Introduction
When developing applications in the fields of e-commerce and electronic payment which should be used by customers from inside the European Union, you will come across the problem of VAT number validation of commercial customers. This article describes how to check the VAT using the official Web Service.
Background
The validation of VAT numbers is necessary because the EU taxation law provides a regulation called Reverse Charge System where the VAT tax rate may be devolved to the customer if he is located within another EU country and can provide a valid VAT number meaning that he is really a commercial customer. Additional information can be found here.
The European Commission's Taxation and Customs Union Directorate-General provides a Web Service therefore, which is available at: http://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/vies/checkVatService.wsdl.
With Visual Studio and the .NET SDK, the usage of this Web Service is straightforward.
Create the Web Service proxy class
First, open up the Visual Studio command prompt. You can find it in your Start menu under the Microsoft Visual Studio 2010/Visual Studio Tools entry. Browse to the directory where you want to create the proxy class at, and type:
wsdl http://ec.europa.eu/taxation_customs/vies/checkVatService.wsdl
into the command prompt.
You should see the following screen now:
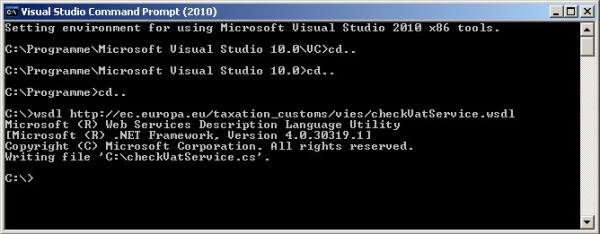
This will create a file called checkVatServices.cs implementing the Web Service proxy with the use of the .wsdl file the European Union has published. Now we are basically done with the creation of the Web Service proxy class. Rapid development, right?
To use this class, simply import it into your project and add a reference to the System.Web.Services.dll library which is part of the .NET SDK. Now you are able to create an instance of the checkVatService class and call its checkVat(...) method.
The created file implements a class object with the methods defined within the .wsdl XML definition file. Furthermore, you will find methods for implementing the Web Service asynchronously inside your application. For further information about asynchronous usage of Web Services, you can read this interesting CodeProject article.
When using the service, please also be aware of the fact that Austrian VAT numbers must start with a heading "U" character (Q19 of the VIES FAQ).
For easy usage of this Web Service, I implemented a wrapper class as well as a demo project to show the usage by example.
The wrapper class
Within the zip file attached to this article, you can find a small wrapper class called ViesVatCheck which adds a heading character for Austrian VATs when its CheckVat() method is called.
The ViesVatCheck class implements two input and four output attributes, which are shown in the table below:
| Attribute | Description | Direction |
|---|
CountryCode | The country code of the VAT number | Input |
VATNumber | The VAT number to check | Input |
Name | The name of the company the VAT number belongs to | Output |
Address | The address of the company | Output |
IsValid | true if the VAT could be validated, otherwise false | Output |
RetDate | The request date the Web Service returns | Output |
The first input attribute is the country code of the VAT number to check. This attribute can be one of the country codes below:
| Country | Country code |
|---|
| Austria | AT |
| Belgium | BE |
| Bulgaria | BG |
| Cyprus | CY |
| Czech Republic | CZ |
| Germany | DE |
| Denmark | DK |
| Estonia | EE |
| Greece | EL |
| Spain | ES |
| Finland | FI |
| France | FR |
| United Kingdom | GB |
| Hungary | HU |
| Ireland | IE |
| Italy | IT |
| Lithuania | LT |
| Luxembourg | LU |
| Malta | MT |
| The Netherlands | NL |
| Poland | PL |
| Portugal | PT |
| Romania | RO |
| Sweden | SE |
| Slovenia | SI |
| Slovakia | SK |
If you do take a closer look at the FAQ of the VAT service published by the European Union, you can see that some of these countries are not always available for checking VAT numbers like described in Q11 of the FAQ. So this service can be used to pre- check VAT numbers, but a manual checking may be still needed for invalid VAT numbers.
The second attribute of the wrapper class is the VAT number itself. You do not need to add a heading U character for Austrian VAT as this is done for you by the wrapper class.
The output attributes of the class are available after the CheckVat member method is called.
Using the wrapper class
To use the wrapper class, simply download the zip and build the VATChecker project. This will create an assembly you can use within your project. Furthermore, the demo project contains a small WPF project which uses the ViesVatChecker class.
You can see the screen of the demo application in the following figure:

Once you have added the assembly file, the wrapper class may be used within the demo application where you can find this code behind the event handler for the Validate button:
private void button1_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (comboBoxCountries.SelectedItem == null)
{
comboBoxCountries.Focus();
return;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(textBoxVatNumber.Text))
{
textBoxVatNumber.Focus();
return;
}
ViesVatCheck check = new ViesVatCheck();
check.VATNumber = textBoxVatNumber.Text;
check.CountryCode = ((ComboBoxItem)comboBoxCountries.SelectedItem).Tag.ToString();
bool bValid = check.CheckVat();
if (bValid)
{
imageValid.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
imageInvalid.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Hidden;
labelAddress.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
labelCompanyName.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
labelRequestDate.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
labelAddress.Content = check.Address;
labelCompanyName.Content = check.Name;
labelRequestDate.Content = check.RetDate.ToShortDateString();
textBoxVatNumber.Text = check.VATNumber;
}
else
{
imageValid.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Hidden;
imageInvalid.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
labelAddress.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Hidden;
labelCompanyName.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Hidden;
labelRequestDate.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Hidden;
}
}
The project was created and built with Visual Studio 2010 and .NET 4. If you are using a previous version of the .NET Framework, follow the steps described above to create your own VIES Web Service proxy class.
