Crystal and Reporting Services FAQ
This FAQ will give you a quick start for two report giant’s crystal and reporting services.
Crystal reports comes with Visual studio setup itself. Right click the solution explorer add new item and you can see a crystal report template as shown in figure ‘Crystal report template’. You can add an ‘.rpt’ file using this template.
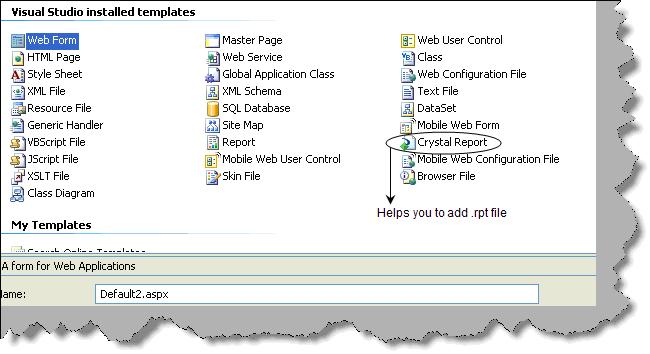
Figure 1:- Crystal report template
There are four major components in crystal reports Report designer, Reports engine, Report viewer and object models.
Report designer gives a graphical interface to create and modify reports. To view the designer add a new crystal report file and double click on it you should see the report designer as shown in figure ‘Report designer’.

Figure 2 :- Report designer
Reports engine does the formatting and conversion part of crystal reports. It helps convert the contents of reports in word, excel, PDF, HTML and other formats. Report viewers are controls which you can see on the visual studio tool box; you can drag and drop those controls on an ASPX page or windows application to view reports made using crystal. Object models help us manage crystal reports objects during design time and run time.
To understand this sample let display a simple report using crystal.
Step1:- Create a web application project.
Step2:- Add new item and select crystal report from the template. This adds a new RPT file in your solution explorer.
Step3 :- Double click on the RPT file click on Crystal reports Field explorer as shown in figure below. You should see the field explorer toolbar.

Figure 3:- Field explorer toolbar
Step 4 Right click on ‘Database fields’ on the field explorer then click on database expert Expand create new connection Expand OLE DB ADO Select Microsoft OLEDB provider for SQL Server ( this depends on what kind of data you want to connect ) Give the server credentials Click finish and done.
Step5 Right click on ‘Database fields’ on the field explorer then click on database expert Expand the server , database and select table which you want to add to the report. Below figure ‘Table added in reports’ shows the right pane showing the table added using database expert.

Figure 4 :- Table added in reports
Step 6 Expand database fields table ( in this case it is ‘FactCurrencyRate’ table). Now you can drag and drop the fields on the report.

Figure 5 : - Drag fields on the report
Step 7 We now need to display the report on the ASPX page. For that we need the ‘CrystalReportViewer’ control. So expand the crystal reports section of the toolbar and drag the component on the ASPX page

Figure 6 : - ‘Crystalreportviewer’ control
Step 8:- Now we need to go to code behind and specify the report source. That’s it now compile and run the project you can see your report live in action.

Figure 7 : - Specify the crystal report source
Right click on the ‘RPT’ file and click ‘Publish as web service’ as shown in figure ‘Publish crystal as web service’.

Figure 8 : - Publish Crystal as web service
We can consume the web service as a normal web service in .NET. The easiest way is by using the ‘ReportViewerControl’ and specifying the ASMX URL in the report source property.
To add any formula in crystal report is a three step procedure. Below figure ‘Add formula in crystal report’ shows the three steps in a pictorial format. Step 1 Go to field explorer and right click and click new formula. Step 2 Give and name to the formulae and click on ‘Use Editor’. Step 3 You will be presented with UI which has all the formulas and function.

Figure 9 : - Add formula in crystal report
Some times we want to accept input parameter and the report works according to the parameter. To add a input parameter go to field explorer , go to parameter fields , right click , create parameter and you should be popped with a dialog box as shown in the figure ‘Parameter field’. Give a name to the parameter , type and that’s it you are in action.

Figure 10 :- Parameter fields
There are two way of using the export option one is when we display a report using crystal report viewer you can see a export icon as shown in figure ‘Export’ below. You can the select in which format you want to export.

Figure 11 : - Export
Second option is through coding. Below is a simple code snippet which shows how we can export a report. Create a object of the crystal report and call the ‘ExportToDisk’ method specifying in which format you want to export.
Dim Report as New CrystalReport1
Report.ExportToDisk(CrystalDecisions.Shared.ExportFormatType.WordForWindows,"c:\my.doc”)
In print we have two ways by which we can print one is when you display the report using crystal report viewer you have a print option and second is by code. Below is a simple code snippet which shows how we have created a object called as report from the rpt file , specified the printer name , paper size and then called the ‘PrintToPrinter’ method.
Report.PrintOptions.PrinterName = "MyPrinter"
Report.PrintOptions.PaperSize = CrystalDecisions.Shared.PaperSize.PaperA4
Report.PrintOptions.PaperOrientation = CrystalDecisions.Shared.PaperOrientation.Landscape
Report.PrintToPrinter(1, True, 1, 3)
When we go for creating a new report you can see the cross –tab option.

Figure 12 : - Cross tab reports
For grouping in crystal you need to use the group expert wizard.
Crystal report uses the three pass method for parsing reports. Before we understand what does it means lets define what is a pass ?. Pass is a process used by crystal reports to read and manipulate data as per the report format. Below figure ‘Three pass method’ shows how the parsing happens. Let’s understand the same step by step. In Pre-Pass1 crystal report engine evaluates constants like x=1 and pie=3.14 for a report. Pass 1 does two important things get data from the database and sort records with given conditions. Once this is done it’s saved in memory and given to pre-pass2 for further parsing and manipulation. Pre-pass2 is all about grouping and sorting the records according to conditions specified in the crystal report. Pass 2 formats a report, applies condition and groups them. Pass 3 is the final tunnel it just counts the pages and generates reports.

Figure 13 :- Three pass method
Reporting services is mainly used to generate reports. Below are the main components of reporting services as shown in figure ‘Reporting Services Architecture’. Reporting services has four major components Client, Web services, report server/manager and reporting services database. Let’s understand all the major components and the sub components of the same.

Figure 14 : - Reporting Services Architecture
Client: - These are the consumers of reporting services functionality. It can be the report manager or report server (we will discuss report server and manager in more details further) or ASPX and windows application.
Reporting Web service: - Microsoft chose XML to expose the functionality of reporting services. So all the functionality is exposed through web services. One of the most important gains for a web service is that it can be platform independent.
Report server / manager: - Report server and manager forms the core engine of reporting services. They two important systems one is ‘Report processor’ and the other is
‘Scheduling and Delivery processor’. Reporting processor is the main driver to deliver reports. They take request from the end user and process the report and send it to the end client. Figure ‘Report Processor’ shows how the flow moves. We have seven basic steps which can help us understand in more detail how the report processor works. Step 1 Any client like ASPX or windows application will request to the web service for reports. Step 2 and 3 Web service will forward the request to the report processor and get the report definition from the report server DB. Step 4 Reporting services uses the security extensions to authenticate the end user. Step 5 Data processing extension calls queries the application database to get data. With data processing extension we can connect to standard data sources like SQL Server, ODBC, Oracle etc. You can also extend the data processing extension to adapt it to some custom data processing extension. Step 6 Rendering extension then renders the report applies format and sends the same to the end client. Using rendering extension you can deliver reports in Excel, PDF, HTML, CSV and XML. You can also extend the rendering extension to deliver in custom formats.

Figure 15 : - Report Processor
The second system is ‘Scheduling and Delivery processor’. Delivery extensions makes reports with the specified format and sends the same to an output target like file, email, FTP etc. Scheduling and delivery processor does two important steps schedules reports and delivers them the same to a output like FTP,Email etc. Schedule and delivery processor using delivery extension to deliver reports to the defined output. So users can subscribe to the reports and depending on these subscriptions the delivery is done by schedule and delivery processor. There are two steps in this one is the subscription process and the other is deliver process. Lets first try to understand the subscription process. There are three steps basically:-
Step 1 First is the requests a subscription to the report.
Step 2 This subscription is then stored in the report server DB.
Step 3 A new SQL Server agent is created for this subscription. So we have completed the subscription process.

Figure 16 : - Subscription process
Now that the subscription is created lets see how the delivery process works. Here are five basic steps in delivery process. Step 1 When the event occurs SQL Server agent makes an entry in the report server DB. Step 2 and 3 RS windows service keeps polling SQL Server for any events. If a event has occurred it gets the event from the database and sends a message to the ‘Scheduling and Delivery Processor’. Step 4 The report is then processed by the report processor and sent to the delivery extension who finally delivers it on a output which can be a email address, folder, FTP or any other kind of output.

Figure 17 : - Delivery process
Reporting Services Database:- When you install reporting services you will see two databases ‘ReportServer’ and ‘ReportServerTempDB’.’ReportServer’ database contains report definitions, schedule, subscriptions, security details and snapshots. ‘ReportServerTempDB’ stores temporary information like session state about reports which is needed in between HTTP requests and report cache information. Please note snapshots are stored in reportserver and not in tempDB.

Figure 18 :- Databases of reporting services
For further reading do watch the below interview preparation videos and step by step video series.
