )
$lg.Columns.Add("Group " + $group + " Subitem 2", 150 )
$lg.Name = ("Group " + $group)
for ($j = 1; $j -le 5; $j++){
[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem]$item = $lg.Items.Add(("Item " + $j.ToString()))
$item.SubItems.Add($item.Text + " SubItem 1")
$item.SubItems.Add($item.Text + " SubItem 2")
}
$glc.Controls.Add($lg)
}
$f.Controls.Add($glc)
$glc.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
$result = $caller.Message
$caller = $null
return $result
}
$show_buttons_arg = $false
if ($PSBoundParameters["show_buttons"]) {
$show_buttons_arg = $true
}
To pass the real data to display, use the following structure:
$configuration_discovery_results = @{
'Web.config' = @{
'COMMENT' = 'Web Server';
'DOMAIN' = '';
'CONFIGURATIONS' = @{
'Exit SSL cms targetted offers' = $Extract_appSetting;
'Force Non Https for Home Page' = $Extract_appSetting;
'To new deck plans page' = $Extract_RuleActionurl ;
'imagesCdnHostToPrepend' = $Extract_RuleActionurl ;
};
};
[scriptblock]$Extract_appSetting = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$object_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$result_ref,
[string]$key = $null
)
if ($key -eq $null -or $key -eq '') {
throw 'Key cannot be null'
}
[scriptblock]$Extract_RuleActionurl = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$object_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$result_ref,
[string]$key = $null
)
if ($key -eq $null -or $key -eq '') {
throw 'Key cannot be null'
}
$data = @{}
$nodes = $object_ref.Value.Configuration.Location.'system.webServer'.rewrite.rules.rule
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Host $nodes.count
}
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $nodes.count; $cnt++) {
$k = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('name')
$v = $nodes[$cnt].action.Getattribute('url')
if ($k -match $key) {
$data[$k] += $v
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Output $k; Write-Output $v
}
}
}
$result_ref.Value = $data[$key]
}
$data = @{}
$nodes = $object_ref.Value.Configuration.Location.appSettings.Add
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $nodes.count; $cnt++) {
$k = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('key')
$v = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('value')
if ($k -match $key) {
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Host $k
Write-Host $key
Write-Host $v
}
$data[$k] += $v
}
}
$result_ref.Value = $data[$key]
}
To collect the data from various *.config files use e.g. code
function collect_config_data {
param(
[ValidateNotNull()]
[string]$target_domain,
[string]$target_unc_path,
[scriptblock]$script_block,
[bool]$verbose,
[bool]$debug
)
$local:result = @()
if (($target_domain -eq $null) -or ($target_domain -eq '')) {
if ($powerless) {
return $local:result
} else {
throw 'unspecified DOMAIN'
}
}
[xml]$xml_config = Get-Content -Path $target_unc_path
$object_ref = ([ref]$xml_config)
$result_ref = ([ref]$local:result)
Invoke-Command $script_block -ArgumentList $object_ref,$result_ref,$verbose,$debug
if ($verbose) {
Write-Host ("Result:`r`n---`r`n{0}`r`n---`r`n" -f ($local:result -join "`r`n"))
}
}
To fill the List, use
foreach ($key in $configuration_discovery_results.Keys) {
$values = $configuration_discovery_results[$key]
$configurations = $values['CONFIGURATIONS']
[GroupedListControl.ListGroup]$lg = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.ListGroup'
$lg.Columns.Add($values['COMMENT'],120)
$lg.Columns.Add("Key",150)
$lg.Columns.Add("Value",300)
foreach ($k in $configurations.Keys) {
$v = $configurations[$k]
[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem]$item = $lg.Items.Add($key)
$item.SubItems.Add($k)
$item.SubItems.Add($v)
}
$glc.Controls.Add($lg)
}

Next example covers drag and drop listboxes. There is a big number of events to craft and it is unpractical and error prone to convert the MSDN examplehttp://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.windows.forms.control.dodragdrop%28v=vs.100%29.aspx from C# to Powershell syntax entirely. One only needs the final ListDragTarget.Items, so one adds a string getter method to Add-Type leaving the rest of the snippet intact sans the main entry point:
public class DragNDrop : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private string _message;
public string Message
{
get {
_message = "";
List<string> _items = new List<string>();
foreach (object _item in ListDragTarget.Items) {
_items.Add(_item.ToString());
}
_message = String.Join(",", _items.ToArray() );
return _message;
}
set { _message = value; }
private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox ListDragSource;
private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox ListDragTarget;
private System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox UseCustomCursorsCheck;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label DropLocationLabel;
private int indexOfItemUnderMouseToDrag;
private int indexOfItemUnderMouseToDrop;
private Rectangle dragBoxFromMouseDown;
private Point screenOffset;
private Cursor MyNoDropCursor;
private Cursor MyNormalCursor;
public DragNDrop(String message)
{
and changes the constructor to accept a String message. Also, after making DragNDrop class inherit from System.Windows.Forms.Panel rather than ystem.Windows.Forms.Form it will be placed on the form:
function PromptWithDragDropNish {
param
(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel = New-Object DragNDrop($caller.Message)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(288, 248)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $panel ))
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
one uses the $caller object to handle the Message here, keeping in mind potential additional functionality though it is not strictly necessary. Finally, the script is receiving the result:
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$result = $panel.Message
$panel.Dispose()
$f.Dispose()
$caller = $null
return $result
}
$data = @(
'one','two','three','four','five',
'six','seven','nine','ten','eleven'
)
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$caller.Message = $data -join ','
$result = PromptWithDragDropNish 'Items' $caller
$result -split ',' | format-table -autosize

The form adjusts the cursor appropriately - this is not captured in the screenshot. After the form is closed the script prints the selected items. Such widget may be handy for e.g. arranging of Selenium tests into subsets (conversion to and from the *.orderedtests resource not shown). The full script source is available in the source zip file.

DF5B1F66EB484A2E8DDC06BD183B0E3F
For time interval selection one can use either DateTimePicker with a suitable System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePickerFormat
or even a DomainUpDown-derived custom time picker class:
public class CustomTimePicker : System.Windows.Forms.DomainUpDown
public CustomTimePicker()
{
for (double time = 23.5; time >= 0; time -= 0.5)
{
int hour = (int)time;
int minutes = (int)((time - hour) * 60);
this.Items.Add(hour.ToString("00") + ":" + minutes.ToString("00"));
}
this.SelectedIndex = Items.IndexOf("09:00");
this.Wrap = true;
}

$form_onload = {
$script:numeric_value = 0
$script:time_value = ''
$script:custom_value= ''
function UpDownsPrompt
param(
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing',
'System.Collections.Generic',
'System.Collections',
'System.ComponentModel',
'System.Windows.Forms',
'System.Text',
'System.Data'
) | ForEach-Object { $assembly = $_; [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($assembly) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (180,120)
$n = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
$n.SuspendLayout()
$n.Parent = $this
$n.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,80)
$n.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (50,20)
$n.Value = 1
$n.Minimum = 0
$n.Maximum = 1000
$n.Increment = 1
$n.DecimalPlaces = 0
$n.ReadOnly = $false
$n.TextAlign = [System.Windows.Forms.HorizontalAlignment]::Right
($n.add_ValueChanged).Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$script:numeric_value = $n.Value
}
)
$c = New-Object CustomTimePicker
$c.Parent = $f
$c.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,50)
$c.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,20)
$c.TextAlign = [System.Windows.Forms.HorizontalAlignment]::Left
$c.ReadOnly = $true
($c.add_TextChanged).Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$script:custom_value = $c.SelectedItem.ToString()
}
)
$c.SuspendLayout()
$c.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$c.ReadOnly = $true
$c.TabIndex = 0
$c.TabStop = $false
$s = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePicker
$s.Parent = $f
$s.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,20)
$s.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$s.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,20)
$s.Format = [System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePickerFormat]::Custom
$s.CustomFormat = 'hh:mm'
$s.ShowUpDown = $true
$s.Checked = $false
$s.Add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs)
$script:datetime_value = $s.Value
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (180,120)
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $c,$n,$s))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'UpDown Sample'
$c.ResumeLayout($false)
$n.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.add_Load($form_onload)
$f.Dispose()
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
Write-Debug ('Time Selection is : {0}' -f $script:datetime_value )
Write-Debug ('Numeric Value is : {0}' -f $script:numeric_value)
Write-Debug ('Custom contol Value is : {0}' -f $script:custom_value)

One may adapt the Floating/Sliding/Moving Menu in C#.NET for C# code to only contain ribbon slider control with Timers while definition of UserControl1 moved to Powershell by subclassing the Panel (orig. Form1) from Panel rather than Form and get rid of the default constructor:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Ribbon
{
public class Panel : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel2;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button2;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel3;
private System.Windows.Forms.Timer timer1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Timer timer2;
private System.Windows.Forms.UserControl _usrCtrl;
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
public Panel(System.Windows.Forms.UserControl u)
{
if (u == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("Usercontrol required");
this._usrCtrl = u;
InitializeComponent();
}
Then designing all buttons and subpanels in Powershell semantics:
function PromptRibbon {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,135)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$u = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.UserControl
$p1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$p2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$l2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b4 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b5 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b6 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b7 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b8 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b9 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b10 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b11 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b12 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b13 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b14 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b15 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b16 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b17 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b18 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b19 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b20 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p1.SuspendLayout()
$p2.SuspendLayout()
$u.SuspendLayout()
function button_click {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing {0}.`rThere is no callback defined yet." -f $who))
}
$callbacks = @{
'b1' = [scriptblock]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing`rcallback function for {0}." -f $who))
};
'b3' = [scriptblock]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing`rcallback function defined for {0}." -f $who))
};
}
$cnt = 0
@(
([ref]$p1),
([ref]$p2)
) | ForEach-Object {
$p = $_.Value
$p.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$p.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$p.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Left
$p.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point ((440 * $cnt),0)
$p.Name = ('panel {0}' -f $cnt)
$p.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (440,100)
$p.TabIndex = $cnt
$cnt++
}
$cnt = 0
@(
([ref]$l1),
([ref]$l2)
) | ForEach-Object {
$l = $_.Value
$l.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$l.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$l.Name = ('label {0}' -f $cnt)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (176,23)
$l.TabIndex = 0
$l.Text = ('Menu Group {0}' -f $cnt)
$l.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$cnt++
}
$positions = @{
'b1' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 27; };
'b2' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 64; };
'b3' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 27; };
'b4' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 64; };
'b5' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 27; };
'b6' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 64; };
'b7' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 27; };
'b8' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 64; };
'b9' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 27; };
'b10' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 64; };
'b11' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 27; };
'b12' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 64; };
'b13' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 27; };
'b14' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 64; };
'b15' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 27; };
'b16' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 64; };
'b17' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 27; };
'b18' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 64; };
'b19' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 27; };
'b20' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 64; };
}
$cnt = 1
@(
([ref]$b1),
([ref]$b2),
([ref]$b3),
([ref]$b4),
([ref]$b5),
([ref]$b6),
([ref]$b7),
([ref]$b8),
([ref]$b9),
([ref]$b10),
([ref]$b11),
([ref]$b12),
([ref]$b13),
([ref]$b14),
([ref]$b15),
([ref]$b16),
([ref]$b17),
([ref]$b18),
([ref]$b19),
([ref]$b20)
) | ForEach-Object {
$b = $_.Value
$b.Name = ('b{0}' -f $cnt)
$x = $positions[$b.Name].x
$y = $positions[$b.Name].y
Write-Debug ('button{0} x = {1} y = {2}' -f $cnt,$x,$y)
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point ($x,$y)
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (80,30)
$b.TabIndex = 1
$b.Text = ('Button {0}' -f $cnt)
$b.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $true
if ($callbacks[$b.Name]) {
$b.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[scriptblock]$s = $callbacks[$sender.Name]
$local:result = $null
Invoke-Command $s -ArgumentList $sender,$eventargs
})
} else {
$b.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
button_click -Sender $sender -eventargs $eventargs
})
}
$cnt++
}
$p1.Controls.Add($l1)
$p1.Controls.AddRange(@( $b10,$b9,$b8,$b7,$b6,$b5,$b4,$b3,$b2,$b1))
$p2.Controls.AddRange(@( $b20,$b19,$b18,$b17,$b16,$b15,$b14,$b13,$b12,$b11))
$p2.Controls.Add($l2)
$u.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6,13)
$u.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$u.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gainsboro
$u.Controls.AddRange(@( $p2,$p1))
$u.Name = 'UserControl1'
$u.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (948,100)
$p1.ResumeLayout($false)
$p2.ResumeLayout($false)
$u.ResumeLayout($false)
and displaying the form with the ribbon buttons:

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptRibbon -Title 'Floating Menu Sample Project' -caller $caller
write-output $caller.Data
When the callback exists for a button, it is run, otherwise generic button_clisk is called.The full script source is available in the source zip file.
Next example displays the Custom Message Box variants with C# code converted to Powershell semantics
function return_response
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[string ]$button_text = ([System.Windows.Forms.Button]$sender[0]).Text
if ($button_text -match '(Yes|No|OK|Cancel|Abort|Retry|Ignore)') {
$script:Result = $button_text
}
$f.Dispose()
}
function add_buttons {
param([psobject]$param)
switch ($param) {
('None') {
$button_ok.Width = 80
$button_ok.Height = 24
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ok)
$button_ok.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('OK') {
$button_ok.Width = 80
$button_ok.Height = 24
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ok)
$button_ok.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('YesNo') {
$button_no.Width = 80
$button_no.Height = 24
$button_no.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_no.Text = 'No'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_no)
$button_no.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_yes.Width = 80
$button_yes.Height = 24
$button_yes.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_no.Location.X - $button_no.Width - 2),114)
$button_yes.Text = 'Yes'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_yes)
$button_yes.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('YesNoCancel') {
$button_cancel.Width = 80
$button_cancel.Height = 24
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_cancel)
$button_cancel.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_no.Width = 80
$button_no.Height = 24
$button_no.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_cancel.Location.X - $button_cancel.Width - 2),114)
$button_no.Text = 'No'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_no)
$button_no.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_yes.Width = 80
$button_yes.Height = 24
$button_yes.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_no.Location.X - $button_no.Width - 2),114)
$button_yes.Text = 'Yes'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_yes)
$button_yes_Response.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('RetryCancel') {
$button_cancel.Width = 80
$button_cancel.Height = 24
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_cancel)
$button_cancel.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_retry.Width = 80
$button_retry.Height = 24
$button_retry.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_cancel.Location.X - $button_cancel.Width - 2),114)
$button_retry.Text = 'Retry'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_retry)
$button_retry.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('AbortRetryIgnore') {
$button_ignore.Width = 80
$button_ignore.Height = 24
$button_ignore.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ignore.Text = 'Ignore'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ignore)
$button_ignore.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_retry.Width = 80
$button_retry.Height = 24
$button_retry.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_ignore.Location.X - $button_ignore.Width - 2),114)
$button_retry.Text = 'Retry'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_retry)
$button_retry.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_abort.Width = 80
$button_abort.Height = 24
$button_abort.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_retry.Location.X - $button_retry.Width - 2),114)
$button_abort.Text = 'Abort'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_abort)
$button_abort.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
default {}
}
}
function add_icon_bitmap {
param([psobject]$param)
switch ($param)
{
('Error') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Error).ToBitmap()
}
('Information') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Information).ToBitmap()
}
('Question') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Question).ToBitmap()
}
('Warning') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Warning).ToBitmap()
}
default {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Information).ToBitmap()
}
}
}
function click_handler
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventArgs
)
if ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'collapse')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height + $txtDescription.Height + 6
$button_details.Tag = 'expand'
$button_details.Text = 'Hide Details'
$txtDescription.WordWrap = true
}
elseif ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'expand')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height - $txtDescription.Height - 6
$button_details.Tag = 'collapse'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
}
}
function set_message_text
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$Title,
[string]$Description
)
$label_message.Text = $messageText
if (($Description -ne $null) -and ($Description -ne ''))
{
$txtDescription.Text = $Description
}
else
{
$button_details.Visible = $false
}
if (($Title -ne $null) -and ($Title -ne ''))
{
$f.Text = $Title
}
else
{
$f.Text = 'Your Message Box'
}
}
function Show1
{
param(
[string]$messageText
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText '' $null
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Information'
add_buttons -param 'OK'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
$script:Result
}
function Show2
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Information'
add_buttons -param 'OK'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function Show3
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description,
[object]$IcOn,
[object]$btn
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param $IcOn
add_buttons -param $btn
$script:Result = 'Cancel'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function show_exception
{
param([System.Exception]$ex)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text -Title 'Exception' -messageText $ex.Message -Description $ex.StackTrace
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Error'
add_buttons -param 'YesNo'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function DrawBox
{
$f.Controls.Add($panel)
$panel.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$icon_bitmap.Height = 36
$icon_bitmap.Width = 40
$icon_bitmap.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,11)
$panel.Controls.Add($icon_bitmap)
$txtDescription.Multiline = $true
$txtDescription.Height = 183
$txtDescription.Width = 464
$txtDescription.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (6,143)
$txtDescription.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::Fixed3D
$txtDescription.ScrollBars = [System.Windows.Forms.ScrollBars]::Both
$txtDescription.ReadOnly = $true
$panel.Controls.Add($txtDescription)
$button_details.Height = 24
$button_details.Width = 80
$button_details.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (6,114)
$button_details.Tag = 'expand'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_details)
$button_details.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
click_handler ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$label_message.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (64,22)
$label_message.AutoSize = $true
$panel.Controls.Add($label_message)
$f.Height = 360
$f.Width = 483
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$f.MaximizeBox = $false
$f.MinimizeBox = $false
$f.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::ButtonFace
$f.Icon = New-Object System.Drawing.Icon ([System.IO.Path]::Combine((Get-ScriptDirectory),"Martz90-Circle-Files.ico"))
if ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'expand')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height - $txtDescription.Height - 6
$button_details.Tag = 'collapse'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
}
}
combined with Pure Powershell Assert functon from http://poshcode.org:
function assert {
[CmdletBinding()]
param(
[Parameter(Position = 0,ParameterSetName = 'Script',Mandatory = $true)]
[scriptblock]$Script,
[Parameter(Position = 0,ParameterSetName = 'Condition',Mandatory = $true)]
[bool]$Condition,
[Parameter(Position = 1,Mandatory = $true)]
[string]$message)
$message = "ASSERT FAILED: $message"
if ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName -eq 'Script') {
try {
$ErrorActionPreference = 'STOP'
$success = & $Script
} catch {
$success = $false
$message = "$message`nEXCEPTION THROWN: $($_.Exception.GetType().FullName)"
}
}
if ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName -eq 'Condition') {
try {
$ErrorActionPreference = 'STOP'
$success = $Condition
} catch {
$success = $false
$message = "$message`nEXCEPTION THROWN: $($_.Exception.GetType().FullName)"
}
}
if (!$success) {
$action = Show3 -messageText $message `
-messageTitle 'Assert failed' `
-icon $MSGICON.Error `
-Btn $MSGBUTTON.RetryCancle `
-Description ("Try:{0}`r`nScript:{1}`r`nLine:{2}`r`nFunction:{3}" -f $Script,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].ScriptName,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].ScriptLineNumber,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].FunctionName)
if ($action -ne $MSGRESPONSE.Ignore) {
throw $message
}
}
}
slightly modified to display the exception dialog box

and call stack information in the dialog and optionally continue execution:
function Show3
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description,
[object]$IcOn,
[object]$btn
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param $IcOn
add_buttons -param $btn
$script:Result = 'Cancel'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
One can use the snippet to handle regular exceptions as well:

or a variety of button combinations. The full example is available in the source zip file (two versions: one preserving original C# code and a simplified one).
Now, suppose the task needs to authenticate to the source control, CI or some other remote service that uses its own authentication mechanism and does not accept NTLM. The following code helps prompting the username/password. It uses standard Windows Form practice of masking the password text box:

function PromptPassword(
[String] $title,
[String] $user,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.MaximizeBox = $false;
$f.MinimizeBox = $false;
$f.Text = $title
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,20)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,20)
$l1.Text = 'Username'
$f.Controls.Add($l1)
$f.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 10, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$t1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(120, 20)
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(140, 20)
$t1.Text = $user;
$t1.Name = 'txtUser';
$f.Controls.Add($t1);
$l2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,50)
$l2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,20)
$l2.Text = 'Password'
$f.Controls.Add($l2)
$t2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(120, 50)
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(140, 20)
$t2.Text = ''
$t2.Name = 'txtPassword'
$t2.PasswordChar = '*'
$f.Controls.Add($t2)
$btnOK = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$x2 = 20
$y1 = ($t1.Location.Y + $t1.Size.Height + + $btnOK.Size.Height + 20)
$btnOK.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point($x2 , $y1 )
$btnOK.Text = "OK";
$btnOK.Name = "btnOK";
$f.Controls.Add($btnOK);
$btnCancel = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$x1 = (($f.Size.Width - $btnCancel.Size.Width) - 20 )
$btnCancel.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point($x1, $y1 );
$btnCancel.Text = 'Cancel';
$btnCancel.Name = 'btnCancel';
$f.Controls.Add($btnCancel);
$s1 = ($f.Size.Width - $btnCancel.Size.Width) - 20
$y2 = ($t1.Location.Y + $t1.Size.Height + $btnOK.Size.Height)
$f.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size($f.Size.Width, (($btnCancel.Location.Y +
$btnCancel.Size.Height + 40)))
$btnCancel.Add_Click({$caller.txtPassword = $null ; $caller.txtUser = $null ;$f.Close()})
$btnOK.Add_Click({$caller.Data = $RESULT_OK;$caller.txtPassword = $t2.Text ; $caller.txtUser = $t1.Text; $f.Close()})
$f.Controls.Add($l)
$f.Topmost = $true
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
In this script, we store User and password in separate fields:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptPassword -title 'Enter credentials' -user 'admin' -caller $caller
if ($caller.Data -ne $RESULT_CANCEL) {
write-debug ("Result is : {0} / {1} " -f $caller.TxtUser , $caller.TxtPassword )
}
Note the above example is not intended to collect NTLM credentials of the user, like e.g., changing the newly installed Windows service to execute with desired user credentials. For this case, use Microsoft Get-Credential cmdlet:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$target_service_name = 'MsDepSvc'
$domain = $env:USERDOMAIN
if ($domain -like 'UAT') {
$user = '_uatmsdeploy'
}
elseif ($domain -like 'PROD') {
$user = '_msdeploy'
}
else {
$user = $env:USERNAME
}
$target_account = "${domain}\${user}"
$credential = Get-Credential -username $target_account -message 'Please authenticate'
if ($credential -ne $null) {
$target_account = $credential.Username
$target_password = $credential.GetNetworkCredential().Password
write-Debug $target_password
} else {
}
return
Code for credentials verify, admin rights, modify the newly installed service emitted from the display.

Another possible login scenario is when user can authenticate with his/her domain credentials, but the system internally uses session cookie in the browser.
One can create a dialog with WebBrowser and monitor when the user successfully logs in, then collect the session global cookie.
For that purpose, the wininet.dll p/invoke code is added to $caller object and called when appropriate. Dealing with browser cookies is explained in various sources e.g. here.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// ... c sharp code
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Runtime.InteropServices.dll', 'System.Net.dll'
with the code:
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private string _cookies;
private string _url;
public string Cookies
{
get { return _cookies; }
set { _cookies = value; }
}
public string Url
{
get { return _url; }
set { _url = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
[DllImport("wininet.dll", SetLastError = true)]
public static extern bool InternetGetCookieEx(
string url,
string cookieName,
StringBuilder cookieData,
ref int size,
Int32 dwFlags,
IntPtr lpReserved);
private const int INTERNET_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = 0x00002000;
private const int INTERNET_OPTION_END_BROWSER_SESSION = 42;
public string GetGlobalCookies(string uri)
{
int datasize = 1024;
StringBuilder cookieData = new StringBuilder((int)datasize);
if (InternetGetCookieEx(uri, null, cookieData, ref datasize, INTERNET_COOKIE_HTTPONLY, IntPtr.Zero)
&& cookieData.Length > 0)
{
return cookieData.ToString().Replace(';', ',');
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
There is nothing preventing one from storing arbitrary valid C# code with Add-Type.

and handle the Navigated event in the $browser object:
function promptForContinueWithCookies(
[String] $login_url = $null,
[Object] $caller= $null
)
{
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$timer1 = new-object System.Timers.Timer
$label1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$f.SuspendLayout()
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$browser = new-object System.Windows.Forms.WebBrowser
$f.SuspendLayout();
$browser.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$browser.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(0, 0)
$browser.Name = "webBrowser1"
$browser.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(600, 600)
$browser.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = new-object System.Drawing.SizeF(6, 13)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(600, 600)
$f.Controls.Add($browser)
$f.Text = "Login to octopus"
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Add_Load({
param ([Object] $sender, [System.EventArgs] $eventArgs )
$browser.Navigate($login_url);
})
$browser.Add_Navigated(
{
param ([Object] $sender, [System.Windows.Forms.WebBrowserNavigatedEventArgs] $eventArgs )
$url = $browser.Url.ToString()
if ($caller -ne $null -and $url -ne $null -and $url -match $caller.Url ) {
$caller.Cookies = $caller.GetGlobalCookies($url)
}
}
)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
}

$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$service_host = 'http://localhost:8088'
$login_route = 'app#/users/sign-in'
$login_url = ('{0}/{1}' -f $service_host , $login_route)
$caller.Url = 'app#/environments'
promptForContinueWithCookies $login_url $caller
write-host ("{0}->{1}" -f , $caller.Url, $caller.Cookies)
The cookie will look like:
OctopusIdentificationToken = 6pivzR9B%2fEOyJwbBkA2XfYe1BW4BNuXUqCtpW7VX943Em%2fkBZataiWxOVRDnsiBz
Common dialogs is a good candidate to become a Powershell module (WIP):
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
function TextInputBox {
param(
$prompt_message = 'Enter the Value',
$caption = 'Inputbox Test'
)
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$text_input = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_prompt.Anchor = [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right
$label_prompt.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (12,9)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (302,82)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 3
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$button_ok.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,8)
$button_ok.Name = 'button_ok'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 1
$button_ok.Text = '&OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $text_input.Text
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$button_cancel.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,40)
$button_cancel.Name = 'button_cancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 2
$button_cancel.Text = '&Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$text_input.Text = ''
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_input.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (8,100)
$text_input.Name = 'text_input'
$text_input.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (379,20)
$text_input.TabIndex = 0
$text_input.Text = ''
$text_input.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (398,128)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($text_input,$button_cancel,$button_ok,$label_prompt))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'InputBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$form.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$response = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$result = ''
$text_input.Text = ''
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$text_input.SelectionStart = 0;
$text_input.SelectionLength = $text_input.Text.Length
$text_input.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $Trues
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog()
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

function ComboInputBox {
param(
[string]$prompt_message = 'Select or Enter the Country',
[string[]]$items = @(),
[string]$caption = 'combo test'
)
function PopulateCombo ()
{
param([string[]]$comboBoxItems)
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $comboBoxItems.Length; $i++)
{
$str = $comboBoxItems[$i]
if ($str -ne $null)
{
[void]$combobox.Items.Add($str)
}
}
}
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::None;
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$combobox = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_prompt.Anchor = [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right
$label_prompt.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',8.25,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (12,9)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (302,82)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 3
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$button_ok.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,8)
$button_ok.Name = 'btnOK'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 1
$button_ok.Text = '&OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $combobox.Text
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$button_cancel.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,40)
$button_cancel.Name = 'btnCancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 2
$button_cancel.Text = '&Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$combobox.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (8,100)
$combobox.Name = 'CmBxComboBox'
$combobox.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (379,20)
$combobox.TabIndex = 0
$combobox.Text = ''
$combobox.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$combobox.Add_TextChanged({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
})
$combobox.Add_KeyPress({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.Windows.Forms.KeyPressEventArgs]$e
)
})
$combobox.Add_TextChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e
)
})
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (398,128)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($combobox,$button_cancel,$button_ok,$label_prompt))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'ComboBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$script:result.status = ''
PopulateCombo -comboBoxItems $items
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$combobox.SelectionStart = 0
$combobox.SelectionLength = $combobox.Text.Length
$combobox.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $True
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog($caller)
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

function ChangePasswordDialogBox {
param(
[string]$prompt_message = 'Change the password',
[string]$caption = 'Default Caption',
[string]$old_password = 'password'
)
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_old_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_new_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_confirm_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$text_old_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text_new_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text_confirm_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_old_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_old_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,88)
$label_old_password.Name = 'lblOldPassword'
$label_old_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_old_password.TabIndex = 1
$label_old_password.Text = 'Old Password'
$label_old_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_new_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_new_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,112)
$label_new_password.Name = 'lblNewPassword'
$label_new_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_new_password.TabIndex = 2
$label_new_password.Text = 'New Password'
$label_new_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_confirm_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_confirm_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,136)
$label_confirm_password.Name = 'lblConfirmPassword'
$label_confirm_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_confirm_password.TabIndex = 3
$label_confirm_password.Text = 'Confirm New Password';
$label_confirm_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,8)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (280,72)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 9
$label_prompt.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_old_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_old_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,88)
$text_old_password.Name = 'txtbxOldPassword'
$text_old_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21);
$text_old_password.TabIndex = 4
$text_old_password.Text = ''
$text_old_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$text_new_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0);
$text_new_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,112)
$text_new_password.Name = 'txtbxNewPassword'
$text_new_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21)
$text_new_password.TabIndex = 5
$text_new_password.Text = ''
$text_new_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$text_confirm_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_confirm_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,136)
$text_confirm_password.Name = 'txtbxConfirmPassword'
$text_confirm_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21)
$text_confirm_password.TabIndex = 6
$text_confirm_password.Text = ''
$text_confirm_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (312,16)
$button_ok.Name = 'button_ok'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 7
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
if ($text_old_password.Text.Trim() -ne $old_password) {
$text_old_password.SelectionStart = 0
$text_old_password.SelectionLength = $text_old_password.Text.Length
$text_old_password.Focus()
} else {
if ($text_new_password.Text.Trim() -ne $text_confirm_password.Text.Trim()) {
$text_confirm_password.SelectionStart = 0
$text_confirm_passwordSelectionLength = $text_confirm_password.Text.Length
$text_confirm_password.Focus()
} else {
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $text_new_password.Text
$form.Dispose()
} }
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (312,48)
$button_cancel.Name = 'btnCancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 8
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$text_input.Text = ''
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
}
)
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (400,182)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($text_old_password,
$text_new_password,
$text_confirm_password,
$button_cancel,
$button_ok,
$label_prompt,
$label_old_password,
$label_new_password,
$label_confirm_password))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'InputBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$form.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$label_old_password.Text = 'Old Password'
$label_new_password.Text = 'New Password'
$label_confirm_password.Text = 'Confirm New Password'
$text_old_password.Text = $old_password
$text_new_password.Text = ''
$text_confirm_password.Text = ''
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$text_old_password.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $Trues
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog()
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$shared_assemblies = @(
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$f.Text = $title
$f.SuspendLayout()
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (210,105)
$button_combobox_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_combobox_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_combobox_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,10)
$button_combobox_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_combobox_test.Text = 'Combobox Test'
$button_combobox_test.Add_Click({
$countries = @(
"India",
"USA",
"UK",
"Russia",
"Bulgaria",
"Singapore",
"Malayasia",
"Japan",
"Thailand"
)
$prompt_message = 'Select or Enter the Country'
$caption = 'Combobox Test'
$o = ComboInputBox -items $countries -caption $caption -prompt_message $prompt_message
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_combobox_test)
$button_change_password_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_change_password_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_change_password_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,40)
$button_change_password_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_change_password_test.Text = 'Change Password Test'
$button_change_password_test.Add_Click({
$prompt_message = 'Change the Password'
$caption = 'Change Password Test'
$old_password = '123'
$o = ChangePasswordDialogBox -prompt_message $prompt_message -caption $caption -old_password $old_password
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_change_password_test)
$button_inputbox_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_inputbox_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_inputbox_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,70)
$button_inputbox_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_inputbox_test.Text = 'Inputbox test'
$button_inputbox_test.Add_Click({
$prompt_message = 'Enter the Value'
$caption = 'Inputbox test'
$o = TextInputBox -caption $caption -prompt_message $prompt_message
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_inputbox_test)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = 'Standard Input Dialogs'
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $Trues
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog($caller)
$f.Dispose()
Write-Output $caller.Data
The full example is available in the source zip file.
The next big topic is tabbed dialogs. The code implementing such basically repeats what was shown already with one additional feature - it prevents the user from leaving the textbox until there is an input. At the time the form is drawn, the specific tab and input are set to be selected.
If the user attempts to switch to the other tab or input without filing some text, a warning message is displayed under the TextBox.

When the input is provided, the warning message is cleared:

The code responsible for that is highlighted below:
function PromptWithTabs(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$textbox1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$button1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Controls.Add($textbox1)
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 52)
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Input Tab"
$textbox1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(72, 7)
$textbox1.Name = "textBoxMessage"
$textbox1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(100, 20)
$textbox1.TabIndex = 0
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(72,32)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,16)
$l1.Text = ''
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$panel2.Controls.Add($l1)
$textbox1.Add_Leave( {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
if ($sender.Text.length -eq 0) {
$l1.Text = 'Input required'
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$sender.Select()
$result = $sender.Focus()
} else {
$l1.Text = ''
}
})
$panel1.Controls.Add($button1)
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 52)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Action Tab"
$button1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(74, 7)
$button1.Name = "buttonShowMessage"
$button1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(107, 24)
$button1.TabIndex = 0
$button1.Text = "Show Message"
$button1_Click = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$caller.Message = $textbox1.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show($textbox1.Text);
}
$button1.Add_Click($button1_Click)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$textbox1.Select()
$textbox1.Enabled = $true
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 88)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 108)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ActiveControl = $textbox1
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
Note: The order of operations matters in the above fragment. There are subtle differences between focus() and select(), not covered here.

Clicking the button launches a messagebox along with storing the result in $caller.Message.
Next example uses Windows Forms-based custom ProgressBar Host to display, e.g., the status of Powershell jobs performing some dump task on remote hosts to the user.
The source code defining the control class is imported in the script.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
namespace ProgressBarHost
{
public class Progress : System.Windows.Forms.UserControl
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Data.dll', 'System.ComponentModel.dll'
The method PerformStep will be used without modifications in this example, but it is likely to be customized in domain-specific way.
The Powershell script does what Form designer is normally doing,
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Progress' = [ProgressBarHost.Progress] $null ;
})
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
function Progressbar(
[String] $title,
[String] $message
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(650,120)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$p = new-object ProgressBarHost.Progress
$p.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 8)
$p.Name = 'status'
$p.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(272, 88)
$p.TabIndex = 0
$so.Progress = $p
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(140, 152)
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(92, 24)
$b.Text = 'forward'
$b.Add_Click({ $p.PerformStep()
if ($p.Maximum -eq $p.Value) {
$b.Enabled = false;
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($b)
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 14)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 194)
$f.Controls.Add($p )
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog( )
$f.Dispose()
}
Progressbar -title $title -message $message
})
clear-host
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 3
$max_cnt = 10
$cnt = 0
while ($cnt -lt $max_cnt) {
$cnt ++
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
$so.Progress.PerformStep()
}

For debugging purposes, the Forward button with the same handler is added to the form. To keep execution of script possible, the form is launched from a second Powershell runspace. Instead of caller argument, a Synchronized HashTable object is used to communicate. This technique is used heavily with WPF controls.
Next example uses a sligtly modified Timer Powershell to show elapsing timer, while the main Powershell script continues performing some lengthy task(s).
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
foreach ($work_step_cnt in @( 1,2,3,5,6,7)) {
Write-Output ('Doing lengthy work step {0}' -f $work_step_cnt)
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
Write-Output 'All Work done'
$wait_timer_step = 0
$wait_timer_max = 2
After tasks are finished, if the timer is still visible it is stopped:
while (-not $handle.IsCompleted) {
Write-Output 'waiting on timer to finish'
$wait_timer_step++
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
if ($wait_timer_step -ge $wait_timer_max) {
$so.Progress.Value = $so.Progress.Maximum
Write-Output 'Stopping timer'
break
}
}
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()
return

The Form containing progressbar and timer is entirely in Powershell:
function GenerateForm {
param(
[int]$timeout_sec
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.MaximumSize = $f.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (220,65)
$so.Form = $f
$f.Text = 'Timer'
$f.Name = 'form_main'
$f.ShowIcon = $False
$f.StartPosition = 1
$f.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.MinimumSize.Width - 10),($f.MinimumSize.Height - 10))
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.SuspendLayout()
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Timer
$p = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
$p.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$p.Maximum = $timeout_sec
$p.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.ClientSize.Width - 10),($f.ClientSize.Height - 20))
$p.Step = 1
$p.TabIndex = 0
$p.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (5,5)
$p.Style = 1
$p.Name = 'progressBar1'
$so.Progress = $p
$InitialFormWindowState = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
function start_timer {
$t.Enabled = $true
$t.Start()
}
$t_OnTick = {
$p.PerformStep()
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($p.Maximum - $p.Value)
$f.Text = ('{0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds)
if ($p.Value -eq $p.Maximum) {
$t.Enabled = $false
$f.Close()
}
}
$OnLoadForm_StateCorrection = {
$f.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
start_timer
}
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($p.Maximum - $p.Value)
$f.Text = ('{0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$t.Interval = 1000
$t.add_tick($t_OnTick)
$InitialFormWindowState = $f.WindowState
$f.add_Load($OnLoadForm_StateCorrection)
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
}
Next, by combining Progressbar and Timer examples with Task List Progress assembly one produces the same for long running multi-step Powershell script.
Below, the script source is provide (script can also be found in the source zip. Explaining the mechanics of the form and enabling the Skip forward button is ongoing work in progress:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$shared_assemblies = @(
'ProgressTaskList.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assmblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
Write-Debug ('Using environment: {0}' -f $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH)
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assmblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
Write-Debug $assembly
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $assembly
}
Add-Type -Path $assembly
}
popd
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if ($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
elseif ($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
In this version the existing functionality of ProgressTaskList.dll will be used, no modifications made, and the assembly is built in Visual Studio and placed into $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
The actual work steps will be performed in the main script, therefore form is executed in separate Runspace
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Title' = [string]'';
'Visible' = [bool]$false;
'ScriptDirectory' = [string]'';
'Form' = [System.Windows.Forms.Form]$null;
'DebugMessage' = '';
'Current' = 0;
'Previous' = 0;
'Last' = 0;
'Tasks' = [System.Management.Automation.PSReference];
'Progress' = [Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList]$null;
})
The $so.Current, $so.Last and $so.Previous are used in the timer callback in the form's runspace to detect when it is time to call NextTask() on Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList object that is placed on the form:
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$rs = [runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so',$so)
$run_script = [powershell]::Create().AddScript({
In the form, a System.Windows.Forms.Timer object is instantiated to inspect the state of the Tasks, that are executed in the main script. There is also a System.Windows.Forms.Button to push the curent task, its functionality is unfinished, therefore its state is disabled.
function ProgressbarTasklist {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$tasks_ref,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$so.Form = $f
$f.Text = $title
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Timer
$so.DebugMessage = '"in form"'
function start_timer {
$t.Enabled = $true
$t.Start()
}
$t_OnTick = {
if ($so.Current -eq $so.Last) {
$t.Enabled = $false
$so.DebugMessage = '"Complete"'
$f.Close()
} else {
$so.DebugMessage = '"in timer"'
if ($so.Current -gt $so.Previous) {
$o.NextTask()
$so.Previous = $so.Current
$so.DebugMessage = ('Finished "{0}"' -f $so.Previous )
}
}
}
$t.Interval = 300
$t.add_tick($t_OnTick)
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (650,150)
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,14)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (292,144)
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$panel.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (210,114)
$b.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$b.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$b.Text = 'Skip forward'
[scriptblock]$progress = {
if (-not $o.Visible) {
$o.Visible = $true
$so.Current = 1
$o.Start()
} else {
$so.Current = $so.Current + 1
$so.DebugMessage = ('Skipped "{0}"' -f $so.Current )
$o.NextTask()
}
}
$progress_click = $b.add_click
$progress_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
if ($so.Current -eq $so.Last)
{
$b.Enabled = $false
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 300
$so.Current = $so.Current + 1
$so.Visible = $false
} else {
Invoke-Command $progress -ArgumentList @()
}
})
$b.Enabled = $false
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList' -ArgumentList @()
$o.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$o.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$o.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$o.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$o.Name = "progressTaskList1"
$o.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (288,159)
$o.TabIndex = 2
$so.Progress = $o
$o.TaskItems.AddRange(@( [string[]]$tasks_ref.Value))
$so.Last = $tasks_ref.Value.Count + 1
$o.Visible = $false
$panel.SuspendLayout()
$panel.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Black
$panel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$panel.Name = 'panel'
$panel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width),($f.Size.Height))
$panel.TabIndex = 1
$panel.Controls.Add($o)
$panel.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel.PerformLayout()
$InitialFormWindowState = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $b,$panel))
$f.Topmost = $True
$so.Visible = $true
$f.Add_Shown({
$f.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
$f.Activate()
Invoke-Command $progress -ArgumentList @()
start_timer
})
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
}
$tasks_ref = $so.Tasks
ProgressbarTasklist -tasks_ref $tasks_ref -Title $so.Title
Write-Output ("Processed:`n{0}" -f ($tasks_ref.Value -join "`n"))
})
The caller script that runs in default runspace updates the $so.Current thus signaling the form's timer after performing the appropriate step - currently it sleeps a random time not exceeding 5 seconds. In addidion it prints a progress message to the console, though good syncronization is not the main purpose of this example. Presumably the actual work produces a lot of extra screen output making it difficult to discover when certain step is completed.
$tasks = @(
'Verifying cabinet integrity',
'Checking necessary disk space',
'Extracting files',
'Modifying registry',
'Installing files',
'Removing temporary files')
$task_status = @{}
$tasks | ForEach-Object { $task_status[$_] = $null }
$so.Tasks = ([ref]$tasks)
$so.Title = 'Task List'
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
function PerformStep {
param(
[int]$step,
[switch]$skip
)
$task_status[$step] = $true
$so.Current = $step
}
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 100
while ($so.Visible) {
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $tasks.Count; $cnt++) {
$step_name = $tasks[$cnt]
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 5000)
PerformStep -Step $cnt
Write-Host ('Completes step [{0}] "{1}"' -f $cnt,$step_name)
}
$so.Visible = $false
}
Write-Output $so.DebugMessage
$so.Form.Close()
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()
After everything is done the Form closes itself and runspace is destroyed.

If one is about to make modifications to the Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList source, first one stores the Designer generated code and of the class inside the script as a Add-Type TypeDefinition argument. The only modification needed is to download suitable 16x16 icons from https://www.iconfinder.com and replace
this.imageList1.ImageStream = ((System.Windows.Forms.ImageListStreamer)(resources.GetObject("imageList1.ImageStream")))
with
private string[] iconPaths = new string[] {
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429962_216151.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429337_5880.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429523_62690.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429596_9866.ico"
} ;
...
foreach (string iconPath in this.iconPaths)
{
this.imageList1.Images.Add(new Icon(iconPath));
}
the next step is to refactor the Powershell script temporarily getting rid of extra runspace and of the timer object and focus on the button:
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (210,114)
$b.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$b.Text = 'forward'
$b.add_click({
if ($caller.Current -eq $caller.Last)
{
$b.Enabled = false
} else {
if (-not $o.Visible) {
$o.Visible = $true
$caller.Current = 1
$o.Start()
} else {
$o.NextTask()
$caller.Current = $caller.Current + 1
}
}
})
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'WIP.ProgressTaskList' -ArgumentList @()
In the above, the $caller object is introduced to store the Current and Last indices.

Next example combines Asynchronous GUI with ProgressCircle-progress control to produce a single process circle progress indicator controlled by direct invokation of form elements across Powershell runspaces.
The form (sans the Add-Type of ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle ) is
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'System.Windows.Forms'
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'System.Drawing'
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles')
$Form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$is= New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
$Form.Text = 'Demo Form'
$Form.Name = 'Form'
$Form.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$Form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (216,121)
$l1.Name = 'progress_label'
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (70,34)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (100,23)
$l1.Text = 'Round:'
$c1 = New-Object -TypeName 'ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle'
$c1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (20,20)
$c1.Name = "progress_circle"
$c1.PCElapsedTimeColor1 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Chartreuse
$c1.PCElapsedTimeColor2 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Yellow
$c1.PCLinearGradientMode = [System.Drawing.Drawing2D.LinearGradientMode]::Vertical
$c1.PCRemainingTimeColor1 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Navy
$c1.PCRemainingTimeColor2 = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightBlue
$c1.PCTotalTime = 25
$c1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (47,45)
$c1.TabIndex = 3
$progress_complete = $c1.add_PCCompleted
$progress_complete.Invoke({
param([object]$sender,[string]$message)
$l1.Text = ('Task completed!')
})
$Form.Controls.AddRange(@($l1,$c1))
$is= $Form.WindowState
$Form.add_Load({
$Form.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
})
The caller constructs the System.EventArgs objects to execute the delegate on the ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle control which increments and updates the correspondent Label found by name. Note there are several ways to do that.
$rs = [Management.Automation.Runspaces.RunspaceFactory]::CreateRunspace($Host)
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('Form',$Form)
$po = [System.Management.Automation.PowerShell]::Create()
$po.Runspace = $rs
$po.AddScript({
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::EnableVisualStyles()
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::Run($Form)
})
$res = $po.BeginInvoke()
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
Write-Output 'Pause'
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
$eventargs = New-Object -TypeName 'System.EventArgs'
Add-Member -InputObject $eventargs -MemberType 'NoteProperty' -Name 'Increment' -Value 0 -Force
Add-Member -InputObject $eventargs -MemberType 'NoteProperty' -Name 'Total' -Value 0 -Force
$handler = [System.EventHandler]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$e
)
$local:increment = $e.Increment
$local:total = $e.Total
$sender.Increment($local:increment)
$sender.Text = $e.MyText
try {
$elems = $sender.Parent.Controls.Find('progress_label',$false)
} catch [exception]{
}
if ($elems -ne $null) {
$elems[0].Text = ('Round: {0}' -f $local:total)
}
}
1..25 | ForEach-Object {
$eventargs.Total = $_
$eventargs.Increment = 1
[void]$c1.BeginInvoke($handler,($c1,([System.EventArgs]$eventargs)))
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 1000)
}
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
Write-Output 'Pause'
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 2000
}
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::Exit()
$po.EndInvoke($res)
$rs.Close()
$po.Dispose()
NOTE: To make the script work on W2K3 one has to trigger another invocation (updated script is available in the source zip):
1..($total_steps ) | ForEach-Object {
$current_step = $_
$message = $eventargs.Text =( 'Processed {0} / {1}' -f $current_step , $total_steps )
$eventargs.Increment = 1
[void]$c1.BeginInvoke($handler,($c1,([System.EventArgs]$eventargs)))
if ($host.Version.Major -eq 2) {
$c1.Invoke(
[System.Action[int, string]] {
param(
[int]$increment,
[string]$message
)
$sender.Increment($increment)
try {
$elems = $sender.Parent.Controls.Find('progress_label',$false)
} catch [exception]{
}
if ($elems -ne $null) {
$elems[0].Text = $message
}
},
@(1, $message)
)
}
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 1000)
}
Generalization to multiple job progress tracking is work in progress. Full example code provided in the source zip.
The Mac OS X style progress circle can be used with minimal modifications to C# code:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ProgressControl
{
public partial class CircularProgressControl : UserControl
{
public enum Direction
{
CLOCKWISE,
ANTICLOCKWISE
}
public Direction Rotation { get; set; }
private bool m_clockwise;
public bool Clockwise
{
get
{
return m_clockwise;
}
set
{
m_clockwise = value;
if (m_clockwise){
this.Rotation = Direction.CLOCKWISE;
} else {
this.Rotation = Direction.ANTICLOCKWISE;
}
}
}
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
The Powershell part of the script is:
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightGray
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (170,140)
$button1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$cbc1 = New-Object ProgressControl.CircularProgressControl
$cbc2 = New-Object ProgressControl.CircularProgressControl
$f.SuspendLayout()
$button1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (70,80)
$button1.Name = "button1"
$button1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$button1.TabIndex = 0
$button1.Text = "Start"
$button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
$button1.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
if ($button1.Text -eq "Start")
{
$button1.Text = 'Stop'
$cbc1.Start()
$cbc2.Start()
}
else
{
$button1.Text = 'Start'
$cbc1.Stop()
$cbc2.Stop()
}
})
$cbc1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$cbc1.Interval = 60
$cbc1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,20)
$cbc1.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc1.Name = "circularProgressControl1"
$cbc1.Clockwise = $true
$cbc1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc1.StartAngle = 270
$cbc1.TabIndex = 1
$cbc1.TickColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkBlue
$cbc2.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$cbc2.Interval = 60
$cbc2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,80)
$cbc2.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc2.Name = "$cbc2"
$cbc2.Clockwise = $false
$cbc2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc2.StartAngle = 270
$cbc2.TabIndex = 2
$cbc2.TickColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Yellow
$f.Controls.Add($cbc2)
$f.Controls.Add($button1)
$f.Controls.Add($cbc1)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = 'OS X Progress Control'
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
[void]$f.ShowDialog()

The next example customizes the Filesystem-TreeView to Powershell. In the Add-Type -TypeDefinition one combines the implementation of FileSystemTreeView and ShellIcon classes :
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Collections;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace C2C.FileSystem
{
public class FileSystemTreeView : TreeView
{
...
}
public class ShellIcon
{
...
}
}
In Powershell part one adds AfterSelect handler to C2C.FileSystem.FileSystemTreeView in which the selected TreeNode FullPath is stored and written in the textbox. The $show_files_checkbox checkbox allows switching LoadFiles on and off on the fly.

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$chooser = New-Object -TypeName 'C2C.FileSystem.FileSystemTreeView' -ArgumentList ($caller)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
# set up form
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.Text = $title
$form.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (700,450)
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$btnDirectory = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$label1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$txtDirectory = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$treePanel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$form.SuspendLayout()
#
# panel1
#
$panel1.Controls.Add($btnDirectory)
$panel1.Controls.Add($label1)
$panel1.Controls.Add($txtDirectory)
$panel1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$panel1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$panel1.Name = 'panel1'
$panel1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (681,57)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$show_files_checkbox = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$show_files_checkbox.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (515,27)
$show_files_checkbox.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (120,20)
$show_files_checkbox.Text = 'Files'
$panel1.Controls.Add($show_files_checkbox)
$show_files_checkbox.add_click({ if ($show_files_checkbox.Checked -eq $true) { $chooser.ShowFiles = $true } else { $chooser.ShowFiles = $false } })
#
# btnDirectory
#
$btnDirectory.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (560,27)
$btnDirectory.Name = "btnDirectory"
$btnDirectory.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (60,21)
$btnDirectory.TabIndex = 2
$btnDirectory.Text = 'Select'
$btnDirectory.add_click({ if ($caller.Data -ne $null) { $form.Close() } })
#
# label1
#
$label1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (9,9)
$label1.Name = 'label1'
$label1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (102,18)
$label1.TabIndex = 1
$label1.Text = 'Selection:'
#
# txtDirectory
#
$txtDirectory.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (9,27)
$txtDirectory.Name = "txtDirectory"
$txtDirectory.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (503,20)
$txtDirectory.TabIndex = 0
$txtDirectory.Text = ""
#
# treePanel
#
$treePanel.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$treePanel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,57)
$treePanel.Name = "treePanel"
$treePanel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (621,130)
$treePanel.TabIndex = 1
$treePanel.Controls.Add($chooser)
$chooser.ShowFiles = $false
$chooser.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$chooser.Add_AfterSelect({ $txtDirectory.Text = $caller.Data = $chooser.Data })
$chooser.Load('C:\')
# Form1
#
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (621,427)
$form.Controls.Add($treePanel)
$form.Controls.Add($panel1)
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.Text = 'Demo Chooser'
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
$form.KeyPreview = $True
$form.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $null }
else { return }
$form.Close()
})
[void]$form.ShowDialog([win32window ]($caller))
$form.Dispose()
Write-Output $caller.Data
The full script source is available in the source zip file.

Designing the Windows Presentation Foundation XAML is even simpler:
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml =
@"
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Row GridSplitter Example">
<StackPanel Height="Auto">
<Grid Height="400">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="50*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="50*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="0"
Grid.Row="0" x:Name="button00" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Quentin Tarantino"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="1"
x:Name="button01" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Larry Dimmick"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="0"
x:Name="button10" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Steve Buscemi"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1"
x:Name="button11" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Tim Roth"/>
</Grid>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
"@
Now, IWin32Window argument is not accepted by the System.Windows.Window.
$colors = @{
'Steve Buscemi' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Pink);
'Larry Dimmick' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::White);
'Quentin Tarantino' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Orange);
'Tim Roth' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Brown);
}
$result = @{ }
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$reader=(New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target=[Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader )
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
For simple behaviors, one way to communicate the result back to the script is via $result hash variable that is defined in the script and is visible in the event handler:
foreach ($button in @("button01" , "button00", "button10", "button11")) {
$control=$target.FindName($button)
$eventMethod=$control.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs ] $eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Content.ToString()
$color = $colors[$who ]
$sender.Background = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush($color)
$result[ $who ] = $true
write-debug $who
})
}
This sample is simple - one and the same event handler is attached to each clickable element in the XAML flow. The details of the sender are stored in the $result while to provide for visual cue code is changing the $sender's background.
Another example one can generate the XAML ComboBox source on the fly from the list of $items with the following code snippet:
$items = @(
'Apple' ,
'Banana' ,
'Orange' ,
'Pineapple' ,
'Plum'
)
$selected = @{ }
$context = @'
<window height="60" title="Window1" width="200" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<stackpanel>
<combobox iseditable="False" margin="5" name="comboBox">
'@
$cnt = 1
$items | foreach-object { $name = "Item_${cnt}" ; $cnt ++ ; $context +="<comboboxitem content="$_" name="${name}">" }
$context += @'
</comboboxitem></combobox>
</stackpanel>
</window>
'@
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = $context
Clear-Host
$reader=(New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target=[Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$handler = {
param ([object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs )
$sender.Background = [ System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::Red
$target.Title = ( 'Added {0} ' -f $sender.Content )
$selected[ $sender.Content ] = $true
}
This code provides minimal but clear visual feedback for items selection.
foreach ($item in ("Item_1", "Item_5", "Item_2","Item_3","Item_4") ){
$combobox_item_control = $target.FindName( $item )
$eventargsventMethod2 = $combobox_item_control.add_Selected
$eventargsventMethod2.Invoke( $handler )
$combobox_item_control = $null
}
yielding:

and prints the selected results in the Powershell fashion.
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
write-output 'Selected items:'$items | where-object {$selected.ContainsKey( $_ ) }

Notably, one can design a very rich user interface in pure XAML while keeping the actual selection processing simple
For example, by repeating (largely) the previous exercise, but draw 3 color-filled arrow polygons on the panel.
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
// .... code below
"@
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Height="100" Width="200" Title="Window1">
<Canvas Height="100" Width="200" Name="Canvas1">
<!-- Draws a triangle with a blue interior. -->
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Blue" Name="Polygon1" Canvas.Left="40" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="40"/>
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Green" Name="Polygon2" Canvas.Left="70" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="30"/>
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Red" Name="Polygon3" Canvas.Left="100" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="20"/>
</Canvas>
</Window>
and in the event handler perform color and ZIndex change of the Mouse-selected arrow and reflect the selected polygon name it in the title of the window:
Clear-Host
$polygon_data = @{}
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$canvas = $target.FindName("Canvas1")
function save_orig_design{
param ([String] $name)
$control = $target.FindName($name)
return @{
'fill' = ( $control.Fill.Color );
'ZIndex' = ( [System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::GetZIndex($control) )
}
}
$polygon_data['Polygon1'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon1'))
$polygon_data['Polygon2'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon2'))
$polygon_data['Polygon3'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon3'))
function restore_orig {
param ( [String] $name )
$control = $target.FindName( $name )
$color = [System.Windows.Media.ColorConverter]::ConvertFromString( [String] $polygon_data[$name]['fill'] )
$control.Fill = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush( $color )
[System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::SetZIndex($control, [Object] $polygon_data[$name]['ZIndex'])
}
$handler = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Input.MouseButtonEventArgs] $e )
@('Polygon1', 'Polygon2', 'Polygon3') | % { restore_orig( $_) }
$sender.Fill = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Orange)
[System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::SetZIndex($sender,[Object]100)
$target.Title="Hello $($sender.Name)"
}
foreach ($item in ('Polygon1', 'Polygon2', 'Polygon3') ){
$control = $target.FindName($item)
$eventMethod = $control.add_MouseDown
$eventMethod.Invoke( $handler )
$control = $null
}
$eventMethod.Invoke($handler)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
one can get distinct visual effect:



But designing code behind may be tough. Arranging the communication between Powershell and WPF properly is well documented and appears to be quite a challenging task.
To arrange the interaction between PowerShell run spaces one creates an optionally strongly-typed synchronized object and creates an additional RunSpace to execute WPF events.
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = '';
'Window' = [System.Windows.Window] $null ;
'TextBox' = [System.Windows.Controls.TextBox] $null ;
})
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
Next, one wraps the XAML handling code in the Add-Script method.
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
<window height="100" title="Example with TextBox" width="300" x:name="Window" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<stackpanel height="100" width="300">
<textblock fontsize="14" fontweight="Bold" text="A spell-checking TextBox:">
<textbox acceptsreturn="True" acceptstab="True" fontsize="14" margin="5" spellcheck.isenabled="True" textwrapping="Wrap" x:name="textbox">
</textbox>
</textblock></stackpanel>
</window>
"@
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load( $reader )
$so.Window = $target
$handler = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Controls.TextChangedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.Result = $sender.Text
}
$control = $target.FindName("textbox")
$so.TextBox = $control
$event = $control.Add_TextChanged
$event.Invoke( $handler )
$eventMethod.Invoke($handler)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
})
Then design accessor functions operating via the shared object $so. Note that certain properties that have to be accessible cannot be evaluated on a different thread. The calling thread cannot access this object because a different thread owns it exception is only raised at runtime.
function send_text {
Param (
$content,
[switch] $append
)
$so.Textbox.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
if ($PSBoundParameters['append_content']) {
$so.TextBox.AppendText($content)
} else {
$so.TextBox.Text = $content
}
$so.Result = $so.TextBox.Text
}, 'Normal')
}
function close_dialog {
$so.Window.Dispatcher.invoke([action]{
$so.Window.Close()
}, 'Normal')
}
Finally, the main script invokes the dynamically created one and controls the form.
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
Clear-Host
$data = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 1
write-host $so.Result
send_text -Content 'The qick red focks jumped over the lasy brown dog.'
$cnt = 10
[bool] $done = $false
while (($cnt -ne 0 ) -and -not $done) {
write-output ('Text: {0} ' -f $so.Result )
if ($so.Result -eq 'The quick red fox jumped over the lazy brown dog.' ){
$done = $true;
}
else {
start-sleep 10
}
$cnt --
}
close_dialog
if ( -not $done ){
write-output 'Time is up!'
} else {
write-output 'Well done!'
}
This example initializes the text with some typos.

and waits for the user to fix the typos. Once the text is corrected or the timeout expired, the form is closed and the summary is printed.

Due to somewhat more complex code needed for Powershell / WPF communication, it is advisable to start with the simpler example and only convert into final form once all event handlers execute as desired. Earlier examples can be reasonably quickly converted this way.
One can also arrange bidirectional communication between Form and script from the Form, e.g., loading some current data into the checkbox tooltip in a slightly modified version of the script below:
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
Elseif($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = [string] '';
'ScriptDirectory' = [string] '';
'Window' = [System.Windows.Window] $null ;
'Control' = [System.Windows.Controls.ToolTip] $null ;
'Contents' = [System.Windows.Controls.TextBox] $null ;
'NeedData' = [bool] $false ;
'HaveData' = [bool] $false ;
})
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
<window height="190" removed="LightGray" title="About WPF" width="168" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation">
<canvas>
<img opacity=".7" source="$('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'clock.jpg' )" width="150" />
<image.tooltip>
<tooltip name="tooltip">
<stackpanel>
<label background="Blue" fontweight="Bold" foreground="White">
The CheckBox
</label>
<stackpanel orientation="Horizontal">
<img margin="2" name="hourglass" source="$('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'hourglass.jpg' )" visibility="Collapsed" width="20" />
<textblock name="tooltip_textbox" padding="10" textwrapping="WrapWithOverflow" width="200">
please wait...
</textblock>
</stackpanel>
</stackpanel>
</tooltip>
</image.tooltip>
</canvas>
</window>
"@
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$so.Window = $target
$control = $target.FindName("tooltip")
$so.Indicator = $target.FindName("hourglass")
$contents = $target.FindName("tooltip_textbox")
$so.Control = $control
$so.Contents = $contents
$handler_opened = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.Contents.Text = 'please wait...'
$so.Indicator.Visibility = 'Visible'
$so.NeedData = $true
$so.Result = ''
}
$handler_closed = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.HaveData = $false
$so.NeedData = $false
}
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod] $event_opened = $control.Add_Opened
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod] $event_closed = $control.Add_Closed
$event_opened.Invoke( $handler_opened )
$event_closed.Invoke( $handler_closed)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
})
function send_text {
Param (
$content,
[switch] $append
)
$so.Indicator.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
$so.Indicator.Visibility = 'Collapsed'
}, 'Normal')
$so.Contents.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
if ($PSBoundParameters['append_content']) {
$so.Contents.AppendText($content)
} else {
$so.Contents.Text = $content
}
$so.Result = $so.Contents.Text
}, 'Normal')
}
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
Clear-Host
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
While (-Not $handle.IsCompleted) {
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 100
if ($so.NeedData -and -not $so.HaveData){
write-output ('Need to provide data' )
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 10
send_text -Content (Date)
write-output ('Sent {0}' -f $so.Result )
$so.HaveData = $true
}
}
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()

In this example, the ToolTip Opened,Closed events are used to set and clear the NeedData flag via Synchronized to the top level script than change the text to please wait and show the hourglass until the data is ready. The rendering of the data is again performed in the send_text. Note that the send_text function now invokes Dispatcher twice and the visual feedback is not perfect. Every time the mouse leaves and re-enters the Tooltip activation area, new data is requested and provided.


Picking specific node from hierarchy grouped in some fashion is often required when launching Powershell script e.g. for metric collection.
function PromptTreeView
{
Param(
[String] $title,
[String] $message)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections.Generic')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Text')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.SuspendLayout();
$t.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t.ImageList = $i
$t.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t.ImageIndex = -1
$t.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t.Name = "treeFood"
$t.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 256)
$t.TabIndex = 1;
$t_AfterSelect = $t.add_AfterSelect
$t_AfterSelect.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewEventArgs] $eventargs
)
if ($eventargs.Action -eq [System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewAction]::ByMouse)
{
write-host $eventargs.Node.FullPath
}
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 266)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $t))
$f.Name = "TreeViewExample"
$f.Text = "TreeView Example"
$f_Load = $f.add_Load
$f_Load.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Fruits")
$node.Nodes.Add("Apple")
$node.Nodes.Add("Peach")
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Vegetables")
$node.Nodes.Add("Tomato")
$node.Nodes.Add("Eggplant")
})
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'TreeView Sample'
$t.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $false
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$t.Dispose()
$f.Dispose()
}
By adding the ScriptDirectory property...
private string _script_directory;
public string ScriptDirectory
{
get { return _script_directory; }
set { _script_directory = value; }
}
...and updating the PromptTreeView signature to receive the $caller the script can pass its location to the Form via $caller.
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$caller.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$result = PromptTreeView 'Items' $caller
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
}
and the latter will be able to load custom icons:
try {
$script_path = $caller.ScriptDirectory
} catch [Exception] {
}
if ($script_path -eq '' -or $script_path -eq $null ) {
$script_path = get-location
}
foreach ($n in @(1,2,3)){
$image_path = ( '{0}\color{1}.gif' -f $script_path , $n )
$image = [System.Drawing.Image]::FromFile($image_path)
$i.Images.Add($image)
}

and use distinct icons for individual nodes. Using the same technique, the caller script may describe which icons to render for which node.
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Fruits")
$apple = $node.Nodes.Add("Apple")
$apple.ImageIndex = 1
$node.Nodes.Add("Peach")
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Vegetables")
$tomato = $node.Nodes.Add("Tomato")
$tomato.ImageIndex = 2
The next iteration of this script also contains a more elaborated version of the event handler. The sample can be used to handle time-consuming validations that may be required when e.g. the object being offered to the user represents a remote location with some latency. It may be desirable to do such validation without forcing the user to quit the dialog. In the code below, the form TreeView element click instantiates a BackgroundWorker to process the operation on separate thread. The form currently provides no visual cue, that $worker has started, though it is clearly possible.
Thus modal dialogs are still OK - since the event handling code is 100% PowerShell, there is no need to arrange on complex synchronization between script and the form - every time the Form desires to run some data validations vis invoking some relevant PowerShell cmdlets, it can do it directly.
$worker = new-object System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
$worker.WorkerReportsProgress = $false;
$worker.WorkerSupportsCancellation = $false;
$worker_DoWork = $worker.Add_DoWork
$worker_DoWork.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.DoWorkEventArgs] $eventargs
)
})
All work is done in the Completed event handler. On the example, a text file 'etc/hosts' is open in Notepad and the thread waits for user to close notepad. This is standard example / recommended practice with Windows.Forms except the Backgroundworker is usually implemented in C#. It is nice to discover it works right out of the box with PowerShell code.
$worker_RunWorkerCompleted = $worker.Add_RunWorkerCompleted
$worker_RunWorkerCompleted.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.ComponentModel.RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$child_proc = [System.Diagnostics.Process]::Start('notepad',"$env:windir\system32\drivers\etc\hosts")
$child_proc.WaitForExit()
})
Tabbed
One would really like to plant tree views not into text boxes, but on tabs. This would make the option selection entirely mouse-driven and is possible.
The minor difference with the earlier example is the name of the event the treeview redraws after - for tabPage it is VisibleChangedEvent.
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
The full source is provided below:
function TabsWithTreeViews(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 352)
$panel2.AutoSize = $true
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Source Node"
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,12)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(220,16)
$l1.Text = 'enter status message here'
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange( @($l1 ))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,230)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(244,32)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'status'
$panel2.Controls.Add($groupBox1)
$t2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t2.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t2.ImageList = $i
$t2.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t2.ImageIndex = -1
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t2.Name = "treeFood"
$t2.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t2.AutoSize = $true
$t2.TabIndex = 1;
$panel2.Controls.AddRange(@($t2))
$panel2.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t2.SuspendLayout()
$t2.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t2.Nodes.Add('Source Environment')
$server = $node.Nodes.Add('Test Server')
$databases = $server.Nodes.Add('Databases')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 1')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 2')
$server.Nodes.Add('Application')
$sites = $server.Nodes.Add('IIS Web Sites')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t2.ResumeLayout($false)
$t2.PerformLayout()
})
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 252)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Destination Node"
$t1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$t1.ImageList = $i
$t1.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t1.ImageIndex = -1
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t1.Name = "treeFood"
$t1.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t1.AutoSize = $true
$t1.TabIndex = 1;
$panel1.Controls.AddRange(@($t1))
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 288)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 308)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}

Code is work in progress, with the intent to use status label for validation warnings and the worker process for more deep validation of selected environments.

To manage Powershell Desired State Configuration Configuration Manager - Node - Provider - Attribute inputs in pre-V4 Powershell environment, one may wish to extend the treeview with combobox. For example, the custom TreeView Control with ComboBox Dropdown Nodes by Mattman206 can be used as follows. After compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, one loads it into the script, and adds to the form freely mixing System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode and DropDownTreeView.DropDownTreeNode nodes when processing the form's Load event:Mattman206 can be used as follows. After compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, one loads it into the script,
One would really like to plant tree views not into text boxes, but on tabs. This would make the option selection entirely mouse-driven and is possible.
The minor difference with the earlier example is the name of the event the treeview redraws after - for tabPage it is VisibleChangedEvent.
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
The full source is provided below:
function TabsWithTreeViews(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 352)
$panel2.AutoSize = $true
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Source Node"
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,12)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(220,16)
$l1.Text = 'enter status message here'
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange( @($l1 ))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,230)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(244,32)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'status'
$panel2.Controls.Add($groupBox1)
$t2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t2.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t2.ImageList = $i
$t2.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t2.ImageIndex = -1
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t2.Name = "treeFood"
$t2.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t2.AutoSize = $true
$t2.TabIndex = 1;
$panel2.Controls.AddRange(@($t2))
$panel2.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t2.SuspendLayout()
$t2.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t2.Nodes.Add('Source Environment')
$server = $node.Nodes.Add('Test Server')
$databases = $server.Nodes.Add('Databases')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 1')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 2')
$server.Nodes.Add('Application')
$sites = $server.Nodes.Add('IIS Web Sites')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t2.ResumeLayout($false)
$t2.PerformLayout()
})
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 252)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Destination Node"
$t1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$t1.ImageList = $i
$t1.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t1.ImageIndex = -1
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t1.Name = "treeFood"
$t1.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t1.AutoSize = $true
$t1.TabIndex = 1;
$panel1.Controls.AddRange(@($t1))
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 288)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 308)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}

Code is work in progress, with the intent to use status label for validation warnings and the worker process for more deep validation of selected environments.

With Powershell allowing administrator to manage large volume of data, it is often desirable to update complex object collections and a tristate treeview may be the to rescue. The following example wraps the custom TriStateTreeView class by RikTheVeggie. In fact the source TriStateTreeView.cs and has been embedded in the script unmodified - the only part that required modification was PopulateTree and triStateTreeView1_BeforeExpand from the test example - these methods have converted to Powershell semantics:
function populateTree {
param(
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeNodeCollection]$parent_nodes,
[string]$text
)
for ($i = 0; $i -lt 5; $i++) {
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode]$tn = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode (("{0}{1}" -f $text,($i + 1)))
if (($i % 2) -eq 0) {
$tn.Nodes.Add("")
}
$parent_nodes.Add($tn)
}
}
$t = New-Object -typeName 'RikTheVeggie.TriStateTreeView'
$t.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$t.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$t.Name = 'triStateTreeView1'
$t.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (284,262)
$t.TabIndex = 0
populateTree -parent_nodes $t.Nodes -text ""
$treeview_BeforeExpand = $t.add_BeforeExpand
$treeview_BeforeExpand.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewCancelEventArgs]$e
)
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeView]$tv = $sender
$tv.UseWaitCursor = $true
if (($e.Node.Nodes.Count -eq 1) -and ($e.Node.Nodes[0].Text -eq '')) {
$e.Node.Nodes.RemoveAt(0)
populateTree -parent_nodes $e.Node.Nodes -text $e.Node.Text
}
$tv.UseWaitCursor = $false
})
The selected nodes information is stored in the $caller object and passed to the script in AfterCheck event handler which P.O.C:
$treeview_AfterCheck = $t.add_AfterCheck
$treeview_AfterCheck.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewEventArgs]$eventargs
)
if ( $eventargs.Node.Checked ) {
if ($eventargs.Node.Text -ne '') {
$caller.Message += ('{0},' -f $eventargs.Node.Text)
}
}
})

A more practically useful example combines Tri-State-Tree-View with the example fromMSDN, to collect all 'checked' nodes ina button click handler, loads the following sample data into RikTheVeggie.TriStateTreeView in Powershell (most of the System.Windows.Forms.TreeView operations are in C# part of the script):
$tree = @{
'Vegetable' = @{
'Allium sativum' = @{
'garlic' = '$null';
};
'Phaseolus' = @{
'green bean' = '$null';
'haricot bean' = '$null';
'French bean' = '$null';
'runner bean' = '$null';
'Lima bean' = '$null';
};
};
'Fruit' = @{
'Hesperidium' = @{
'Lemon' = '$null';
'Grapefruit' = '$null';
'Lime' = '$null';
'Orange' = '$null';
};
'Pepo' = '$null';
'True berry' = @{
'Lucuma' = '$null';
'Blueberry' = '$null';
...
- of course it can process arbitrary deeply-nested tree like:
$deeply_nested_tree =
@{
'a' = @{
'aa' = @{
'aaa' = @{
'aaaa' = @{
'aaaaa' = '$null';
}
};
'aab' = @{
'aaba' = '$null';
};
'aac' = '$null';
};
'ab' = @{
'aba' = @{
'abaa' = '$null';
'abab' = '$null'
}
};
'ac' = @{
'aca' = '$null';
'acb' = '$null';
'acc' = '$null';
'acd' = '$null';
'ace' = '$null';
'acf' = '$null';
'acg' = '$null';
'ach' = '$null';
};
'ad' = '$null';
};
'b' = @{
'ba' = '$null'
'bb' = '$null';
'bc' = '$null';
'bd' = '$null';
'be' = '$null';
};
'c ' = '$null';
}
with the help of the following function:
function populateTree {
param(
[Object]$Object,
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode]$parent_node
)
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode]$new_node
if ( $Object -is [hashtable] ) {
foreach ( $pair in $Object.GetEnumerator() ){
if ($parent_node -eq $null) {
$new_node = $t.treeView1.Nodes.Add($pair.Key)
} else {
$new_node = $parent_node.Nodes.Add($pair.Key)
}
populateTree -object $pair.Value -parent_node $new_node
}
}
}
and processes the selections via HashSet sampe code taken from www.java2s.com
if ($caller.Count -gt 0) {
Write-Output 'Selection is : '
$caller.GetEnumerator() | ForEach-Object { Write-Output $_ }
} else {
Write-Output 'Nothing was selected.'
}
The treeView1_AfterCheck correctly updates the node checked state:
private void treeView1_AfterCheck(object sender, TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
if (isDrawing) return;
isDrawing = true;
if (!e.Node.Checked)
{
if (e.Node.Parent!= null && !HasCheckedChildNodes(e.Node.Parent))
{
try
{
e.Node.Parent.Checked = false;
}
catch { }
}
}
try
{
checkNodes(e.Node, e.Node.Checked);
}
finally
{
isDrawing = false;
}
}
The Show Selected Items button is collecting the nodes with checked (grand) children. The removal of the event handler does not work well when coded in Powershell, so everything is left in C#:
private void showCheckedNodesButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
treeView1.BeginUpdate();
treeView1.CollapseAll();
treeView1.BeforeExpand += checkForCheckedChildren;
treeView1.ExpandAll();
treeView1.BeforeExpand -= checkForCheckedChildren;
treeView1.EndUpdate();
}
Next example utilized the beautiful TreeTabControl. A Tree of Tab Items for Powershell.
There is a little public method to add to TreeTab/TreeTab/TreeTabControl.xaml.cs class to make Powershell use the class :
public TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE ConvertType(string _typestring ){
TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE _type;
if (String.Compare(_typestring, "MAIN", true) == 0)
_type = TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE.MAIN;
else
_type = TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE.GROUP;
return _type;
}
because the
public enum TREEITEM_TYPE
{
MAIN,
GROUP
}
is inaccessible to Powershell.
One uses the original container XAML practically unmodified:
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:custom="clr-namespace:TreeTab;assembly=TreeTab" Title="Window1" Margin="0,0,0,0" Height="244" Width="633">
<Grid x:Name="Container">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="30"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button x:Name="Hide_Tree" Grid.Column="1">Hide Tree</Button>
<Button x:Name="Show_Tree" Grid.Column="0">Show Tree</Button>
</Grid>
<Grid x:Name="Container2" Grid.Row="1" Margin="5,5,5,5">
<StackPanel x:Name="TreeTabContainer"></StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>

The Powershell script initializes the plumbing code :
$shared_assemblies = @(
'TreeTab.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object { Unblock-File -Path $_; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
Clear-Host
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
and after compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, places the instance of TreeTab.TreeTabControl into the StackPanel:
$t = New-Object -TypeName 'TreeTab.TreeTabControl'
$c = $target.FindName('TreeTabContainer')
$t.IsTreeExpanded = $true
$t.Name = 'treeTab'
[void]$t.HideTree()
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Global','Global',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),'')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Staging_Environment','Staging Environment',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),'')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Test_Environment','Test Environment',$false,$t.ConvertType($t.ConvertType('GROUP')),'')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp0 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Staging_Environment')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItem]$tItem = $t.AddTabItem('Certificates','Certificates',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp0)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('IIS_Web_Sites','IIS Web Sites',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp0)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Databases','Databases',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp0)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp02 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Databases')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_1','DB 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp02)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_2','DB 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp02)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp03 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('IIS_Web_Sites')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_1','Site 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_2','Site 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_3','Site 3',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_4','Site 4',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp01 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Test_Environment')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItem]$t23 = $t.AddTabItem('Certificates1','Certificates',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp01)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('IIS_Web_Sites2','IIS Web Sites',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp01)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Databases2','Databases',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp01)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp12 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Databases2')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_11','DB 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp12)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_12','DB 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp12)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp13 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('IIS_Web_Sites2')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_11','Site 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_12','Site 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_13','Site 3',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_14','Site 4',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.ShowTree()
[void]$c.AddChild($t)
$target.FindName("Hide_Tree").add_click.Invoke({
[void]$t.HideTree()
})
$target.FindName("Show_Tree").add_click.Invoke({
[void]$t.ShowTree()
})
$target.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
The class autmates the tab navigation. Next is to fill the tabs with standard WPF inputs and provide the domain-specific callbacks:
E.g. given
[xml]$parent_markup = @"
<pre lang="xml">
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Window1" Margin="5,5,5,5" Height="310" Width="420">
<ScrollViewer>
<WrapPanel>
<Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot">
</Grid>
</WrapPanel>
</ScrollViewer>
</Window>
"@
and
[xml]$child_markup = @"
="1.0"
<StackPanel xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<StackPanel.Resources>
<Style TargetType="{x:Type TextBox}">
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,10,0,0"/>
</Style>
</StackPanel.Resources>
<Label x:Name="lblNumberOfTargetHits" HorizontalAlignment="Center">Input:</Label>
<TextBox Width="120" x:Name="txtTargetKeyFocus" FontSize="12"/>
<TextBox x:Name="txtTargetFocus" TextWrapping="Wrap" FontSize="12"/>
</StackPanel>
"@
nesting controls is accomplished just like:
$parent_reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $parent_markup)
$parent_target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($parent_reader)
$LayoutRoot = $parent_target.FindName("LayoutRoot")
$child_reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $child_markup)
$child_target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($child_reader)
$LayoutRoot.add_Loaded.Invoke({
$LayoutRoot.Children.Add($child_target)
})
To run code in WPF control event handlers one makes sure the controls are found by their markup x:Name attribute by $child, not $parent e.g:
$target = $child_target
$control = $target.FindName("txtTargetKeyFocus")
$handler_got_keyboard_focus = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Input.KeyboardFocusChangedEventArgs]$e
)
$source = $e.Source
$source.Background = [System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::LightBlue
$source.Clear()
}
$handler_lost_keyboard_focus = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Input.KeyboardFocusChangedEventArgs]$e
)
$source = $e.Source
$source.Background = [System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::White
}
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod]$event_got_keyboard_focus = $control.Add_GotKeyboardFocus
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod]$event_lost_keyboard_focus = $control.Add_LostKeyboardFocus
$event_got_keyboard_focus.Invoke($handler_got_keyboard_focus)
$event_lost_keyboard_focus.Invoke($handler_lost_keyboard_focus)
$control = $null
continued with the remainder of controls.
Note: with the help of System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators assembly, one may save oneself from typing the full class names in the script:
$ta = [PSObject].Assembly.GetType('System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators')
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'PresentationCore','PresentationFramework' -Passthru |
Where-Object IsPublic |
ForEach-Object {
$_class = $_
try {
$ta::Add($_class.Name,$_class)
} catch {
( 'Failed to add {0} accelerator resolving to {1}' -f $_class.Name , $_class.FullName )
}
}
with the help of the code above the following fragment
# http:
[Window]@{
Width = 310
Height = 110
WindowStyle = 'SingleBorderWindow'
AllowsTransparency = $false
TopMost = $true
Content = & {
$c1 = [StackPanel]@{
Margin = '5'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
HorizontalAlignment = 'Center'
Orientation='Horizontal'
}
$t = [textblock]@{}
$t.AddChild([label]@{
Margin = '5'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
HorizontalAlignment = 'Center'
FontSize = '11'
FontFamily = 'Calibri'
Foreground = 'Black'
Content = 'Enter Password:'
}
)
$c1.AddChild($t)
$c1.AddChild(
[passwordbox]@{
Name = 'passwordBox'
PasswordChar = '*'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
Width = '120'
}
)
$c1.AddChild(
[button]@{
Content = 'OK'
IsDefault = 'True'
Margin = '5'
Name = 'button1'
Width = '50'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
}
)
,$c1} | ForEach-Object {
$_.Add_MouseLeftButtonDown({
$this.DragMove()
})
$_.Add_MouseRightButtonDown({
$this.Close()
})
$_.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
}
produces the similar effect as
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Window1" Margin="5,5,5,5" Height="110" Width="310">
<StackPanel xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" Orientation="Horizontal" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment = "Center">
<TextBlock Margin="5" FontSize = "11" FontFamily = "Calibri">
Enter Password:
</TextBlock>
<PasswordBox Name="passwordBox" PasswordChar="*" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="120"/>
<Button Content="OK" IsDefault="True" Margin="5" Name="button1" Width="50" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
In the majority of cases this leads to no ambiguity in event handlers
Say the script is running a series of steps with verbose logs and takes a lot of time to complete. It is natural to spawn a Windows System tray Notification icon that would indicate what the ongoing process is doing. The key is how to arrange the code so the control remains in the main script.
With minimal modifications, the Notification icon in the system tray example provided by ScriptIT one can make the main script manifest its state to the Balloon Tip message and the console, and the build log file is used to render the tray icon menu and to pass additional information to it.

Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
Elseif($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = [string] '';
'ConfigFile' = [string] '';
'ScriptDirectory' = [string] '';
'Form' = [System.Windows.Forms.Form] $null ;
'NotifyIcon' = [System.Windows.Controls.ToolTip] $null ;
'ContextMenu' = [System.Windows.Forms.ContextMenu] $null ;
})
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$so.Form = $f
$notify_icon = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.NotifyIcon
$so.NotifyIcon = $notify_icon
$context_menu = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ContextMenu
$exit_menu_item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
$AddContentMenuItem = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
$build_log = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'build.log' )
function Read-Config {
$context_menu.MenuItems.Clear()
if(Test-Path $build_log){
$ConfigData = Get-Content $build_log
$i = 0
foreach($line in $ConfigData){
if($line.Length -gt 0){
$line = $line.Split(",")
$Name = $line[0]
$FilePath = $line[1]
$context_menu | Build-ContextMenu -index $i -text $Name -Action $FilePath
$i++
}
}
}
$exit_menu_item.Index = $i+1
$exit_menu_item.Text = 'E&xit'
$exit_menu_item.add_Click({
$f.Close()
$notify_icon.visible = $false
})
$context_menu.MenuItems.Add($exit_menu_item) | Out-Null
}
function new-scriptblock([string]$textofscriptblock)
{
$executioncontext.InvokeCommand.NewScriptBlock($textofscriptblock)
}
function Build-ContextMenu {
param (
[int]$index = 0,
[string]$Text,
[string] $Action
)
begin
{
$menu_item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
}
process
{
$ContextMenu = $_
}
end
{
$menu_item.Text = $Text
$scriptAction = $(new-scriptblock "Invoke-Item $Action")
$menu_item.add_Click($scriptAction)
$ContextMenu.MenuItems.Add($menu_item) | Out-Null
}
}
$notify_icon.Icon = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'sample.ico' )
$notify_icon.Text = 'Context Menu Test'
$notify_icon.ContextMenu = $context_menu
$f.ContextMenu = $context_menu
$notify_icon.Visible = $true
$f.Visible = $false
$f.WindowState = 'minimized'
$f.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$f.add_Closing({ $f.ShowInTaskBar = $False })
$context_menu.Add_Popup({Read-Config})
$f.ShowDialog()
})
function send_text {
Param (
[String] $title = 'script',
[String] $message,
[int] $timeout = 10 ,
[switch] $append
)
$so.NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip($timeout, $title , $message, [System.Windows.Forms.ToolTipIcon]::Info)
write-output -InputObject ( '{0}:{1}' -f $title, $message)
}
clear-host
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$cnt = 0
$total = 4
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 1
send_text -title 'script' -message 'Starting...' -timeout 10
$so.ConfigFile = $build_log = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'build.log' )
set-Content -path $build_log -value ''
While (-Not $handle.IsCompleted -and $cnt -lt $total) {
start-sleep -Milliseconds 10000
$cnt ++
send_text -title 'script' -message ("Finished {0} of {1} items..." -f $cnt, $total ) -timeout 10
write-output ("Subtask {0} ..." -f $cnt ) | out-file -FilePath $build_log -Append -encoding ascii
}
$so.Form.Close()
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle) | out-null
$rs.Close()
write-output 'All finished'

Next example shows performing a Selenium WebDriver transaction from PowerShell. There is still a lot of code to add to this example, but the portion developed already is hopefully worth seeing. A simple transaction is chosen for illustration here. It was converted from the following MS Test example.
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using Microsoft.Activities.UnitTesting;
using Moq;
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Remote;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI;
using OpenQA.Selenium.IE;
using OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Safari;
namespace SeleniumTests
{
[TestClass]
public class SeleniumTest
{
private static IWebDriver driver;
private static StringBuilder verificationErrors = new StringBuilder();
private string baseURL;
private bool acceptNextAlert = true;
[ClassCleanup()]
public static void MyClassCleanup() {
try {
driver.Quit();
} catch (Exception) {
}
Assert.AreEqual("", verificationErrors.ToString());
}
[TestInitialize()]
public void MyTestInitialize()
{
driver = new SafariDriver();
Assert.IsNotNull(driver );
driver.Url = baseURL = "http://www.wikipedia.org";
driver.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait( TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10 )) ;
verificationErrors = new StringBuilder();
}
[TestCleanup()]
public void MyTestCleanup() {
}
[TestMethod]
public void Test()
{
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl(baseURL + "/");
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)) ;
IWebElement queryBox = driver.FindElement(By.Id("searchInput"));
queryBox.Clear();
queryBox.SendKeys("Selenium");
queryBox.SendKeys(Keys.ArrowDown);
queryBox.Submit();
driver.FindElement(By.LinkText("Selenium (software)")).Click();
Assert.IsTrue(driver.Title.IndexOf("Selenium (software)") > -1, driver.Title);
}
}
}
which in turn is essentially an MS Test decorated Selenium IDE recording.
The conversion to Powershell was made using similar approach as the rest of the examples in this article - mainly through consulting the API documents.
The script uses PhantomeJS Selenium driver for quick test run and a real Firefox browser for a thorough run.
All standard Selenium C# client API dlls are placed in the folder pointed to by SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH environment.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'Selenium.WebDriverBackedSelenium.dll',
'Moq.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | foreach-object { Unblock-File -Path $_ ; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
Naturally, if there is a business logic layer or DSL wrapping low level WebDriver calls, it can be compiled from C# into a standalone assembly DLL and made available to the PowerShell in much the same way
$testSuite = [System.Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName('${assembly_path}\BusinessTestSuite.dll')
$framework = [System.Reflection.Assembly]::ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(
'${assembly_path}\BusinessSpecificWebDriverFramework.dll')
To avoid copying the Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll but load from where it is installed on the machine, and make the familiar assertion calls available in the script, the following code performs a quick discovery. For simplicity just the Microsoft Test Agent InstallLocation registry key scan is shown, additional keys need to be tried, note that Visual Studio Express Edition does not install this dll, while the Enterprize installs several copies.
function read_registry{
param ([string] $registry_path,
[string] $package_name
)
pushd HKLM:
cd -path $registry_path
$settings = get-childitem -Path . | where-object { $_.Property -ne $null } | where-object {$_.name -match $package_name } | select-object -first 1
$values = $settings.GetValueNames()
if ( -not ($values.GetType().BaseType.Name -match 'Array' ) ) {
throw 'Unexpected result type'
}
$result = $null
$values | where-object {$_ -match 'InstallLocation'} | foreach-object {$result = $settings.GetValue($_).ToString() ; write-debug $result}
popd
$result
}
$shared_assemblies = @(
'Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = ( "{0}\{1}" -f ( read_registry -registry_path '/HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SOFTWARE/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Uninstall' -package_name '{6088FCFB-2FA4-3C74-A1D1-F687C5F14A0D}' ) , 'Common7\IDE\PublicAssemblies' )
$shared_assemblies_path =
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | foreach-object { Unblock-File -Path $_ ; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
[Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting.Assert]::AreEqual("true", (@('true','false') | select-object -first 1) )
Based on switch, the script initializes either phantom or real browser driver ...
if ($PSBoundParameters['browser']) {
Try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect('127.0.0.1',4444)
$connection.Close()
}
catch {
$selemium_driver_folder = 'c:\java\selenium'
start-process -filepath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -argumentlist "start cmd.exe /c ${selemium_driver_folder}\hub.cmd"
start-process -filepath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -argumentlist "start cmd.exe /c ${selemium_driver_folder}\node.cmd"
start-sleep 10
}
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
$uri = [System.Uri]('http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub')
$driver = new-object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver($uri , $capability)
} else {
$phantomjs_executable_folder = 'C:\tools\phantomjs'
$driver = new-object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$driver.Capabilities.SetCapability('ssl-protocol', 'any' );
$driver.Capabilities.SetCapability('ignore-ssl-errors', $true);
$driver.capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot", $false );
$driver.capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
}
There is no need to explicitly start PhantomJS driver.
Finally, the test begins (the implementations of Get-ScriptDirectory and Assert are not shown and can be found in the attached source zip and author's github repo).
[void]$driver.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait( [System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(10 ))
[string]$baseURL = $driver.Url = 'http://www.wikipedia.org';
$driver.Navigate().GoToUrl(('{0}/' -f $baseURL ))
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$queryBox = $driver.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id('searchInput'))
$queryBox.Clear()
$queryBox.SendKeys('Selenium')
$queryBox.SendKeys([OpenQA.Selenium.Keys]::ArrowDown)
$queryBox.Submit()
$driver.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::LinkText('Selenium (software)')).Click()
$title = $driver.Title
assert -Script { ($title.IndexOf('Selenium (software)') -gt -1 ) } -message $title
Pretending that the test failed, the script navigates to the URL identifying the browser and takes a screenshot.
$driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("https://www.whatismybrowser.com/")
[OpenQA.Selenium.Screenshot]$screenshot = $driver.GetScreenshot()
$screenshot_path = $env:SCREENSHOT_PATH
$screenshot.SaveAsFile(('{0}\{1}' -f $screenshot_path, 'a.png' ), [System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat]::Png)

and finishes the test run.
try {
$driver.Quit()
} catch [Exception] {
}
One would possibly introduce a separate script via proper CreateRunspace call and develop Synchronized object to allow controlling the invocation of $driver.GetScreenshot call when some test fails, from a separate Powershell runspace connected to main script (this is currently work in progress) in a similar way the System Tray Notification icon has controlled in an earlier example.
The Selenium RC version of the script would be loading different libraries and switch to Nunit library Asserts.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'ThoughtWorks.Selenium.Core.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
and invoke different methods:
$verificationErrors = new-object System.Text.StringBuilder
$selenium = new-object Selenium.DefaultSelenium('localhost', 4444, '*firefox', 'http://www.wikipedia.org/')
$selenium.Start()
$selenium.Open('/')
$selenium.Click('css=strong')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
$selenium.Type('id=searchInput', 'selenium')
$selenium.Click('id=searchButton')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
$selenium.Click('link=Selenium (software)')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
the rest of the script will be unchanged.

Naturally one can craft script directly in Powershell ISE which would save a lt of developer time.

To work with laterst version of Firefox (e.g. 33) one needs ensure the specific versions of Selenium C# libraries are loaded - similar version check is important for Nunit to access StringAssert:
$shared_assemblies = @{
'WebDriver.dll' = 2.44;
'WebDriver.Support.dll' = '2.44';
'nunit.core.dll' = $null;
'nunit.framework.dll' = '2.6.3';
}
$shared_assemblies.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
$assembly_path = [System.IO.Path]::Combine($shared_assemblies_path,$assembly)
$assembly_version = [Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName($assembly_path).Version
$assembly_version_string = ('{0}.{1}' -f $assembly_version.Major,$assembly_version.Minor)
if ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -ne $null) {
if (-not ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -match $assembly_version_string)) {
Write-Output ('Need {0} {1}, got {2}' -f $assembly,$shared_assemblies[$assembly],$assembly_path)
Write-Output $assembly_version
throw ('invalid version :{0}' -f $assembly)
}
}
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
One very promising potential enhancement is related to handling File download dialogs or multi-option Internet Explorer Alert popups. These not well supported by pure Selenium. Either a separate tool like Autoit is to be bundled in the test framework or one of many workarounds need to be adopted - the latter option sometimes feels somewhat quirky.
When the Selenium test is executed by Powershell, one may incorporate the class that invokes win32 API from C# and uses EnumWindows, GetWindowInfo, EnumPropsEx, GetProp, GetWindowText, GetWindowTextLength, GetWindowThreadProcessId win32 API from user32.dll via [DllImport()] and loads numerous necessary structures defined in Windows.h to access the window handle and invoke PostMessage or SendMessage on desired button or simply CloseWindow on the Alert / File Download dialog found by title. The latter would cause one test to fail but will prevent the entire test suite from hanging after browser loses the mouse focus. This is explained in several resources in the web.
and " save="" as"="" dialog="" is="" closed="" by="" sending="" it="" a="" WM_CLOSE Windows message.
With a little more P/invoke
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern Int32 SendMessage(IntPtr hwnd, UInt32 Msg, IntPtr wParam, [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)] string lParam);
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.SysUInt)]
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, SetLastError = false)]
static extern IntPtr SendMessage(IntPtr hWnd, UInt32 Msg, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam);
[DllImport("user32.dll", SetLastError = true, CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
static extern int GetClassName(IntPtr hWnd, StringBuilder lpClassName, int nMaxCount);
public static string GetText(IntPtr hWnd)
{
int length = GetWindowTextLength(hWnd);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(length + 1);
GetWindowText(hWnd, sb, sb.Capacity);
return sb.ToString();
}
private static string GetWindowClassName(IntPtr hWnd)
{
int nRet;
StringBuilder ClassName = new StringBuilder(256);
nRet = GetClassName(hWnd, ClassName, ClassName.Capacity);
return (nRet != 0) ? ClassName.ToString() : null;
}
public static void SetText(IntPtr hWnd, String text)
{
UInt32 WM_SETTEXT = 0x000C;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(text);
int result = SendMessage(hWnd, WM_SETTEXT, (IntPtr)sb.Length, (String)sb.ToString());
}
one may locate the elements of the dialog and enter some text into file name text box and send a buttonclick to save as button.
private static bool EnumWindow(IntPtr handle, IntPtr pointer)
{
GCHandle gch = GCHandle.FromIntPtr(pointer);
String window_class_name = GetWindowClassName(handle);
if (string.Compare(window_class_name, "Edit", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0 ) {
const UInt32 WM_CHAR = 0x0102;
const UInt32 WM_KEYDOWN = 0x0100;
const UInt32 WM_KEYUP = 0x0101;
const UInt32 VK_RETURN = 0x0D;
SendMessage(handle, WM_CHAR, new IntPtr(WM_KEYDOWN), IntPtr.Zero);
SetText(handle, @"c:\temp\my random filename");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
SendMessage(handle, WM_CHAR, new IntPtr(VK_RETURN), IntPtr.Zero);
}
if (string.Compare(window_class_name, "Button", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0 ) {
string button_text = GetText(handle);
if (string.Compare(button_text, "&Save", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0) {
SetText(handle, "About to click");
const UInt32 BM_CLICK = 0x00F5;
Thread.Sleep(1000);
SendMessage(handle, BM_CLICK, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero);
}
}
List<IntPtr> list = gch.Target as List<IntPtr>;
if (list == null)
throw new InvalidCastException("cast exception");
list.Add(handle);
return true;
}

Note that without sending the "Enter" key the Windows Explorer would have ignored the text entered behind the scene and saved the file in the original location / name.

The modified code is provided in the archive. With minimal effort one has the class integrated with PowerShell, but extending the example to be really useful is more work and somewhat beyond the scope of this article.
Another interesting possible scenario is when the target web site is hosted on Tomcat running on Linux host but the Internet Explorer integration tests are required to run. With the following boilerplate Perl code snippet, one would be able to launch the PowerShell script remotely through ssh: cygwin, TeamCity, Jenkins, etc.
use Net::SSH::Perl;
use Data::Dumper;
use constant DEBUG => 0;
our ($HOSTNAME, $USER, $PASSWORD );
my $POWERSHELL_SCRIPT = ...
$HOSTNAME = '192.168.56.102';
$USER = 'cyg_server';
$PASSWORD = 'cyg_server';
my $ssh_command =
"cat /dev/null|\
/cygdrive/c/Windows/system32/WindowsPowerShell/v1.0/powershell.exe \
-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -command \"&{ $POWERSHELL_SCRIPT }\"";
print STDERR $ssh_command if (DEBUG) ;
my $ssh = Net::SSH::Perl->new( $HOSTNAME, debug => 0 );
$ssh->login( $USER, $PASSWORD );
my ( $stdout, $stderr, $exitcode ) = $ssh->cmd( $ssh_command, undef );
print STDERR Dumper \[ $stdout, $stderr, $exitcode ];
1;
END
This clearly is not necessary with Selenium grid test script, but may be used for other situations.
For example by running the following textbook Powershell script through ssh
Import-module WebAdministration
$WebSiteAlias = 'Test'
$AppPoolAlias = 'Test'
pushd 'IIS:\Sites\Default Web Site'
$IISPath = "..\$WebSiteAlias"
if (Test-Path $IISPath) {
Write-Host "Web Site '$WebSiteAlias' exists."
}
$IISPath = "IIS:\AppPools"
cd $IISPath
if (Test-Path ".$AppPoolAlias") {
Write-Host "Application Pool '$AppPoolAlias' exists."
}
The result will be available to a caller script...

This is useful when the business runs a mixed Tomcat / IIS web sites, and for some reason deployment has to be orchestrated from Linux machine. In this case, more complex Powershell code will be user for, e.g. performing some app pools checks, invoking msdeploy.exe, followed by the business-specific web sites "priming", from Linux
The following Selenium automation script fragment selects the Carribbean honeymoon vacation cruise from one of cruise vendors. The code for selecting Destination, Date range and Number of Travelers is quite redundant and is shown only partially. The full working script is available in the zip.
$value1 = 'dest'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'Select a destination' ))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = 'C'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$value1 = 'dat'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'Select a date'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = '"022015"'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$value1 = 'numGuests'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'How many travelers'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = '"2"'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$css_selector1 = 'div.actions > a.search'
try {
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'SEARCH'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 10
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Screenshot]$screenshot = $selenium.GetScreenshot()
$guid = [guid]::NewGuid()
$image_name = ($guid.ToString())
[string]$image_path = ('{0}\{1}\{2}.{3}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),'temp',$image_name,'.jpg')
$screenshot.SaveAsFile($image_path,[System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat]::Jpeg)
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output $_.Exception.Message
}
try {
$selenium.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
}

The script can successfully replay in any browser except IE 11. The following code selects the browser:
param(
[string]$browser,
[int]$version
)
...
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect("127.0.0.1",4444)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd"
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}"
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
if ($version -ne $null -and $version -ne 0) {
$capability.SetCapability("version", $version.ToString());
}
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$uri = [System.Uri]("http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub")
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs'
...
When executed the script prints minimal breadcrumps indicating actions taken.
The following example translates a text on www.freetranslation.com. The page contains the following fragment:

<div class="gw-upload-action clearfix">
<div id="upload-button" class="btn"><img class="gw-icon upload" alt="" src="http://d2yxcfsf8zdogl.cloudfront.net/home-php/assets/home/img/pixel.gif"/>
Choose File(s)
<div class="ajaxupload-wrapper" style="width: 300px; height: 50px;"><input class="ajaxupload-input" type="file" name="file" multiple=""/></div>
</div>
</div>
The scripts writes text to a file and uploads it:
[void]$selenium.Manage().timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(60))
$base_url = 'http://www.freetranslation.com/'
$text_file = ('{0}\{1}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),'testfile.txt')
Write-Output 'good morning driver' | Out-File -FilePath $text_file -Encoding ascii
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$selenium.Manage().Window.Maximize()
$upload_element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::ClassName('ajaxupload-input'))
$upload_element.SendKeys($text_file)
then waits until the following element is present:

<a href="..." class="gw-download-link">
<img class="gw-icon download" src="http://d2yxcfsf8zdogl.cloudfront.net/home-php/assets/home/img/pixel.gif"/>
Download
</a>
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 100
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element1 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::ClassName("gw-download-link")))
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector('img.gw-icon')))
$text_url = $element1.getAttribute('href')
and downloads the results:
$result = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $text_url
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($result.RawContent -match 'Bonjour pilote'))
and verifies the result against a known translation.
Next, one would exclude C# from the pipeline and record Powershell transaction directly in Selenium IDE. Custom formatting is fully supported; one does not need to bother with packaging the xpi at the early development phase.
To proceed, author forks one of the existing repositories, by David Zwarg and modifies the C# formatter to follow Powershell syntax and do other necessary adjustments. All that is needed to create formatter is one file.

One thing to be careful is not to start with Selenium Remote Control - based plugins: The RC plugin can be developed but protocol is outdated and in particular no headless drivers is available.
The full JavaScript source of the formatter is not displayed here yet: it is an alpha-quality design, with pull request pending. Conversion between IDE commands, intermediate JavaScript method prototypes and final C# method calls is quite a pain.
The source is available on the author's github repo.
The plugin inherits from the webdriver.js,
if (!this.formatterType) {
var subScriptLoader = Components.classes['@mozilla.org/moz/jssubscript-loader;1'].getService(Components.interfaces.mozIJSSubScriptLoader);
subScriptLoader.loadSubScript('chrome://selenium-ide/content/formats/webdriver.js', this);
}
and currently adds minimal functionality of its own - currently there exist quite a few formatters with nearly identical code.
The modifications consists of providing full class paths in all method references, e.g.
WDAPI.Utils.isElementPresent = function(how, what) {
return "IsElementPresent(" + WDAPI.Driver.searchContext(how, what) + ")";
};
becomes:
WDAPI.Utils.isElementPresent = function(how, what) {
return '[Selenium.Internal.SeleniumEmulation]::IsElementPresent(' + WDAPI.Driver.searchContext(how, what) + ')';
};
and tweaking semantics, e.g:
Equals.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.e1.toString() + ' == ' + this.e2.toString() ;
}
becomes:
Equals.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.e1.toString() + ' -eq ' + this.e2.toString();
};
It looks natural to use Nunit.dll however accessing the StringAssert appears to be a little problematic, thus one may choose to use Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll as shown earlier
All Powershell initialization code from the earlier example goes into header option of the driver class:
this.options = {
receiver: '$selenium',
base_url: 'http://docs.seleniumhq.org/docs/02_selenium_ide.jsp',
driver_namespace: "OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox",
driver_capabilities: "Firefox()",
showSelenese: 'false',
indent: '4',
initialIndents: '3',
header:
'Param (\n'+
indents(1) + '[switch] $browser\n'+
')\n'
'$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::${driver_capabilities}\n' +
footer:
'# Cleanup\n' +
'try {\n' +
indents(1) + '$selenium.Quit()\n' +
'} catch [Exception] {\n' +
indents(1) + '# Ignore errors if unable to close the browser\n' +
'}\n',
defaultExtension: 'ps1'
};
Key properties converted into regular formatter Inputs:
this.configForm =
'<description>Selenium instance name</description>' +
'<textbox id="options_receiver" />' +
'<description>WebDriver Capabilities</description>' +
'<menulist id="options_driver_capabilities"><menupopup>' +
'<menuitem label="Firefox" value="Firefox()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Google Chrome" value="Chrome()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Safari" value="Safari()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Internet Explorer" value="InternetExplorer()"/>' +
'</menupopup></menulist>'+

At the later stage of the development, one will arrange the sources as appropriate for xpi and craft the chrome.manifest, install.rdf and format-loader.xul, e.g.
="1.0"
="chrome://global/skin/"="text/css"
<overlay id="webdriver_format_loader_overlay"
xmlns="http://www.mozilla.org/keymaster/gatekeeper/there.is.only.xul"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<script type="application/x-javascript" src="chrome://selenium-ide/content/api.js"/>
<html:script type="application/javascript">
var ide_api = new API();
ide_api.addPlugin("powershell-webdriver-formatter@serguei.kouzmine");
ide_api.addPluginProvidedFormatter("powershell-webdriver", "Powershell - WebDriver", "chrome://powershell-webdriver-formatter/content/formats/powershell-webdriver.js");
ide_api.addPluginProvidedFormatter("powershell-remotecontrol", "Powershell - RC", "chrome://powershell-webdriver-formatter/content/formats/powershell-remotecontrol.js");
</html:script>
</overlay>
This enables packaging into standalone Firefox Add-On via simple batch command (or equivalent bash script)
@echo off
setlocal
pushd %~dp0
set APP_NAME="powershell-webdriver-formatter"
set CHROME_PROVIDERS="content"
set ROOT_DIR=%CD%
set TMP_DIR="build"
del /Q %APP_NAME%.xpi
del /S /Q %TMP_DIR%
mkdir %TMP_DIR%\chrome\content
robocopy.exe content %TMP_DIR%\chrome\content /E
robocopy.exe locale %TMP_DIR%\chrome\locale /E
robocopy.exe skin %TMP_DIR%\chrome\skin /E
robocopy.exe defaults %TMP_DIR%\defaults /E
copy install.rdf %TMP_DIR%
copy chrome.manifest.production %TMP_DIR%\chrome.manifest
cd %TMP_DIR%
echo "Generating %APP_NAME%.xpi..."
PATH=%PATH%;%ProgramFiles%\7-Zip;%ProgramFiles(x86)%\7-Zip
7z.exe a -r -y -tzip ../%APP_NAME%.zip *
cd %ROOT_DIR%
rename %APP_NAME%.zip %APP_NAME%.xpi
endlocal

To use the formatter,
- Open Selenium IDE, record the transaction
- Select Options from the Options menu
- Select the "Formats" tab
- Fill the inputs if the formatter xpi was loaded or
- Click on the "Add" button
- Name the format
- Paste and save the Javascript source (losing the inputs)
- In the "File" "Export Test Case as..." select the format
If everything is done right, the generated Powershell script will need no modifications and can be run right away.
For example, in the following fragment, after loading the required assemblies and launching the Selenium, draws a border around the Google logo by executing a Javascript code in the context of the loaded page, through Selenium.
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl('http://www.google.com')
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement] $element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id("hplogo"))[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);", $element, "color: yellow; border: 4px solid yellow;")
start-sleep 3
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);", $element, '')

Clearly the Javascript is the only part that matters here. Sacrificing the overhead of C# project seems to be appropriate.
Another possible examle would execute $selenium.Manage().Timeouts().setScriptTimeout and [OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteAsyncScript followed by $selenium.FindElement to either "stamp" the build information into the page or, instead perform checks and store the answer into a dynamically appended div element and communicate the assertion results back to the script (work in progress).
Small-time development activities e.g. standard CI post-deployment web site "warm-up" are also likely to be easier through Selenium IDE with subsequent launch from Powershell rather then via coding a separate application.
The following example combines code from Hosting And Changing Controls In Other Applicationswith a typical Selenium transaction (this one involving frames). Some web sites are really coded to be sensitive to mouse hover events. This example shows debugging the transaction in the situation when additional monitor is not available e.g. in VirtualBox, and the browser is maximized to fill the screen leaving no room to trace the execution.
The code from Hosting And Changing Controls In Other Applications responsible for adding an extra control to already running window, is used without modifications, but some changes being planned, one keeps the source together with the script rather than compiling it into an assembly
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
namespace System.Windows
{
class Win32WindowEvents
{
//...
public static class WinAPI
{
//...
public static class Win32ControlType
{
public static string Button = "Button";
//...
///
The goal is to stock the Windows control on a TaskBar
function custom_debug {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$local:button_ref,
[string]$message
)
Write-Debug $message
$local:button = $local:button_ref.Value
if ($local:button -eq $null) {
$exlorer_window = [System.Windows.Win32Window]::FromProcessName('explorer')
$exlorer_window.Title = "A control WINDOW";
$local:button = New-Object System.Windows.Win32Button
$local:button.TopMost = $true
$local:button.Width = 600
$local:button.Height = 60
$x = ($exlorer_window.Position.Right - $local:button.Width)
$y = -20
$local:button.Pos_X = $x
$local:button.Pos_Y = $y
$local:button.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$exlorer_window.AddControl($local:button)
$local:button_ref.Value = $local:button
}
$local:button.Text = $message
}

This button is used to display debugging messages and (WIP) pause the execution of the script.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($host.Version.Major -gt 2)
$hub_host = '127.0.0.1'
$hub_port = '4444'
$uri = [System.Uri](('http://{0}:{1}/wd/hub' -f $hub_host,$hub_port))
[object]$button = $null
custom_debug ([ref]$button) 'Starting firefox'
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect($hub_host,[int]$hub_port)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -ArgumentList 'start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd'
Start-Process -FilePath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -ArgumentList 'start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd'
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}"
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "c:\tools\phantomjs"
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs'
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver ($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ssl-protocol","any")
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ignore-ssl-errors",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent","Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
$options = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSOptions
$options.AddAdditionalCapability("phantomjs.executable.path",$phantomjs_executable_folder)
}
[void]$selenium.Manage().timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(60))
$selenium.url = $base_url = 'http://translation2.paralink.com'
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl(($base_url + '/'))
[string]$xpath = "//frame[@id='topfr']"
[object]$top_frame = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$selenium) ([ref]$top_frame) $xpath
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame($top_frame)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newtop.asp'),$current_frame.url)
Write-Debug ('Switched to {0} {1}' -f $current_frame.url,$xpath)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0} {1}' -f $current_frame.url,$xpath)
$top_frame = $null
[string]$text = 'Spanish-Russian translation'
$css_selector = 'select#directions > option[value="es/ru"]'
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_css_selector ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $css_selector
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($text,$element.Text,$element.Text)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('selected "{0}"' -f $text)
$element.Click()
$element = $null
custom_pause
[string]$xpath2 = "//textarea[@id='source']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $xpath2
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($current_frame)
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
$text = @"
Yo, Juan Gallo de Andrada, escribano de C?mara del Rey nuestro se?or, de los que residen en su Consejo, certifico y doy fe que, habiendo visto por los se?ores d?l un libro intitulado El ingenioso hidalgo de la Mancha, compuesto por Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra, tasaron cada pliego del dicho libro a tres maraved?s y medio; el cual tiene ochenta y tres pliegos, que al dicho precio monta el dicho libro docientos y noventa maraved?s y medio, en que se ha de vender en papel;.
"@
[void]$element.SendKeys($text)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Entered "{0}"' -f $text.Substring(0,100))
$element = $null
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
$css_selector = 'img[src*="btn-en-tran.gif"]'
$title = 'Translate'
find_page_element_by_css_selector ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $css_selector
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($title,$element.GetAttribute('title'),$element.GetAttribute('title'))
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($current_frame)
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Clicked on "{0}"' -f $title)
$element = $null
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
[string]$xpath = "//frame[@id='botfr']"
[object]$bot_frame = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$selenium) ([ref]$bot_frame) $xpath
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame($bot_frame)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newbot.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0}' -f $current_frame.url)
$bot_frame = $null
[string]$xpath2 = "//textarea[@id='target']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $xpath2
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
$text = $element.Text
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Read "{0}"' -f $text.Substring(0,100))
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame(1)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newbot.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame(0)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newtop.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0}' -f $current_frame.url)
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
Write-Debug ('Switched to {0}' -f $selenium.url)
cleanup ([ref]$selenium)
$button.Visible = $false

The full source is available in the zip.
The following is a quick example of SeleniumEventFiringWebDriver access from Powershell. One captures the result of an Ajax auto-suggestion by running code after Selenium events
param(
[string]$browser = 'firefox',
[int]$event_delay = 250,
[switch]$pause
)
function netstat_check
{
param(
[string]$selenium_http_port = 4444
)
$results = Invoke-Expression -Command "netsh interface ipv4 show tcpconnections"
$t = $results -split "`r`n" | Where-Object { ($_ -match "\s$selenium_http_port\s") }
(($t -ne '') -and $t -ne $null)
}
function cleanup
{
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref
)
try {
$selenium_ref.Value.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0]
}
}
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "C:\tools\phantomjs"
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect("127.0.0.1",4444)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd"
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}" -foreground 'Yellow'
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
if ($version -ne $null -and $version -ne 0) {
$capability.SetCapability("version",$version.ToString());
}
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$uri = [System.Uri]("http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub")
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs' -foreground 'Yellow'
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "C:\tools\phantomjs"
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver ($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ssl-protocol","any")
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ignore-ssl-errors",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent","Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
$options = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSOptions
$options.AddAdditionalCapability("phantomjs.executable.path",$phantomjs_executable_folder)
}
if ($host.Version.Major -le 2) {
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (600,400)
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
} else {
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = @{ 'Height' = 400; 'Width' = 600; }
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = @{ 'X' = 0; 'Y' = 0 }
}
$window_position = $selenium.Manage().Window.Position
$window_size = $selenium.Manage().Window.Size
$base_url = 'http://www.google.com/'
$event = New-Object -Type 'OpenQA.Selenium.Support.Events.EventFiringWebDriver' -ArgumentList @( $selenium)
$element_value_changing_handler = $event.add_ElementValueChanging
$element_value_changing_handler.Invoke(
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.Events.WebElementEventArgs]$eventargs
)
Write-Host 'Value Change handler' -foreground 'Yellow'
if ($eventargs.Element.GetAttribute('id') -eq 'gbqfq') {
$xpath1 = "//div[@class='sbsb_a']"
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$local:element = $sender.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath1))
} catch [exception]{
}
Write-Host $local:element.Text -foreground 'Blue'
}
})
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$base_url = 'http://www.google.com'
$event.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($event,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(10))
$wait.PollingInterval = 50
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id("hplogo")))
$xpath = "//input[@id='gbqfq']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $event.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath))
$element.SendKeys('Sele')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys('nium')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' webdriver')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' C#')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' tutorial')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys([OpenQA.Selenium.Keys]::Enter)
Start-Sleep 10
cleanup ([ref]$event)

One can port the Console Monitor from c# to Powershell to periodically collect desktop screen shots on the grid computer as needed by some Continuous Integration build automation
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
public class WindowHelper
{
private int _count = 0;
public int Count
{
get { return _count; }
set { _count = value; }
}
public String TakeScreenshot()
{
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Width, Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Height);
Graphics gr = Graphics.FromImage(bmp);
gr.CopyFromScreen(0, 0, 0, 0, bmp.Size);
string str = string.Format(@"C:\temp\Snap[{0}].jpeg", _count);
bmp.Save(str, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
bmp.Dispose();
gr.Dispose();
return str;
}
public WindowHelper()
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
$timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
[int32]$max_iterations = 20
[int32]$iteration = 0
$action = {
Write-Host "Iteration # ${iteration}"
Write-Host "Timer Elapse Event: $(get-date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')"
$owner = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$owner.count = $iteration
$owner.Screenshot()
$iteration++
if ($iteration -ge $max_iterations)
{
Write-Host 'Stopping'
$timer.stop()
Unregister-Event thetimer -Force
Write-Host 'Completed'
}
}
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action
Note that one ca not pass the data by reference to the script function called from the timer event and hence one can not execute the Add-Type remotely
$action = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference] $ref_screen_grabber
)
[Win32Window]$screen_grabber = $ref_screen_grabber.Value
followed by
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action -MessageData ([ref]$owner )
will break. Debugging this further is Work in progress
To toggle the Powershell console window minimize when the form is displayed, one can use the following code:
Add-Type -Name Window -Namespace Console -MemberDefinition @"
// "
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll")]
public static extern IntPtr GetConsoleWindow();
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
public static extern bool ShowWindow(IntPtr hWnd, Int32 nCmdShow);
"@
One can port the Console Monitor from c# to Powershell to periodically collect desktop screen shots on the grid computer as needed by some Continuous Integration build automation
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
public class WindowHelper
{
private int _count = 0;
public int Count
{
get { return _count; }
set { _count = value; }
}
public String TakeScreenshot()
{
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Width, Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Height);
Graphics gr = Graphics.FromImage(bmp);
gr.CopyFromScreen(0, 0, 0, 0, bmp.Size);
string str = string.Format(@"C:\temp\Snap[{0}].jpeg", _count);
bmp.Save(str, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
bmp.Dispose();
gr.Dispose();
return str;
}
public WindowHelper()
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
$timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
[int32]$max_iterations = 20
[int32]$iteration = 0
$action = {
Write-Host "Iteration # ${iteration}"
Write-Host "Timer Elapse Event: $(get-date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')"
$owner = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$owner.count = $iteration
$owner.Screenshot()
$iteration++
if ($iteration -ge $max_iterations)
{
Write-Host 'Stopping'
$timer.stop()
Unregister-Event thetimer -Force
Write-Host 'Completed'
}
}
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action
Note that one ca not pass the data by reference to the script function called from the timer event and hence one can not execute the Add-Type remotely
$action = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference] $ref_screen_grabber
)
[Win32Window]$screen_grabber = $ref_screen_grabber.Value
followed by
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action -MessageData ([ref]$owner )
will break. Debugging this further is Work in progress
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("System.Windows.Forms")
$Form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$showButton = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$showButton.Text = 'ShowConsole'
$showButton.Top = 10
$showButton.Left = 10
$showButton.Width = 100
$showButton.add_Click({Show-Console})
$form.controls.Add($showButton)
$hideButton = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$hideButton.Text = 'HideConsole'
$hideButton.Top = 60
$hideButton.Left = 10
$hideButton.Width = 100
$hideButton.add_Click({hide-Console})
$form.controls.Add($hideButton)
$Form.ShowDialog()

The functions operate constants from winuser.h
function Show-Console {
$consolePtr = [Console.Window]::GetConsoleWindow()
[Console.Window]::ShowWindow($consolePtr, 5)
}
function Hide-Console {
$consolePtr = [Console.Window]::GetConsoleWindow()
[Console.Window]::ShowWindow($consolePtr, 0)
}

One can find it convenient to use Poweshell ISE together with Firebug or other Browser-hosted Developer tool to craft the actual scrtipt:
param(
[string]$hub_host = '127.0.0.1',
[string]$browser,
[string]$version,
[string]$profile = 'Selenium',
[switch]$pause = $true
)
function set_timeouts {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref,
[int]$explicit = 120,
[int]$page_load = 600,
[int]$script = 3000
)
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($explicit)))
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().SetPageLoadTimeout([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($pageload)))
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().SetScriptTimeout([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($script)))
}
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value
if ($Invocation.PSScriptRoot) {
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot
}
elseif ($Invocation.MyCommand.Path) {
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
} else {
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf(""))
}
}
function cleanup
{
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref
)
try {
$selenium_ref.Value.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0]
}
}
$shared_assemblies = @{
'WebDriver.dll' = 2.44;
'WebDriver.Support.dll' = '2.44';
'nunit.core.dll' = $null;
'nunit.framework.dll' = '2.6.3';
}
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
$assembly_path = [System.IO.Path]::Combine($shared_assemblies_path,$assembly)
$assembly_version = [Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName($assembly_path).Version
$assembly_version_string = ('{0}.{1}' -f $assembly_version.Major,$assembly_version.Minor)
if ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -ne $null) {
if (-not ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -match $assembly_version_string)) {
Write-Output ('Need {0} {1}, got {2}' -f $assembly,$shared_assemblies[$assembly],$assembly_path)
Write-Output $assembly_version
throw ('invalid version :{0}' -f $assembly)
}
}
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$hub_port = '4444'
$uri = [System.Uri](('http://{0}:{1}/wd/hub' -f $hub_host,$hub_port))
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect($hub_host,[int]$hub_port)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\selenium.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 3
}
[object]$profile_manager = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfileManager
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile]$selected_profile_object = $profile_manager.GetProfile($profile)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile]$selected_profile_object = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile ($profile)
$selected_profile_object.setPreference('general.useragent.override','Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_0 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Mobile/7A341 Safari/528.16')
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxDriver ($selected_profile_object)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile[]]$profiles = $profile_manager.ExistingProfiles
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$base_url = 'http://www.codeproject.com/'
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = @{ 'Height' = 600; 'Width' = 480; }
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = @{ 'X' = 0; 'Y' = 0 }
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
set_timeouts ([ref]$selenium)
$css_selector = 'span.member-signin'
Write-Debug ('Trying CSS Selector "{0}"' -f $css_selector)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(1))
try {
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector)))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception with {0}: {1} ...`n(ignored)" -f $id1,(($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
Write-Debug ('Found via CSS Selector "{0}"' -f $css_selector )
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector))
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);",$element,'border: 2px solid red;')
Start-Sleep 3
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);",$element,'')
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
try {
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
} catch [OpenQA.Selenium.WebDriverTimeoutException]{
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($_.Exception.Message -match '(?:Timed out waiting for page load.)')
}
$input_name = 'ctl01$MC$MemberLogOn$CurrentEmail'
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(1))
$wait.PollingInterval = 100
$xpath = ( "//input[@name='{0}']" -f $input_name)
Write-Debug ('Trying XPath "{0}"' -f $xpath)
try {
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementIsVisible([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath)))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception with {0}: {1} ...`n(ignored)" -f $id1,(($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
Write-Debug ('Found XPath "{0}"' -f $xpath)
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($element.GetAttribute('type') -match 'email')
$email_str = 'kouzmine_serguei@yahoo.com'
$element.SendKeys($email_str)
if (-not ($host.name -match 'ISE') ) {
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
cleanup ([ref]$selenium)
}
Lets dissect this script. The following screenshot illustrates the proces.

For an example of relatively big syntax difference between C# and Powershell consider converting the custom input element handler responsible for processing the ipv4 address input fields from IpBox in C# for beginners article by Mervick.
The C# version (fragment):
private void OnTextChange(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
int box_type = 0;
CultureInfo MyCultureInfo = new CultureInfo("en-GB");
double d;
if( sender.Equals( ip1 ) )
box_type = 1;
if( sender.Equals( ip2 ) )
box_type = 2;
if( sender.Equals( ip3 ) )
box_type = 3;
if( sender.Equals( ip4 ) )
box_type = 4;
switch( box_type )
{
case 1:
if( this.ip1.Text.Length > 0 && this.ip1.Text.ToCharArray()[this.ip1.Text.Length - 1] == '.' )
{
this.ip1.Text = this.ip1.Text.TrimEnd( '.' );
ip1.Text = (this.ip1.Text.Length > 0 ) ? int.Parse( this.ip1.Text ).ToString() : "0" ;
ip2.Focus();
return;
}
if( double.TryParse(
this.ip1.Text,
System.Globalization.NumberStyles.Integer,
MyCultureInfo,
out d ) == false
)
{
this.ip1.Text = this.ip1.Text.Remove( 0, this.ip1.Text.Length );
return;
}
if( this.ip1.Text.Length == 3 )
{
if( int.Parse( this.ip1.Text ) >= 255 )
this.ip1.Text = "255";
else
ip1.Text = int.Parse( ip1.Text ).ToString();
ip2.Focus();
}
break;
case 2:
...
The equivalent Powershell version:
function text_changed () {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[int]$box_type = 0
[System.Globalization.CultureInfo]$ci = New-Object System.Globalization.CultureInfo ("en-GB")
[double]$d = 0
if ($sender -eq $ip1) {
$box_type = 1 }
if ($sender -eq $ip2) {
$box_type = 2 }
if ($sender -eq $ip3) {
$box_type = 3 }
if ($sender -eq $ip4) {
$box_type = 4 }
switch ($box_type)
{
1 {
if (($ip1.Text.Length -gt 0) -and ($ip1.Text.ToCharArray()[$ip1.Text.Length - 1] -eq '.'))
{
$ip1.Text = $ip1.Text.TrimEnd('.')
if ($ip1.Text.Length -gt 0) {
$ip1.Text = [int]::Parse($ip1.Text).ToString()
} else {
$ip1.Text = '0'
}
$ip2.Focus()
return
}
if ([double]::TryParse(
$ip1.Text,
[System.Globalization.NumberStyles]::Integer,
$ci,
([ref]$d)) -eq $false
)
{
$ip1.Text = $ip1.Text.Remove(0,$ip1.Text.Length)
return
}
if ($ip1.Text.Length -eq 3) {
if ([int]::Parse($ip1.Text) -ge 255) {
$ip1.Text = '255'
} else {
$ip1.Text = [int]::Parse($ip1.Text).ToString()
}
$ip2.Focus()
}
}
2 {
...

In this example, conversion should probably be avoided. The full script source is available in the source zip file.
In this section, we convert C# to a runnable Powershell script one step at a time, in 3 steps followed by 2 more steps.
-
Download the code from http://www.java2s.com/Code/CSharp/GUI-Windows-Form/MyClockForm.htm, save is in a text file timer.cs. Compile and ensure it runs in console:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\csc.exe timer.cs
invoke-expression -command './timer.exe'
-
Create a blank text file timer_iter1.ps1, put the following boilerplate code there:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// -- about to paste the c# code below. Any class would do
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Data.dll', 'System.ComponentModel.dll'
$clock = New-Object MyClock.MyClockForm
$clock.ShowDialog()
$clock.Dispose()
Inspect the namespace and class name of the class being converted, make sure Powershell is creating the instance of the same class.
namespace MyClock
{
public class MyClockForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form {
/// implementation
} }
hence New-Object MyClock.MyClockForm.
Figure out which are the needed assemblies from the 'using' area of the C# class:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
Paste the code of the class into the Powershell script Add-Type cmdlet TypeDefinition's text argument and ensure it is runnable.
. ./timer_iter1.ps1
-
If receiving the error:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. The type name 'Win32Window' already exists.
the Powershell window needs to be recycled. Of course if one receives:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. Compilation errors occurred.
FullyQualifiedErrorId : SOURCE_CODE_ERROR,
you will need to fix the code.
The Powershell version of the class should look and feel the same as compiled executable but clearly there is no obvious way to share the data between script and dialog yet.
-
Now turn the script process into the caller of the dialog explicitly.
Note that http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.windows.forms.form.showdialog(v=vs.90).aspx describes two alternative signatures of the ShowDialog method every Windows Form responds to. The latter of the two is accepting the owner object.
ShowDialog(IWin32Window) | Shows the form as a modal dialog box with the specified caller. |
Any class implementing IWin32Window can become the owner of the windows modal dialog with an arbitrary Window Forms inside.
So we repeat the earlier Add-Type code blend exercise with a plain C# object code source passed in:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private int _data;
private string _message;
public int Data
{
get { return _data; }
set { _data = value; }
}
public string Message
{
get { return _message; }
set { _message = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
The code above is implemented the single method required for the interfact IWin32Window - constructor with a handle to the window. The other properties in the code above Data and Message properties are not required by the interface but are essential to tie the parts together.
-
Finally, change the code to deal with the caller.
- Pass the argument to
Windows.Forms:
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle )
$timer.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($process_window) ) | out-null
write-output $process_window.GetHashCode()
- Access the object from within the form:
You need to add a member variable to the class and modify the following two methods. Note this is not required when implementing the PowerShell version. There must be a better way to illustrate this. For now, the goal is to move to Powershell version, and eventually discard the modified class. This sort of 'justifies' the hack.
private void OnTimerElapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
label1.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
label1.Text = String.Format("My Clock {0} {1}", caller.ToString(), caller.GetHashCode() );
}
public new DialogResult ShowDialog(IWin32Window caller){
this.caller = caller ;
return base.ShowDialog(caller);
}
On the other hand, when the code being ported is a more complex form than in this example, it would be helpful to exchange all domain specific data the same object $caller regardless of the complexity. One can test either side of the pipeline in Visual Studio or in Powershell ISE and mock the opposite side without worrying much about details.
Save the code as timer_iter2.ps1 and confirm it still runs.
Running the script yields the same object available to both script and form.

The next step is to selectively re-write the methods and elements of the form in Powershell and get rid of 'chimera' code. It would not be easy to make the C# compiler accept the fact that the $caller responds to many additional data messages . Another option, to use reflection, does not lead to compact or pretty code.
The required code edits are all semantic.
- Get rid of instance references (
this) and the class decorations, constructors, namespaces and such. The member this.timer1 becomes $timer1 and so on. The this becomes simply the $f - the form object. - Amend the semantics of method calls:
new System.Timers.Timer(); becomes new-object System.Timers.Timer, etc. When found class instantiation inside the method call argument, it appears safe to separate the nested method calls. - Change the semantics of constant resolutions:
System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter becomes [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleCenter etc. Always provide fully resolved class names: ImageList il = new ImageList(); would have to become $il = new-object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList etc. If uncertain, check through MSDN. - Watch for minor semantic difference like
-eq instead of ==, -bor instead of | and the like -
Initially run the visual layout, but comment the event propagation. Once the form begins to show, deal with events.
Make sure that event handler(s) is defined before using those with events: for example moving the first lines in the following code to the top
$button1_Click = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show('hello');
}
$button1.Add_Click($button1_Click)
would lead to the form to cease showing the blank messagebox when $button1 is clicked.
- Create a wrapping PowerShell function, add the code to make the form visible.
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Activate()
$f.Displose()
Move the $caller and showDialog(...) inside the Powershell function.
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
The result would look like the following:
function exampleTimer(
[Object] $caller= $null
)
{
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$timer1 = new-object System.Timers.Timer
$label1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$f.SuspendLayout()
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$label1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font("Microsoft Sans Serif", 14.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$label1.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Highlight
$label1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(24, 8)
$label1.Name = "label1"
$label1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(224, 48)
$label1.TabIndex = 0;
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
$label1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleCenter
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 69)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $label1))
$f.Name = 'MyClockForm';
$f.Text = 'My Clock';
$eventMethod=$label1.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({$f.Text="You clicked my label $((Get-Date).ToString('G'))"})
$f.Add_Load({
param ([Object] $sender, [System.EventArgs] $eventArgs )
$timer1.Interval = 1000
$timer1.Start()
$timer1.Enabled = $true
})
$timer1.Add_Elapsed({
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
})
$global:timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
$global:timer.Interval = 1000
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $global:timer -EventName Elapsed -SourceIdentifier theTimer -Action {AddToLog('') }
$global:timer.Start()
$global:timer.Enabled = $true
function AddToLog()
{
param ([string] $text )
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
}
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.ShowDialog([Win32Window] ($caller) )
}
This will have almost everything in place except for the event handler that does not seem to be triggered - the time stamp is not updating. This code apparently needs to be fixed.
Debugging the Timer Problem
After some debugging, it appears that the script is not properly dealing with the timer object that was owned by the Windows.Form class instance but no longer is. This constitutes a separate issue to fix, and work is underway. To prove that most of the event handlers can be converted to run Powershell code with nearly zero effort, the click handler was added to the label
$eventMethod=$label1.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({$f.Text="You clicked my label $((Get-Date).ToString('G'))"})

and clicked. The result looks as expected.
To recap writing the equivalent code in Powershell based on C# blueprint for the form layout and handling the events were the two remaining steps promised earlier in this chapter.
The visual design replication step is clearly a no brainer, a typing exercise at best. With Windows Presentation Foundation it is even unnecessary: one is able to load the same XAML.
Event management on the contrary may consume some effort to tame.
In the PowerShell samples through this article, a slightly different semantics for event handling code had been attempted every time. This diversity was introduced intentionally - all the variants are equivalent - the .NET Framework generates a lot of code behind the scenes to support MulticastDelegate.
To recap, replicating the visual design in Powershell based on C# blueprint and handling events are two remaining steps promised earlier in this chapter. The visual design step is a no-brainer, a typing exercise at best. On the contrary, the event management may take some effort to tame. In the Powershell samples though this article, a slightly different semantics of event handling code had been chosen every time. The Diversity was introduced intentionally - all the variants are equivalent. Under the hood, MS .NET generates a lot of code behind the scenes to subclass the MulticastDelegate.
PromptForChoice
The prompting mechanism built into PowerShell is intended primarily to control destructive actions . Its exact presentation depends on the host in which Powershell script is run. The endless loop solution suggested in http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff730939.aspx for a basic multi-choice select Yes? No? Maybe is barely an acceptable one. It sends a clear message: "Forget about multi-select prompts".
$heads = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Heads", "Select Heads."
$tails = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Tails", "Select Tails."
$cancel = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Cancel", "Skip to the next step."
$options = [System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription[]]($heads, $tails, $cancel)
$host.ui.PromptForChoice("Call it","----", $options,2 )

It renders differently based on the host capabilities in ConsoleHost vs. Windows PowerShell ISE Host

and returns the index - 0,1,2 in the selected option.
Platform Compatibility
The Powershell Scripts presented in this article have been verified to work on the following platforms:
| Windows Server 2012 - Desktop-Experience | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 - Minimal Server Interface, Windows Server 2012 - Windows Server Core | Most of examples work, except one: toggle_display.ps1 manages to show the form, and hide, but never shows Powershell console back. |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 | Yes |
| Windows Server 2003 | Yes |
| Windows 8 | ? |
| Windows 7 | Yes |
| Windows Vista | Yes |
| Windows XP | Yes |
| Windows 2000 | No |
The work started with automating the daily dev ops routine configuring vanilla UAT environments full of Microsoft Software, hosted in private cloud. One particularly cumbersome step was with selectively cloning SQL configurations via SQL Server Client Network Utility. The latter being remarkably user un-friendly.

Under the hood, all information is stored in a single registry key. This makes loading this information from remote host a good candidate for automation, but the operator's role is still vital for as long as the subtle difference between the environments landscapes: which IIS applications is hosted on which computer. This would not be a problem had the settings been converted to the Puppet-style node definitions.
For most examples, complete source is provided in the article and in the attached zip. One can also clone the completed source from Github:
Release History
- 2014-07-21 - Initial version
- 2014-07-21 - Added more samples
- 2014-07-22 - Added comment on code conversion
- 2014-07-22 - Added XAML example
- 2014-07-23 - Added
TreeView example - 2014-07-24 - Added Dissect Conversion example
- 2014-07-25 - Added Custom Icons with
Treeview - 2014-07-25 - Added remark regarding Get-Credential cmdlet
- 2014-07-26 - Added TabControl and Focus sample
- 2014-07-26 - Added TOC
- 2014-07-26 - Added Tabbed
Treeviews - 2014-07-26 - Refactored example code snippets
- 2014-07-27 - Added
WebBrowser1 sample - 2014-07-27 - Added Platform compatibility matrix
- 2014-07-28 - Added generation of XAML dialog on the fly example
- 2014-07-29 - Added script parameter prompt
DataGridView example - 2014-07-29 - Added Fill Color and
ZIndex manipulation example - 2014-07-29 - Added WPF Form Text manipulation example
- 2014-07-29 - Added bidirectional Form Script Text communication example
- 2014-08-09 - Added Selenium Script example
- 2014-08-09 - Modified Selenium Grid Test example to execute on Safari browser
- 2014-08-09 - Added a note of File Download dialog handling
- 2014-08-10 - Added
TreeView Control with ComboBox example - 2014-08-10 - Added Workaround for code formatting defect
- 2014-08-11 - Added
ProgressBar example - 2014-08-13 - Added Selenium IE dialog processor example
- 2014-08-13 - Fixed formatting and separates some inline XAML code for readability
- 2014-08-16 - Added Selenium IDE Powershell Formatter example
- 2014-08-16 - Updated links to author's Powershell Selenium IDE Formatter git repository
- 2014-08-19 - Added Drag and Drop example
- 2014-08-22 - Added running Javascript through Selenium example
- 2014-08-22 - Added Microsoft Test Agent DLL discovery example
- 2014-08-22 - Added overview and build instructions for the xpi
- 2014-08-23 - Added clicking button on Save Dialog example
- 2014-08-23 - Added running Powershell from Linux example
- 2014-08-24 - Updated version of Save Dialog example to accept the specified download file path
- 2014-09-03 - Added Web Driver Drag and Drop example
- 2014-09-09 - Added Misc. Web Driver example
- 2014-09-09 - Added Hide Powershell console window example
- 2014-09-09 - Added note regarding Powershell UI in Windows Server Core
- 2014-09-21 - Added Bar Chart (VB.Net) example
- 2014-09-24 - Added Up Down picker example
- 2014-09-26 - Added Timing out confirmation dialog example
- 2014-10-07 - Added Extreme case example, recovered few damaged sections, performed minor HTML formatting cleanup
- 2014-10-07 - Added Selenium SendKeys example
- 2014-10-07 - Recovered Selenium IDE Powershell Formatter section
- 2014-10-07 - Recovered DropDown ComboBox section
- 2014-11-01 - Added Filesystem Treeview example
- 2014-11-03 - Updated Source Zip with final Filesystem Treeview and custom MsgBox examples
- 2014-11-04 - Added Custom MsgBox examples
- 2014-11-14 - Added Ribbon example
- 2014-11-14 - Added Selenium Powershell ISE example
- 2014-12-07 - Added Collapsible List example
- 2014-12-14 - Added Checked Combo Listbox example
- 2014-12-20 - Added Pie and Bar Chart Draw example
- 2014-12-22 - Added Timer example
- 2015-01-04 - Added Task List Progress example
- 2015-01-05 - Commented Task List Progress
- 2015-01-14 - Added Accordion Menu example
- 2015-01-14 - Added Accordion Menu code refactoring example
- 2015-01-17 - Added Circle Progress Indicator example
- 2015-01-19 - Added Circle Progress Indicator W2K3 compatiliblity patch
- 2015-02-07 - Refactred Ribbon buttons example
- 2015-02-15 - Added Selenium Debugging messages on Explorer Taskbar example
- 2015-02-16 - Added Selenium EventFiring WebDriver example *WIP
- 2015-02-17 - Fixed formatting defects
- 2015-02-27 - Added TreeTabControl example
- 2015-02-27 - Continued TreeTabControl example *WIP
- 2015-03-10 - Added alternative Add-Type syntax example. Trimmed blank lines.
- 2015-03-22 - Provided alternative $script: syntax example and uploaded a typo fix.
- 2015-03-23 - Added note regarding
System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators. - 2015-03-25 - Added test configuration display example.
- 2015-04-04 - Replaced and somewhat simplified Custom Debugging Message Box example.
- 2015-04-05 - Added OS X Circle Progress Indicator example.
- 2015-04-10 - Added sortable ListView example.
- 2015-04-17 - Added filling GridView example.
- 2015-05-31 - Added Common Dialogs example.
- 2015-05-3 - Added Common Dialogs example.
Powershell is an advanced scripting framework, typically script is run in console host, most often remotely, but the Powershell scripts are still relatively frequently used interactively on a Windows computer. When a generic script executes, it is likely to need more than one option to be selected. Multiple options need to offered to the user in a cascading manner, with complex selection scenarios often desirable. For certain data selections, GUI in more intuitive and faster than CLI - in the console, even basic choice does not look very pretty.
For many situations, plain old Windows Forms is still a convenient means of prompting the user. This is the main focus of this article. We examine few elementary examples from http://www.java2s.com/ and convert those to Powershell. Later, we use the earlier samples as building blocks for something more complex. The fact all code of these examples in available in a one single file and no separate designer code needs to be merged, greatly simplifies the conversion. The focus is to keep the emerging Powershell code to a minimum required for processing various data selection scenarios for prompt, password, checkbox, radio, checked list, grid, treeview, tabbed dialogs and combination of those. In addition, it will be demonstrated that form element-specific event handlers will execute PowerShell code. Finally, controls like TreeView visualize the data very well on its own and potentially make few rounds of prompts unnecessary.
On the other hand, the Windows Presentation Foundation might feel somewhat heavy to embark and/or debug but entirely doable - examples are provided at the middle of this article. Interacting with WPF requires multithreading and this technique is also valuable for asynchronous status reporting of long running scripts.
A pleasant note is that all scripts continue to function in Minimal Server Interface and even in Server Core Windows Server 2012 GUI levels. The reason is: even after both "Server Graphical Shell" and "Server Graphical Management Tools & Infrastructure" Windows Features are "removed", full Microsoft .Net Framework is still present. The ultimate goal of the examples of offering a familiar user interface to complex custom data - can still be met on Windows Server Core. Note that since mouse is available even in Server Core, adding keyboard shortcuts to form elements isn't required.
In further examples, it is shown how to construct Powershell Selenium scripts from C# equivalents manually or record in Selenium IDE automatically; definite benefits of using Powershell to run Selenium recordings are illustrated.
Finally, the step-by-step conversion exercise is covered in detail.
One will recognize the Powershell version of the code to be practically identical to the C# version with only semantic differences. All sources available on the author's github repo and new code are being developed daily.
We currently need to construct the helper class responsible for passing information to the Powershell script caller in plain C# and make its properties available to Windows Form in the event handlers, though all dialogs will be drawn modally. Without such tight link, some hard-to- debug race condition errors might be possible. The analysis of these assumptions is deferred to the future article.
The samples provided in the article are hopefully easily tailored to any purpose the reader finds them fit.
The class that will be used to share information from the form to Powershell is quite basic. All it needs is to implement IWin32Window interface; it will also have various private data members with getters and setters and methods - to be used in the form in some examples below.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private int _data;
public int Data
{
get { return _data; }
set { _data = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
The Powershell stores its own Window Handle in the class:
if ($process_window -eq $null ){
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
The entries selection and the overall status is read from $caller.Message and $caller.Data:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
if($process_window.Data -ne $RESULT_CANCEL) {
write-debug ('Selection is : {0}' -f , $process_window.Message )
} else {
write-debug ('Result is : {0} ({1})' -f
$Readable.Item($process_window.Data) , $process_window.Data )
}
Alternative syntax can be
$guid = [guid]::NewGuid()
$helper_namespace = ("Util_{0}" -f ($guid -replace '-',''))
$helper_name = 'Helper'
Add-Type -UsingNamespace @(
'System.Drawing',
'System.IO',
'System.Windows.Forms',
'System.Drawing.Imaging',
'System.Collections.Generic',
'System.Text' `
) `
-MemberDefinition @"
// inline C# code without class decoration
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies @( 'System.Windows.Forms.dll',`
'System.Drawing.dll',`
'System.Data.dll',`
'System.Xml.dll') `
-Namespace $helper_namespace -Name $helper_name -ErrorAction Stop
$helper = New-Object -TypeName ('{0}.{1}' -f $helper_namespace,$helper_type)
This way one does not worry about seeing the annoying warning every time the inline C# code is modified:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. The type name 'Win32Window' already exists.
At C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\treeview_c.ps1:21 char:1
+ Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
NOTE, that few namespaces are already included by default and should not be provided explicitly in the invocation agument to avid
Warning as Error:
The using directive for 'System' appeared previously in this namespace
The using directive for 'System.Runtime.InteropServices' appeared previously in this namespace
Multiple Choice Prompt

The multiple choice decision prompt is the simplest example that requires no communication between form elements - the form sets the $caller.Data independently in each button Click event handlers.
function PromptAuto(
[String] $title,
[String] $message,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(650,120)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Y') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_POSITIVE }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'N') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_NEGATIVE }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(50,40)
$b1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b1.Text = 'Yes!'
$b1.Add_Click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_POSITIVE; $f.Close(); })
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(125,40)
$b2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b2.Text = 'No!'
$b2.Add_Click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_NEGATIVE; $f.Close(); })
$b3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(200,40)
$b3.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(75,23)
$b3.Text = 'Maybe'
$b3.Add_Click({$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL ; $f.Close()})
$l = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,20)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(280,20)
$l.Text = $message
$f.Controls.Add($b1)
$f.Controls.Add($b3)
$f.Controls.Add($b2)
$f.Controls.Add($l)
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
The options text and definitions are hard coded in the function.
$RESULT_POSITIVE = 0
$RESULT_NEGATIVE = 1
$RESULT_CANCEL = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_NEGATIVE = 'NO!';
$RESULT_POSITIVE = 'YES!' ;
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'MAYBE...'
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$title = 'Question'
$message = "Continue to Next step?"
$result = PromptAuto -title $title -message $message -caller $process_window
write-debug ("Result is : {0} ({1})" -f $Readable.Item($process_window.Data) , $process_window.Data )
One popular feature of closing the idle input box after some timeout can be provided by e.g. adding to the script a System.Windows.Forms.Panel subclass which houses a System.Timers.Timer :
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class TimerPanel : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private System.Timers.Timer _timer;
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public System.Timers.Timer Timer
{
get
{
return _timer;
}
set { _timer = value; }
}
public TimerPanel()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
_timer.Stop();
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this._timer = new System.Timers.Timer();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this._timer)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
this._timer.Interval = 1000;
this._timer.Start();
this._timer.Enabled = true;
this._timer.SynchronizingObject = this;
this._timer.Elapsed += new System.Timers.ElapsedEventHandler(this.OnTimerElapsed);
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this._timer)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
private void OnTimerElapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
}
}
then placing all inputs on the panel.
$p = New-Object TimerPanel
$p.Size = $f.Size
$end = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$end = ([int]$end + 60)
$p.Timer.Stop()
$p.Timer.Interval = 5000;
$p.Timer.Start()
$p.Timer.add_Elapsed({
$start = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($start - $end)
$l.Text = ('Remaining time {0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds,($end - $start))
if ($end - $start -lt 0) {
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Close()
}
})
The properties and methods of Timer being public, therefore the script provides the event handler(s) - in the example above the one minute interval in seconds is harf coded

The full example is shown below and is available in the source zip file.
$RESULT_OK = 0
$RESULT_CANCEL = 1
$RESULT_TIMEOUT = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_OK = 'OK';
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'CANCEL';
$RESULT_TIMEOUT = 'TIMEOUT';
}
function PromptTimedAutoClose {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message,
[object]$caller
)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (240,110)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'O') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_OK }
elseif ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (50,40)
$b1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$b1.Text = 'OK'
$b1.add_click({ $caller.Data = $RESULT_OK; $f.Close(); })
$p = New-Object TimerPanel
$p.Size = $f.Size
$p.Controls.Add($b1)
$end = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$end = ([int]$end + 60)
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (130,40)
$b2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$b2.Text = 'Cancel'
$b2.add_click({
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Close();
})
$p.Controls.Add($b2)
$l = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (10,20)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (280,20)
$l.Text = $message
$p.Controls.Add($l)
$p.Timer.Stop()
$p.Timer.Interval = 5000;
$p.Timer.Start()
$p.Timer.add_Elapsed({
$start = (Get-Date -UFormat "%s")
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($start - $end)
$l.Text = ('Remaining time {0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds,($end - $start))
if ($end - $start -lt 0) {
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller.Data = $RESULT_TIMEOUT;
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window ]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
}
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$title = 'Prompt w/timeout'
$message = "Continue ?"
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptTimedAutoClose -Title $title -Message $message -caller $caller
$result = $caller.Data
Write-Debug ("Result is : {0} ({1})" -f $Readable.Item($result),$result)

This example code is more interesting because the script will collect the state from several grouped element. Managing the individual checkbox and radiobutton behavior is left intact and only implements button Click handler where the Form draws the selected elements summary and stores it into the $caller - for simplicity, both $shapes and $color are placed into one $caller.Message.
function PromptWithCheckboxesAndRadionbuttons(
[String] $title,
[String] $message,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$checkBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$checkBox2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$checkBox3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$radioButton1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$radioButton2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$radioButton3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
$button1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$color = ''
$shapes = @()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange(
@(
$radioButton1,
$radioButton2,
$radioButton3
))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 120)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(120, 144)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'Color'
$checkBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 8)
$checkBox1.Name = 'checkBox1'
$checkBox1.TabIndex = 1
$checkBox1.Text = 'Circle'
$checkBox2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 40)
$checkBox2.Name = 'checkBox2'
$checkBox2.TabIndex = 2
$checkBox2.Text = 'Rectangle'
$checkBox3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 72)
$checkBox3.Name = 'checkBox3'
$checkBox3.TabIndex = 3
$checkBox3.Text = 'Triangle'
$radioButton1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 32)
$radioButton1.Name = 'radioButton1'
$radioButton1.TabIndex = 4
$radioButton1.Text = 'Red'
$radioButton1.Add_CheckedChanged({ })
$radioButton2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 64)
$radioButton2.Name = 'radioButton2'
$radioButton2.TabIndex = 5
$radioButton2.Text = 'Green'
$radioButton3.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 96)
$radioButton3.Name = 'radioButton3'
$radioButton3.TabIndex = 6
$radioButton3.Text = 'Blue'
$button1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 280)
$button1.Name = 'button1'
$button1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(112, 32)
$button1.TabIndex = 4
$button1.Text = 'Draw'
$button1.Add_Click({
$color = ''
$shapes = @()
foreach ($o in @($radioButton1, $radioButton2, $radioButton3)){
if ($o.Checked){
$color = $o.Text}
}
foreach ($o in @($checkBox1, $checkBox2, $checkBox3)){
if ($o.Checked){
$shapes += $o.Text}
}
$g = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromHwnd($f.Handle)
$rc = New-Object System.Drawing.Rectangle(150, 50, 250, 250)
$brush = New-Object System.Drawing.SolidBrush([System.Drawing.Color]::White)
$g.FillRectangle($brush, $rc)
$font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Verdana', 12)
$col = New-Object System.Drawing.SolidBrush([System.Drawing.Color]::Black)
$str = [String]::Join(';', $shapes )
$pos1 = New-Object System.Drawing.PointF(160, 60)
$pos2 = New-Object System.Drawing.PointF(160, 80)
$g.DrawString($color, $font, $col , $pos1)
$g.DrawString($str, $font, $col , $pos2)
start-sleep 1
$caller.Message = ('color:{0} shapes:{1}' -f $color , $str)
$f.Close()
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(408, 317)
$f.Controls.AddRange( @(
$button1,
$checkBox3,
$checkBox2,
$checkBox1,
$groupBox1))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'CheckBox and RadioButton Sample'
$groupBox1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { }
$f.Close()
})
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$F.Dispose()
return $caller.Data
}

The next iteration is to let the form receive a string of text from Powershell and display individual words as checked listbox items, waiting for the user to select individual words by clicking the checkbox next to word.
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$result = PromptCheckedList '' 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit'
write-debug ('Selection is : {0}' -f , $result )
The listbox on the right provides a visual cue to the user. When the 'Done' button is pressed, the selections are saved in the $caller object and form is closed and disposed.
This time, we return the $caller.Message explicitly, though it not really required. Note the event handler code highlighted in bold.
function PromptCheckedList
{
Param(
[String] $title,
[String] $message)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections.Generic')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Text')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$i = new-object System.Windows.Forms.CheckedListBox
$d = new-object System.Windows.Forms.ListBox
$d.SuspendLayout()
$i.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$i.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 11,
[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$i.FormattingEnabled = $true;
$i.Items.AddRange(( $message -split '[ ,]+' ));
$i.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(17, 12)
$i.Name = 'inputCheckedListBox'
$i.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(202, 188)
$i.TabIndex = 0
$i.TabStop = $false
$event_handler = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.ItemCheckEventArgs ] $eventargs
)
$item = $i.SelectedItem
if ( $eventargs.NewValue -eq [System.Windows.Forms.CheckState]::Checked ) {
$d.Items.Add( $item );
} else {
$d.Items.Remove( $item );
}
}
$i.Add_ItemCheck($event_handler)
$d.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Verdana', 11)
$d.FormattingEnabled = $true
$d.ItemHeight = 20;
$d.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(236, 12);
$d.Name = 'displayListBox';
$d.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(190, 184);
$d.TabIndex = 1;
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8, 280)
$b.Name = 'button1'
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(112, 32)
$b.TabIndex = 4
$b.Text = 'Done'
$b.Add_Click({
$shapes = @()
foreach ($o in $d.Items){
$shapes += $o
}
$caller.Message = [String]::Join(';', $shapes )
$f.Close()
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(408, 317)
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.Controls.AddRange( @( $i, $d, $b))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'CheckListBox Sample'
$i.ResumeLayout($false)
$d.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
$result = $caller.Message
$caller = $null
return $result
}
Here, the event handler in written in PowerShell but it operates the standard event arguments therefore the Powershell function is called from Form elements essentially connection them to one another. It is virtually indistinguishable from the class method it have been converted from.
this.inputCheckedListBox.ItemCheck +=
new System.Windows.Forms.ItemCheckEventHandler(this.inputCheckedListBox_ItemCheck);
...
private void inputCheckedListBox_ItemCheck(object sender, ItemCheckEventArgs e )
{
string item = inputCheckedListBox.SelectedItem.ToString();
if ( e.NewValue == CheckState.Checked )
displayListBox.Items.Add( item );
else
displayListBox.Items.Remove( item );
}
Next example comes from conversion Accordion Collapsible Panel from C# to Powershell. Naturally, the code is extremely redundant. Only portion is shown. Full script is in the source zip.

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$f.Text = $title
$f.SuspendLayout()
$p = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$m = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$p_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_3_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_3_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_3_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_2_4 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_2_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$b_1_2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b_1_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$g_1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$lblMenu = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$m.SuspendLayout()
$p_3.SuspendLayout()
$p_2.SuspendLayout()
$p_1.SuspendLayout()
$p.SuspendLayout()
..
$p_1.Controls.AddRange(@($b_1_2, $b_1_1, $g_1) )
$p_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$p_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,23)
$p_1.Name = "p_1"
$p_1.TabIndex = 1
$b_1_1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$b_1_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$b_1_1.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$b_1_1.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$b_1_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * 2))
$b_1_1.Name = "b_1_1"
$b_1_1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$b_1_1.TabIndex = 2
$b_1_1.Text = "Group 1 Sub Menu 1"
$b_1_1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$b_1_1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$b_1_1_click = $b_1_1.add_Click
$b_1_1_click.Invoke({
param([object]$sender,[string]$message)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('{0} clicked!' -f $sender.Text) )
})
$b_1_2.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$b_1_2.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$b_1_2.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$b_1_2.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$b_1_2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * 3))
$b_1_2.Name = "$b_1_2"
$b_1_2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$b_1_2.TabIndex = 3
$b_1_2.Text = "Group 1 Sub Menu 2"
$b_1_2.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$b_1_2.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$g_1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gray
$g_1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$g_1.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gray
$g_1.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$g_1.ImageAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleRight
$g_1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$g_1.Name = "g_1"
$g_1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$g_1.TabIndex = 0
$g_1.Text = "Menu Group 1"
$g_1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$g_1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$g_1_click = $g_1.add_click
$g_1_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$ref_panel = ([ref]$p_1)
$ref_button_menu_group = ([ref]$g_1)
$num_buttons = 3
if ($ref_panel.Value.Height -eq $global:button_panel_height)
{
$ref_panel.Value.Height = ($global:button_panel_height * $num_buttons) + 2
$ref_button_menu_group.Value.Image = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap ("C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\unfinished\up.png")
}
else
{
$ref_panel.Value.Height = $global:button_panel_height
$ref_button_menu_group.Value.Image = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap ("C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\unfinished\down.png")
}
})
$m.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_3.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_2.ResumeLayout($false)
$p_1.ResumeLayout($false)
$p.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (210,280)
$f.Controls.Add($c1)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$f.Controls.Add($b1)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = "ProgressCircle"
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()

To fight redundancy one may introduce utility functions e.g.
function add_button {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$button_data_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$button_ref
)
$button_data = $button_data_ref.Value
$local:b = $button_ref.Value
$local:b.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$local:b.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$local:b.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$local:b.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Flat
$local:b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,($global:button_panel_height * $button_data['cnt']))
$local:b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($global:button_panel_width,$global:button_panel_height)
$local:b.TabIndex = 3
$local:b.Name = $button_data['name']
$local:b.Text = $button_data['text']
$local:b.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$local:b.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $false
$local:click_handler = $local:b.add_Click
if ($button_data.ContainsKey('callback')) {
$local:click_handler.Invoke($button_data['callback'])
}
else {
$local:click_handler.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('{0} default click handler!' -f $sender.Text))
})
}
$button_ref.Value = $local:b
}
and refactor the code to pack together code references, menu text, etc.:
[scriptblock]$b3_3_callback_ref = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = 'something'
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(('This is custom callback for {0} click!' -f $sender.Text))
}
add_button -button_ref ([ref]$b3_3) `
-button_data_ref ([ref]@{
'cnt' = 3;
'text' = 'Menu 3 Sub Menu 3';
'name' = 'b3_3';
'callback' = $b3_3_callback_ref;
})
The eventual layout of button data objects and callback action code is of course highly domain-specific
Next example uses the code from ComboBox with a CheckedListBox as a Dropdown article. Unlike most of examples in this article, this script does not use $caller object - the CheckedComboBox class has plenty of proprties on its own - to return the selection data as text - but rather passes the hash of objects by reference to the form:
$albums = @{
'Ring Ring (1973)' = $false;
'Waterloo (1974)' = $false;
'ABBA (1975)' = $true;
'Arrival (1976)' = $false;
'The Album (1977)' = $true;
'Voulez-Vous (1979)' = $false;
'Super Trouper (1980)' = $false;
'The Visitors (1981)' = $false;
}
PromptCheckedCombo -Title 'Checked ComboBox Sample Project' -data_ref ([ref]$albums)
Write-Output ('Result is: {0}' -f $caller.Message)
$albums
Here the signature of the function is:
function PromptCheckedCombo {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$data_ref
)
...
$ccb = New-Object -TypeName 'CheckComboBoxTest.CheckedComboBox'
$data = $data_ref.Value
$cnt = 0
$data.Keys | ForEach-Object { $display_item = $_;
[CheckComboBoxTest.CCBoxItem]$item = New-Object CheckComboBoxTest.CCBoxItem ($display_item,$cnt)
$ccb.Items.Add($item) | Out-Null
if ($data[$display_item]) {
$ccb.SetItemChecked($cnt,$true)
}
$cnt++
}

In the Form delegate, one iterates of the referenced data keys and clears / sets the hash values
$eventMethod_ccb = $ccb.add_DropDownClosed
$eventMethod_ccb.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$data = $data_ref.Value
$data.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$display_item = $_;
$data_ref.Value[$display_item] = $false
}
foreach ($item in $ccb.CheckedItems) {
$data_ref.Value[$item.Name] = $true
}
$data_ref.Value = $data
})

Next example shows custom-drawn Bar Chart which has no third-party charting library dependencies. The VB.NET example code from Drawing a Bar Chart article is used, with few minor refactoring and modifications:
Add-Type -Language 'VisualBasic' -TypeDefinition @"
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
Imports System
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Drawing.Drawing2D
Imports System.Collections
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Public Class BarChart
Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Protected Overloads Overrides Sub Dispose(ByVal disposing As Boolean)
If disposing Then
If Not (components Is Nothing) Then
components.Dispose()
End If
End If
MyBase.Dispose(disposing)
End Sub
Private components As System.ComponentModel.IContainer
<System.Diagnostics.DebuggerStepThrough()> Private Sub InitializeComponent()
Me.AutoScaleBaseSize = New System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
Me.ClientSize = New System.Drawing.Size(344, 302)
Me.FormBorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle.Sizable
Me.Name = "BarChart"
Me.Text = "BarChart"
Me.components = New System.ComponentModel.Container
Me.ttHint = New System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip(Me.components)
End Sub
Dim blnFormLoaded As Boolean = False
Dim objHashTableG As New Hashtable(100)
Dim objColorArray(150) As Brush
Private Sub BarChart_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
End Sub
Public Sub LoadData(ByVal objCallerHashTable As Hashtable )
objHashTableG = objCallerHashTable.Clone()
End Sub
Public Sub RenderData
Me.BarChart_Paint(Nothing, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs( _
CreateGraphics(), _
New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height) _
))
End Sub
Private Sub BarChart_Paint(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs _
) Handles MyBase.Paint
Try
Dim intMaxWidth As Integer
Dim intMaxHeight As Integer
Dim intXaxis As Integer
Dim intYaxis As Integer
Me.SuspendLayout()
Me.LoadColorArray()
intMaxHeight = CType((Me.Height / 2) - (Me.Height / 12), Integer)
intMaxWidth = CType(Me.Width - (Me.Width / 4), Integer)
intXaxis = CType(Me.Width / 12, Integer)
intYaxis = CType(Me.Height / 2, Integer)
drawBarChart(objHashTableG.GetEnumerator , _
objHashTableG.Count, _
"Graph 1", _
intXaxis, _
intYaxis, _
intMaxWidth, _
intMaxHeight, _
True, _
False)
blnFormLoaded = True
Me.ResumeLayout(False)
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ex
End Try
End Sub
Public Sub drawBarChart(ByVal objEnum As IDictionaryEnumerator, _
ByVal intItemCount As Integer, _
ByVal strGraphTitle As String, _
ByVal Xaxis As Integer, _
ByVal Yaxis As Integer, _
ByVal MaxWidth As Int16, _
ByVal MaxHt As Int16, _
ByVal clearForm As Boolean, _
Optional ByVal SpaceRequired As Boolean = False)
Dim intGraphXaxis As Integer = Xaxis
Dim intGraphYaxis As Integer = Yaxis
Dim intWidthMax As Integer = MaxWidth
Dim intHeightMax As Integer = MaxHt
Dim intSpaceHeight As Integer
Dim intMaxValue As Integer = 0
Dim intCounter As Integer
Dim intBarWidthMax
Dim intBarHeight
Dim strText As String
Try
Dim grfx As Graphics = CreateGraphics()
If clearForm = True Then
grfx.Clear(BackColor)
End If
grfx.DrawString(strGraphTitle, New Font("Verdana", 12.0, FontStyle.Bold, GraphicsUnit.Point), Brushes.DeepPink, intGraphXaxis + (intWidthMax / 4), (intGraphYaxis - intHeightMax) - 40)
intBarHeight = CInt(intHeightMax / intItemCount)
intSpaceHeight = CInt((intHeightMax / (intItemCount - 1)) - intBarHeight)
If Not objEnum Is Nothing Then
While objEnum.MoveNext = True
If objEnum.Value > intMaxValue Then
intMaxValue = objEnum.Value
End If
End While
End If
intBarWidthMax = CInt(intWidthMax / intMaxValue)
If Not objEnum Is Nothing Then
intCounter = 1
objEnum.Reset()
While objEnum.MoveNext = True
intGraphYaxis = intGraphYaxis - intBarHeight
Dim objRec as Rectangle
objRec = New System.Drawing.Rectangle(intGraphXaxis, intGraphYaxis, intBarWidthMax * objEnum.Value, intBarHeight)
grfx.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, objRec)
grfx.FillRectangle(objColorArray(intCounter), objRec )
strText = objEnum.Key & "=" & objEnum.Value
Dim objLabelFont as Font
objLabelFont = New Font("Verdana", 7.2, FontStyle.Regular, GraphicsUnit.Point)
Dim textLabelArea As SizeF : textLabelArea = grfx.MeasureString(strText, objLabelFont)
Dim linePen As Pen: linePen = New Pen(Color.Gray, 1)
linePen.DashStyle = Drawing2D.DashStyle.Dash
Dim fontRatio As Single
fontRatio = objLabelFont.Height / objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetLineSpacing(FontStyle.Regular)
Dim ascentSize As Single
ascentSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetCellAscent(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim descentSize As Single
descentSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetCellDescent(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim emSize As Single
emSize = objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetEmHeight(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio
Dim cellHeight As Single
cellHeight = ascentSize + descentSize
Dim internalLeading As Single
internalLeading = cellHeight - emSize
Dim externalLeading As Single
externalLeading = (objLabelFont.FontFamily.GetLineSpacing(FontStyle.Regular) * fontRatio) - cellHeight
Dim labelLeft As Single : labelLeft = intGraphXaxis + (intBarWidthMax * objEnum.Value)
labelLeft = intGraphXaxis
Dim labelBottom As Single: labelBottom = intGraphYaxis
Dim labelRight As Single : labelRight = labelLeft + textLabelArea.Width
Dim labelTop As Single : labelTop = textLabelArea.Height + labelBottom
Dim objLabelRec as Rectangle
objLabelRec = New System.Drawing.Rectangle(labelLeft, labelBottom, textLabelArea.Width , textLabelArea.Height )
grfx.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, objLabelRec)
grfx.FillRectangle(Brushes.White, objLabelRec )
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelTop, labelLeft , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelRight, labelTop, labelRight , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelTop, labelRight , labelTop)
grfx.DrawLine(linePen, labelLeft, labelBottom, labelRight , labelBottom)
grfx.DrawString(strText, objLabelFont, Brushes.Black, labelLeft, labelBottom)
intCounter += 1
If SpaceRequired = True Then
intGraphYaxis = intGraphYaxis - intSpaceHeight
End If
If intCounter > objColorArray.GetUpperBound(0) Then
intCounter = 1
End If
End While
If clearForm = True Then
grfx.Dispose()
End If
End If
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ex
End Try
End Sub
Public Sub LoadColorArray()
objColorArray(1) = Brushes.Blue
objColorArray(2) = Brushes.Pink
objColorArray(3) = Brushes.Brown
objColorArray(4) = Brushes.BurlyWood
objColorArray(5) = Brushes.CadetBlue
objColorArray(6) = Brushes.Chartreuse
objColorArray(7) = Brushes.Chocolate
objColorArray(8) = Brushes.Coral
objColorArray(9) = Brushes.CornflowerBlue
objColorArray(10) = Brushes.Cornsilk
objColorArray(11) = Brushes.Crimson
objColorArray(12) = Brushes.Cyan
objColorArray(13) = Brushes.DarkBlue
objColorArray(14) = Brushes.DarkCyan
objColorArray(15) = Brushes.DarkGoldenrod
objColorArray(16) = Brushes.DarkGray
objColorArray(17) = Brushes.DarkGreen
objColorArray(18) = Brushes.DarkKhaki
objColorArray(19) = Brushes.DarkMagenta
objColorArray(20) = Brushes.DarkOliveGreen
objColorArray(21) = Brushes.DarkOrange
objColorArray(22) = Brushes.DarkOrchid
objColorArray(23) = Brushes.DarkRed
objColorArray(24) = Brushes.DarkSalmon
objColorArray(25) = Brushes.DarkSeaGreen
objColorArray(26) = Brushes.DarkSlateBlue
objColorArray(27) = Brushes.DarkSlateGray
objColorArray(28) = Brushes.DarkTurquoise
objColorArray(29) = Brushes.DarkViolet
objColorArray(30) = Brushes.DeepPink
objColorArray(31) = Brushes.DeepSkyBlue
objColorArray(32) = Brushes.DimGray
objColorArray(33) = Brushes.DodgerBlue
objColorArray(34) = Brushes.Firebrick
objColorArray(35) = Brushes.FloralWhite
objColorArray(36) = Brushes.ForestGreen
objColorArray(37) = Brushes.Fuchsia
objColorArray(38) = Brushes.Gainsboro
objColorArray(39) = Brushes.GhostWhite
objColorArray(40) = Brushes.Gold
objColorArray(41) = Brushes.Goldenrod
objColorArray(42) = Brushes.Gray
objColorArray(43) = Brushes.Green
objColorArray(44) = Brushes.GreenYellow
objColorArray(45) = Brushes.Honeydew
objColorArray(46) = Brushes.HotPink
objColorArray(47) = Brushes.IndianRed
objColorArray(48) = Brushes.Indigo
objColorArray(49) = Brushes.Ivory
objColorArray(50) = Brushes.Khaki
objColorArray(51) = Brushes.Lavender
objColorArray(52) = Brushes.LavenderBlush
objColorArray(53) = Brushes.LawnGreen
objColorArray(54) = Brushes.LemonChiffon
objColorArray(55) = Brushes.LightBlue
objColorArray(56) = Brushes.LightCoral
objColorArray(57) = Brushes.LightCyan
objColorArray(58) = Brushes.LightGoldenrodYellow
objColorArray(59) = Brushes.LightGray
objColorArray(60) = Brushes.LightGreen
objColorArray(61) = Brushes.LightPink
objColorArray(62) = Brushes.LightSalmon
objColorArray(63) = Brushes.LightSeaGreen
objColorArray(64) = Brushes.LightSkyBlue
objColorArray(65) = Brushes.LightSlateGray
objColorArray(66) = Brushes.LightSteelBlue
objColorArray(67) = Brushes.LightYellow
objColorArray(68) = Brushes.Lime
objColorArray(69) = Brushes.LimeGreen
objColorArray(70) = Brushes.Linen
objColorArray(71) = Brushes.Magenta
objColorArray(72) = Brushes.Maroon
objColorArray(73) = Brushes.MediumAquamarine
objColorArray(74) = Brushes.MediumBlue
objColorArray(75) = Brushes.MediumOrchid
objColorArray(76) = Brushes.MediumPurple
objColorArray(77) = Brushes.MediumSeaGreen
objColorArray(78) = Brushes.MediumSlateBlue
objColorArray(79) = Brushes.MediumSpringGreen
objColorArray(80) = Brushes.MediumTurquoise
objColorArray(81) = Brushes.MediumVioletRed
objColorArray(82) = Brushes.MidnightBlue
objColorArray(83) = Brushes.MintCream
objColorArray(84) = Brushes.MistyRose
objColorArray(85) = Brushes.Moccasin
objColorArray(86) = Brushes.NavajoWhite
objColorArray(87) = Brushes.Navy
objColorArray(88) = Brushes.OldLace
objColorArray(89) = Brushes.Olive
objColorArray(90) = Brushes.OliveDrab
objColorArray(91) = Brushes.Orange
objColorArray(92) = Brushes.OrangeRed
objColorArray(93) = Brushes.Orchid
objColorArray(94) = Brushes.PaleGoldenrod
objColorArray(95) = Brushes.PaleGreen
objColorArray(96) = Brushes.PaleTurquoise
objColorArray(97) = Brushes.PaleVioletRed
objColorArray(98) = Brushes.PapayaWhip
objColorArray(99) = Brushes.PeachPuff
objColorArray(100) = Brushes.Peru
objColorArray(101) = Brushes.Pink
objColorArray(102) = Brushes.Plum
objColorArray(103) = Brushes.PowderBlue
objColorArray(104) = Brushes.Purple
objColorArray(105) = Brushes.Red
objColorArray(106) = Brushes.RosyBrown
objColorArray(107) = Brushes.RoyalBlue
objColorArray(108) = Brushes.SaddleBrown
objColorArray(109) = Brushes.Salmon
objColorArray(110) = Brushes.SandyBrown
objColorArray(111) = Brushes.SeaGreen
objColorArray(112) = Brushes.SeaShell
objColorArray(113) = Brushes.Sienna
objColorArray(114) = Brushes.Silver
objColorArray(115) = Brushes.SkyBlue
objColorArray(116) = Brushes.SlateBlue
objColorArray(117) = Brushes.SlateGray
objColorArray(118) = Brushes.Snow
objColorArray(119) = Brushes.SpringGreen
objColorArray(120) = Brushes.SteelBlue
objColorArray(121) = Brushes.Tan
objColorArray(122) = Brushes.Teal
objColorArray(123) = Brushes.Thistle
objColorArray(124) = Brushes.Tomato
objColorArray(125) = Brushes.Transparent
objColorArray(126) = Brushes.Turquoise
objColorArray(127) = Brushes.Violet
objColorArray(128) = Brushes.Wheat
objColorArray(129) = Brushes.White
objColorArray(130) = Brushes.WhiteSmoke
objColorArray(131) = Brushes.Yellow
objColorArray(132) = Brushes.YellowGreen
End Sub
Private Sub BarChart_Resize(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Resize
If blnFormLoaded = True Then
BarChart_Paint(Me, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs(CreateGraphics(), New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height)))
End If
End Sub
Friend WithEvents ttHint As System.Windows.Forms.ToolTip
End Class
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll'
In this demo, Powershell opens the Form and sends two data samples to it, waiting for few seconds after each sample is rendered, then closes the Form.

$object = New-Object -TypeName 'BarChart'
$data1 = New-Object System.Collections.Hashtable(10)
$data1.Add("Product1", 25)
$data1.Add("Product2", 15)
$data1.Add("Product3", 35)
$object.LoadData([System.Collections.Hashtable] $data1)
[void]$object.Show()
start-sleep -seconds 5
$data2 = New-Object System.Collections.Hashtable(100)
$data2.Add("Item1", 50)
$data2.Add("Item2", 150)
$data2.Add("Item3", 250)
$data2.Add("Item4", 20)
$data2.Add("Item5", 100)
$data2.Add("Item6", 125)
$data2.Add("Item7", 148)
$data2.Add("Item8", 199)
$data2.Add("Item9", 267)
$object.LoadData([System.Collections.Hashtable] $data2)
$object.RenderData()
start-sleep -seconds 5
$object.Close()
$object.Dispose()
Two public methods LoadData and RenderData have been added to allow controlling the form from the script. To prevent modifying the original example, the first method clones the data from the caller, while the latter creates a dummy event Args and calls the handler:

Public Sub LoadData(ByVal objCallerHashTable As Hashtable )
objHashTableG = objCallerHashTable.Clone()
End Sub
Public Sub RenderData
Me.BarChart_Paint(Nothing, New System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs( _
CreateGraphics(), _
New System.Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, Me.Width, Me.Height) _
))
End Sub
No communication back from Form to the script is present, thus no separate object implementing IWin32Window is needed. For the sake of the example, a VB.Net version is still provided below:
Add-Type -Language 'VisualBasic' -TypeDefinition @"
Public Class MyWin32Window
Implements System.Windows.Forms.IWin32Window
Dim _hWnd As System.IntPtr
Public Sub New(ByVal handle As System.IntPtr)
_hWnd = handle
End Sub
Public ReadOnly Property Handle() As System.IntPtr Implements System.Windows.Forms.IWin32Window.Handle
Get
Handle = _hWnd
End Get
End Property
End Class
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'MyWin32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
To provide real world data samples for the Bar Chart (alternatively one may even render data via Gantt Chart) one would like to capture the Web Site Page element load duration for some performance meaurement scenario. This is easily done with the help of FiddlerCore assembly. The c# part of the script contains a modified fiddlercore-demo example, with the focus on subset of metrics returned by Fiddler:
Add-Type @"
using System;
using Fiddler;
namespace WebTester
{
public class Monitor
{
public Monitor()
{
#region AttachEventListeners
FiddlerApplication.OnNotification += delegate(object sender, NotificationEventArgs oNEA) { Console.WriteLine("** NotifyUser: " + oNEA.NotifyString); };
FiddlerApplication.Log.OnLogString += delegate(object sender, LogEventArgs oLEA) { Console.WriteLine("** LogString: " + oLEA.LogString); };
FiddlerApplication.BeforeRequest += (s) =>
{
s.bBufferResponse = true;
};
FiddlerApplication.BeforeResponse += (s) =>
{
};
FiddlerApplication.AfterSessionComplete += (fiddler_session) =>
{
if (fiddler_session.RequestMethod == "CONNECT")
return;
if (fiddler_session == null || fiddler_session.oRequest == null || fiddler_session.oRequest.headers == null)
return;
var full_url = fiddler_session.fullUrl;
Console.WriteLine("URL: " + full_url);
HTTPResponseHeaders response_headers = fiddler_session.ResponseHeaders;
Console.WriteLine("HTTP Response: " + response_headers.HTTPResponseCode.ToString());
var timers = fiddler_session.Timers;
var duration = timers.ClientDoneResponse - timers.ClientBeginRequest;
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Duration: {0:F10}", duration.Milliseconds));
};
#endregion AttachEventListeners
}
public void Start()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting FiddlerCore...");
CONFIG.IgnoreServerCertErrors = false;
FiddlerApplication.Startup(8877, true, true);
Console.WriteLine("Hit CTRL+C to end session.");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Shutdown.");
FiddlerApplication.Shutdown();
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1);
}
public static Monitor m;
static void Console_CancelKeyPress(object sender, ConsoleCancelEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Stop.");
m.Stop();
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1);
}
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.dll','System.Data.dll',"${shared_assemblies_path}\FiddlerCore4.dll"
Modifications mostly made to AfterSessionComplete delegate. This class is embedded in Powershell, and sets to listen to the traffic roughly for the duration of the $selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url) call:
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'WebTester.Monitor'
$o.Start()
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$o.Stop()
[bool]$fullstop = [bool]$PSBoundParameters['pause'].IsPresent
The other option to collect durations is to simply invoke in Chrome browser through Selenium:
using System;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Remote;
namespace WebTester
{
public static class Extensions
{
static int cnt = 0;
public static T Execute<t>(this IWebDriver driver, string script)
{
return (T)((IJavaScriptExecutor)driver).ExecuteScript(script);
}
public static List<dictionary<string, string="">> Performance(this IWebDriver driver)
{
string performance_script = @"
var ua = window.navigator.userAgent;
if (ua.match(/PhantomJS/)) {
return 'Cannot measure on ' + ua;
} else {
var performance =
window.performance ||
window.mozPerformance ||
window.msPerformance ||
window.webkitPerformance || {};
// var timings = performance.timing || {};
// return timings;
var network = performance.getEntries() || {};
return network;
}
";
List<dictionary<string, string="">> result = new List<dictionary<string, string="">>();
IEnumerable<Object> raw_data = driver.Execute<ienumerable<object>>(performance_script);
foreach (var element in (IEnumerable<Object>)raw_data)
{
Dictionary<string, string=""> row = new Dictionary<string, string="">();
Dictionary<string, object=""> dic = (Dictionary<string, object="">)element;
foreach (object key in dic.Keys)
{
Object val = null;
if (!dic.TryGetValue(key.ToString(), out val)) { val = ""; }
row.Add(key.ToString(), val.ToString());
}
result.Add(row);
}
return result;
}
public static void WaitDocumentReadyState(
IWebDriver driver, string expected_state, int max_cnt = 10)
{
cnt = 0;
var wait = new OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait(driver, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30.00));
wait.PollingInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.50);
wait.Until(dummy =>
{
string result = driver.Execute<string>("return document.readyState").ToString();
Console.Error.WriteLine(String.Format("result = {0}", result));
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("cnt = {0}", cnt));
cnt++;
return ((result.Equals(expected_state) || cnt > max_cnt));
});
}
}
}
</string></string,></string,></string,></string,></ienumerable<object></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,></t>
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$expected_states = @( "interactive", "complete" );
[WebTester.Extensions]::WaitDocumentReadyState($selenium, $expected_states[1])
$script = @"
var ua = window.navigator.userAgent;
if (ua.match(/PhantomJS/)) {
return 'Cannot measure on '+ ua;
}
else{
var performance =
window.performance ||
window.mozPerformance ||
window.msPerformance ||
window.webkitPerformance || {};
// var timings = performance.timing || {};
// return timings;
// NOTE: performance.timing will not return anything with Chrome
// timing is returned by FF
// timing is returned by Phantom
var network = performance.getEntries() || {};
return network;
}
"@
$savedata = $true
if ($headless) {
$result = ([OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver]$selenium).ExecutePhantomJS($script,[System.Object[]]@())
$result | Format-List
return
} else {
$result = ([OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium).executeScript($script)
$result | ForEach-Object {
$element_result = $_
Write-Output $element_result.Name
Write-Output $element_result.duration
$o = New-Object PSObject
$caption = 'test'
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'url' $element_result.Name
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'caption' $caption
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty 'load_time' $element_result.duration
$o | Format-List
if ($savedata) {
insert_database3 -data $o -database "$script_directory\timings.db"
}
$o = $null
The full script is available in the attached zip file.
Next example shows another custom-drawn Line, Bar and Pie Chart library which also is implemented in a single C# class:

Add-Type @"
// "
/*
*********************************************************************************************
* FILE NAME : DrawGraph.cs *
* DESCRIPTION : Generates Bar, Line & Pie graph for a set of values [maximum limit= 10] *
* AUTHOR : Anoop Unnikrishnan (AUK)
// ... currently we use unmodified code ...
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll','System.Xml.dll'
The form is limited to selection of the graph shape. Note there are few more shapes available in library (not shown here)
function DrawGraph {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$data_ref,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,385)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.SuspendLayout()
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Anoop.Graph.DrawGraph' -ArgumentList @( [string[]]$data_ref.Value.Keys,
[float[]]$data_ref.Value.Values,
$null,
$null,
'Arial',
200
)
[System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox]$b = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox'
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (40,20)
$b.Name = 'p5'
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width - 20),($f.Size.Height - 100))
$b.SizeMode = [System.Windows.Forms.PictureBoxSizeMode]::AutoSize
$b.TabIndex = 1
$b.TabStop = $false
$m = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.MenuStrip'
$file_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m2 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$shape_m3 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$exit_m1 = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripMenuItem'
$m.SuspendLayout()
$m.Items.AddRange(@( $file_m1,$exit_m1))
$m.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$m.Name = "m0"
$m.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width),24)
$m.TabIndex = 0
$m.Text = "m0"
$shape_m1.Name = "LineGraphToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m1.Text = "Line Graph"
$eventMethod_shape_m1 = $shape_m1.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m1.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.DrawLineGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$shape_m2.Name = "BarGraphToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m2.Text = "Bar Graph"
$eventMethod_shape_m2 = $shape_m2.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m2.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.DrawBarGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$shape_m3.Name = "3dPieChartToolStripMenuItem"
$shape_m3.Text = "3d Pie Chart"
$eventMethod_shape_m3 = $shape_m3.add_click
$eventMethod_shape_m3.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$b.Image = $o.Draw3DPieGraph()
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
})
$dash = New-Object -TypeName System.Windows.Forms.ToolStripSeparator
$exit_m1.Name = "exitToolStripMenuItem"
$exit_m1.Text = "Exit"
$eventMethod_exit_m1 = $exit_m1.add_click
$eventMethod_exit_m1.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
$f.Close()
})
$file_m1.DropDownItems.AddRange(@( $shape_m1, $shape_m2, $dash, $shape_m3))
$file_m1.Name = "DrawToolStripMenuItem1"
$file_m1.Text = "Draw"
$m.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (1,1)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $m,$b))
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
}

The caller passes the data by reference
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$data = @{
"USA" = 10;
"UK" = 30;
"Japan" = 60;
"China" = 40;
"Bhutan" = 5;
"India" = 60;
}
[void](DrawGraph -Title $title -caller $caller -data_ref ([ref]$data))

The grid is notably the most complex object to offer to the user to manipulate.
function PromptGrid(
[System.Collections.IList] $data,
[Object] $caller = $null
){
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartiaName('System.Windows.Forms') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | out-null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = 'how do we open these stones? '
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid
$grid.PreferredColumnWidth = 100
$System_Drawing_Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.HeaderForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::FromArgb(255,0,0,0)
$grid.Name = "dataGrid1"
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$System_Drawing_Point = New-Object System.Drawing.Point
$System_Drawing_Point.X = 13;
$System_Drawing_Point.Y = 48 ;
$grid.Location = $System_Drawing_Point
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Open'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add( $button )
$f.Controls.Add( $grid )
$button.add_Click({
if ($grid.IsSelected(0)){
$caller.Data = 42;
}
$f.Close()
})
$grid.DataSource = $data
$f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller)) | out-null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.refresh()
$f.Dispose()
}
function display_result{
param ([Object] $result)
$array = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($key in $result.keys){
$value = $result[$key]
$o = New-Object PSObject
$o | add-member Noteproperty 'Substance' $value[0]
$o | add-member Noteproperty 'Action' $value[1]
$array.Add($o)
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList
([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$ret = (PromptGrid $array $process_window)
}
$data = @{ 1 = @('wind', 'blows...');
2 = @('fire', 'burns...');
3 = @('water', 'falls...')
}
display_result $data
Here, the event handler is temporarily left as an exercise to the reader - it can be quite domain specific. Please visit the author's github repository for the updates to this script.
For example, one can use GridListView to prompt the user for missing parameters. If the script parameters are
[CmdletBinding()]param ( [string] $string_param1 = '' ,
[string] $string_param2 = '' ,
[string] $string_param3 = '' ,
[boolean] $boolean_param = $false,
[int] $int_param
)
and the invocation only passes some but not all, one can discover the parameters state with the help of the following code snippet:
[CmdletBinding()]
$CommandName = $PSCmdlet.MyInvocation.InvocationName
$ParameterList = (Get-Command -Name $CommandName).Parameters
$parameters = @{}
foreach ($Parameter in $ParameterList) {
$value = Get-Variable -Name $Parameter.Values.Name -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
Then fill the $parameters Hashtable and pass it to the Form:
$parameters = @{ }
$value | foreach-object {$parameters[$_.Name] = $_.Value }
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
Edit_Parameters -parameters ($parameters) -caller $caller -title 'Provide parameters: '
that is defined like that:
function Edit_Parameters {
Param(
[Hashtable] $parameters,
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller= $null
)
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | out-null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | out-null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.SuspendLayout();
$f.Text = $title
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView
$grid.Autosize = $true
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.Name = 'dataGrid1'
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$grid.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13,50)
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$grid.ColumnCount = 2
$grid.Columns[0].Name = 'Parameter Name'
$grid.Columns[1].Name = 'Value'
$parameters.Keys | foreach-object {
$row1 = @( $_, $parameters[$_].ToString())
$grid.Rows.Add($row1)
}
$grid.Columns[0].ReadOnly = $true;
foreach ($row in $grid.Rows){
$row.cells[0].Style.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightGray
$row.cells[0].Style.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::White
$row.cells[1].Style.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font('Lucida Console', 9)
}
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Run'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add( $button)
$f.Controls.Add( $grid )
$grid.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$button.add_Click({
foreach ($row in $grid.Rows){
if (($row.cells[0].Value -ne $null -and $row.cells[0].Value -ne '' ) -and ($row.cells[1].Value -eq $null -or $row.cells[1].Value -eq '')) {
$row.cells[0].Style.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Red
$grid.CurrentCell = $row.cells[1]
return;
}
}
$f.Close()
})
$f.ShowDialog($caller) | out-null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.refresh()
$f.Dispose()
}
In the button handler, we prevent closing the form until there are blank parameters. The input focus it brought to the cell where the input is expected. For simplicity, we accept text input for all parameters regardless of the type here.

Now suppose one runs a series of loose (e.g. Selenium) tests utilizing Excel file for test parameters and results:

To read the settings
$data_name = 'Servers.xls'
[string]$filename = ('{0}\{1}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),$data_name)
$sheet_name = 'ServerList$'
[string]$oledb_provider = 'Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0'
$data_source = "Data Source = $filename"
$ext_arg = "Extended Properties=Excel 8.0"
# TODO: hard coded id
[string]$query = "Select * from [${sheet_name}] where [id] <> 0"
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection]$connection = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection ("$oledb_provider;$data_source;$ext_arg")
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand]$command = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand ($query)
[System.Data.DataTable]$data_table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter]$ole_db_adapter = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter
$ole_db_adapter.SelectCommand = $command
$command.Connection = $connection
($rows = $ole_db_adapter.Fill($data_table)) | Out-Null
$connection.open()
$data_reader = $command.ExecuteReader()
$plain_data = @()
$row_num = 1
[System.Data.DataRow]$data_record = $null
if ($data_table -eq $null) {}
else {
foreach ($data_record in $data_table) {
$data_record | Out-Null
# Reading the columns of the current row
$row_data = @{
'id' = $null;
'baseUrl' = $null;
'status' = $null;
'date' = $null;
'result' = $null;
'guid' = $null;
'environment' = $null ;
'testName' = $null;
}
[string[]]($row_data.Keys) | ForEach-Object {
# An error occurred while enumerating through a collection: Collection was
# modified; enumeration operation may not execute..
$cell_name = $_
$cell_value = $data_record."${cell_name}"
$row_data[$cell_name] = $cell_value
}
Write-Output ("row[{0}]" -f $row_num)
$row_data
Write-Output "`n"
# format needs to be different
$plain_data += $row_data
$row_num++
}
}
$data_reader.Close()
$command.Dispose()
$connection.Close()
and write the results
function update_single_field {
param(
[string]$sql,
# [ref]$connection does not seem to work here
# [System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$connection_ref,
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection]$connection,
[string]$where_column_name,
[object]$where_column_value,
[string]$update_column_name,
[object]$update_column_value,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$update_column_type_ref = ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::VarChar),
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$where_column_type_ref = ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::Numeric)
)
[System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand]$local:command = New-Object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand
$local:command.Connection = $connection
$local:command.Parameters.Add($update_column_name,$update_column_type_ref.Value).Value = $update_column_value
$local:command.Parameters.Add($where_column_name,$where_column_type_ref.Value).Value = $where_column_value
$local:command.CommandText = $sql
# TODO: Exception calling "Prepare" with "0" argument(s): "OleDbCommand.Prepare method requires all variable length parameters to have an explicitly set non-zero Size."
# $command.Prepare()
$local:result = $local:command.ExecuteNonQuery()
Write-Output ('Update query: {0}' -f (($sql -replace $update_column_name,$update_column_value) -replace $where_column_name,$where_column_value))
Write-Output ('Update result: {0}' -f $local:result)
$local:command.Dispose()
return $local:result
}
update_single_field `
-connection $connection `
-sql "UPDATE [${sheet_name}] SET [status] = @status WHERE [id] = @id" `
-update_column_name "@status" `
-update_column_value $false `
-update_column_type_ref ([ref][System.Data.OleDb.OleDbType]::Boolean) `
-where_column_name '@id' `
-where_column_value 2
some home-brewed functions are written. There may be no Excel installed on the test box (e.g. Spoon.Net) and when the number of tests grows, it will not be handy to select certain tests to rerun. A gridview comes to rescue (arguably this is just an initial solution, better ones may exist):
$RESULT_OK = 0
$RESULT_CANCEL = 2
$Readable = @{
$RESULT_OK = 'OK'
$RESULT_CANCEL = 'CANCEL'
}
# http:
# for singlee column spreadsheets see also
# http:
function PromptGrid (
[System.Collections.IList]$data,
[object]$caller = $null
) {
if ($caller -eq $null) {
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data') | Out-Null
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing') | Out-Null
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = 'Test suite'
$f.AutoSize = $true
$grid = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid
$grid.PreferredColumnWidth = 100
$System_Drawing_Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size
$grid.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$grid.HeaderForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::FromArgb(255,0,0,0)
$grid.Name = 'dataGrid1'
$grid.DataMember = ''
$grid.TabIndex = 0
$System_Drawing_Point = New-Object System.Drawing.Point
$System_Drawing_Point.X = 13;
$System_Drawing_Point.Y = 48;
$grid.Location = $System_Drawing_Point
$grid.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = 'Open'
$button.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Bottom
$f.Controls.Add($button)
$f.Controls.Add($grid)
$button.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
# http:
# TODO:
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewSelectedRowCollection]$rows = $grid.SelectedRows
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewRow]$row = $null
# [System.Windows.Forms.DataGridViewSelectedCellCollection] $selected_cells = $grid.SelectedCells;
$script:Data = 0
$script:Status = $RESULT_CANCEL
# $last_row = ($grid.Rows.Count)
$last_row = $data.Count
for ($counter = 0; $counter -lt $last_row;$counter++) {
if ($grid.IsSelected($counter)) {
$row = $data[$counter]
$script:Data = $row.Guid
$script:Status = $RESULT_OK
}
}
$f.Close()
})
$grid.DataSource = $data
$f.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Refresh()
}
function display_result {
param([object[]]$result)
$script:Data = 0
$array = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($row_data in $result) {
$o = New-Object PSObject
foreach ($row_data_key in $row_data.Keys) {
$row_data_value = $row_data[$row_data_key]
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty $row_data_key $row_data_value
}
[void]$array.Add($o)
}
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$ret = (PromptGrid $array $process_window)
if ($script:Status -eq $RESULT_OK ) {
Write-Output @( 'Rerun ->', $script:Data )
}
}

The full script source is available in the source zip file.
The pure ListView container is rendered like:
function PromptListView
{
param(
[System.Collections.IList]$data_rows,
[string[]]$column_names = $null,
[string[]]$column_tags,
[bool]$debug
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$numCols = $column_names.Count
$width = $numCols * 120
$title = 'Select process'
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,400)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $true
$select_button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$select_button.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (10,10)
$select_button.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,23)
$select_button.Text = 'Select'
$select_button.add_click({
})
$button_panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$button_panel.Height = 40
$button_panel.Dock = 'Bottom'
$button_panel.Controls.AddRange(@( $select_button))
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel.Dock = 'Fill'
$f.Controls.Add($panel)
$list_view = New-Object windows.forms.ListView
$panel.Controls.AddRange(@( $list_view,$button_panel))
$list_view.View = [System.Windows.Forms.View]'Details'
$list_view.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,350)
$list_view.FullRowSelect = $true
$list_view.GridLines = $true
$list_view.Dock = 'Fill'
foreach ($col in $column_names) {
[void]$list_view.Columns.Add($col,100)
}
foreach ($data_row in $data_rows) {
$cell = (Invoke-Expression (('$data_row.{0}' -f $column_names[0]))).ToString()
$item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem ($cell)
for ($i = 1; $i -lt $column_names.Count; $i++) {
$cell = (Invoke-Expression ('$data_row.{0}' -f $column_names[$i]))
if ($cell -eq $null) {
$cell = ''
}
[void]$item.SubItems.Add($cell.ToString())
}
$item.Tag = $data_row
[void]$list_view.Items.Add($item)
}
$list_view.add_ItemSelectionChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItemSelectionChangedEventArgs]$e)
[System.Windows.Forms.ListView]$lw = [System.Windows.Forms.ListView]$sender
[int]$process_id = 0
[int32]::TryParse(($e.Item.SubItems[0]).Text,([ref]$process_id))
$script:Item = $process_id
})
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $column_tags.Count; $i++) {
$list_view.Columns[$i].Tag = $column_tags[$i]
}
$list_view.Add_ColumnClick({
$list_view.ListViewItemSorter = New-Object ListViewItemComparer ($_.Column,$script:IsAscending)
$script:IsAscending = !$script:IsAscending
})
$script:Item = 0
$script:IsAscending = $false
$f.Topmost = $True
$script:IsAscending = $false
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
$x = $f.ShowDialog()
}
with sort
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
public class ListViewItemComparer : System.Collections.IComparer
{
public int col = 0;
public System.Windows.Forms.SortOrder Order;
public ListViewItemComparer()
{
col = 0;
}
public ListViewItemComparer(int column, bool asc)
{
col = column;
if (asc)
{ Order = SortOrder.Ascending; }
else
{ Order = SortOrder.Descending; }
}
public int Compare(object x, object y)
{
if (!(x is ListViewItem)) return (0);
if (!(y is ListViewItem)) return (0);
ListViewItem l1 = (ListViewItem)x;
ListViewItem l2 = (ListViewItem)y;
if (l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag == null)
{
l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag = "Text";
}
if (l1.ListView.Columns[col].Tag.ToString() == "Numeric")
{
float fl1 = float.Parse(l1.SubItems[col].Text);
float fl2 = float.Parse(l2.SubItems[col].Text);
return (Order == SortOrder.Ascending) ? fl1.CompareTo(fl2) : fl2.CompareTo(fl1);
}
else
{
string str1 = l1.SubItems[col].Text;
string str2 = l2.SubItems[col].Text;
return (Order == SortOrder.Ascending) ? str1.CompareTo(str2) : str2.CompareTo(str1);
}
}
}

function display_result {
param([object[]]$result)
$column_names = @(
'id',
'dest',
'port',
'state',
'title',
'link'
)
$column_tags = @(
'Numeric',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text',
'Text'
)
$data_rows = New-Object System.Collections.ArrayList
foreach ($row_data in $result) {
$o = New-Object PSObject
foreach ($row_data_key in $column_names) {
$row_data_value = $row_data[$row_data_key]
$o | Add-Member Noteproperty $row_data_key $row_data_value
}
[void]$data_rows.Add($o)
}
[void](PromptListView -data_rows $data_rows -column_names $column_names -column_tags $column_tags)
}
Loading data into the grid or listview one entry at a time may not be the desired interface. Generic list of dictionaries seems to not work, as a workaround one may store it inside a suitable class:
public class DictionaryContainer
{
private List<Dictionary<string, object>> _data = new List<Dictionary<string, object>> { };
public List<Dictionary<string, object>> Data
{
get { return _data; }
}
public void add_row(Dictionary<string, object> row)
{
_data.Add(row);
}
public DictionaryContainer()
{
}
}
in this example, the DataGridView with a Togggle All States class was used for rendering the data :
function SelectAllGrid {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,235)
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$urls = @( 'http://www.travelocity.com/','http://www.bcdtravel.com/','http://www.airbnb.com','http://www.priceline.com','http://www.tripadvisor.com')
# https:
$array_of_dictionaries_container = New-Object -Type 'Custom.DictionaryContainer'
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne 5; $cnt++) {
$item = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]'
$item.Add('RandomNo',(Get-Random -Minimum 1 -Maximum 10001))
$item.Add('date',(Date))
$item.Add('url',$urls[$cnt])
$array_of_dictionaries_container.add_row($item)
}
$r = New-Object -TypeName 'Custom.SelectAllGrid' -ArgumentList $array_of_dictionaries_container
$r.Size = $f.Size
$f.Controls.Add($r)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
}
$script:Data = $null
SelectAllGrid -Title 'Selection Grid Sample Project'
It had been modified to become a Panel rather than Form and to accept:
private System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView dgvSelectAll;
public SelectAllGrid(DictionaryContainer userDataContainer = null)
{
this.dgvSelectAll = new System.Windows.Forms.DataGridView();
dgvSelectAll.DataSource = GetDataSource(userDataContainer);
}
public DataTable GetDataSource(DictionaryContainer userDataContainer = null)
{
DataTable dTable = new DataTable();
DataRow dRow = null;
List<dictionary<string, object="">> sampleData;
if (userDataContainer == null)
{
Random rnd = new Random();
sampleData = new List<dictionary<string, object="">> {
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.facebook.com"}} ,
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.linkedin.com"}} ,
new Dictionary<string, object=""> { { "RandomNo", rnd.NextDouble()}, { "Date", DateTime.Now.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") }, { "url", "www.odesk.com"}}
};
}
else
{
sampleData = userDataContainer.Data;
}
Dictionary<string, object=""> openWith = sampleData[0];
Dictionary<string, object="">.KeyCollection keyColl = openWith.Keys;
dTable.Columns.Add("IsChecked", System.Type.GetType("System.Boolean"));
foreach (string s in keyColl)
{
dTable.Columns.Add(s);
}
foreach (Dictionary<string, object=""> objitem in sampleData)
{
dRow = dTable.NewRow();
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object=""> kvp in objitem)
{
dRow[kvp.Key] = kvp.Value.ToString();
}
dTable.Rows.Add(dRow);
dTable.AcceptChanges();
}
return dTable;
}
</string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></string,></dictionary<string,></dictionary<string,>

Note that modifying the SelectAllGridto take List<Dictionary<string, object>> directly and passing the data via
$array_of_dictionaries = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.List[System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]]'
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne 5; $cnt++) {
$item = New-Object 'System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[String,Object]'
$item.Add('RandomNo',(Get-Random -Minimum 1 -Maximum 10001))
$item.Add('date',(Date))
$item.Add('url',$urls[$cnt])
$array_of_dictionaries.Add($item)
}
$array_of_dictionaries | ForEach-Object { $row = $_
$row | Format-List
}
$r = New-Object -TypeName 'Custom.SelectAllGrid' -ArgumentList $array_of_dictionaries
fails with the error:
New-Object : Cannot find an overload for "SelectAllGrid" and the argument count: "5".
and that one had to add System.Data.dll to the list of referenced assemblies of Custom.SelectAllGrid to prevent the error:
Add-Type : c:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Local Settings\Temp\ypffadcb.0.cs(90) :
The type 'System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable' is defined in an assembly that is not referenced.
You must add a reference to assembly
'System.Xml, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089'.
Next example uses Collapsible Groups Control to offer to the user the aggregated configration information:
function GroupedListBox
{
param(
[string]$title,
[bool]$show_buttons)
@('System.Drawing','System.Collections', 'System.Collections.Generic' , 'System.Drawing', 'System.ComponentModel', 'System.Windows.Forms', 'System.Data') | foreach-object { [void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$width = 500
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size ($width,400)
$glc = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.GroupListControl'
$glc.SuspendLayout()
$glc.AutoScroll = $true
$glc.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$glc.FlowDirection = [System.Windows.Forms.FlowDirection]::TopDown
$glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion = $false
$glc.WrapContents = $false
$glc.Anchor = ([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles](0 `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right `
))
$f.SuspendLayout()
if ($show_buttons) {
[System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox]$cb1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox'
$cb1.AutoSize = $true
$cb1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 52)
$cb1.Name = "chkSingleItemOnlyMode"
$cb1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(224, 17)
$cb1.Text = 'Single-Group toggle'
$cb1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $true
function chkSingleItemOnlyMode_CheckedChanged
{
param([Object] $sender, [EventArgs] $e)
$glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion = $cb1.Checked
if ($glc.SingleItemOnlyExpansion) {
$glc.CollapseAll()
} else {
$glc.ExpandAll()
}
}
$cb1.Add_CheckedChanged({ chkSingleItemOnlyMode_CheckedChanged } )
[System.Windows.Forms.Label]$label1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Label'
$label1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 13)
$label1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(230, 18)
$label1.Text = 'Grouped List Control Demo'
[System.Windows.Forms.Button]$button1 = new-object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Button'
$button1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(303, 46)
$button1.Name = "button1"
$button1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(166, 23)
$button1.TabIndex = 3
$button1.Text = 'Add Data Items (disconnected)'
$button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
$button1.Add_Click( { write-host $glc.GetType()
$x = $glc | get-member
write-host ($x -join "`n")
})
$f.Controls.Add($cb1)
$f.Controls.Add($button1)
$f.Controls.Add($label1)
$glc.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(0, 75)
$glc.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size($f.size.Width, ($f.size.Height - 75))
} else {
$glc.Size = $f.Size
}
for ($group = 1; $group -le 5; $group++)
{
[GroupedListControl.ListGroup]$lg = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.ListGroup'
$lg.Columns.Add("List Group " + $group.ToString(), 120 )
$lg.Columns.Add("Group " + $group + " SubItem 1", 150 )
$lg.Columns.Add("Group " + $group + " Subitem 2", 150 )
$lg.Name = ("Group " + $group)
for ($j = 1; $j -le 5; $j++){
[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem]$item = $lg.Items.Add(("Item " + $j.ToString()))
$item.SubItems.Add($item.Text + " SubItem 1")
$item.SubItems.Add($item.Text + " SubItem 2")
}
$glc.Controls.Add($lg)
}
$f.Controls.Add($glc)
$glc.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog([win32window]($caller))
$f.Dispose()
$result = $caller.Message
$caller = $null
return $result
}
$show_buttons_arg = $false
if ($PSBoundParameters["show_buttons"]) {
$show_buttons_arg = $true
}
To pass the real data to display, use the following structure:
$configuration_discovery_results = @{
'Web.config' = @{
'COMMENT' = 'Web Server';
'DOMAIN' = '';
'CONFIGURATIONS' = @{
'Exit SSL cms targetted offers' = $Extract_appSetting;
'Force Non Https for Home Page' = $Extract_appSetting;
'To new deck plans page' = $Extract_RuleActionurl ;
'imagesCdnHostToPrepend' = $Extract_RuleActionurl ;
};
};
[scriptblock]$Extract_appSetting = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$object_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$result_ref,
[string]$key = $null
)
if ($key -eq $null -or $key -eq '') {
throw 'Key cannot be null'
}
[scriptblock]$Extract_RuleActionurl = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$object_ref,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$result_ref,
[string]$key = $null
)
if ($key -eq $null -or $key -eq '') {
throw 'Key cannot be null'
}
$data = @{}
$nodes = $object_ref.Value.Configuration.Location.'system.webServer'.rewrite.rules.rule
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Host $nodes.count
}
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $nodes.count; $cnt++) {
$k = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('name')
$v = $nodes[$cnt].action.Getattribute('url')
if ($k -match $key) {
$data[$k] += $v
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Output $k; Write-Output $v
}
}
}
$result_ref.Value = $data[$key]
}
$data = @{}
$nodes = $object_ref.Value.Configuration.Location.appSettings.Add
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $nodes.count; $cnt++) {
$k = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('key')
$v = $nodes[$cnt].Getattribute('value')
if ($k -match $key) {
if ($global:debug) {
Write-Host $k
Write-Host $key
Write-Host $v
}
$data[$k] += $v
}
}
$result_ref.Value = $data[$key]
}
To collect the data from various *.config files use e.g. code
function collect_config_data {
param(
[ValidateNotNull()]
[string]$target_domain,
[string]$target_unc_path,
[scriptblock]$script_block,
[bool]$verbose,
[bool]$debug
)
$local:result = @()
if (($target_domain -eq $null) -or ($target_domain -eq '')) {
if ($powerless) {
return $local:result
} else {
throw 'unspecified DOMAIN'
}
}
[xml]$xml_config = Get-Content -Path $target_unc_path
$object_ref = ([ref]$xml_config)
$result_ref = ([ref]$local:result)
Invoke-Command $script_block -ArgumentList $object_ref,$result_ref,$verbose,$debug
if ($verbose) {
Write-Host ("Result:`r`n---`r`n{0}`r`n---`r`n" -f ($local:result -join "`r`n"))
}
}
To fill the List, use
foreach ($key in $configuration_discovery_results.Keys) {
$values = $configuration_discovery_results[$key]
$configurations = $values['CONFIGURATIONS']
[GroupedListControl.ListGroup]$lg = New-Object -TypeName 'GroupedListControl.ListGroup'
$lg.Columns.Add($values['COMMENT'],120)
$lg.Columns.Add("Key",150)
$lg.Columns.Add("Value",300)
foreach ($k in $configurations.Keys) {
$v = $configurations[$k]
[System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItem]$item = $lg.Items.Add($key)
$item.SubItems.Add($k)
$item.SubItems.Add($v)
}
$glc.Controls.Add($lg)
}

Next example covers drag and drop listboxes. There is a big number of events to craft and it is unpractical and error prone to convert the MSDN examplehttp://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.windows.forms.control.dodragdrop%28v=vs.100%29.aspx from C# to Powershell syntax entirely. One only needs the final ListDragTarget.Items, so one adds a string getter method to Add-Type leaving the rest of the snippet intact sans the main entry point:
public class DragNDrop : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private string _message;
public string Message
{
get {
_message = "";
List<string> _items = new List<string>();
foreach (object _item in ListDragTarget.Items) {
_items.Add(_item.ToString());
}
_message = String.Join(",", _items.ToArray() );
return _message;
}
set { _message = value; }
private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox ListDragSource;
private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox ListDragTarget;
private System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox UseCustomCursorsCheck;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label DropLocationLabel;
private int indexOfItemUnderMouseToDrag;
private int indexOfItemUnderMouseToDrop;
private Rectangle dragBoxFromMouseDown;
private Point screenOffset;
private Cursor MyNoDropCursor;
private Cursor MyNormalCursor;
public DragNDrop(String message)
{
and changes the constructor to accept a String message. Also, after making DragNDrop class inherit from System.Windows.Forms.Panel rather than ystem.Windows.Forms.Form it will be placed on the form:
function PromptWithDragDropNish {
param
(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel = New-Object DragNDrop($caller.Message)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(288, 248)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $panel ))
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
one uses the $caller object to handle the Message here, keeping in mind potential additional functionality though it is not strictly necessary. Finally, the script is receiving the result:
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$result = $panel.Message
$panel.Dispose()
$f.Dispose()
$caller = $null
return $result
}
$data = @(
'one','two','three','four','five',
'six','seven','nine','ten','eleven'
)
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$caller.Message = $data -join ','
$result = PromptWithDragDropNish 'Items' $caller
$result -split ',' | format-table -autosize

The form adjusts the cursor appropriately - this is not captured in the screenshot. After the form is closed the script prints the selected items. Such widget may be handy for e.g. arranging of Selenium tests into subsets (conversion to and from the *.orderedtests resource not shown). The full script source is available in the source zip file.

DF5B1F66EB484A2E8DDC06BD183B0E3F
For time interval selection one can use either DateTimePicker with a suitable System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePickerFormat
or even a DomainUpDown-derived custom time picker class:
public class CustomTimePicker : System.Windows.Forms.DomainUpDown
public CustomTimePicker()
{
for (double time = 23.5; time >= 0; time -= 0.5)
{
int hour = (int)time;
int minutes = (int)((time - hour) * 60);
this.Items.Add(hour.ToString("00") + ":" + minutes.ToString("00"));
}
this.SelectedIndex = Items.IndexOf("09:00");
this.Wrap = true;
}

$form_onload = {
$script:numeric_value = 0
$script:time_value = ''
$script:custom_value= ''
function UpDownsPrompt
param(
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing',
'System.Collections.Generic',
'System.Collections',
'System.ComponentModel',
'System.Windows.Forms',
'System.Text',
'System.Data'
) | ForEach-Object { $assembly = $_; [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($assembly) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (180,120)
$n = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
$n.SuspendLayout()
$n.Parent = $this
$n.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,80)
$n.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (50,20)
$n.Value = 1
$n.Minimum = 0
$n.Maximum = 1000
$n.Increment = 1
$n.DecimalPlaces = 0
$n.ReadOnly = $false
$n.TextAlign = [System.Windows.Forms.HorizontalAlignment]::Right
($n.add_ValueChanged).Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$script:numeric_value = $n.Value
}
)
$c = New-Object CustomTimePicker
$c.Parent = $f
$c.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,50)
$c.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,20)
$c.TextAlign = [System.Windows.Forms.HorizontalAlignment]::Left
$c.ReadOnly = $true
($c.add_TextChanged).Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$script:custom_value = $c.SelectedItem.ToString()
}
)
$c.SuspendLayout()
$c.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$c.ReadOnly = $true
$c.TabIndex = 0
$c.TabStop = $false
$s = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePicker
$s.Parent = $f
$s.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (30,20)
$s.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$s.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (70,20)
$s.Format = [System.Windows.Forms.DateTimePickerFormat]::Custom
$s.CustomFormat = 'hh:mm'
$s.ShowUpDown = $true
$s.Checked = $false
$s.Add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs)
$script:datetime_value = $s.Value
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (180,120)
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $c,$n,$s))
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'UpDown Sample'
$c.ResumeLayout($false)
$n.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.add_Load($form_onload)
$f.Dispose()
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
Write-Debug ('Time Selection is : {0}' -f $script:datetime_value )
Write-Debug ('Numeric Value is : {0}' -f $script:numeric_value)
Write-Debug ('Custom contol Value is : {0}' -f $script:custom_value)

One may adapt the Floating/Sliding/Moving Menu in C#.NET for C# code to only contain ribbon slider control with Timers while definition of UserControl1 moved to Powershell by subclassing the Panel (orig. Form1) from Panel rather than Form and get rid of the default constructor:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Ribbon
{
public class Panel : System.Windows.Forms.Panel
{
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel2;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button2;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Panel panel3;
private System.Windows.Forms.Timer timer1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Timer timer2;
private System.Windows.Forms.UserControl _usrCtrl;
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
public Panel(System.Windows.Forms.UserControl u)
{
if (u == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("Usercontrol required");
this._usrCtrl = u;
InitializeComponent();
}
Then designing all buttons and subpanels in Powershell semantics:
function PromptRibbon {
param(
[string]$title,
[string]$message,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (470,135)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$u = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.UserControl
$p1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$p2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$l2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$b1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b3 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b4 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b5 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b6 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b7 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b8 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b9 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b10 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b11 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b12 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b13 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b14 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b15 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b16 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b17 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b18 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b19 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b20 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$p1.SuspendLayout()
$p2.SuspendLayout()
$u.SuspendLayout()
function button_click {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing {0}.`rThere is no callback defined yet." -f $who))
}
$callbacks = @{
'b1' = [scriptblock]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing`rcallback function for {0}." -f $who))
};
'b3' = [scriptblock]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show(("We are processing`rcallback function defined for {0}." -f $who))
};
}
$cnt = 0
@(
([ref]$p1),
([ref]$p2)
) | ForEach-Object {
$p = $_.Value
$p.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$p.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$p.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Left
$p.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point ((440 * $cnt),0)
$p.Name = ('panel {0}' -f $cnt)
$p.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (440,100)
$p.TabIndex = $cnt
$cnt++
}
$cnt = 0
@(
([ref]$l1),
([ref]$l2)
) | ForEach-Object {
$l = $_.Value
$l.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkGray
$l.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$l.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$l.Name = ('label {0}' -f $cnt)
$l.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (176,23)
$l.TabIndex = 0
$l.Text = ('Menu Group {0}' -f $cnt)
$l.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$cnt++
}
$positions = @{
'b1' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 27; };
'b2' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 64; };
'b3' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 27; };
'b4' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 64; };
'b5' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 27; };
'b6' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 64; };
'b7' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 27; };
'b8' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 64; };
'b9' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 27; };
'b10' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 64; };
'b11' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 27; };
'b12' = @{ 'x' = 6; 'y' = 64; };
'b13' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 27; };
'b14' = @{ 'x' = 92; 'y' = 64; };
'b15' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 27; };
'b16' = @{ 'x' = 178; 'y' = 64; };
'b17' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 27; };
'b18' = @{ 'x' = 264; 'y' = 64; };
'b19' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 27; };
'b20' = @{ 'x' = 350; 'y' = 64; };
}
$cnt = 1
@(
([ref]$b1),
([ref]$b2),
([ref]$b3),
([ref]$b4),
([ref]$b5),
([ref]$b6),
([ref]$b7),
([ref]$b8),
([ref]$b9),
([ref]$b10),
([ref]$b11),
([ref]$b12),
([ref]$b13),
([ref]$b14),
([ref]$b15),
([ref]$b16),
([ref]$b17),
([ref]$b18),
([ref]$b19),
([ref]$b20)
) | ForEach-Object {
$b = $_.Value
$b.Name = ('b{0}' -f $cnt)
$x = $positions[$b.Name].x
$y = $positions[$b.Name].y
Write-Debug ('button{0} x = {1} y = {2}' -f $cnt,$x,$y)
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point ($x,$y)
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (80,30)
$b.TabIndex = 1
$b.Text = ('Button {0}' -f $cnt)
$b.UseVisualStyleBackColor = $true
if ($callbacks[$b.Name]) {
$b.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[scriptblock]$s = $callbacks[$sender.Name]
$local:result = $null
Invoke-Command $s -ArgumentList $sender,$eventargs
})
} else {
$b.add_click({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$caller.Data = $sender.Text
button_click -Sender $sender -eventargs $eventargs
})
}
$cnt++
}
$p1.Controls.Add($l1)
$p1.Controls.AddRange(@( $b10,$b9,$b8,$b7,$b6,$b5,$b4,$b3,$b2,$b1))
$p2.Controls.AddRange(@( $b20,$b19,$b18,$b17,$b16,$b15,$b14,$b13,$b12,$b11))
$p2.Controls.Add($l2)
$u.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6,13)
$u.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$u.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Gainsboro
$u.Controls.AddRange(@( $p2,$p1))
$u.Name = 'UserControl1'
$u.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (948,100)
$p1.ResumeLayout($false)
$p2.ResumeLayout($false)
$u.ResumeLayout($false)
and displaying the form with the ribbon buttons:

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptRibbon -Title 'Floating Menu Sample Project' -caller $caller
write-output $caller.Data
When the callback exists for a button, it is run, otherwise generic button_clisk is called.The full script source is available in the source zip file.
Next example displays the Custom Message Box variants with C# code converted to Powershell semantics
function return_response
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[string ]$button_text = ([System.Windows.Forms.Button]$sender[0]).Text
if ($button_text -match '(Yes|No|OK|Cancel|Abort|Retry|Ignore)') {
$script:Result = $button_text
}
$f.Dispose()
}
function add_buttons {
param([psobject]$param)
switch ($param) {
('None') {
$button_ok.Width = 80
$button_ok.Height = 24
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ok)
$button_ok.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('OK') {
$button_ok.Width = 80
$button_ok.Height = 24
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ok)
$button_ok.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('YesNo') {
$button_no.Width = 80
$button_no.Height = 24
$button_no.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_no.Text = 'No'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_no)
$button_no.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_yes.Width = 80
$button_yes.Height = 24
$button_yes.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_no.Location.X - $button_no.Width - 2),114)
$button_yes.Text = 'Yes'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_yes)
$button_yes.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('YesNoCancel') {
$button_cancel.Width = 80
$button_cancel.Height = 24
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_cancel)
$button_cancel.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_no.Width = 80
$button_no.Height = 24
$button_no.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_cancel.Location.X - $button_cancel.Width - 2),114)
$button_no.Text = 'No'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_no)
$button_no.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_yes.Width = 80
$button_yes.Height = 24
$button_yes.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_no.Location.X - $button_no.Width - 2),114)
$button_yes.Text = 'Yes'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_yes)
$button_yes_Response.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('RetryCancel') {
$button_cancel.Width = 80
$button_cancel.Height = 24
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_cancel)
$button_cancel.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_retry.Width = 80
$button_retry.Height = 24
$button_retry.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_cancel.Location.X - $button_cancel.Width - 2),114)
$button_retry.Text = 'Retry'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_retry)
$button_retry.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
('AbortRetryIgnore') {
$button_ignore.Width = 80
$button_ignore.Height = 24
$button_ignore.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (391,114)
$button_ignore.Text = 'Ignore'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_ignore)
$button_ignore.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_retry.Width = 80
$button_retry.Height = 24
$button_retry.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_ignore.Location.X - $button_ignore.Width - 2),114)
$button_retry.Text = 'Retry'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_retry)
$button_retry.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$button_abort.Width = 80
$button_abort.Height = 24
$button_abort.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (($button_retry.Location.X - $button_retry.Width - 2),114)
$button_abort.Text = 'Abort'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_abort)
$button_abort.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
return_response ($sender,$eventargs)
})
}
default {}
}
}
function add_icon_bitmap {
param([psobject]$param)
switch ($param)
{
('Error') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Error).ToBitmap()
}
('Information') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Information).ToBitmap()
}
('Question') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Question).ToBitmap()
}
('Warning') {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Warning).ToBitmap()
}
default {
$icon_bitmap.Image = ([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Information).ToBitmap()
}
}
}
function click_handler
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventArgs
)
if ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'collapse')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height + $txtDescription.Height + 6
$button_details.Tag = 'expand'
$button_details.Text = 'Hide Details'
$txtDescription.WordWrap = true
}
elseif ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'expand')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height - $txtDescription.Height - 6
$button_details.Tag = 'collapse'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
}
}
function set_message_text
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$Title,
[string]$Description
)
$label_message.Text = $messageText
if (($Description -ne $null) -and ($Description -ne ''))
{
$txtDescription.Text = $Description
}
else
{
$button_details.Visible = $false
}
if (($Title -ne $null) -and ($Title -ne ''))
{
$f.Text = $Title
}
else
{
$f.Text = 'Your Message Box'
}
}
function Show1
{
param(
[string]$messageText
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText '' $null
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Information'
add_buttons -param 'OK'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
$script:Result
}
function Show2
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Information'
add_buttons -param 'OK'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function Show3
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description,
[object]$IcOn,
[object]$btn
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param $IcOn
add_buttons -param $btn
$script:Result = 'Cancel'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function show_exception
{
param([System.Exception]$ex)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text -Title 'Exception' -messageText $ex.Message -Description $ex.StackTrace
add_icon_bitmap -param 'Error'
add_buttons -param 'YesNo'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
function DrawBox
{
$f.Controls.Add($panel)
$panel.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$icon_bitmap.Height = 36
$icon_bitmap.Width = 40
$icon_bitmap.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,11)
$panel.Controls.Add($icon_bitmap)
$txtDescription.Multiline = $true
$txtDescription.Height = 183
$txtDescription.Width = 464
$txtDescription.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (6,143)
$txtDescription.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::Fixed3D
$txtDescription.ScrollBars = [System.Windows.Forms.ScrollBars]::Both
$txtDescription.ReadOnly = $true
$panel.Controls.Add($txtDescription)
$button_details.Height = 24
$button_details.Width = 80
$button_details.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (6,114)
$button_details.Tag = 'expand'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
$panel.Controls.Add($button_details)
$button_details.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
click_handler ($sender,$eventargs)
})
$label_message.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (64,22)
$label_message.AutoSize = $true
$panel.Controls.Add($label_message)
$f.Height = 360
$f.Width = 483
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$f.MaximizeBox = $false
$f.MinimizeBox = $false
$f.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::ButtonFace
$f.Icon = New-Object System.Drawing.Icon ([System.IO.Path]::Combine((Get-ScriptDirectory),"Martz90-Circle-Files.ico"))
if ($button_details.Tag.ToString() -match 'expand')
{
$f.Height = $f.Height - $txtDescription.Height - 6
$button_details.Tag = 'collapse'
$button_details.Text = 'Show Details'
}
}
combined with Pure Powershell Assert functon from http://poshcode.org:
function assert {
[CmdletBinding()]
param(
[Parameter(Position = 0,ParameterSetName = 'Script',Mandatory = $true)]
[scriptblock]$Script,
[Parameter(Position = 0,ParameterSetName = 'Condition',Mandatory = $true)]
[bool]$Condition,
[Parameter(Position = 1,Mandatory = $true)]
[string]$message)
$message = "ASSERT FAILED: $message"
if ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName -eq 'Script') {
try {
$ErrorActionPreference = 'STOP'
$success = & $Script
} catch {
$success = $false
$message = "$message`nEXCEPTION THROWN: $($_.Exception.GetType().FullName)"
}
}
if ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName -eq 'Condition') {
try {
$ErrorActionPreference = 'STOP'
$success = $Condition
} catch {
$success = $false
$message = "$message`nEXCEPTION THROWN: $($_.Exception.GetType().FullName)"
}
}
if (!$success) {
$action = Show3 -messageText $message `
-messageTitle 'Assert failed' `
-icon $MSGICON.Error `
-Btn $MSGBUTTON.RetryCancle `
-Description ("Try:{0}`r`nScript:{1}`r`nLine:{2}`r`nFunction:{3}" -f $Script,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].ScriptName,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].ScriptLineNumber,(Get-PSCallStack)[1].FunctionName)
if ($action -ne $MSGRESPONSE.Ignore) {
throw $message
}
}
}
slightly modified to display the exception dialog box

and call stack information in the dialog and optionally continue execution:
function Show3
{
param(
[string]$messageText,
[string]$messageTitle,
[string]$description,
[object]$IcOn,
[object]$btn
)
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$button_details = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_yes = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_no = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_abort = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_retry = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_ignore = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$txtDescription = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$icon_bitmap = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$label_message = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
set_message_text $messageText $messageTitle $description
add_icon_bitmap -param $IcOn
add_buttons -param $btn
$script:Result = 'Cancel'
DrawBox
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
Write-Host ('$script:Result = ' + $script:Result)
return $script:Result
}
One can use the snippet to handle regular exceptions as well:

or a variety of button combinations. The full example is available in the source zip file (two versions: one preserving original C# code and a simplified one).
Now, suppose the task needs to authenticate to the source control, CI or some other remote service that uses its own authentication mechanism and does not accept NTLM. The following code helps prompting the username/password. It uses standard Windows Form practice of masking the password text box:

function PromptPassword(
[String] $title,
[String] $user,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.MaximizeBox = $false;
$f.MinimizeBox = $false;
$f.Text = $title
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,20)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,20)
$l1.Text = 'Username'
$f.Controls.Add($l1)
$f.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 10, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$t1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(120, 20)
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(140, 20)
$t1.Text = $user;
$t1.Name = 'txtUser';
$f.Controls.Add($t1);
$l2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(10,50)
$l2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,20)
$l2.Text = 'Password'
$f.Controls.Add($l2)
$t2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(120, 50)
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(140, 20)
$t2.Text = ''
$t2.Name = 'txtPassword'
$t2.PasswordChar = '*'
$f.Controls.Add($t2)
$btnOK = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$x2 = 20
$y1 = ($t1.Location.Y + $t1.Size.Height + + $btnOK.Size.Height + 20)
$btnOK.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point($x2 , $y1 )
$btnOK.Text = "OK";
$btnOK.Name = "btnOK";
$f.Controls.Add($btnOK);
$btnCancel = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$x1 = (($f.Size.Width - $btnCancel.Size.Width) - 20 )
$btnCancel.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point($x1, $y1 );
$btnCancel.Text = 'Cancel';
$btnCancel.Name = 'btnCancel';
$f.Controls.Add($btnCancel);
$s1 = ($f.Size.Width - $btnCancel.Size.Width) - 20
$y2 = ($t1.Location.Y + $t1.Size.Height + $btnOK.Size.Height)
$f.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size($f.Size.Width, (($btnCancel.Location.Y +
$btnCancel.Size.Height + 40)))
$btnCancel.Add_Click({$caller.txtPassword = $null ; $caller.txtUser = $null ;$f.Close()})
$btnOK.Add_Click({$caller.Data = $RESULT_OK;$caller.txtPassword = $t2.Text ; $caller.txtUser = $t1.Text; $f.Close()})
$f.Controls.Add($l)
$f.Topmost = $true
$caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL;
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
$f.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $RESULT_CANCEL }
else { return }
$f.Close()
})
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
In this script, we store User and password in separate fields:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
PromptPassword -title 'Enter credentials' -user 'admin' -caller $caller
if ($caller.Data -ne $RESULT_CANCEL) {
write-debug ("Result is : {0} / {1} " -f $caller.TxtUser , $caller.TxtPassword )
}
Note the above example is not intended to collect NTLM credentials of the user, like e.g., changing the newly installed Windows service to execute with desired user credentials. For this case, use Microsoft Get-Credential cmdlet:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$target_service_name = 'MsDepSvc'
$domain = $env:USERDOMAIN
if ($domain -like 'UAT') {
$user = '_uatmsdeploy'
}
elseif ($domain -like 'PROD') {
$user = '_msdeploy'
}
else {
$user = $env:USERNAME
}
$target_account = "${domain}\${user}"
$credential = Get-Credential -username $target_account -message 'Please authenticate'
if ($credential -ne $null) {
$target_account = $credential.Username
$target_password = $credential.GetNetworkCredential().Password
write-Debug $target_password
} else {
}
return
Code for credentials verify, admin rights, modify the newly installed service emitted from the display.

Another possible login scenario is when user can authenticate with his/her domain credentials, but the system internally uses session cookie in the browser.
One can create a dialog with WebBrowser and monitor when the user successfully logs in, then collect the session global cookie.
For that purpose, the wininet.dll p/invoke code is added to $caller object and called when appropriate. Dealing with browser cookies is explained in various sources e.g. here.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// ... c sharp code
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Runtime.InteropServices.dll', 'System.Net.dll'
with the code:
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private string _cookies;
private string _url;
public string Cookies
{
get { return _cookies; }
set { _cookies = value; }
}
public string Url
{
get { return _url; }
set { _url = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
[DllImport("wininet.dll", SetLastError = true)]
public static extern bool InternetGetCookieEx(
string url,
string cookieName,
StringBuilder cookieData,
ref int size,
Int32 dwFlags,
IntPtr lpReserved);
private const int INTERNET_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = 0x00002000;
private const int INTERNET_OPTION_END_BROWSER_SESSION = 42;
public string GetGlobalCookies(string uri)
{
int datasize = 1024;
StringBuilder cookieData = new StringBuilder((int)datasize);
if (InternetGetCookieEx(uri, null, cookieData, ref datasize, INTERNET_COOKIE_HTTPONLY, IntPtr.Zero)
&& cookieData.Length > 0)
{
return cookieData.ToString().Replace(';', ',');
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
There is nothing preventing one from storing arbitrary valid C# code with Add-Type.

and handle the Navigated event in the $browser object:
function promptForContinueWithCookies(
[String] $login_url = $null,
[Object] $caller= $null
)
{
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$timer1 = new-object System.Timers.Timer
$label1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$f.SuspendLayout()
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$browser = new-object System.Windows.Forms.WebBrowser
$f.SuspendLayout();
$browser.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$browser.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(0, 0)
$browser.Name = "webBrowser1"
$browser.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(600, 600)
$browser.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = new-object System.Drawing.SizeF(6, 13)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(600, 600)
$f.Controls.Add($browser)
$f.Text = "Login to octopus"
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Add_Load({
param ([Object] $sender, [System.EventArgs] $eventArgs )
$browser.Navigate($login_url);
})
$browser.Add_Navigated(
{
param ([Object] $sender, [System.Windows.Forms.WebBrowserNavigatedEventArgs] $eventArgs )
$url = $browser.Url.ToString()
if ($caller -ne $null -and $url -ne $null -and $url -match $caller.Url ) {
$caller.Cookies = $caller.GetGlobalCookies($url)
}
}
)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
}

$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$service_host = 'http://localhost:8088'
$login_route = 'app#/users/sign-in'
$login_url = ('{0}/{1}' -f $service_host , $login_route)
$caller.Url = 'app#/environments'
promptForContinueWithCookies $login_url $caller
write-host ("{0}->{1}" -f , $caller.Url, $caller.Cookies)
The cookie will look like:
OctopusIdentificationToken = 6pivzR9B%2fEOyJwbBkA2XfYe1BW4BNuXUqCtpW7VX943Em%2fkBZataiWxOVRDnsiBz
Common dialogs is a good candidate to become a Powershell module (WIP):
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
function TextInputBox {
param(
$prompt_message = 'Enter the Value',
$caption = 'Inputbox Test'
)
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$text_input = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_prompt.Anchor = [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right
$label_prompt.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (12,9)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (302,82)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 3
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$button_ok.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,8)
$button_ok.Name = 'button_ok'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 1
$button_ok.Text = '&OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $text_input.Text
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$button_cancel.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,40)
$button_cancel.Name = 'button_cancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 2
$button_cancel.Text = '&Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$text_input.Text = ''
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_input.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (8,100)
$text_input.Name = 'text_input'
$text_input.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (379,20)
$text_input.TabIndex = 0
$text_input.Text = ''
$text_input.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (398,128)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($text_input,$button_cancel,$button_ok,$label_prompt))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'InputBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$form.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$response = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$result = ''
$text_input.Text = ''
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$text_input.SelectionStart = 0;
$text_input.SelectionLength = $text_input.Text.Length
$text_input.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $Trues
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog()
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

function ComboInputBox {
param(
[string]$prompt_message = 'Select or Enter the Country',
[string[]]$items = @(),
[string]$caption = 'combo test'
)
function PopulateCombo ()
{
param([string[]]$comboBoxItems)
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $comboBoxItems.Length; $i++)
{
$str = $comboBoxItems[$i]
if ($str -ne $null)
{
[void]$combobox.Items.Add($str)
}
}
}
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::None;
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$combobox = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_prompt.Anchor = [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right
$label_prompt.BackColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Control
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',8.25,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (12,9)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (302,82)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 3
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$button_ok.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,8)
$button_ok.Name = 'btnOK'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 1
$button_ok.Text = '&OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $combobox.Text
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$button_cancel.FlatStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle]::Standard
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (326,40)
$button_cancel.Name = 'btnCancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 2
$button_cancel.Text = '&Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$combobox.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (8,100)
$combobox.Name = 'CmBxComboBox'
$combobox.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (379,20)
$combobox.TabIndex = 0
$combobox.Text = ''
$combobox.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$combobox.Add_TextChanged({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
})
$combobox.Add_KeyPress({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.Windows.Forms.KeyPressEventArgs]$e
)
})
$combobox.Add_TextChanged({
param(
[object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e
)
})
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (398,128)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($combobox,$button_cancel,$button_ok,$label_prompt))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'ComboBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$script:result.status = ''
PopulateCombo -comboBoxItems $items
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$combobox.SelectionStart = 0
$combobox.SelectionLength = $combobox.Text.Length
$combobox.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $True
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog($caller)
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

function ChangePasswordDialogBox {
param(
[string]$prompt_message = 'Change the password',
[string]$caption = 'Default Caption',
[string]$old_password = 'password'
)
$script:result = @{ 'text' = ''; 'status' = $null; }
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$label_old_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_new_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_prompt = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label_confirm_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$button_ok = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_cancel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$text_old_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text_new_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$text_confirm_password = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$form.SuspendLayout()
$label_old_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_old_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,88)
$label_old_password.Name = 'lblOldPassword'
$label_old_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_old_password.TabIndex = 1
$label_old_password.Text = 'Old Password'
$label_old_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_new_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_new_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,112)
$label_new_password.Name = 'lblNewPassword'
$label_new_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_new_password.TabIndex = 2
$label_new_password.Text = 'New Password'
$label_new_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_confirm_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_confirm_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,136)
$label_confirm_password.Name = 'lblConfirmPassword'
$label_confirm_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (168,24)
$label_confirm_password.TabIndex = 3
$label_confirm_password.Text = 'Confirm New Password';
$label_confirm_password.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$label_prompt.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (16,8)
$label_prompt.Name = 'lblPrompt'
$label_prompt.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (280,72)
$label_prompt.TabIndex = 9
$label_prompt.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleLeft
$label_prompt.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_old_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_old_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,88)
$text_old_password.Name = 'txtbxOldPassword'
$text_old_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21);
$text_old_password.TabIndex = 4
$text_old_password.Text = ''
$text_old_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$text_new_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0);
$text_new_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,112)
$text_new_password.Name = 'txtbxNewPassword'
$text_new_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21)
$text_new_password.TabIndex = 5
$text_new_password.Text = ''
$text_new_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$text_confirm_password.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$text_confirm_password.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (192,136)
$text_confirm_password.Name = 'txtbxConfirmPassword'
$text_confirm_password.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (184,21)
$text_confirm_password.TabIndex = 6
$text_confirm_password.Text = ''
$text_confirm_password.PasswordChar = '*'
$button_ok.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_ok.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (312,16)
$button_ok.Name = 'button_ok'
$button_ok.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_ok.TabIndex = 7
$button_ok.Text = 'OK'
$button_ok.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
if ($text_old_password.Text.Trim() -ne $old_password) {
$text_old_password.SelectionStart = 0
$text_old_password.SelectionLength = $text_old_password.Text.Length
$text_old_password.Focus()
} else {
if ($text_new_password.Text.Trim() -ne $text_confirm_password.Text.Trim()) {
$text_confirm_password.SelectionStart = 0
$text_confirm_passwordSelectionLength = $text_confirm_password.Text.Length
$text_confirm_password.Focus()
} else {
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$script:result.Text = $text_new_password.Text
$form.Dispose()
} }
})
$button_cancel.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_cancel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (312,48)
$button_cancel.Name = 'btnCancel'
$button_cancel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (64,24)
$button_cancel.TabIndex = 8
$button_cancel.Text = 'Cancel'
$button_cancel.Add_Click({
param([object]$sender,[System.EventArgs]$e)
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Cancel
$text_input.Text = ''
$script:result.Text = ''
$form.Dispose()
}
)
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (400,182)
$form.Controls.AddRange(@($text_old_password,
$text_new_password,
$text_confirm_password,
$button_cancel,
$button_ok,
$label_prompt,
$label_old_password,
$label_new_password,
$label_confirm_password))
$form.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedDialog
$form.MaximizeBox = $false
$form.MinimizeBox = $false
$form.Name = 'InputBoxDialog'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.AcceptButton = $button_ok
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$form.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$script:result.status = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::Ignore
$label_prompt.Text = $prompt_message
$label_old_password.Text = 'Old Password'
$label_new_password.Text = 'New Password'
$label_confirm_password.Text = 'Confirm New Password'
$text_old_password.Text = $old_password
$text_new_password.Text = ''
$text_confirm_password.Text = ''
$form.Text = $caption
$form.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$text_old_password.Focus()
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Topmost = $Trues
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
[void]$form.ShowDialog()
$form.Dispose()
$form = $null
return $script:result
}

@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$shared_assemblies = @(
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$f.Text = $title
$f.SuspendLayout()
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (210,105)
$button_combobox_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_combobox_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_combobox_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,10)
$button_combobox_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_combobox_test.Text = 'Combobox Test'
$button_combobox_test.Add_Click({
$countries = @(
"India",
"USA",
"UK",
"Russia",
"Bulgaria",
"Singapore",
"Malayasia",
"Japan",
"Thailand"
)
$prompt_message = 'Select or Enter the Country'
$caption = 'Combobox Test'
$o = ComboInputBox -items $countries -caption $caption -prompt_message $prompt_message
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_combobox_test)
$button_change_password_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_change_password_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_change_password_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,40)
$button_change_password_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_change_password_test.Text = 'Change Password Test'
$button_change_password_test.Add_Click({
$prompt_message = 'Change the Password'
$caption = 'Change Password Test'
$old_password = '123'
$o = ChangePasswordDialogBox -prompt_message $prompt_message -caption $caption -old_password $old_password
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_change_password_test)
$button_inputbox_test = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button_inputbox_test.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Arial',10,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$button_inputbox_test.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,70)
$button_inputbox_test.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (135,23)
$button_inputbox_test.Text = 'Inputbox test'
$button_inputbox_test.Add_Click({
$prompt_message = 'Enter the Value'
$caption = 'Inputbox test'
$o = TextInputBox -caption $caption -prompt_message $prompt_message
if ($o.status -match 'OK') {
$caller.Data = $o.Text
$f.Close()
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($button_inputbox_test)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = 'Standard Input Dialogs'
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $Trues
$f.Add_Shown({ $f.Activate() })
[void]$f.ShowDialog($caller)
$f.Dispose()
Write-Output $caller.Data
The full example is available in the source zip file.
The next big topic is tabbed dialogs. The code implementing such basically repeats what was shown already with one additional feature - it prevents the user from leaving the textbox until there is an input. At the time the form is drawn, the specific tab and input are set to be selected.
If the user attempts to switch to the other tab or input without filing some text, a warning message is displayed under the TextBox.

When the input is provided, the warning message is cleared:

The code responsible for that is highlighted below:
function PromptWithTabs(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$textbox1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$button1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Controls.Add($textbox1)
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 52)
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Input Tab"
$textbox1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(72, 7)
$textbox1.Name = "textBoxMessage"
$textbox1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(100, 20)
$textbox1.TabIndex = 0
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(72,32)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(100,16)
$l1.Text = ''
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$panel2.Controls.Add($l1)
$textbox1.Add_Leave( {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
if ($sender.Text.length -eq 0) {
$l1.Text = 'Input required'
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$sender.Select()
$result = $sender.Focus()
} else {
$l1.Text = ''
}
})
$panel1.Controls.Add($button1)
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 52)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Action Tab"
$button1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(74, 7)
$button1.Name = "buttonShowMessage"
$button1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(107, 24)
$button1.TabIndex = 0
$button1.Text = "Show Message"
$button1_Click = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$caller.Message = $textbox1.Text
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show($textbox1.Text);
}
$button1.Add_Click($button1_Click)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$textbox1.Select()
$textbox1.Enabled = $true
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 88)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 108)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ActiveControl = $textbox1
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}
Note: The order of operations matters in the above fragment. There are subtle differences between focus() and select(), not covered here.

Clicking the button launches a messagebox along with storing the result in $caller.Message.
Next example uses Windows Forms-based custom ProgressBar Host to display, e.g., the status of Powershell jobs performing some dump task on remote hosts to the user.
The source code defining the control class is imported in the script.
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
namespace ProgressBarHost
{
public class Progress : System.Windows.Forms.UserControl
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Data.dll', 'System.ComponentModel.dll'
The method PerformStep will be used without modifications in this example, but it is likely to be customized in domain-specific way.
The Powershell script does what Form designer is normally doing,
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Progress' = [ProgressBarHost.Progress] $null ;
})
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
function Progressbar(
[String] $title,
[String] $message
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(650,120)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$p = new-object ProgressBarHost.Progress
$p.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(12, 8)
$p.Name = 'status'
$p.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(272, 88)
$p.TabIndex = 0
$so.Progress = $p
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(140, 152)
$b.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(92, 24)
$b.Text = 'forward'
$b.Add_Click({ $p.PerformStep()
if ($p.Maximum -eq $p.Value) {
$b.Enabled = false;
}
})
$f.Controls.Add($b)
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 14)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 194)
$f.Controls.Add($p )
$f.Topmost = $True
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog( )
$f.Dispose()
}
Progressbar -title $title -message $message
})
clear-host
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 3
$max_cnt = 10
$cnt = 0
while ($cnt -lt $max_cnt) {
$cnt ++
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
$so.Progress.PerformStep()
}

For debugging purposes, the Forward button with the same handler is added to the form. To keep execution of script possible, the form is launched from a second Powershell runspace. Instead of caller argument, a Synchronized HashTable object is used to communicate. This technique is used heavily with WPF controls.
Next example uses a sligtly modified Timer Powershell to show elapsing timer, while the main Powershell script continues performing some lengthy task(s).
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
foreach ($work_step_cnt in @( 1,2,3,5,6,7)) {
Write-Output ('Doing lengthy work step {0}' -f $work_step_cnt)
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
Write-Output 'All Work done'
$wait_timer_step = 0
$wait_timer_max = 2
After tasks are finished, if the timer is still visible it is stopped:
while (-not $handle.IsCompleted) {
Write-Output 'waiting on timer to finish'
$wait_timer_step++
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
if ($wait_timer_step -ge $wait_timer_max) {
$so.Progress.Value = $so.Progress.Maximum
Write-Output 'Stopping timer'
break
}
}
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()
return

The Form containing progressbar and timer is entirely in Powershell:
function GenerateForm {
param(
[int]$timeout_sec
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.MaximumSize = $f.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (220,65)
$so.Form = $f
$f.Text = 'Timer'
$f.Name = 'form_main'
$f.ShowIcon = $False
$f.StartPosition = 1
$f.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.MinimumSize.Width - 10),($f.MinimumSize.Height - 10))
$components = New-Object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.FormBorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle]::FixedToolWindow
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.SuspendLayout()
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Timer
$p = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
$p.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$p.Maximum = $timeout_sec
$p.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.ClientSize.Width - 10),($f.ClientSize.Height - 20))
$p.Step = 1
$p.TabIndex = 0
$p.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (5,5)
$p.Style = 1
$p.Name = 'progressBar1'
$so.Progress = $p
$InitialFormWindowState = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
function start_timer {
$t.Enabled = $true
$t.Start()
}
$t_OnTick = {
$p.PerformStep()
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($p.Maximum - $p.Value)
$f.Text = ('{0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds)
if ($p.Value -eq $p.Maximum) {
$t.Enabled = $false
$f.Close()
}
}
$OnLoadForm_StateCorrection = {
$f.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
start_timer
}
$elapsed = New-TimeSpan -Seconds ($p.Maximum - $p.Value)
$f.Text = ('{0:00}:{1:00}:{2:00}' -f $elapsed.Hours,$elapsed.Minutes,$elapsed.Seconds)
$f.Controls.Add($p)
$t.Interval = 1000
$t.add_tick($t_OnTick)
$InitialFormWindowState = $f.WindowState
$f.add_Load($OnLoadForm_StateCorrection)
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
}
Next, by combining Progressbar and Timer examples with Task List Progress assembly one produces the same for long running multi-step Powershell script.
Below, the script source is provide (script can also be found in the source zip. Explaining the mechanics of the form and enabling the Skip forward button is ongoing work in progress:
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$shared_assemblies = @(
'ProgressTaskList.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assmblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
Write-Debug ('Using environment: {0}' -f $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH)
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assmblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
Write-Debug $assembly
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $assembly
}
Add-Type -Path $assembly
}
popd
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if ($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
elseif ($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
In this version the existing functionality of ProgressTaskList.dll will be used, no modifications made, and the assembly is built in Visual Studio and placed into $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
The actual work steps will be performed in the main script, therefore form is executed in separate Runspace
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Title' = [string]'';
'Visible' = [bool]$false;
'ScriptDirectory' = [string]'';
'Form' = [System.Windows.Forms.Form]$null;
'DebugMessage' = '';
'Current' = 0;
'Previous' = 0;
'Last' = 0;
'Tasks' = [System.Management.Automation.PSReference];
'Progress' = [Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList]$null;
})
The $so.Current, $so.Last and $so.Previous are used in the timer callback in the form's runspace to detect when it is time to call NextTask() on Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList object that is placed on the form:
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$rs = [runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so',$so)
$run_script = [powershell]::Create().AddScript({
In the form, a System.Windows.Forms.Timer object is instantiated to inspect the state of the Tasks, that are executed in the main script. There is also a System.Windows.Forms.Button to push the curent task, its functionality is unfinished, therefore its state is disabled.
function ProgressbarTasklist {
param(
[string]$title,
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$tasks_ref,
[object]$caller
)
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object -TypeName 'System.Windows.Forms.Form'
$so.Form = $f
$f.Text = $title
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Timer
$so.DebugMessage = '"in form"'
function start_timer {
$t.Enabled = $true
$t.Start()
}
$t_OnTick = {
if ($so.Current -eq $so.Last) {
$t.Enabled = $false
$so.DebugMessage = '"Complete"'
$f.Close()
} else {
$so.DebugMessage = '"in timer"'
if ($so.Current -gt $so.Previous) {
$o.NextTask()
$so.Previous = $so.Current
$so.DebugMessage = ('Finished "{0}"' -f $so.Previous )
}
}
}
$t.Interval = 300
$t.add_tick($t_OnTick)
$f.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (650,150)
$f.StartPosition = [System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition]::CenterScreen
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,14)
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (292,144)
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Silver
$panel.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (210,114)
$b.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$b.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$b.Text = 'Skip forward'
[scriptblock]$progress = {
if (-not $o.Visible) {
$o.Visible = $true
$so.Current = 1
$o.Start()
} else {
$so.Current = $so.Current + 1
$so.DebugMessage = ('Skipped "{0}"' -f $so.Current )
$o.NextTask()
}
}
$progress_click = $b.add_click
$progress_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
if ($so.Current -eq $so.Last)
{
$b.Enabled = $false
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 300
$so.Current = $so.Current + 1
$so.Visible = $false
} else {
Invoke-Command $progress -ArgumentList @()
}
})
$b.Enabled = $false
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList' -ArgumentList @()
$o.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$o.BorderStyle = [System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle]::FixedSingle
$o.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$o.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$o.Name = "progressTaskList1"
$o.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (288,159)
$o.TabIndex = 2
$so.Progress = $o
$o.TaskItems.AddRange(@( [string[]]$tasks_ref.Value))
$so.Last = $tasks_ref.Value.Count + 1
$o.Visible = $false
$panel.SuspendLayout()
$panel.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Black
$panel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$panel.Name = 'panel'
$panel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (($f.Size.Width),($f.Size.Height))
$panel.TabIndex = 1
$panel.Controls.Add($o)
$panel.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel.PerformLayout()
$InitialFormWindowState = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $b,$panel))
$f.Topmost = $True
$so.Visible = $true
$f.Add_Shown({
$f.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
$f.Activate()
Invoke-Command $progress -ArgumentList @()
start_timer
})
[void]$f.ShowDialog()
$f.Dispose()
}
$tasks_ref = $so.Tasks
ProgressbarTasklist -tasks_ref $tasks_ref -Title $so.Title
Write-Output ("Processed:`n{0}" -f ($tasks_ref.Value -join "`n"))
})
The caller script that runs in default runspace updates the $so.Current thus signaling the form's timer after performing the appropriate step - currently it sleeps a random time not exceeding 5 seconds. In addidion it prints a progress message to the console, though good syncronization is not the main purpose of this example. Presumably the actual work produces a lot of extra screen output making it difficult to discover when certain step is completed.
$tasks = @(
'Verifying cabinet integrity',
'Checking necessary disk space',
'Extracting files',
'Modifying registry',
'Installing files',
'Removing temporary files')
$task_status = @{}
$tasks | ForEach-Object { $task_status[$_] = $null }
$so.Tasks = ([ref]$tasks)
$so.Title = 'Task List'
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
function PerformStep {
param(
[int]$step,
[switch]$skip
)
$task_status[$step] = $true
$so.Current = $step
}
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 100
while ($so.Visible) {
for ($cnt = 0; $cnt -ne $tasks.Count; $cnt++) {
$step_name = $tasks[$cnt]
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 5000)
PerformStep -Step $cnt
Write-Host ('Completes step [{0}] "{1}"' -f $cnt,$step_name)
}
$so.Visible = $false
}
Write-Output $so.DebugMessage
$so.Form.Close()
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()
After everything is done the Form closes itself and runspace is destroyed.

If one is about to make modifications to the Ibenza.UI.Winforms.ProgressTaskList source, first one stores the Designer generated code and of the class inside the script as a Add-Type TypeDefinition argument. The only modification needed is to download suitable 16x16 icons from https://www.iconfinder.com and replace
this.imageList1.ImageStream = ((System.Windows.Forms.ImageListStreamer)(resources.GetObject("imageList1.ImageStream")))
with
private string[] iconPaths = new string[] {
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429962_216151.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429337_5880.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429523_62690.ico",
@"C:\developer\sergueik\powershell_ui_samples\1420429596_9866.ico"
} ;
...
foreach (string iconPath in this.iconPaths)
{
this.imageList1.Images.Add(new Icon(iconPath));
}
the next step is to refactor the Powershell script temporarily getting rid of extra runspace and of the timer object and focus on the button:
$b = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$b.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (210,114)
$b.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$b.Text = 'forward'
$b.add_click({
if ($caller.Current -eq $caller.Last)
{
$b.Enabled = false
} else {
if (-not $o.Visible) {
$o.Visible = $true
$caller.Current = 1
$o.Start()
} else {
$o.NextTask()
$caller.Current = $caller.Current + 1
}
}
})
$o = New-Object -TypeName 'WIP.ProgressTaskList' -ArgumentList @()
In the above, the $caller object is introduced to store the Current and Last indices.

Next example combines Asynchronous GUI with ProgressCircle-progress control to produce a single process circle progress indicator controlled by direct invokation of form elements across Powershell runspaces.
The form (sans the Add-Type of ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle ) is
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'System.Windows.Forms'
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'System.Drawing'
[void][Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles')
$Form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$is= New-Object System.Windows.Forms.FormWindowState
$Form.Text = 'Demo Form'
$Form.Name = 'Form'
$Form.DataBindings.DefaultDataSourceUpdateMode = 0
$Form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (216,121)
$l1.Name = 'progress_label'
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (70,34)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (100,23)
$l1.Text = 'Round:'
$c1 = New-Object -TypeName 'ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle'
$c1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (20,20)
$c1.Name = "progress_circle"
$c1.PCElapsedTimeColor1 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Chartreuse
$c1.PCElapsedTimeColor2 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Yellow
$c1.PCLinearGradientMode = [System.Drawing.Drawing2D.LinearGradientMode]::Vertical
$c1.PCRemainingTimeColor1 = [System.Drawing.Color]::Navy
$c1.PCRemainingTimeColor2 = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightBlue
$c1.PCTotalTime = 25
$c1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (47,45)
$c1.TabIndex = 3
$progress_complete = $c1.add_PCCompleted
$progress_complete.Invoke({
param([object]$sender,[string]$message)
$l1.Text = ('Task completed!')
})
$Form.Controls.AddRange(@($l1,$c1))
$is= $Form.WindowState
$Form.add_Load({
$Form.WindowState = $InitialFormWindowState
})
The caller constructs the System.EventArgs objects to execute the delegate on the ProgressCircle.ProgressCircle control which increments and updates the correspondent Label found by name. Note there are several ways to do that.
$rs = [Management.Automation.Runspaces.RunspaceFactory]::CreateRunspace($Host)
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('Form',$Form)
$po = [System.Management.Automation.PowerShell]::Create()
$po.Runspace = $rs
$po.AddScript({
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::EnableVisualStyles()
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::Run($Form)
})
$res = $po.BeginInvoke()
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
Write-Output 'Pause'
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
$eventargs = New-Object -TypeName 'System.EventArgs'
Add-Member -InputObject $eventargs -MemberType 'NoteProperty' -Name 'Increment' -Value 0 -Force
Add-Member -InputObject $eventargs -MemberType 'NoteProperty' -Name 'Total' -Value 0 -Force
$handler = [System.EventHandler]{
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$e
)
$local:increment = $e.Increment
$local:total = $e.Total
$sender.Increment($local:increment)
$sender.Text = $e.MyText
try {
$elems = $sender.Parent.Controls.Find('progress_label',$false)
} catch [exception]{
}
if ($elems -ne $null) {
$elems[0].Text = ('Round: {0}' -f $local:total)
}
}
1..25 | ForEach-Object {
$eventargs.Total = $_
$eventargs.Increment = 1
[void]$c1.BeginInvoke($handler,($c1,([System.EventArgs]$eventargs)))
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 1000)
}
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
Write-Output 'Pause'
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 2000
}
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::Exit()
$po.EndInvoke($res)
$rs.Close()
$po.Dispose()
NOTE: To make the script work on W2K3 one has to trigger another invocation (updated script is available in the source zip):
1..($total_steps ) | ForEach-Object {
$current_step = $_
$message = $eventargs.Text =( 'Processed {0} / {1}' -f $current_step , $total_steps )
$eventargs.Increment = 1
[void]$c1.BeginInvoke($handler,($c1,([System.EventArgs]$eventargs)))
if ($host.Version.Major -eq 2) {
$c1.Invoke(
[System.Action[int, string]] {
param(
[int]$increment,
[string]$message
)
$sender.Increment($increment)
try {
$elems = $sender.Parent.Controls.Find('progress_label',$false)
} catch [exception]{
}
if ($elems -ne $null) {
$elems[0].Text = $message
}
},
@(1, $message)
)
}
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds (Get-Random -Maximum 1000)
}
Generalization to multiple job progress tracking is work in progress. Full example code provided in the source zip.
The Mac OS X style progress circle can be used with minimal modifications to C# code:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace ProgressControl
{
public partial class CircularProgressControl : UserControl
{
public enum Direction
{
CLOCKWISE,
ANTICLOCKWISE
}
public Direction Rotation { get; set; }
private bool m_clockwise;
public bool Clockwise
{
get
{
return m_clockwise;
}
set
{
m_clockwise = value;
if (m_clockwise){
this.Rotation = Direction.CLOCKWISE;
} else {
this.Rotation = Direction.ANTICLOCKWISE;
}
}
}
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
The Powershell part of the script is:
@( 'System.Drawing','System.Windows.Forms') | ForEach-Object { [void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName($_) }
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.AutoScaleDimensions = New-Object System.Drawing.SizeF (6.0,13.0)
$f.AutoScaleMode = [System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode]::Font
$f.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::LightGray
$f.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (170,140)
$button1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$cbc1 = New-Object ProgressControl.CircularProgressControl
$cbc2 = New-Object ProgressControl.CircularProgressControl
$f.SuspendLayout()
$button1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (70,80)
$button1.Name = "button1"
$button1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (75,23)
$button1.TabIndex = 0
$button1.Text = "Start"
$button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
$button1.add_click.Invoke({
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
if ($button1.Text -eq "Start")
{
$button1.Text = 'Stop'
$cbc1.Start()
$cbc2.Start()
}
else
{
$button1.Text = 'Start'
$cbc1.Stop()
$cbc2.Stop()
}
})
$cbc1.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$cbc1.Interval = 60
$cbc1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,20)
$cbc1.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc1.Name = "circularProgressControl1"
$cbc1.Clockwise = $true
$cbc1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc1.StartAngle = 270
$cbc1.TabIndex = 1
$cbc1.TickColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::DarkBlue
$cbc2.BackColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Transparent
$cbc2.Interval = 60
$cbc2.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (10,80)
$cbc2.MinimumSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc2.Name = "$cbc2"
$cbc2.Clockwise = $false
$cbc2.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (56,56)
$cbc2.StartAngle = 270
$cbc2.TabIndex = 2
$cbc2.TickColor = [System.Drawing.Color]::Yellow
$f.Controls.Add($cbc2)
$f.Controls.Add($button1)
$f.Controls.Add($cbc1)
$f.Name = "Form1"
$f.Text = 'OS X Progress Control'
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
[void]$f.ShowDialog()

The next example customizes the Filesystem-TreeView to Powershell. In the Add-Type -TypeDefinition one combines the implementation of FileSystemTreeView and ShellIcon classes :
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Collections;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace C2C.FileSystem
{
public class FileSystemTreeView : TreeView
{
...
}
public class ShellIcon
{
...
}
}
In Powershell part one adds AfterSelect handler to C2C.FileSystem.FileSystemTreeView in which the selected TreeNode FullPath is stored and written in the textbox. The $show_files_checkbox checkbox allows switching LoadFiles on and off on the fly.

$caller = New-Object -TypeName 'Win32Window' -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$chooser = New-Object -TypeName 'C2C.FileSystem.FileSystemTreeView' -ArgumentList ($caller)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
# set up form
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.Text = $title
$form.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (700,450)
$panel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$btnDirectory = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$label1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$txtDirectory = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
$treePanel = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Panel
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$form.SuspendLayout()
#
# panel1
#
$panel1.Controls.Add($btnDirectory)
$panel1.Controls.Add($label1)
$panel1.Controls.Add($txtDirectory)
$panel1.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Top
$panel1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
$panel1.Name = 'panel1'
$panel1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (681,57)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$show_files_checkbox = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
$show_files_checkbox.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (515,27)
$show_files_checkbox.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (120,20)
$show_files_checkbox.Text = 'Files'
$panel1.Controls.Add($show_files_checkbox)
$show_files_checkbox.add_click({ if ($show_files_checkbox.Checked -eq $true) { $chooser.ShowFiles = $true } else { $chooser.ShowFiles = $false } })
#
# btnDirectory
#
$btnDirectory.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (560,27)
$btnDirectory.Name = "btnDirectory"
$btnDirectory.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (60,21)
$btnDirectory.TabIndex = 2
$btnDirectory.Text = 'Select'
$btnDirectory.add_click({ if ($caller.Data -ne $null) { $form.Close() } })
#
# label1
#
$label1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (9,9)
$label1.Name = 'label1'
$label1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (102,18)
$label1.TabIndex = 1
$label1.Text = 'Selection:'
#
# txtDirectory
#
$txtDirectory.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (9,27)
$txtDirectory.Name = "txtDirectory"
$txtDirectory.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (503,20)
$txtDirectory.TabIndex = 0
$txtDirectory.Text = ""
#
# treePanel
#
$treePanel.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$treePanel.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,57)
$treePanel.Name = "treePanel"
$treePanel.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (621,130)
$treePanel.TabIndex = 1
$treePanel.Controls.Add($chooser)
$chooser.ShowFiles = $false
$chooser.Dock = [System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle]::Fill
$chooser.Add_AfterSelect({ $txtDirectory.Text = $caller.Data = $chooser.Data })
$chooser.Load('C:\')
# Form1
#
$form.AutoScaleBaseSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (5,13)
$form.ClientSize = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (621,427)
$form.Controls.Add($treePanel)
$form.Controls.Add($panel1)
$form.Name = 'Form1'
$form.Text = 'Demo Chooser'
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.ResumeLayout($false)
$form.Add_Shown({ $form.Activate() })
$form.KeyPreview = $True
$form.Add_KeyDown({
if ($_.KeyCode -eq 'Escape') { $caller.Data = $null }
else { return }
$form.Close()
})
[void]$form.ShowDialog([win32window ]($caller))
$form.Dispose()
Write-Output $caller.Data
The full script source is available in the source zip file.

Designing the Windows Presentation Foundation XAML is even simpler:
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml =
@"
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Row GridSplitter Example">
<StackPanel Height="Auto">
<Grid Height="400">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="50*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="50*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="0"
Grid.Row="0" x:Name="button00" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Quentin Tarantino"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="1"
x:Name="button01" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Larry Dimmick"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="0"
x:Name="button10" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Steve Buscemi"/>
<Button Background="gray" Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1"
x:Name="button11" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch" Content="Tim Roth"/>
</Grid>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
"@
Now, IWin32Window argument is not accepted by the System.Windows.Window.
$colors = @{
'Steve Buscemi' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Pink);
'Larry Dimmick' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::White);
'Quentin Tarantino' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Orange);
'Tim Roth' = ([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Brown);
}
$result = @{ }
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$reader=(New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target=[Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader )
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
For simple behaviors, one way to communicate the result back to the script is via $result hash variable that is defined in the script and is visible in the event handler:
foreach ($button in @("button01" , "button00", "button10", "button11")) {
$control=$target.FindName($button)
$eventMethod=$control.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs ] $eventargs
)
$who = $sender.Content.ToString()
$color = $colors[$who ]
$sender.Background = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush($color)
$result[ $who ] = $true
write-debug $who
})
}
This sample is simple - one and the same event handler is attached to each clickable element in the XAML flow. The details of the sender are stored in the $result while to provide for visual cue code is changing the $sender's background.
Another example one can generate the XAML ComboBox source on the fly from the list of $items with the following code snippet:
$items = @(
'Apple' ,
'Banana' ,
'Orange' ,
'Pineapple' ,
'Plum'
)
$selected = @{ }
$context = @'
<window height="60" title="Window1" width="200" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<stackpanel>
<combobox iseditable="False" margin="5" name="comboBox">
'@
$cnt = 1
$items | foreach-object { $name = "Item_${cnt}" ; $cnt ++ ; $context +="<comboboxitem content="$_" name="${name}">" }
$context += @'
</comboboxitem></combobox>
</stackpanel>
</window>
'@
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = $context
Clear-Host
$reader=(New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target=[Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$handler = {
param ([object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs )
$sender.Background = [ System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::Red
$target.Title = ( 'Added {0} ' -f $sender.Content )
$selected[ $sender.Content ] = $true
}
This code provides minimal but clear visual feedback for items selection.
foreach ($item in ("Item_1", "Item_5", "Item_2","Item_3","Item_4") ){
$combobox_item_control = $target.FindName( $item )
$eventargsventMethod2 = $combobox_item_control.add_Selected
$eventargsventMethod2.Invoke( $handler )
$combobox_item_control = $null
}
yielding:

and prints the selected results in the Powershell fashion.
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
write-output 'Selected items:'$items | where-object {$selected.ContainsKey( $_ ) }

Notably, one can design a very rich user interface in pure XAML while keeping the actual selection processing simple
For example, by repeating (largely) the previous exercise, but draw 3 color-filled arrow polygons on the panel.
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
// .... code below
"@
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Height="100" Width="200" Title="Window1">
<Canvas Height="100" Width="200" Name="Canvas1">
<!-- Draws a triangle with a blue interior. -->
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Blue" Name="Polygon1" Canvas.Left="40" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="40"/>
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Green" Name="Polygon2" Canvas.Left="70" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="30"/>
<Polygon Points="0,0 0,30 0,10 30,10 30,-10 45,10 30,30 30,20 0,20 0,0 30,0 30,10 0,10" Fill="Red" Name="Polygon3" Canvas.Left="100" Canvas.Top="30" Canvas.ZIndex="20"/>
</Canvas>
</Window>
and in the event handler perform color and ZIndex change of the Mouse-selected arrow and reflect the selected polygon name it in the title of the window:
Clear-Host
$polygon_data = @{}
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$canvas = $target.FindName("Canvas1")
function save_orig_design{
param ([String] $name)
$control = $target.FindName($name)
return @{
'fill' = ( $control.Fill.Color );
'ZIndex' = ( [System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::GetZIndex($control) )
}
}
$polygon_data['Polygon1'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon1'))
$polygon_data['Polygon2'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon2'))
$polygon_data['Polygon3'] = (save_orig_design('Polygon3'))
function restore_orig {
param ( [String] $name )
$control = $target.FindName( $name )
$color = [System.Windows.Media.ColorConverter]::ConvertFromString( [String] $polygon_data[$name]['fill'] )
$control.Fill = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush( $color )
[System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::SetZIndex($control, [Object] $polygon_data[$name]['ZIndex'])
}
$handler = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Input.MouseButtonEventArgs] $e )
@('Polygon1', 'Polygon2', 'Polygon3') | % { restore_orig( $_) }
$sender.Fill = new-Object System.Windows.Media.SolidColorBrush([System.Windows.Media.Colors]::Orange)
[System.Windows.Controls.Canvas]::SetZIndex($sender,[Object]100)
$target.Title="Hello $($sender.Name)"
}
foreach ($item in ('Polygon1', 'Polygon2', 'Polygon3') ){
$control = $target.FindName($item)
$eventMethod = $control.add_MouseDown
$eventMethod.Invoke( $handler )
$control = $null
}
$eventMethod.Invoke($handler)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
one can get distinct visual effect:



But designing code behind may be tough. Arranging the communication between Powershell and WPF properly is well documented and appears to be quite a challenging task.
To arrange the interaction between PowerShell run spaces one creates an optionally strongly-typed synchronized object and creates an additional RunSpace to execute WPF events.
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = '';
'Window' = [System.Windows.Window] $null ;
'TextBox' = [System.Windows.Controls.TextBox] $null ;
})
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
Next, one wraps the XAML handling code in the Add-Script method.
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
<window height="100" title="Example with TextBox" width="300" x:name="Window" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<stackpanel height="100" width="300">
<textblock fontsize="14" fontweight="Bold" text="A spell-checking TextBox:">
<textbox acceptsreturn="True" acceptstab="True" fontsize="14" margin="5" spellcheck.isenabled="True" textwrapping="Wrap" x:name="textbox">
</textbox>
</textblock></stackpanel>
</window>
"@
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load( $reader )
$so.Window = $target
$handler = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Controls.TextChangedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.Result = $sender.Text
}
$control = $target.FindName("textbox")
$so.TextBox = $control
$event = $control.Add_TextChanged
$event.Invoke( $handler )
$eventMethod.Invoke($handler)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
})
Then design accessor functions operating via the shared object $so. Note that certain properties that have to be accessible cannot be evaluated on a different thread. The calling thread cannot access this object because a different thread owns it exception is only raised at runtime.
function send_text {
Param (
$content,
[switch] $append
)
$so.Textbox.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
if ($PSBoundParameters['append_content']) {
$so.TextBox.AppendText($content)
} else {
$so.TextBox.Text = $content
}
$so.Result = $so.TextBox.Text
}, 'Normal')
}
function close_dialog {
$so.Window.Dispatcher.invoke([action]{
$so.Window.Close()
}, 'Normal')
}
Finally, the main script invokes the dynamically created one and controls the form.
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
Clear-Host
$data = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 1
write-host $so.Result
send_text -Content 'The qick red focks jumped over the lasy brown dog.'
$cnt = 10
[bool] $done = $false
while (($cnt -ne 0 ) -and -not $done) {
write-output ('Text: {0} ' -f $so.Result )
if ($so.Result -eq 'The quick red fox jumped over the lazy brown dog.' ){
$done = $true;
}
else {
start-sleep 10
}
$cnt --
}
close_dialog
if ( -not $done ){
write-output 'Time is up!'
} else {
write-output 'Well done!'
}
This example initializes the text with some typos.

and waits for the user to fix the typos. Once the text is corrected or the timeout expired, the form is closed and the summary is printed.

Due to somewhat more complex code needed for Powershell / WPF communication, it is advisable to start with the simpler example and only convert into final form once all event handlers execute as desired. Earlier examples can be reasonably quickly converted this way.
One can also arrange bidirectional communication between Form and script from the Form, e.g., loading some current data into the checkbox tooltip in a slightly modified version of the script below:
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
Elseif($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = [string] '';
'ScriptDirectory' = [string] '';
'Window' = [System.Windows.Window] $null ;
'Control' = [System.Windows.Controls.ToolTip] $null ;
'Contents' = [System.Windows.Controls.TextBox] $null ;
'NeedData' = [bool] $false ;
'HaveData' = [bool] $false ;
})
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
[xml]$xaml = @"
<window height="190" removed="LightGray" title="About WPF" width="168" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation">
<canvas>
<img opacity=".7" source="$('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'clock.jpg' )" width="150" />
<image.tooltip>
<tooltip name="tooltip">
<stackpanel>
<label background="Blue" fontweight="Bold" foreground="White">
The CheckBox
</label>
<stackpanel orientation="Horizontal">
<img margin="2" name="hourglass" source="$('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'hourglass.jpg' )" visibility="Collapsed" width="20" />
<textblock name="tooltip_textbox" padding="10" textwrapping="WrapWithOverflow" width="200">
please wait...
</textblock>
</stackpanel>
</stackpanel>
</tooltip>
</image.tooltip>
</canvas>
</window>
"@
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
$so.Window = $target
$control = $target.FindName("tooltip")
$so.Indicator = $target.FindName("hourglass")
$contents = $target.FindName("tooltip_textbox")
$so.Control = $control
$so.Contents = $contents
$handler_opened = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.Contents.Text = 'please wait...'
$so.Indicator.Visibility = 'Visible'
$so.NeedData = $true
$so.Result = ''
}
$handler_closed = {
param (
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.RoutedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$so.HaveData = $false
$so.NeedData = $false
}
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod] $event_opened = $control.Add_Opened
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod] $event_closed = $control.Add_Closed
$event_opened.Invoke( $handler_opened )
$event_closed.Invoke( $handler_closed)
$target.ShowDialog() | out-null
})
function send_text {
Param (
$content,
[switch] $append
)
$so.Indicator.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
$so.Indicator.Visibility = 'Collapsed'
}, 'Normal')
$so.Contents.Dispatcher.invoke([System.Action]{
if ($PSBoundParameters['append_content']) {
$so.Contents.AppendText($content)
} else {
$so.Contents.Text = $content
}
$so.Result = $so.Contents.Text
}, 'Normal')
}
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
Clear-Host
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
While (-Not $handle.IsCompleted) {
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 100
if ($so.NeedData -and -not $so.HaveData){
write-output ('Need to provide data' )
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 10
send_text -Content (Date)
write-output ('Sent {0}' -f $so.Result )
$so.HaveData = $true
}
}
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle)
$rs.Close()

In this example, the ToolTip Opened,Closed events are used to set and clear the NeedData flag via Synchronized to the top level script than change the text to please wait and show the hourglass until the data is ready. The rendering of the data is again performed in the send_text. Note that the send_text function now invokes Dispatcher twice and the visual feedback is not perfect. Every time the mouse leaves and re-enters the Tooltip activation area, new data is requested and provided.


Picking specific node from hierarchy grouped in some fashion is often required when launching Powershell script e.g. for metric collection.
function PromptTreeView
{
Param(
[String] $title,
[String] $message)
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections.Generic')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Collections')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.ComponentModel')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Text')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Data')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$t = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$f.SuspendLayout();
$t.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t.ImageList = $i
$t.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t.ImageIndex = -1
$t.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t.Name = "treeFood"
$t.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 256)
$t.TabIndex = 1;
$t_AfterSelect = $t.add_AfterSelect
$t_AfterSelect.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewEventArgs] $eventargs
)
if ($eventargs.Action -eq [System.Windows.Forms.TreeViewAction]::ByMouse)
{
write-host $eventargs.Node.FullPath
}
})
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 266)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $t))
$f.Name = "TreeViewExample"
$f.Text = "TreeView Example"
$f_Load = $f.add_Load
$f_Load.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Fruits")
$node.Nodes.Add("Apple")
$node.Nodes.Add("Peach")
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Vegetables")
$node.Nodes.Add("Tomato")
$node.Nodes.Add("Eggplant")
})
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Name = 'Form1'
$f.Text = 'TreeView Sample'
$t.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.StartPosition = 'CenterScreen'
$f.KeyPreview = $false
$f.Topmost = $True
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$t.Dispose()
$f.Dispose()
}
By adding the ScriptDirectory property...
private string _script_directory;
public string ScriptDirectory
{
get { return _script_directory; }
set { _script_directory = value; }
}
...and updating the PromptTreeView signature to receive the $caller the script can pass its location to the Form via $caller.
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$caller.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$result = PromptTreeView 'Items' $caller
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
}
and the latter will be able to load custom icons:
try {
$script_path = $caller.ScriptDirectory
} catch [Exception] {
}
if ($script_path -eq '' -or $script_path -eq $null ) {
$script_path = get-location
}
foreach ($n in @(1,2,3)){
$image_path = ( '{0}\color{1}.gif' -f $script_path , $n )
$image = [System.Drawing.Image]::FromFile($image_path)
$i.Images.Add($image)
}

and use distinct icons for individual nodes. Using the same technique, the caller script may describe which icons to render for which node.
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Fruits")
$apple = $node.Nodes.Add("Apple")
$apple.ImageIndex = 1
$node.Nodes.Add("Peach")
$node = $t.Nodes.Add("Vegetables")
$tomato = $node.Nodes.Add("Tomato")
$tomato.ImageIndex = 2
The next iteration of this script also contains a more elaborated version of the event handler. The sample can be used to handle time-consuming validations that may be required when e.g. the object being offered to the user represents a remote location with some latency. It may be desirable to do such validation without forcing the user to quit the dialog. In the code below, the form TreeView element click instantiates a BackgroundWorker to process the operation on separate thread. The form currently provides no visual cue, that $worker has started, though it is clearly possible.
Thus modal dialogs are still OK - since the event handling code is 100% PowerShell, there is no need to arrange on complex synchronization between script and the form - every time the Form desires to run some data validations vis invoking some relevant PowerShell cmdlets, it can do it directly.
$worker = new-object System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
$worker.WorkerReportsProgress = $false;
$worker.WorkerSupportsCancellation = $false;
$worker_DoWork = $worker.Add_DoWork
$worker_DoWork.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.Windows.Forms.DoWorkEventArgs] $eventargs
)
})
All work is done in the Completed event handler. On the example, a text file 'etc/hosts' is open in Notepad and the thread waits for user to close notepad. This is standard example / recommended practice with Windows.Forms except the Backgroundworker is usually implemented in C#. It is nice to discover it works right out of the box with PowerShell code.
$worker_RunWorkerCompleted = $worker.Add_RunWorkerCompleted
$worker_RunWorkerCompleted.Invoke({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.ComponentModel.RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs] $eventargs
)
$child_proc = [System.Diagnostics.Process]::Start('notepad',"$env:windir\system32\drivers\etc\hosts")
$child_proc.WaitForExit()
})
Tabbed
One would really like to plant tree views not into text boxes, but on tabs. This would make the option selection entirely mouse-driven and is possible.
The minor difference with the earlier example is the name of the event the treeview redraws after - for tabPage it is VisibleChangedEvent.
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
The full source is provided below:
function TabsWithTreeViews(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 352)
$panel2.AutoSize = $true
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Source Node"
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,12)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(220,16)
$l1.Text = 'enter status message here'
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange( @($l1 ))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,230)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(244,32)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'status'
$panel2.Controls.Add($groupBox1)
$t2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t2.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t2.ImageList = $i
$t2.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t2.ImageIndex = -1
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t2.Name = "treeFood"
$t2.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t2.AutoSize = $true
$t2.TabIndex = 1;
$panel2.Controls.AddRange(@($t2))
$panel2.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t2.SuspendLayout()
$t2.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t2.Nodes.Add('Source Environment')
$server = $node.Nodes.Add('Test Server')
$databases = $server.Nodes.Add('Databases')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 1')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 2')
$server.Nodes.Add('Application')
$sites = $server.Nodes.Add('IIS Web Sites')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t2.ResumeLayout($false)
$t2.PerformLayout()
})
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 252)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Destination Node"
$t1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$t1.ImageList = $i
$t1.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t1.ImageIndex = -1
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t1.Name = "treeFood"
$t1.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t1.AutoSize = $true
$t1.TabIndex = 1;
$panel1.Controls.AddRange(@($t1))
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 288)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 308)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}

Code is work in progress, with the intent to use status label for validation warnings and the worker process for more deep validation of selected environments.

To manage Powershell Desired State Configuration Configuration Manager - Node - Provider - Attribute inputs in pre-V4 Powershell environment, one may wish to extend the treeview with combobox. For example, the custom TreeView Control with ComboBox Dropdown Nodes by Mattman206 can be used as follows. After compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, one loads it into the script, and adds to the form freely mixing System.Windows.Forms.TreeNode and DropDownTreeView.DropDownTreeNode nodes when processing the form's Load event:Mattman206 can be used as follows. After compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, one loads it into the script,
One would really like to plant tree views not into text boxes, but on tabs. This would make the option selection entirely mouse-driven and is possible.
The minor difference with the earlier example is the name of the event the treeview redraws after - for tabPage it is VisibleChangedEvent.
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
The full source is provided below:
function TabsWithTreeViews(
[String] $title,
[Object] $caller
){
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Drawing')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$panel2 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$panel1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabPage
$tab_contol1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.TabControl
$panel2.SuspendLayout()
$panel1.SuspendLayout()
$tab_contol1.SuspendLayout()
$f.SuspendLayout()
$panel2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel2.Name = "tabPage2"
$panel2.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 352)
$panel2.AutoSize = $true
$panel2.TabIndex = 1
$panel2.Text = "Source Node"
$l1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$l1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,12)
$l1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(220,16)
$l1.Text = 'enter status message here'
$l1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, 0);
$groupBox1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.GroupBox
$groupBox1.SuspendLayout()
$groupBox1.Controls.AddRange( @($l1 ))
$groupBox1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(8,230)
$groupBox1.Name = 'groupBox1'
$groupBox1.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(244,32)
$groupBox1.TabIndex = 0
$groupBox1.TabStop = $false
$groupBox1.Text = 'status'
$panel2.Controls.Add($groupBox1)
$t2 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t2.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$i = new-Object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList($components)
$i.Images.Add([System.Drawing.SystemIcons]::Application)
$t2.ImageList = $i
$t2.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t2.ImageIndex = -1
$t2.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t2.Name = "treeFood"
$t2.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t2.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t2.AutoSize = $true
$t2.TabIndex = 1;
$panel2.Controls.AddRange(@($t2))
$panel2.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t2.SuspendLayout()
$t2.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t2.Nodes.Add('Source Environment')
$server = $node.Nodes.Add('Test Server')
$databases = $server.Nodes.Add('Databases')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 1')
$server.Nodes.Add('DB 2')
$server.Nodes.Add('Application')
$sites = $server.Nodes.Add('IIS Web Sites')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t2.ResumeLayout($false)
$t2.PerformLayout()
})
$panel1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 22)
$panel1.Name = "tabPage1"
$panel1.Padding = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Padding(3)
$panel1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(259, 252)
$panel1.TabIndex = 0
$panel1.Text = "Destination Node"
$t1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.TreeView
$t1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font('Tahoma', 10.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$t1.ImageList = $i
$t1.Anchor = ((([System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Top -bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Bottom) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Left) `
-bor [System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles]::Right)
$t1.ImageIndex = -1
$t1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(4, 5)
$t1.Name = "treeFood"
$t1.SelectedImageIndex = -1
$t1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(284, 224)
$t1.AutoSize = $true
$t1.TabIndex = 1;
$panel1.Controls.AddRange(@($t1))
$panel1.add_VisibleChanged({
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
$t1.SuspendLayout()
$t1.Nodes.Clear()
$node = $t1.Nodes.Add('Target Environment')
$node.Nodes.Add('Database Server')
$node.Nodes.Add('Application Server')
$sites = $node.Nodes.Add('Web Server')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 1')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 2')
$sites.Nodes.Add('Site 3')
$t1.ResumeLayout($false)
$t1.PerformLayout()
})
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel1)
$tab_contol1.Controls.Add($panel2)
$tab_contol1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(13, 13)
$tab_contol1.Name = "tabControl1"
$tab_contol1.SelectedIndex = 1
$tab_contol1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(267, 288)
$tab_contol1.TabIndex = 0
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 308)
$f.Controls.Add($tab_contol1)
$panel2.ResumeLayout($false)
$panel2.PerformLayout()
$panel1.ResumeLayout($false)
$tab_contol1.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.KeyPreview = $True
[Void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
$f.Dispose()
}

Code is work in progress, with the intent to use status label for validation warnings and the worker process for more deep validation of selected environments.

Next example utilized the beautiful TreeTabControl. A Tree of Tab Items for Powershell.
There is a little public method to add to TreeTab/TreeTab/TreeTabControl.xaml.cs class to make Powershell use the class :
public TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE ConvertType(string _typestring ){
TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE _type;
if (String.Compare(_typestring, "MAIN", true) == 0)
_type = TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE.MAIN;
else
_type = TreeItem.TREEITEM_TYPE.GROUP;
return _type;
}
because the
public enum TREEITEM_TYPE
{
MAIN,
GROUP
}
is inaccessible to Powershell.
One uses the original container XAML practically unmodified:
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:custom="clr-namespace:TreeTab;assembly=TreeTab" Title="Window1" Margin="0,0,0,0" Height="244" Width="633">
<Grid x:Name="Container">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="30"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button x:Name="Hide_Tree" Grid.Column="1">Hide Tree</Button>
<Button x:Name="Show_Tree" Grid.Column="0">Show Tree</Button>
</Grid>
<Grid x:Name="Container2" Grid.Row="1" Margin="5,5,5,5">
<StackPanel x:Name="TreeTabContainer"></StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>

The Powershell script initializes the plumbing code :
$shared_assemblies = @(
'TreeTab.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object { Unblock-File -Path $_; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
Clear-Host
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
and after compiling the class and placing the assembly in SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH folder, places the instance of TreeTab.TreeTabControl into the StackPanel:
$t = New-Object -TypeName 'TreeTab.TreeTabControl'
$c = $target.FindName('TreeTabContainer')
$t.IsTreeExpanded = $true
$t.Name = 'treeTab'
[void]$t.HideTree()
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Global','Global',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),'')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Staging_Environment','Staging Environment',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),'')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Test_Environment','Test Environment',$false,$t.ConvertType($t.ConvertType('GROUP')),'')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp0 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Staging_Environment')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItem]$tItem = $t.AddTabItem('Certificates','Certificates',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp0)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('IIS_Web_Sites','IIS Web Sites',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp0)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Databases','Databases',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp0)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp02 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Databases')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_1','DB 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp02)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_2','DB 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp02)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp03 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('IIS_Web_Sites')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_1','Site 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_2','Site 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_3','Site 3',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_4','Site 4',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp03)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp01 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Test_Environment')
[TreeTab.TreeTabItem]$t23 = $t.AddTabItem('Certificates1','Certificates',$false,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp01)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('IIS_Web_Sites2','IIS Web Sites',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp01)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Databases2','Databases',$false,$t.ConvertType('GROUP'),$tp01)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp12 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('Databases2')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_11','DB 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp12)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('DB_12','DB 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp12)
[TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$tp13 = [TreeTab.TreeTabItemGroup]$t.GetTabItemById('IIS_Web_Sites2')
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_11','Site 1',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_12','Site 2',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_13','Site 3',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.AddTabItem('Site_14','Site 4',$true,$t.ConvertType('MAIN'),$tp13)
[void]$t.ShowTree()
[void]$c.AddChild($t)
$target.FindName("Hide_Tree").add_click.Invoke({
[void]$t.HideTree()
})
$target.FindName("Show_Tree").add_click.Invoke({
[void]$t.ShowTree()
})
$target.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
The class autmates the tab navigation. Next is to fill the tabs with standard WPF inputs and provide the domain-specific callbacks:
E.g. given
[xml]$parent_markup = @"
<pre lang="xml">
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Window1" Margin="5,5,5,5" Height="310" Width="420">
<ScrollViewer>
<WrapPanel>
<Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot">
</Grid>
</WrapPanel>
</ScrollViewer>
</Window>
"@
and
[xml]$child_markup = @"
="1.0"
<StackPanel xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml">
<StackPanel.Resources>
<Style TargetType="{x:Type TextBox}">
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,10,0,0"/>
</Style>
</StackPanel.Resources>
<Label x:Name="lblNumberOfTargetHits" HorizontalAlignment="Center">Input:</Label>
<TextBox Width="120" x:Name="txtTargetKeyFocus" FontSize="12"/>
<TextBox x:Name="txtTargetFocus" TextWrapping="Wrap" FontSize="12"/>
</StackPanel>
"@
nesting controls is accomplished just like:
$parent_reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $parent_markup)
$parent_target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($parent_reader)
$LayoutRoot = $parent_target.FindName("LayoutRoot")
$child_reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $child_markup)
$child_target = [Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($child_reader)
$LayoutRoot.add_Loaded.Invoke({
$LayoutRoot.Children.Add($child_target)
})
To run code in WPF control event handlers one makes sure the controls are found by their markup x:Name attribute by $child, not $parent e.g:
$target = $child_target
$control = $target.FindName("txtTargetKeyFocus")
$handler_got_keyboard_focus = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Input.KeyboardFocusChangedEventArgs]$e
)
$source = $e.Source
$source.Background = [System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::LightBlue
$source.Clear()
}
$handler_lost_keyboard_focus = {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.Windows.Input.KeyboardFocusChangedEventArgs]$e
)
$source = $e.Source
$source.Background = [System.Windows.Media.Brushes]::White
}
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod]$event_got_keyboard_focus = $control.Add_GotKeyboardFocus
[System.Management.Automation.PSMethod]$event_lost_keyboard_focus = $control.Add_LostKeyboardFocus
$event_got_keyboard_focus.Invoke($handler_got_keyboard_focus)
$event_lost_keyboard_focus.Invoke($handler_lost_keyboard_focus)
$control = $null
continued with the remainder of controls.
Note: with the help of System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators assembly, one may save oneself from typing the full class names in the script:
$ta = [PSObject].Assembly.GetType('System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators')
Add-Type -AssemblyName 'PresentationCore','PresentationFramework' -Passthru |
Where-Object IsPublic |
ForEach-Object {
$_class = $_
try {
$ta::Add($_class.Name,$_class)
} catch {
( 'Failed to add {0} accelerator resolving to {1}' -f $_class.Name , $_class.FullName )
}
}
with the help of the code above the following fragment
# http:
[Window]@{
Width = 310
Height = 110
WindowStyle = 'SingleBorderWindow'
AllowsTransparency = $false
TopMost = $true
Content = & {
$c1 = [StackPanel]@{
Margin = '5'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
HorizontalAlignment = 'Center'
Orientation='Horizontal'
}
$t = [textblock]@{}
$t.AddChild([label]@{
Margin = '5'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
HorizontalAlignment = 'Center'
FontSize = '11'
FontFamily = 'Calibri'
Foreground = 'Black'
Content = 'Enter Password:'
}
)
$c1.AddChild($t)
$c1.AddChild(
[passwordbox]@{
Name = 'passwordBox'
PasswordChar = '*'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
Width = '120'
}
)
$c1.AddChild(
[button]@{
Content = 'OK'
IsDefault = 'True'
Margin = '5'
Name = 'button1'
Width = '50'
VerticalAlignment = 'Center'
}
)
,$c1} | ForEach-Object {
$_.Add_MouseLeftButtonDown({
$this.DragMove()
})
$_.Add_MouseRightButtonDown({
$this.Close()
})
$_.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
}
produces the similar effect as
="1.0"
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Window1" Margin="5,5,5,5" Height="110" Width="310">
<StackPanel xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" Orientation="Horizontal" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment = "Center">
<TextBlock Margin="5" FontSize = "11" FontFamily = "Calibri">
Enter Password:
</TextBlock>
<PasswordBox Name="passwordBox" PasswordChar="*" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="120"/>
<Button Content="OK" IsDefault="True" Margin="5" Name="button1" Width="50" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
In the majority of cases this leads to no ambiguity in event handlers
Say the script is running a series of steps with verbose logs and takes a lot of time to complete. It is natural to spawn a Windows System tray Notification icon that would indicate what the ongoing process is doing. The key is how to arrange the code so the control remains in the main script.
With minimal modifications, the Notification icon in the system tray example provided by ScriptIT one can make the main script manifest its state to the Balloon Tip message and the console, and the build log file is used to render the tray icon menu and to pass additional information to it.

Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value;
if($Invocation.PSScriptRoot)
{
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot;
}
Elseif($Invocation.MyCommand.Path)
{
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
}
else
{
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf("\"));
}
}
$so = [hashtable]::Synchronized(@{
'Result' = [string] '';
'ConfigFile' = [string] '';
'ScriptDirectory' = [string] '';
'Form' = [System.Windows.Forms.Form] $null ;
'NotifyIcon' = [System.Windows.Controls.ToolTip] $null ;
'ContextMenu' = [System.Windows.Forms.ContextMenu] $null ;
})
$so.ScriptDirectory = Get-ScriptDirectory
$so.Result = ''
$rs =[runspacefactory]::CreateRunspace()
$rs.ApartmentState = 'STA'
$rs.ThreadOptions = 'ReuseThread'
$rs.Open()
$rs.SessionStateProxy.SetVariable('so', $so)
$run_script = [PowerShell]::Create().AddScript({
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$so.Form = $f
$notify_icon = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.NotifyIcon
$so.NotifyIcon = $notify_icon
$context_menu = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.ContextMenu
$exit_menu_item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
$AddContentMenuItem = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
$build_log = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'build.log' )
function Read-Config {
$context_menu.MenuItems.Clear()
if(Test-Path $build_log){
$ConfigData = Get-Content $build_log
$i = 0
foreach($line in $ConfigData){
if($line.Length -gt 0){
$line = $line.Split(",")
$Name = $line[0]
$FilePath = $line[1]
$context_menu | Build-ContextMenu -index $i -text $Name -Action $FilePath
$i++
}
}
}
$exit_menu_item.Index = $i+1
$exit_menu_item.Text = 'E&xit'
$exit_menu_item.add_Click({
$f.Close()
$notify_icon.visible = $false
})
$context_menu.MenuItems.Add($exit_menu_item) | Out-Null
}
function new-scriptblock([string]$textofscriptblock)
{
$executioncontext.InvokeCommand.NewScriptBlock($textofscriptblock)
}
function Build-ContextMenu {
param (
[int]$index = 0,
[string]$Text,
[string] $Action
)
begin
{
$menu_item = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.MenuItem
}
process
{
$ContextMenu = $_
}
end
{
$menu_item.Text = $Text
$scriptAction = $(new-scriptblock "Invoke-Item $Action")
$menu_item.add_Click($scriptAction)
$ContextMenu.MenuItems.Add($menu_item) | Out-Null
}
}
$notify_icon.Icon = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'sample.ico' )
$notify_icon.Text = 'Context Menu Test'
$notify_icon.ContextMenu = $context_menu
$f.ContextMenu = $context_menu
$notify_icon.Visible = $true
$f.Visible = $false
$f.WindowState = 'minimized'
$f.ShowInTaskbar = $false
$f.add_Closing({ $f.ShowInTaskBar = $False })
$context_menu.Add_Popup({Read-Config})
$f.ShowDialog()
})
function send_text {
Param (
[String] $title = 'script',
[String] $message,
[int] $timeout = 10 ,
[switch] $append
)
$so.NotifyIcon.ShowBalloonTip($timeout, $title , $message, [System.Windows.Forms.ToolTipIcon]::Info)
write-output -InputObject ( '{0}:{1}' -f $title, $message)
}
clear-host
$run_script.Runspace = $rs
$cnt = 0
$total = 4
$handle = $run_script.BeginInvoke()
start-sleep 1
send_text -title 'script' -message 'Starting...' -timeout 10
$so.ConfigFile = $build_log = ('{0}\{1}' -f $so.ScriptDirectory, 'build.log' )
set-Content -path $build_log -value ''
While (-Not $handle.IsCompleted -and $cnt -lt $total) {
start-sleep -Milliseconds 10000
$cnt ++
send_text -title 'script' -message ("Finished {0} of {1} items..." -f $cnt, $total ) -timeout 10
write-output ("Subtask {0} ..." -f $cnt ) | out-file -FilePath $build_log -Append -encoding ascii
}
$so.Form.Close()
$run_script.EndInvoke($handle) | out-null
$rs.Close()
write-output 'All finished'

Next example shows performing a Selenium WebDriver transaction from PowerShell. There is still a lot of code to add to this example, but the portion developed already is hopefully worth seeing. A simple transaction is chosen for illustration here. It was converted from the following MS Test example.
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using Microsoft.Activities.UnitTesting;
using Moq;
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Remote;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI;
using OpenQA.Selenium.IE;
using OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Safari;
namespace SeleniumTests
{
[TestClass]
public class SeleniumTest
{
private static IWebDriver driver;
private static StringBuilder verificationErrors = new StringBuilder();
private string baseURL;
private bool acceptNextAlert = true;
[ClassCleanup()]
public static void MyClassCleanup() {
try {
driver.Quit();
} catch (Exception) {
}
Assert.AreEqual("", verificationErrors.ToString());
}
[TestInitialize()]
public void MyTestInitialize()
{
driver = new SafariDriver();
Assert.IsNotNull(driver );
driver.Url = baseURL = "http://www.wikipedia.org";
driver.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait( TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10 )) ;
verificationErrors = new StringBuilder();
}
[TestCleanup()]
public void MyTestCleanup() {
}
[TestMethod]
public void Test()
{
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl(baseURL + "/");
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)) ;
IWebElement queryBox = driver.FindElement(By.Id("searchInput"));
queryBox.Clear();
queryBox.SendKeys("Selenium");
queryBox.SendKeys(Keys.ArrowDown);
queryBox.Submit();
driver.FindElement(By.LinkText("Selenium (software)")).Click();
Assert.IsTrue(driver.Title.IndexOf("Selenium (software)") > -1, driver.Title);
}
}
}
which in turn is essentially an MS Test decorated Selenium IDE recording.
The conversion to Powershell was made using similar approach as the rest of the examples in this article - mainly through consulting the API documents.
The script uses PhantomeJS Selenium driver for quick test run and a real Firefox browser for a thorough run.
All standard Selenium C# client API dlls are placed in the folder pointed to by SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH environment.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'Selenium.WebDriverBackedSelenium.dll',
'Moq.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | foreach-object { Unblock-File -Path $_ ; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
Naturally, if there is a business logic layer or DSL wrapping low level WebDriver calls, it can be compiled from C# into a standalone assembly DLL and made available to the PowerShell in much the same way
$testSuite = [System.Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName('${assembly_path}\BusinessTestSuite.dll')
$framework = [System.Reflection.Assembly]::ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(
'${assembly_path}\BusinessSpecificWebDriverFramework.dll')
To avoid copying the Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll but load from where it is installed on the machine, and make the familiar assertion calls available in the script, the following code performs a quick discovery. For simplicity just the Microsoft Test Agent InstallLocation registry key scan is shown, additional keys need to be tried, note that Visual Studio Express Edition does not install this dll, while the Enterprize installs several copies.
function read_registry{
param ([string] $registry_path,
[string] $package_name
)
pushd HKLM:
cd -path $registry_path
$settings = get-childitem -Path . | where-object { $_.Property -ne $null } | where-object {$_.name -match $package_name } | select-object -first 1
$values = $settings.GetValueNames()
if ( -not ($values.GetType().BaseType.Name -match 'Array' ) ) {
throw 'Unexpected result type'
}
$result = $null
$values | where-object {$_ -match 'InstallLocation'} | foreach-object {$result = $settings.GetValue($_).ToString() ; write-debug $result}
popd
$result
}
$shared_assemblies = @(
'Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = ( "{0}\{1}" -f ( read_registry -registry_path '/HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SOFTWARE/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Uninstall' -package_name '{6088FCFB-2FA4-3C74-A1D1-F687C5F14A0D}' ) , 'Common7\IDE\PublicAssemblies' )
$shared_assemblies_path =
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | foreach-object { Unblock-File -Path $_ ; Add-Type -Path $_ }
popd
[Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting.Assert]::AreEqual("true", (@('true','false') | select-object -first 1) )
Based on switch, the script initializes either phantom or real browser driver ...
if ($PSBoundParameters['browser']) {
Try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect('127.0.0.1',4444)
$connection.Close()
}
catch {
$selemium_driver_folder = 'c:\java\selenium'
start-process -filepath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -argumentlist "start cmd.exe /c ${selemium_driver_folder}\hub.cmd"
start-process -filepath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -argumentlist "start cmd.exe /c ${selemium_driver_folder}\node.cmd"
start-sleep 10
}
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
$uri = [System.Uri]('http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub')
$driver = new-object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver($uri , $capability)
} else {
$phantomjs_executable_folder = 'C:\tools\phantomjs'
$driver = new-object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$driver.Capabilities.SetCapability('ssl-protocol', 'any' );
$driver.Capabilities.SetCapability('ignore-ssl-errors', $true);
$driver.capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot", $false );
$driver.capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent",
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
}
There is no need to explicitly start PhantomJS driver.
Finally, the test begins (the implementations of Get-ScriptDirectory and Assert are not shown and can be found in the attached source zip and author's github repo).
[void]$driver.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait( [System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(10 ))
[string]$baseURL = $driver.Url = 'http://www.wikipedia.org';
$driver.Navigate().GoToUrl(('{0}/' -f $baseURL ))
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$queryBox = $driver.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id('searchInput'))
$queryBox.Clear()
$queryBox.SendKeys('Selenium')
$queryBox.SendKeys([OpenQA.Selenium.Keys]::ArrowDown)
$queryBox.Submit()
$driver.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::LinkText('Selenium (software)')).Click()
$title = $driver.Title
assert -Script { ($title.IndexOf('Selenium (software)') -gt -1 ) } -message $title
Pretending that the test failed, the script navigates to the URL identifying the browser and takes a screenshot.
$driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("https://www.whatismybrowser.com/")
[OpenQA.Selenium.Screenshot]$screenshot = $driver.GetScreenshot()
$screenshot_path = $env:SCREENSHOT_PATH
$screenshot.SaveAsFile(('{0}\{1}' -f $screenshot_path, 'a.png' ), [System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat]::Png)

and finishes the test run.
try {
$driver.Quit()
} catch [Exception] {
}
One would possibly introduce a separate script via proper CreateRunspace call and develop Synchronized object to allow controlling the invocation of $driver.GetScreenshot call when some test fails, from a separate Powershell runspace connected to main script (this is currently work in progress) in a similar way the System Tray Notification icon has controlled in an earlier example.
The Selenium RC version of the script would be loading different libraries and switch to Nunit library Asserts.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'ThoughtWorks.Selenium.Core.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
and invoke different methods:
$verificationErrors = new-object System.Text.StringBuilder
$selenium = new-object Selenium.DefaultSelenium('localhost', 4444, '*firefox', 'http://www.wikipedia.org/')
$selenium.Start()
$selenium.Open('/')
$selenium.Click('css=strong')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
$selenium.Type('id=searchInput', 'selenium')
$selenium.Click('id=searchButton')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
$selenium.Click('link=Selenium (software)')
$selenium.WaitForPageToLoad('30000')
the rest of the script will be unchanged.

Naturally one can craft script directly in Powershell ISE which would save a lt of developer time.

To work with laterst version of Firefox (e.g. 33) one needs ensure the specific versions of Selenium C# libraries are loaded - similar version check is important for Nunit to access StringAssert:
$shared_assemblies = @{
'WebDriver.dll' = 2.44;
'WebDriver.Support.dll' = '2.44';
'nunit.core.dll' = $null;
'nunit.framework.dll' = '2.6.3';
}
$shared_assemblies.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
$assembly_path = [System.IO.Path]::Combine($shared_assemblies_path,$assembly)
$assembly_version = [Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName($assembly_path).Version
$assembly_version_string = ('{0}.{1}' -f $assembly_version.Major,$assembly_version.Minor)
if ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -ne $null) {
if (-not ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -match $assembly_version_string)) {
Write-Output ('Need {0} {1}, got {2}' -f $assembly,$shared_assemblies[$assembly],$assembly_path)
Write-Output $assembly_version
throw ('invalid version :{0}' -f $assembly)
}
}
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
One very promising potential enhancement is related to handling File download dialogs or multi-option Internet Explorer Alert popups. These not well supported by pure Selenium. Either a separate tool like Autoit is to be bundled in the test framework or one of many workarounds need to be adopted - the latter option sometimes feels somewhat quirky.
When the Selenium test is executed by Powershell, one may incorporate the class that invokes win32 API from C# and uses EnumWindows, GetWindowInfo, EnumPropsEx, GetProp, GetWindowText, GetWindowTextLength, GetWindowThreadProcessId win32 API from user32.dll via [DllImport()] and loads numerous necessary structures defined in Windows.h to access the window handle and invoke PostMessage or SendMessage on desired button or simply CloseWindow on the Alert / File Download dialog found by title. The latter would cause one test to fail but will prevent the entire test suite from hanging after browser loses the mouse focus. This is explained in several resources in the web.
and " save="" as"="" dialog="" is="" closed="" by="" sending="" it="" a="" WM_CLOSE Windows message.
With a little more P/invoke
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern Int32 SendMessage(IntPtr hwnd, UInt32 Msg, IntPtr wParam, [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStr)] string lParam);
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.SysUInt)]
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, SetLastError = false)]
static extern IntPtr SendMessage(IntPtr hWnd, UInt32 Msg, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam);
[DllImport("user32.dll", SetLastError = true, CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
static extern int GetClassName(IntPtr hWnd, StringBuilder lpClassName, int nMaxCount);
public static string GetText(IntPtr hWnd)
{
int length = GetWindowTextLength(hWnd);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(length + 1);
GetWindowText(hWnd, sb, sb.Capacity);
return sb.ToString();
}
private static string GetWindowClassName(IntPtr hWnd)
{
int nRet;
StringBuilder ClassName = new StringBuilder(256);
nRet = GetClassName(hWnd, ClassName, ClassName.Capacity);
return (nRet != 0) ? ClassName.ToString() : null;
}
public static void SetText(IntPtr hWnd, String text)
{
UInt32 WM_SETTEXT = 0x000C;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(text);
int result = SendMessage(hWnd, WM_SETTEXT, (IntPtr)sb.Length, (String)sb.ToString());
}
one may locate the elements of the dialog and enter some text into file name text box and send a buttonclick to save as button.
private static bool EnumWindow(IntPtr handle, IntPtr pointer)
{
GCHandle gch = GCHandle.FromIntPtr(pointer);
String window_class_name = GetWindowClassName(handle);
if (string.Compare(window_class_name, "Edit", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0 ) {
const UInt32 WM_CHAR = 0x0102;
const UInt32 WM_KEYDOWN = 0x0100;
const UInt32 WM_KEYUP = 0x0101;
const UInt32 VK_RETURN = 0x0D;
SendMessage(handle, WM_CHAR, new IntPtr(WM_KEYDOWN), IntPtr.Zero);
SetText(handle, @"c:\temp\my random filename");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
SendMessage(handle, WM_CHAR, new IntPtr(VK_RETURN), IntPtr.Zero);
}
if (string.Compare(window_class_name, "Button", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0 ) {
string button_text = GetText(handle);
if (string.Compare(button_text, "&Save", true, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture) == 0) {
SetText(handle, "About to click");
const UInt32 BM_CLICK = 0x00F5;
Thread.Sleep(1000);
SendMessage(handle, BM_CLICK, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero);
}
}
List<IntPtr> list = gch.Target as List<IntPtr>;
if (list == null)
throw new InvalidCastException("cast exception");
list.Add(handle);
return true;
}

Note that without sending the "Enter" key the Windows Explorer would have ignored the text entered behind the scene and saved the file in the original location / name.

The modified code is provided in the archive. With minimal effort one has the class integrated with PowerShell, but extending the example to be really useful is more work and somewhat beyond the scope of this article.
Another interesting possible scenario is when the target web site is hosted on Tomcat running on Linux host but the Internet Explorer integration tests are required to run. With the following boilerplate Perl code snippet, one would be able to launch the PowerShell script remotely through ssh: cygwin, TeamCity, Jenkins, etc.
use Net::SSH::Perl;
use Data::Dumper;
use constant DEBUG => 0;
our ($HOSTNAME, $USER, $PASSWORD );
my $POWERSHELL_SCRIPT = ...
$HOSTNAME = '192.168.56.102';
$USER = 'cyg_server';
$PASSWORD = 'cyg_server';
my $ssh_command =
"cat /dev/null|\
/cygdrive/c/Windows/system32/WindowsPowerShell/v1.0/powershell.exe \
-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -command \"&{ $POWERSHELL_SCRIPT }\"";
print STDERR $ssh_command if (DEBUG) ;
my $ssh = Net::SSH::Perl->new( $HOSTNAME, debug => 0 );
$ssh->login( $USER, $PASSWORD );
my ( $stdout, $stderr, $exitcode ) = $ssh->cmd( $ssh_command, undef );
print STDERR Dumper \[ $stdout, $stderr, $exitcode ];
1;
END
This clearly is not necessary with Selenium grid test script, but may be used for other situations.
For example by running the following textbook Powershell script through ssh
Import-module WebAdministration
$WebSiteAlias = 'Test'
$AppPoolAlias = 'Test'
pushd 'IIS:\Sites\Default Web Site'
$IISPath = "..\$WebSiteAlias"
if (Test-Path $IISPath) {
Write-Host "Web Site '$WebSiteAlias' exists."
}
$IISPath = "IIS:\AppPools"
cd $IISPath
if (Test-Path ".$AppPoolAlias") {
Write-Host "Application Pool '$AppPoolAlias' exists."
}
The result will be available to a caller script...

This is useful when the business runs a mixed Tomcat / IIS web sites, and for some reason deployment has to be orchestrated from Linux machine. In this case, more complex Powershell code will be user for, e.g. performing some app pools checks, invoking msdeploy.exe, followed by the business-specific web sites "priming", from Linux
The following Selenium automation script fragment selects the Carribbean honeymoon vacation cruise from one of cruise vendors. The code for selecting Destination, Date range and Number of Travelers is quite redundant and is shown only partially. The full working script is available in the zip.
$value1 = 'dest'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'Select a destination' ))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = 'C'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$value1 = 'dat'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'Select a date'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = '"022015"'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$value1 = 'numGuests'
$css_selector1 = ('a[data-param={0}]' -f $value1)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'How many travelers'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 1
$value2 = '"2"'
$css_selector2 = ('a[data-id={0}]' -f $value2)
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 150
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2)))
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element2 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector2))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element2.Text)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions2 = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
$actions2.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element2).Build().Perform()
$actions2.Click().Build().Perform()
Start-Sleep 3
$css_selector1 = 'div.actions > a.search'
try {
[void]$selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception : {0} ...`n" -f (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
$element1 = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector1))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($element1.Text -match 'SEARCH'))
Write-Output ('Clicking on ' + $element1.Text)
$element1.Click()
Start-Sleep 10
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.Screenshot]$screenshot = $selenium.GetScreenshot()
$guid = [guid]::NewGuid()
$image_name = ($guid.ToString())
[string]$image_path = ('{0}\{1}\{2}.{3}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),'temp',$image_name,'.jpg')
$screenshot.SaveAsFile($image_path,[System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat]::Jpeg)
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output $_.Exception.Message
}
try {
$selenium.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
}

The script can successfully replay in any browser except IE 11. The following code selects the browser:
param(
[string]$browser,
[int]$version
)
...
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect("127.0.0.1",4444)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd"
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}"
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
if ($version -ne $null -and $version -ne 0) {
$capability.SetCapability("version", $version.ToString());
}
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$uri = [System.Uri]("http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub")
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs'
...
When executed the script prints minimal breadcrumps indicating actions taken.
The following example translates a text on www.freetranslation.com. The page contains the following fragment:

<div class="gw-upload-action clearfix">
<div id="upload-button" class="btn"><img class="gw-icon upload" alt="" src="http://d2yxcfsf8zdogl.cloudfront.net/home-php/assets/home/img/pixel.gif"/>
Choose File(s)
<div class="ajaxupload-wrapper" style="width: 300px; height: 50px;"><input class="ajaxupload-input" type="file" name="file" multiple=""/></div>
</div>
</div>
The scripts writes text to a file and uploads it:
[void]$selenium.Manage().timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(60))
$base_url = 'http://www.freetranslation.com/'
$text_file = ('{0}\{1}' -f (Get-ScriptDirectory),'testfile.txt')
Write-Output 'good morning driver' | Out-File -FilePath $text_file -Encoding ascii
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
$selenium.Manage().Window.Maximize()
$upload_element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::ClassName('ajaxupload-input'))
$upload_element.SendKeys($text_file)
then waits until the following element is present:

<a href="..." class="gw-download-link">
<img class="gw-icon download" src="http://d2yxcfsf8zdogl.cloudfront.net/home-php/assets/home/img/pixel.gif"/>
Download
</a>
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(3))
$wait.PollingInterval = 100
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element1 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::ClassName("gw-download-link")))
[OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebElement]$element2 = $wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector('img.gw-icon')))
$text_url = $element1.getAttribute('href')
and downloads the results:
$result = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $text_url
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue(($result.RawContent -match 'Bonjour pilote'))
and verifies the result against a known translation.
Next, one would exclude C# from the pipeline and record Powershell transaction directly in Selenium IDE. Custom formatting is fully supported; one does not need to bother with packaging the xpi at the early development phase.
To proceed, author forks one of the existing repositories, by David Zwarg and modifies the C# formatter to follow Powershell syntax and do other necessary adjustments. All that is needed to create formatter is one file.

One thing to be careful is not to start with Selenium Remote Control - based plugins: The RC plugin can be developed but protocol is outdated and in particular no headless drivers is available.
The full JavaScript source of the formatter is not displayed here yet: it is an alpha-quality design, with pull request pending. Conversion between IDE commands, intermediate JavaScript method prototypes and final C# method calls is quite a pain.
The source is available on the author's github repo.
The plugin inherits from the webdriver.js,
if (!this.formatterType) {
var subScriptLoader = Components.classes['@mozilla.org/moz/jssubscript-loader;1'].getService(Components.interfaces.mozIJSSubScriptLoader);
subScriptLoader.loadSubScript('chrome://selenium-ide/content/formats/webdriver.js', this);
}
and currently adds minimal functionality of its own - currently there exist quite a few formatters with nearly identical code.
The modifications consists of providing full class paths in all method references, e.g.
WDAPI.Utils.isElementPresent = function(how, what) {
return "IsElementPresent(" + WDAPI.Driver.searchContext(how, what) + ")";
};
becomes:
WDAPI.Utils.isElementPresent = function(how, what) {
return '[Selenium.Internal.SeleniumEmulation]::IsElementPresent(' + WDAPI.Driver.searchContext(how, what) + ')';
};
and tweaking semantics, e.g:
Equals.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.e1.toString() + ' == ' + this.e2.toString() ;
}
becomes:
Equals.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.e1.toString() + ' -eq ' + this.e2.toString();
};
It looks natural to use Nunit.dll however accessing the StringAssert appears to be a little problematic, thus one may choose to use Microsoft.VisualStudio.QualityTools.UnitTestFramework.dll as shown earlier
All Powershell initialization code from the earlier example goes into header option of the driver class:
this.options = {
receiver: '$selenium',
base_url: 'http://docs.seleniumhq.org/docs/02_selenium_ide.jsp',
driver_namespace: "OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox",
driver_capabilities: "Firefox()",
showSelenese: 'false',
indent: '4',
initialIndents: '3',
header:
'Param (\n'+
indents(1) + '[switch] $browser\n'+
')\n'
'$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::${driver_capabilities}\n' +
footer:
'# Cleanup\n' +
'try {\n' +
indents(1) + '$selenium.Quit()\n' +
'} catch [Exception] {\n' +
indents(1) + '# Ignore errors if unable to close the browser\n' +
'}\n',
defaultExtension: 'ps1'
};
Key properties converted into regular formatter Inputs:
this.configForm =
'<description>Selenium instance name</description>' +
'<textbox id="options_receiver" />' +
'<description>WebDriver Capabilities</description>' +
'<menulist id="options_driver_capabilities"><menupopup>' +
'<menuitem label="Firefox" value="Firefox()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Google Chrome" value="Chrome()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Safari" value="Safari()"/>' +
'<menuitem label="Internet Explorer" value="InternetExplorer()"/>' +
'</menupopup></menulist>'+

At the later stage of the development, one will arrange the sources as appropriate for xpi and craft the chrome.manifest, install.rdf and format-loader.xul, e.g.
="1.0"
="chrome://global/skin/"="text/css"
<overlay id="webdriver_format_loader_overlay"
xmlns="http://www.mozilla.org/keymaster/gatekeeper/there.is.only.xul"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<script type="application/x-javascript" src="chrome://selenium-ide/content/api.js"/>
<html:script type="application/javascript">
var ide_api = new API();
ide_api.addPlugin("powershell-webdriver-formatter@serguei.kouzmine");
ide_api.addPluginProvidedFormatter("powershell-webdriver", "Powershell - WebDriver", "chrome://powershell-webdriver-formatter/content/formats/powershell-webdriver.js");
ide_api.addPluginProvidedFormatter("powershell-remotecontrol", "Powershell - RC", "chrome://powershell-webdriver-formatter/content/formats/powershell-remotecontrol.js");
</html:script>
</overlay>
This enables packaging into standalone Firefox Add-On via simple batch command (or equivalent bash script)
@echo off
setlocal
pushd %~dp0
set APP_NAME="powershell-webdriver-formatter"
set CHROME_PROVIDERS="content"
set ROOT_DIR=%CD%
set TMP_DIR="build"
del /Q %APP_NAME%.xpi
del /S /Q %TMP_DIR%
mkdir %TMP_DIR%\chrome\content
robocopy.exe content %TMP_DIR%\chrome\content /E
robocopy.exe locale %TMP_DIR%\chrome\locale /E
robocopy.exe skin %TMP_DIR%\chrome\skin /E
robocopy.exe defaults %TMP_DIR%\defaults /E
copy install.rdf %TMP_DIR%
copy chrome.manifest.production %TMP_DIR%\chrome.manifest
cd %TMP_DIR%
echo "Generating %APP_NAME%.xpi..."
PATH=%PATH%;%ProgramFiles%\7-Zip;%ProgramFiles(x86)%\7-Zip
7z.exe a -r -y -tzip ../%APP_NAME%.zip *
cd %ROOT_DIR%
rename %APP_NAME%.zip %APP_NAME%.xpi
endlocal

To use the formatter,
- Open Selenium IDE, record the transaction
- Select Options from the Options menu
- Select the "Formats" tab
- Fill the inputs if the formatter xpi was loaded or
- Click on the "Add" button
- Name the format
- Paste and save the Javascript source (losing the inputs)
- In the "File" "Export Test Case as..." select the format
If everything is done right, the generated Powershell script will need no modifications and can be run right away.
For example, in the following fragment, after loading the required assemblies and launching the Selenium, draws a border around the Google logo by executing a Javascript code in the context of the loaded page, through Selenium.
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl('http://www.google.com')
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement] $element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id("hplogo"))[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);", $element, "color: yellow; border: 4px solid yellow;")
start-sleep 3
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);", $element, '')

Clearly the Javascript is the only part that matters here. Sacrificing the overhead of C# project seems to be appropriate.
Another possible examle would execute $selenium.Manage().Timeouts().setScriptTimeout and [OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteAsyncScript followed by $selenium.FindElement to either "stamp" the build information into the page or, instead perform checks and store the answer into a dynamically appended div element and communicate the assertion results back to the script (work in progress).
Small-time development activities e.g. standard CI post-deployment web site "warm-up" are also likely to be easier through Selenium IDE with subsequent launch from Powershell rather then via coding a separate application.
The following example combines code from Hosting And Changing Controls In Other Applicationswith a typical Selenium transaction (this one involving frames). Some web sites are really coded to be sensitive to mouse hover events. This example shows debugging the transaction in the situation when additional monitor is not available e.g. in VirtualBox, and the browser is maximized to fill the screen leaving no room to trace the execution.
The code from Hosting And Changing Controls In Other Applications responsible for adding an extra control to already running window, is used without modifications, but some changes being planned, one keeps the source together with the script rather than compiling it into an assembly
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
namespace System.Windows
{
class Win32WindowEvents
{
//...
public static class WinAPI
{
//...
public static class Win32ControlType
{
public static string Button = "Button";
//...
///
The goal is to stock the Windows control on a TaskBar
function custom_debug {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$local:button_ref,
[string]$message
)
Write-Debug $message
$local:button = $local:button_ref.Value
if ($local:button -eq $null) {
$exlorer_window = [System.Windows.Win32Window]::FromProcessName('explorer')
$exlorer_window.Title = "A control WINDOW";
$local:button = New-Object System.Windows.Win32Button
$local:button.TopMost = $true
$local:button.Width = 600
$local:button.Height = 60
$x = ($exlorer_window.Position.Right - $local:button.Width)
$y = -20
$local:button.Pos_X = $x
$local:button.Pos_Y = $y
$local:button.Font = New-Object System.Drawing.Font ('Microsoft Sans Serif',7,[System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular,[System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point,0)
$exlorer_window.AddControl($local:button)
$local:button_ref.Value = $local:button
}
$local:button.Text = $message
}

This button is used to display debugging messages and (WIP) pause the execution of the script.
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($host.Version.Major -gt 2)
$hub_host = '127.0.0.1'
$hub_port = '4444'
$uri = [System.Uri](('http://{0}:{1}/wd/hub' -f $hub_host,$hub_port))
[object]$button = $null
custom_debug ([ref]$button) 'Starting firefox'
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect($hub_host,[int]$hub_port)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -ArgumentList 'start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd'
Start-Process -FilePath 'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' -ArgumentList 'start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd'
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}"
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "c:\tools\phantomjs"
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs'
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver ($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ssl-protocol","any")
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ignore-ssl-errors",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent","Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
$options = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSOptions
$options.AddAdditionalCapability("phantomjs.executable.path",$phantomjs_executable_folder)
}
[void]$selenium.Manage().timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(60))
$selenium.url = $base_url = 'http://translation2.paralink.com'
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl(($base_url + '/'))
[string]$xpath = "//frame[@id='topfr']"
[object]$top_frame = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$selenium) ([ref]$top_frame) $xpath
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame($top_frame)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newtop.asp'),$current_frame.url)
Write-Debug ('Switched to {0} {1}' -f $current_frame.url,$xpath)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0} {1}' -f $current_frame.url,$xpath)
$top_frame = $null
[string]$text = 'Spanish-Russian translation'
$css_selector = 'select#directions > option[value="es/ru"]'
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_css_selector ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $css_selector
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($text,$element.Text,$element.Text)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('selected "{0}"' -f $text)
$element.Click()
$element = $null
custom_pause
[string]$xpath2 = "//textarea[@id='source']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $xpath2
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($current_frame)
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
$text = @"
Yo, Juan Gallo de Andrada, escribano de C?mara del Rey nuestro se?or, de los que residen en su Consejo, certifico y doy fe que, habiendo visto por los se?ores d?l un libro intitulado El ingenioso hidalgo de la Mancha, compuesto por Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra, tasaron cada pliego del dicho libro a tres maraved?s y medio; el cual tiene ochenta y tres pliegos, que al dicho precio monta el dicho libro docientos y noventa maraved?s y medio, en que se ha de vender en papel;.
"@
[void]$element.SendKeys($text)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Entered "{0}"' -f $text.Substring(0,100))
$element = $null
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 1000
$css_selector = 'img[src*="btn-en-tran.gif"]'
$title = 'Translate'
find_page_element_by_css_selector ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $css_selector
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($title,$element.GetAttribute('title'),$element.GetAttribute('title'))
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($current_frame)
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Clicked on "{0}"' -f $title)
$element = $null
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
[string]$xpath = "//frame[@id='botfr']"
[object]$bot_frame = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$selenium) ([ref]$bot_frame) $xpath
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame($bot_frame)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newbot.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0}' -f $current_frame.url)
$bot_frame = $null
[string]$xpath2 = "//textarea[@id='target']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $null
find_page_element_by_xpath ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element) $xpath2
highlight ([ref]$current_frame) ([ref]$element)
$text = $element.Text
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Read "{0}"' -f $text.Substring(0,100))
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame(1)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newbot.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
$current_frame = $selenium.SwitchTo().Frame(0)
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::AreEqual($current_frame.url,('{0}/{1}' -f $base_url,'newtop.asp'),$current_frame.url)
custom_debug ([ref]$button) ('Switched to {0}' -f $current_frame.url)
custom_pause
[void]$selenium.SwitchTo().DefaultContent()
Write-Debug ('Switched to {0}' -f $selenium.url)
cleanup ([ref]$selenium)
$button.Visible = $false

The full source is available in the zip.
The following is a quick example of SeleniumEventFiringWebDriver access from Powershell. One captures the result of an Ajax auto-suggestion by running code after Selenium events
param(
[string]$browser = 'firefox',
[int]$event_delay = 250,
[switch]$pause
)
function netstat_check
{
param(
[string]$selenium_http_port = 4444
)
$results = Invoke-Expression -Command "netsh interface ipv4 show tcpconnections"
$t = $results -split "`r`n" | Where-Object { ($_ -match "\s$selenium_http_port\s") }
(($t -ne '') -and $t -ne $null)
}
function cleanup
{
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref
)
try {
$selenium_ref.Value.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0]
}
}
$shared_assemblies = @(
'WebDriver.dll',
'WebDriver.Support.dll',
'nunit.core.dll',
'nunit.framework.dll'
)
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies | ForEach-Object {
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "C:\tools\phantomjs"
if ($browser -ne $null -and $browser -ne '') {
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect("127.0.0.1",4444)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\hub.cmd"
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\node.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 10
}
Write-Host "Running on ${browser}" -foreground 'Yellow'
if ($browser -match 'firefox') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Firefox()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'chrome') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Chrome()
}
elseif ($browser -match 'ie') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::InternetExplorer()
if ($version -ne $null -and $version -ne 0) {
$capability.SetCapability("version",$version.ToString());
}
}
elseif ($browser -match 'safari') {
$capability = [OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.DesiredCapabilities]::Safari()
}
else {
throw "unknown browser choice:${browser}"
}
$uri = [System.Uri]("http://127.0.0.1:4444/wd/hub")
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Remote.RemoteWebDriver ($uri,$capability)
} else {
Write-Host 'Running on phantomjs' -foreground 'Yellow'
$phantomjs_executable_folder = "C:\tools\phantomjs"
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSDriver ($phantomjs_executable_folder)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ssl-protocol","any")
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("ignore-ssl-errors",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("takesScreenshot",$true)
$selenium.Capabilities.SetCapability("userAgent","Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/534.34 (KHTML, like Gecko) PhantomJS/1.9.7 Safari/534.34")
$options = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.PhantomJS.PhantomJSOptions
$options.AddAdditionalCapability("phantomjs.executable.path",$phantomjs_executable_folder)
}
if ($host.Version.Major -le 2) {
[void][System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('System.Windows.Forms')
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size (600,400)
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = New-Object System.Drawing.Point (0,0)
} else {
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = @{ 'Height' = 400; 'Width' = 600; }
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = @{ 'X' = 0; 'Y' = 0 }
}
$window_position = $selenium.Manage().Window.Position
$window_size = $selenium.Manage().Window.Size
$base_url = 'http://www.google.com/'
$event = New-Object -Type 'OpenQA.Selenium.Support.Events.EventFiringWebDriver' -ArgumentList @( $selenium)
$element_value_changing_handler = $event.add_ElementValueChanging
$element_value_changing_handler.Invoke(
{
param(
[object]$sender,
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.Events.WebElementEventArgs]$eventargs
)
Write-Host 'Value Change handler' -foreground 'Yellow'
if ($eventargs.Element.GetAttribute('id') -eq 'gbqfq') {
$xpath1 = "//div[@class='sbsb_a']"
try {
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$local:element = $sender.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath1))
} catch [exception]{
}
Write-Host $local:element.Text -foreground 'Blue'
}
})
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$base_url = 'http://www.google.com'
$event.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($event,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(10))
$wait.PollingInterval = 50
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::Id("hplogo")))
$xpath = "//input[@id='gbqfq']"
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $event.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath))
$element.SendKeys('Sele')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys('nium')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' webdriver')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' C#')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys(' tutorial')
Start-Sleep -Millisecond $event_delay
$element.SendKeys([OpenQA.Selenium.Keys]::Enter)
Start-Sleep 10
cleanup ([ref]$event)

One can port the Console Monitor from c# to Powershell to periodically collect desktop screen shots on the grid computer as needed by some Continuous Integration build automation
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
public class WindowHelper
{
private int _count = 0;
public int Count
{
get { return _count; }
set { _count = value; }
}
public String TakeScreenshot()
{
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Width, Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Height);
Graphics gr = Graphics.FromImage(bmp);
gr.CopyFromScreen(0, 0, 0, 0, bmp.Size);
string str = string.Format(@"C:\temp\Snap[{0}].jpeg", _count);
bmp.Save(str, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
bmp.Dispose();
gr.Dispose();
return str;
}
public WindowHelper()
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
$timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
[int32]$max_iterations = 20
[int32]$iteration = 0
$action = {
Write-Host "Iteration # ${iteration}"
Write-Host "Timer Elapse Event: $(get-date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')"
$owner = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$owner.count = $iteration
$owner.Screenshot()
$iteration++
if ($iteration -ge $max_iterations)
{
Write-Host 'Stopping'
$timer.stop()
Unregister-Event thetimer -Force
Write-Host 'Completed'
}
}
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action
Note that one ca not pass the data by reference to the script function called from the timer event and hence one can not execute the Add-Type remotely
$action = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference] $ref_screen_grabber
)
[Win32Window]$screen_grabber = $ref_screen_grabber.Value
followed by
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action -MessageData ([ref]$owner )
will break. Debugging this further is Work in progress
To toggle the Powershell console window minimize when the form is displayed, one can use the following code:
Add-Type -Name Window -Namespace Console -MemberDefinition @"
// "
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll")]
public static extern IntPtr GetConsoleWindow();
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
public static extern bool ShowWindow(IntPtr hWnd, Int32 nCmdShow);
"@
One can port the Console Monitor from c# to Powershell to periodically collect desktop screen shots on the grid computer as needed by some Continuous Integration build automation
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
public class WindowHelper
{
private int _count = 0;
public int Count
{
get { return _count; }
set { _count = value; }
}
public String TakeScreenshot()
{
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Width, Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Height);
Graphics gr = Graphics.FromImage(bmp);
gr.CopyFromScreen(0, 0, 0, 0, bmp.Size);
string str = string.Format(@"C:\temp\Snap[{0}].jpeg", _count);
bmp.Save(str, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
bmp.Dispose();
gr.Dispose();
return str;
}
public WindowHelper()
{
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll','System.Drawing.dll','System.Data.dll'
$timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
[int32]$max_iterations = 20
[int32]$iteration = 0
$action = {
Write-Host "Iteration # ${iteration}"
Write-Host "Timer Elapse Event: $(get-date -Format 'HH:mm:ss')"
$owner = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
$owner.count = $iteration
$owner.Screenshot()
$iteration++
if ($iteration -ge $max_iterations)
{
Write-Host 'Stopping'
$timer.stop()
Unregister-Event thetimer -Force
Write-Host 'Completed'
}
}
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action
Note that one ca not pass the data by reference to the script function called from the timer event and hence one can not execute the Add-Type remotely
$action = {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference] $ref_screen_grabber
)
[Win32Window]$screen_grabber = $ref_screen_grabber.Value
followed by
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $timer -EventName elapsed -SourceIdentifier thetimer -Action $action -MessageData ([ref]$owner )
will break. Debugging this further is Work in progress
[void] [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("System.Windows.Forms")
$Form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$showButton = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$showButton.Text = 'ShowConsole'
$showButton.Top = 10
$showButton.Left = 10
$showButton.Width = 100
$showButton.add_Click({Show-Console})
$form.controls.Add($showButton)
$hideButton = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$hideButton.Text = 'HideConsole'
$hideButton.Top = 60
$hideButton.Left = 10
$hideButton.Width = 100
$hideButton.add_Click({hide-Console})
$form.controls.Add($hideButton)
$Form.ShowDialog()

The functions operate constants from winuser.h
function Show-Console {
$consolePtr = [Console.Window]::GetConsoleWindow()
[Console.Window]::ShowWindow($consolePtr, 5)
}
function Hide-Console {
$consolePtr = [Console.Window]::GetConsoleWindow()
[Console.Window]::ShowWindow($consolePtr, 0)
}

One can find it convenient to use Poweshell ISE together with Firebug or other Browser-hosted Developer tool to craft the actual scrtipt:
param(
[string]$hub_host = '127.0.0.1',
[string]$browser,
[string]$version,
[string]$profile = 'Selenium',
[switch]$pause = $true
)
function set_timeouts {
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref,
[int]$explicit = 120,
[int]$page_load = 600,
[int]$script = 3000
)
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitlyWait([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($explicit)))
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().SetPageLoadTimeout([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($pageload)))
[void]($selenium_ref.Value.Manage().Timeouts().SetScriptTimeout([System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds($script)))
}
function Get-ScriptDirectory
{
$Invocation = (Get-Variable MyInvocation -Scope 1).Value
if ($Invocation.PSScriptRoot) {
$Invocation.PSScriptRoot
}
elseif ($Invocation.MyCommand.Path) {
Split-Path $Invocation.MyCommand.Path
} else {
$Invocation.InvocationName.Substring(0,$Invocation.InvocationName.LastIndexOf(""))
}
}
function cleanup
{
param(
[System.Management.Automation.PSReference]$selenium_ref
)
try {
$selenium_ref.Value.Quit()
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output (($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0]
}
}
$shared_assemblies = @{
'WebDriver.dll' = 2.44;
'WebDriver.Support.dll' = '2.44';
'nunit.core.dll' = $null;
'nunit.framework.dll' = '2.6.3';
}
$shared_assemblies_path = 'c:\developer\sergueik\csharp\SharedAssemblies'
if (($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne $null) -and ($env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH -ne '')) {
$shared_assemblies_path = $env:SHARED_ASSEMBLIES_PATH
}
pushd $shared_assemblies_path
$shared_assemblies.Keys | ForEach-Object {
$assembly = $_
$assembly_path = [System.IO.Path]::Combine($shared_assemblies_path,$assembly)
$assembly_version = [Reflection.AssemblyName]::GetAssemblyName($assembly_path).Version
$assembly_version_string = ('{0}.{1}' -f $assembly_version.Major,$assembly_version.Minor)
if ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -ne $null) {
if (-not ($shared_assemblies[$assembly] -match $assembly_version_string)) {
Write-Output ('Need {0} {1}, got {2}' -f $assembly,$shared_assemblies[$assembly],$assembly_path)
Write-Output $assembly_version
throw ('invalid version :{0}' -f $assembly)
}
}
if ($host.Version.Major -gt 2) {
Unblock-File -Path $_;
}
Write-Debug $_
Add-Type -Path $_
}
popd
$verificationErrors = New-Object System.Text.StringBuilder
$hub_port = '4444'
$uri = [System.Uri](('http://{0}:{1}/wd/hub' -f $hub_host,$hub_port))
try {
$connection = (New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient)
$connection.Connect($hub_host,[int]$hub_port)
$connection.Close()
} catch {
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" -ArgumentList "start cmd.exe /c c:\java\selenium\selenium.cmd"
Start-Sleep -Seconds 3
}
[object]$profile_manager = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfileManager
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile]$selected_profile_object = $profile_manager.GetProfile($profile)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile]$selected_profile_object = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile ($profile)
$selected_profile_object.setPreference('general.useragent.override','Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 3_0 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/528.18 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0 Mobile/7A341 Safari/528.16')
$selenium = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxDriver ($selected_profile_object)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox.FirefoxProfile[]]$profiles = $profile_manager.ExistingProfiles
$DebugPreference = 'Continue'
$base_url = 'http://www.codeproject.com/'
$selenium.Manage().Window.Size = @{ 'Height' = 600; 'Width' = 480; }
$selenium.Manage().Window.Position = @{ 'X' = 0; 'Y' = 0 }
$selenium.Navigate().GoToUrl($base_url)
set_timeouts ([ref]$selenium)
$css_selector = 'span.member-signin'
Write-Debug ('Trying CSS Selector "{0}"' -f $css_selector)
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(1))
try {
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementExists([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector)))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception with {0}: {1} ...`n(ignored)" -f $id1,(($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
Write-Debug ('Found via CSS Selector "{0}"' -f $css_selector )
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::CssSelector($css_selector))
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);",$element,'border: 2px solid red;')
Start-Sleep 3
[OpenQA.Selenium.IJavaScriptExecutor]$selenium.ExecuteScript("arguments[0].setAttribute('style', arguments[1]);",$element,'')
[OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions]$actions = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Interactions.Actions ($selenium)
try {
$actions.MoveToElement([OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element).Click().Build().Perform()
} catch [OpenQA.Selenium.WebDriverTimeoutException]{
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($_.Exception.Message -match '(?:Timed out waiting for page load.)')
}
$input_name = 'ctl01$MC$MemberLogOn$CurrentEmail'
[OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait]$wait = New-Object OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.WebDriverWait ($selenium,[System.TimeSpan]::FromSeconds(1))
$wait.PollingInterval = 100
$xpath = ( "//input[@name='{0}']" -f $input_name)
Write-Debug ('Trying XPath "{0}"' -f $xpath)
try {
[void]$wait.Until([OpenQA.Selenium.Support.UI.ExpectedConditions]::ElementIsVisible([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath)))
} catch [exception]{
Write-Output ("Exception with {0}: {1} ...`n(ignored)" -f $id1,(($_.Exception.Message) -split "`n")[0])
}
Write-Debug ('Found XPath "{0}"' -f $xpath)
[OpenQA.Selenium.IWebElement]$element = $selenium.FindElement([OpenQA.Selenium.By]::XPath($xpath))
[NUnit.Framework.Assert]::IsTrue($element.GetAttribute('type') -match 'email')
$email_str = 'kouzmine_serguei@yahoo.com'
$element.SendKeys($email_str)
if (-not ($host.name -match 'ISE') ) {
if ($PSBoundParameters['pause']) {
try {
[void]$host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown')
} catch [exception]{}
} else {
Start-Sleep -Millisecond 1000
}
cleanup ([ref]$selenium)
}
Lets dissect this script. The following screenshot illustrates the proces.

For an example of relatively big syntax difference between C# and Powershell consider converting the custom input element handler responsible for processing the ipv4 address input fields from IpBox in C# for beginners article by Mervick.
The C# version (fragment):
private void OnTextChange(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
int box_type = 0;
CultureInfo MyCultureInfo = new CultureInfo("en-GB");
double d;
if( sender.Equals( ip1 ) )
box_type = 1;
if( sender.Equals( ip2 ) )
box_type = 2;
if( sender.Equals( ip3 ) )
box_type = 3;
if( sender.Equals( ip4 ) )
box_type = 4;
switch( box_type )
{
case 1:
if( this.ip1.Text.Length > 0 && this.ip1.Text.ToCharArray()[this.ip1.Text.Length - 1] == '.' )
{
this.ip1.Text = this.ip1.Text.TrimEnd( '.' );
ip1.Text = (this.ip1.Text.Length > 0 ) ? int.Parse( this.ip1.Text ).ToString() : "0" ;
ip2.Focus();
return;
}
if( double.TryParse(
this.ip1.Text,
System.Globalization.NumberStyles.Integer,
MyCultureInfo,
out d ) == false
)
{
this.ip1.Text = this.ip1.Text.Remove( 0, this.ip1.Text.Length );
return;
}
if( this.ip1.Text.Length == 3 )
{
if( int.Parse( this.ip1.Text ) >= 255 )
this.ip1.Text = "255";
else
ip1.Text = int.Parse( ip1.Text ).ToString();
ip2.Focus();
}
break;
case 2:
...
The equivalent Powershell version:
function text_changed () {
param(
[object]$sender,
[System.EventArgs]$eventargs
)
[int]$box_type = 0
[System.Globalization.CultureInfo]$ci = New-Object System.Globalization.CultureInfo ("en-GB")
[double]$d = 0
if ($sender -eq $ip1) {
$box_type = 1 }
if ($sender -eq $ip2) {
$box_type = 2 }
if ($sender -eq $ip3) {
$box_type = 3 }
if ($sender -eq $ip4) {
$box_type = 4 }
switch ($box_type)
{
1 {
if (($ip1.Text.Length -gt 0) -and ($ip1.Text.ToCharArray()[$ip1.Text.Length - 1] -eq '.'))
{
$ip1.Text = $ip1.Text.TrimEnd('.')
if ($ip1.Text.Length -gt 0) {
$ip1.Text = [int]::Parse($ip1.Text).ToString()
} else {
$ip1.Text = '0'
}
$ip2.Focus()
return
}
if ([double]::TryParse(
$ip1.Text,
[System.Globalization.NumberStyles]::Integer,
$ci,
([ref]$d)) -eq $false
)
{
$ip1.Text = $ip1.Text.Remove(0,$ip1.Text.Length)
return
}
if ($ip1.Text.Length -eq 3) {
if ([int]::Parse($ip1.Text) -ge 255) {
$ip1.Text = '255'
} else {
$ip1.Text = [int]::Parse($ip1.Text).ToString()
}
$ip2.Focus()
}
}
2 {
...

In this example, conversion should probably be avoided. The full script source is available in the source zip file.
In this section, we convert C# to a runnable Powershell script one step at a time, in 3 steps followed by 2 more steps.
-
Download the code from http://www.java2s.com/Code/CSharp/GUI-Windows-Form/MyClockForm.htm, save is in a text file timer.cs. Compile and ensure it runs in console:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\csc.exe timer.cs
invoke-expression -command './timer.exe'
-
Create a blank text file timer_iter1.ps1, put the following boilerplate code there:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// -- about to paste the c# code below. Any class would do
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll', 'System.Drawing.dll', 'System.Data.dll', 'System.ComponentModel.dll'
$clock = New-Object MyClock.MyClockForm
$clock.ShowDialog()
$clock.Dispose()
Inspect the namespace and class name of the class being converted, make sure Powershell is creating the instance of the same class.
namespace MyClock
{
public class MyClockForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form {
/// implementation
} }
hence New-Object MyClock.MyClockForm.
Figure out which are the needed assemblies from the 'using' area of the C# class:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
Paste the code of the class into the Powershell script Add-Type cmdlet TypeDefinition's text argument and ensure it is runnable.
. ./timer_iter1.ps1
-
If receiving the error:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. The type name 'Win32Window' already exists.
the Powershell window needs to be recycled. Of course if one receives:
Add-Type : Cannot add type. Compilation errors occurred.
FullyQualifiedErrorId : SOURCE_CODE_ERROR,
you will need to fix the code.
The Powershell version of the class should look and feel the same as compiled executable but clearly there is no obvious way to share the data between script and dialog yet.
-
Now turn the script process into the caller of the dialog explicitly.
Note that http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.windows.forms.form.showdialog(v=vs.90).aspx describes two alternative signatures of the ShowDialog method every Windows Form responds to. The latter of the two is accepting the owner object.
ShowDialog(IWin32Window) | Shows the form as a modal dialog box with the specified caller. |
Any class implementing IWin32Window can become the owner of the windows modal dialog with an arbitrary Window Forms inside.
So we repeat the earlier Add-Type code blend exercise with a plain C# object code source passed in:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
// "
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class Win32Window : IWin32Window
{
private IntPtr _hWnd;
private int _data;
private string _message;
public int Data
{
get { return _data; }
set { _data = value; }
}
public string Message
{
get { return _message; }
set { _message = value; }
}
public Win32Window(IntPtr handle)
{
_hWnd = handle;
}
public IntPtr Handle
{
get { return _hWnd; }
}
}
"@ -ReferencedAssemblies 'System.Windows.Forms.dll'
The code above is implemented the single method required for the interfact IWin32Window - constructor with a handle to the window. The other properties in the code above Data and Message properties are not required by the interface but are essential to tie the parts together.
-
Finally, change the code to deal with the caller.
- Pass the argument to
Windows.Forms:
$process_window = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle )
$timer.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($process_window) ) | out-null
write-output $process_window.GetHashCode()
- Access the object from within the form:
You need to add a member variable to the class and modify the following two methods. Note this is not required when implementing the PowerShell version. There must be a better way to illustrate this. For now, the goal is to move to Powershell version, and eventually discard the modified class. This sort of 'justifies' the hack.
private void OnTimerElapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
label1.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
label1.Text = String.Format("My Clock {0} {1}", caller.ToString(), caller.GetHashCode() );
}
public new DialogResult ShowDialog(IWin32Window caller){
this.caller = caller ;
return base.ShowDialog(caller);
}
On the other hand, when the code being ported is a more complex form than in this example, it would be helpful to exchange all domain specific data the same object $caller regardless of the complexity. One can test either side of the pipeline in Visual Studio or in Powershell ISE and mock the opposite side without worrying much about details.
Save the code as timer_iter2.ps1 and confirm it still runs.
Running the script yields the same object available to both script and form.

The next step is to selectively re-write the methods and elements of the form in Powershell and get rid of 'chimera' code. It would not be easy to make the C# compiler accept the fact that the $caller responds to many additional data messages . Another option, to use reflection, does not lead to compact or pretty code.
The required code edits are all semantic.
- Get rid of instance references (
this) and the class decorations, constructors, namespaces and such. The member this.timer1 becomes $timer1 and so on. The this becomes simply the $f - the form object. - Amend the semantics of method calls:
new System.Timers.Timer(); becomes new-object System.Timers.Timer, etc. When found class instantiation inside the method call argument, it appears safe to separate the nested method calls. - Change the semantics of constant resolutions:
System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter becomes [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleCenter etc. Always provide fully resolved class names: ImageList il = new ImageList(); would have to become $il = new-object System.Windows.Forms.ImageList etc. If uncertain, check through MSDN. - Watch for minor semantic difference like
-eq instead of ==, -bor instead of | and the like -
Initially run the visual layout, but comment the event propagation. Once the form begins to show, deal with events.
Make sure that event handler(s) is defined before using those with events: for example moving the first lines in the following code to the top
$button1_Click = {
param(
[Object] $sender,
[System.EventArgs] $eventargs
)
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show('hello');
}
$button1.Add_Click($button1_Click)
would lead to the form to cease showing the blank messagebox when $button1 is clicked.
- Create a wrapping PowerShell function, add the code to make the form visible.
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $true
$f.Activate()
$f.Displose()
Move the $caller and showDialog(...) inside the Powershell function.
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
[void] $f.ShowDialog([Win32Window ] ($caller) )
The result would look like the following:
function exampleTimer(
[Object] $caller= $null
)
{
$f = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$f.Text = $title
$timer1 = new-object System.Timers.Timer
$label1 = new-object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$f.SuspendLayout()
$components = new-object System.ComponentModel.Container
$label1.Font = new-object System.Drawing.Font("Microsoft Sans Serif", 14.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Bold, [System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit]::Point, [System.Byte]0);
$label1.ForeColor = [System.Drawing.SystemColors]::Highlight
$label1.Location = new-object System.Drawing.Point(24, 8)
$label1.Name = "label1"
$label1.Size = new-object System.Drawing.Size(224, 48)
$label1.TabIndex = 0;
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
$label1.TextAlign = [System.Drawing.ContentAlignment]::MiddleCenter
$f.AutoScaleBaseSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(5, 13)
$f.ClientSize = new-object System.Drawing.Size(292, 69)
$f.Controls.AddRange(@( $label1))
$f.Name = 'MyClockForm';
$f.Text = 'My Clock';
$eventMethod=$label1.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({$f.Text="You clicked my label $((Get-Date).ToString('G'))"})
$f.Add_Load({
param ([Object] $sender, [System.EventArgs] $eventArgs )
$timer1.Interval = 1000
$timer1.Start()
$timer1.Enabled = $true
})
$timer1.Add_Elapsed({
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
})
$global:timer = New-Object System.Timers.Timer
$global:timer.Interval = 1000
Register-ObjectEvent -InputObject $global:timer -EventName Elapsed -SourceIdentifier theTimer -Action {AddToLog('') }
$global:timer.Start()
$global:timer.Enabled = $true
function AddToLog()
{
param ([string] $text )
$label1.Text = [System.DateTime]::Now.ToString()
}
$f.ResumeLayout($false)
$f.Topmost = $True
if ($caller -eq $null ){
$caller = New-Object Win32Window -ArgumentList ([System.Diagnostics.Process]::GetCurrentProcess().MainWindowHandle)
}
$f.Add_Shown( { $f.Activate() } )
$f.ShowDialog([Win32Window] ($caller) )
}
This will have almost everything in place except for the event handler that does not seem to be triggered - the time stamp is not updating. This code apparently needs to be fixed.
Debugging the Timer Problem
After some debugging, it appears that the script is not properly dealing with the timer object that was owned by the Windows.Form class instance but no longer is. This constitutes a separate issue to fix, and work is underway. To prove that most of the event handlers can be converted to run Powershell code with nearly zero effort, the click handler was added to the label
$eventMethod=$label1.add_click
$eventMethod.Invoke({$f.Text="You clicked my label $((Get-Date).ToString('G'))"})

and clicked. The result looks as expected.
To recap writing the equivalent code in Powershell based on C# blueprint for the form layout and handling the events were the two remaining steps promised earlier in this chapter.
The visual design replication step is clearly a no brainer, a typing exercise at best. With Windows Presentation Foundation it is even unnecessary: one is able to load the same XAML.
Event management on the contrary may consume some effort to tame.
In the PowerShell samples through this article, a slightly different semantics for event handling code had been attempted every time. This diversity was introduced intentionally - all the variants are equivalent - the .NET Framework generates a lot of code behind the scenes to support MulticastDelegate.
To recap, replicating the visual design in Powershell based on C# blueprint and handling events are two remaining steps promised earlier in this chapter. The visual design step is a no-brainer, a typing exercise at best. On the contrary, the event management may take some effort to tame. In the Powershell samples though this article, a slightly different semantics of event handling code had been chosen every time. The Diversity was introduced intentionally - all the variants are equivalent. Under the hood, MS .NET generates a lot of code behind the scenes to subclass the MulticastDelegate.
PromptForChoice
The prompting mechanism built into PowerShell is intended primarily to control destructive actions . Its exact presentation depends on the host in which Powershell script is run. The endless loop solution suggested in http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff730939.aspx for a basic multi-choice select Yes? No? Maybe is barely an acceptable one. It sends a clear message: "Forget about multi-select prompts".
$heads = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Heads", "Select Heads."
$tails = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Tails", "Select Tails."
$cancel = New-Object System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription "&Cancel", "Skip to the next step."
$options = [System.Management.Automation.Host.ChoiceDescription[]]($heads, $tails, $cancel)
$host.ui.PromptForChoice("Call it","----", $options,2 )

It renders differently based on the host capabilities in ConsoleHost vs. Windows PowerShell ISE Host

and returns the index - 0,1,2 in the selected option.
Platform Compatibility
The Powershell Scripts presented in this article have been verified to work on the following platforms:
| Windows Server 2012 - Desktop-Experience | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 - Minimal Server Interface, Windows Server 2012 - Windows Server Core | Most of examples work, except one: toggle_display.ps1 manages to show the form, and hide, but never shows Powershell console back. |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 | Yes |
| Windows Server 2003 | Yes |
| Windows 8 | ? |
| Windows 7 | Yes |
| Windows Vista | Yes |
| Windows XP | Yes |
| Windows 2000 | No |
The work started with automating the daily dev ops routine configuring vanilla UAT environments full of Microsoft Software, hosted in private cloud. One particularly cumbersome step was with selectively cloning SQL configurations via SQL Server Client Network Utility. The latter being remarkably user un-friendly.

Under the hood, all information is stored in a single registry key. This makes loading this information from remote host a good candidate for automation, but the operator's role is still vital for as long as the subtle difference between the environments landscapes: which IIS applications is hosted on which computer. This would not be a problem had the settings been converted to the Puppet-style node definitions.
For most examples, complete source is provided in the article and in the attached zip. One can also clone the completed source from Github:
Release History
- 2014-07-21 - Initial version
- 2014-07-21 - Added more samples
- 2014-07-22 - Added comment on code conversion
- 2014-07-22 - Added XAML example
- 2014-07-23 - Added
TreeView example - 2014-07-24 - Added Dissect Conversion example
- 2014-07-25 - Added Custom Icons with
Treeview - 2014-07-25 - Added remark regarding Get-Credential cmdlet
- 2014-07-26 - Added TabControl and Focus sample
- 2014-07-26 - Added TOC
- 2014-07-26 - Added Tabbed
Treeviews - 2014-07-26 - Refactored example code snippets
- 2014-07-27 - Added
WebBrowser1 sample - 2014-07-27 - Added Platform compatibility matrix
- 2014-07-28 - Added generation of XAML dialog on the fly example
- 2014-07-29 - Added script parameter prompt
DataGridView example - 2014-07-29 - Added Fill Color and
ZIndex manipulation example - 2014-07-29 - Added WPF Form Text manipulation example
- 2014-07-29 - Added bidirectional Form Script Text communication example
- 2014-08-09 - Added Selenium Script example
- 2014-08-09 - Modified Selenium Grid Test example to execute on Safari browser
- 2014-08-09 - Added a note of File Download dialog handling
- 2014-08-10 - Added
TreeView Control with ComboBox example - 2014-08-10 - Added Workaround for code formatting defect
- 2014-08-11 - Added
ProgressBar example - 2014-08-13 - Added Selenium IE dialog processor example
- 2014-08-13 - Fixed formatting and separates some inline XAML code for readability
- 2014-08-16 - Added Selenium IDE Powershell Formatter example
- 2014-08-16 - Updated links to author's Powershell Selenium IDE Formatter git repository
- 2014-08-19 - Added Drag and Drop example
- 2014-08-22 - Added running Javascript through Selenium example
- 2014-08-22 - Added Microsoft Test Agent DLL discovery example
- 2014-08-22 - Added overview and build instructions for the xpi
- 2014-08-23 - Added clicking button on Save Dialog example
- 2014-08-23 - Added running Powershell from Linux example
- 2014-08-24 - Updated version of Save Dialog example to accept the specified download file path
- 2014-09-03 - Added Web Driver Drag and Drop example
- 2014-09-09 - Added Misc. Web Driver example
- 2014-09-09 - Added Hide Powershell console window example
- 2014-09-09 - Added note regarding Powershell UI in Windows Server Core
- 2014-09-21 - Added Bar Chart (VB.Net) example
- 2014-09-24 - Added Up Down picker example
- 2014-09-26 - Added Timing out confirmation dialog example
- 2014-10-07 - Added Extreme case example, recovered few damaged sections, performed minor HTML formatting cleanup
- 2014-10-07 - Added Selenium SendKeys example
- 2014-10-07 - Recovered Selenium IDE Powershell Formatter section
- 2014-10-07 - Recovered DropDown ComboBox section
- 2014-11-01 - Added Filesystem Treeview example
- 2014-11-03 - Updated Source Zip with final Filesystem Treeview and custom MsgBox examples
- 2014-11-04 - Added Custom MsgBox examples
- 2014-11-14 - Added Ribbon example
- 2014-11-14 - Added Selenium Powershell ISE example
- 2014-12-07 - Added Collapsible List example
- 2014-12-14 - Added Checked Combo Listbox example
- 2014-12-20 - Added Pie and Bar Chart Draw example
- 2014-12-22 - Added Timer example
- 2015-01-04 - Added Task List Progress example
- 2015-01-05 - Commented Task List Progress
- 2015-01-14 - Added Accordion Menu example
- 2015-01-14 - Added Accordion Menu code refactoring example
- 2015-01-17 - Added Circle Progress Indicator example
- 2015-01-19 - Added Circle Progress Indicator W2K3 compatiliblity patch
- 2015-02-07 - Refactred Ribbon buttons example
- 2015-02-15 - Added Selenium Debugging messages on Explorer Taskbar example
- 2015-02-16 - Added Selenium EventFiring WebDriver example *WIP
- 2015-02-17 - Fixed formatting defects
- 2015-02-27 - Added TreeTabControl example
- 2015-02-27 - Continued TreeTabControl example *WIP
- 2015-03-10 - Added alternative Add-Type syntax example. Trimmed blank lines.
- 2015-03-22 - Provided alternative $script: syntax example and uploaded a typo fix.
- 2015-03-23 - Added note regarding
System.Management.Automation.TypeAccelerators. - 2015-03-25 - Added test configuration display example.
- 2015-04-04 - Replaced and somewhat simplified Custom Debugging Message Box example.
- 2015-04-05 - Added OS X Circle Progress Indicator example.
- 2015-04-10 - Added sortable ListView example.
- 2015-04-17 - Added filling GridView example.
- 2015-05-31 - Added Common Dialogs example.
- 2015-12-26 - Added Real World Data for Charts FiddlerCore and Selenium
window.performance.getEntries()example. - 2015-12-26 - Added tristate Tree View example.
- 2016-01-14 - Added tristate Tree View example.
- 2016-02-02 - Updated tristate Tree View example and downloads.
