Overview
Purpose
This article shows how to implement a COM Server in 3 different
configurations:
- The COM Server as an
executable.
- 2
DLLs, one is the COM DLL Server and the other the Proxy/Stub DLL.
- 1
single DLL in which the COM Server and the Proxy/Stub are merged into.
Although Servers seem different, mostly steps to build and
implement COM objects and interfaces into them are common.
Here I will
not explain how to make a COM Server as a Windows NT service. In fact, you can
see this option in the same way as a COM Executable Server with:
- More functions in order to register the service with the operating system.
- Some restrictions when you register your COM Server.
- Some restrictions in using the Windows API.
For Further
information, have a look at the section
Other
points at the end of this article.
Requirements
All the code in these samples have been written in C++,
using Visual C++ 6.0 (sp4) under Windows 2000. They also use the Active-X
Template Library (ATL v3.0).
Other articles in this series
This article is part of a series called
"COM Macro-Architecture Topology". Here are the links to other articles:
COM Servers
All the Server presented in this
article are composed of one COM class (or CoClass) called
CoMacroTopo. It exposes two COM interfaces:
IMacroTopoDisp, it is a dispatch interface.
IMacroTopoCustom, it is a custom interface.
Both
interfaces expose these two simple methods:
ShowHello(), which displays a message box within it the
"Hello" message.
Add(A, B) : C, which adds "A" and "B" (numbers) and return
the result in "C".
The exact method's name for the custom interface
are
ShowHelloCustom() and
AddCustom().
 In order to make a Server, here you are the list of the
steps
In order to make a Server, here you are the list of the
steps:
- Choose a Server Type such as an
Executable, 2
DLLs or 1
DLL allowing proxy merged.
- Edit
project settings (for 1
DLL allowing proxy merged, click here).
- Create
the CoClass definition.
- Add
methods to
IMacroTopoDisp..
- Add
the new interface
IMacroTopoCustom.
- Build
the project.
- Register the server (Executable,
2
DLLs or 1
DLL allowing proxy merged).
- Configure
the security for your Server.
- Unregister the server (Executable,
2
DLLs or 1
DLL allowing proxy merged).
Only steps 1.), 2.), 7.) and 9.) are
different from servers' configurations.
The "
copy files to target
machine" and the "
remove files from the target machine" process have
not been taken into account in this article. Obviously, in real situation you
should consider them: the former will be just after Step 6 and the latter after
Step 9.
To build the COM Server as an executable, follow the steps
define in the
General's
section.
To create the server, you have to follow the steps below
:
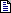
- Start the Visual C++ IDE and Select File, New and fill in
like below:
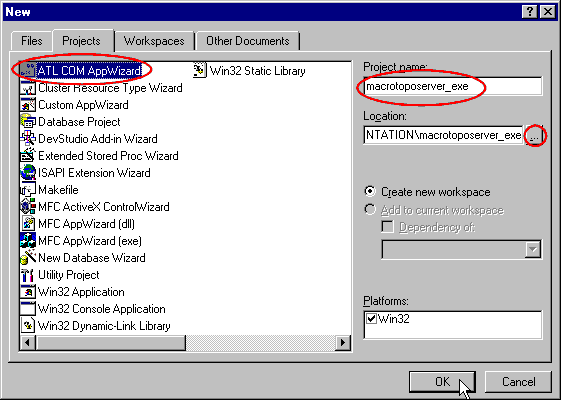
- You want to create an Executable Server so choose Server type's
option like that:
After that, the ATL COM wizard will create these files :
- Workspace:
macrotoposerver_exe.dsw
- Project:
macrotoposerver_exe.dsp
- Initialisation code in
macrotoposerver_exe.cpp and
macrotoposerver_exe.h
- IDL source in
macrotoposerver_exe.idl
- and files for the Proxy/Stub DLL:
macrotoposerver_exeps.mk
macrotoposerver_exeps.def
The final COM
Server name is
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE .
Step 2 to 6 and 8 - Common part 
Follow the common steps:
step
2,
step
3,
step
4,
step
5,
step
6, and
step
8.
As you have used the ATL Wizard to generate your
project, it automatically added the command to register your server (in the
Project Settings window, in the tab of the
Custom build). However,
it does not do anything for the Proxy/Stub DLL, so you have to do it
yourself.
You also have to consider that generally the build machine is
different from the client or server machine.
Local consideration
To register manually, in your build machine, do like
that (
in this order):
- To register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- type the command ">
regsvr32 macrotoposerver_exeps.dll".
- To register the COM server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE -RegServer".
Remote consideration
In this case, you have to perform two
installations: one on the client machine and the other on the server machine.
Here are the instructions for both:
- On the client machine
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL)
using the
command line ">regsvr32 MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL".
- Register the remote server entries.
Generally we do not want (and we
do not need) to register the full Server component on the Client machine. In
that case, we need to create a registry file to add the necessary keys to
enable the remote access of our component on the Server machine. So, create
a new text file with the extension ".reg" (e.g.
registry_client_exe.reg) and add these lines to it: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{12345678-0000-0000-0000-abababababab}]
@="CoMacroTopo Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_ATL}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID\{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_ATL}]
@="macrotoposerver_exe"
"RemoteServerName"="myservercomputer"
"myservercomputer" is the machine name where the COM Server is
installed.
The AppID "{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_ATL}" has been
generated by the ATL wizard and you can find it (not the same value) on your
resource files (e.g. CoMacroTopo.rgs or
macrotoposerver_exe.rgs). So, keep with the same value because
it is now part of your Executable file.
If you have more than one COM
Class object in your server (here, you have only CoMacroTopo), you have to
repeat the first 3 lines for each CLSID you have. Nevertheless,
keep with the same value for the "AppID" key: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{<another COM Class ID>}]
@="CoAnother Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_ATL}"
...
Now you have to register all this information on the registry. Using
Windows Explorer, double-click on your file. The registry will ask you if
you want to add this information to the current registry (if you have the
administrator rights) click "Yes" and that is it.
- On the server machine
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL)
by using the
command line ">regsvr32 MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL".
- Register the server entries stored in your executable file
(MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE)
by using the command line
">MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE -RegServer".
Local consideration
To unregister manually do like that:
- Unregister the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- type the command ">
regsvr32 /u
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL"
- Unregister the COM server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory where is your registered file (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE -UnregServer"
Remote consideration
To unregister manually do like that:
- On the client machine
- On the server machine
- Unregister the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL)
by using
the command line ">regsvr32 /u MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL".
- Unregister the server entries stored in your server machine registry by
using the command line ">MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE -UnregServer".
To build the COM Server as 2 DLLs, follow the steps define
in the
General's
section.
To create the server, you have to follow the steps below
:
- Start the Visual C++ IDE and Select File, New and fill in
like below:
- You want to create a DLL Server without merging the Proxy/Stub code, so
choose Server type's option like that:
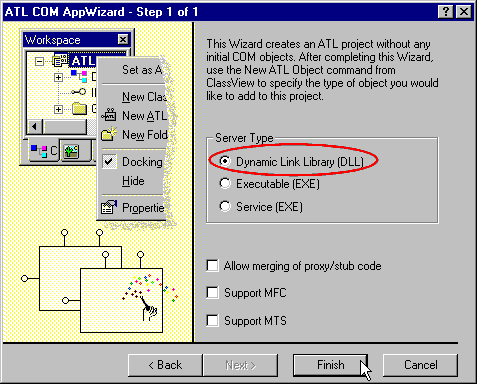
After that, the ATL COM wizard will create these files :
- Workspace:
macrotoposerver_dll_psdll.dsw
- Project:
macrotoposerver_dll_psdll.dsp
- Initialisation code in
macrotoposerver_dll_psdll.cpp and
macrotoposerver_exe.h
- IDL source in
macrotoposerver_dll_psdll.idl
- and files for the Proxy/Stub DLL:
macrotoposerver_dll_psdllps.mk
macrotoposerver_dll_psdllps.def
The final
COM Server name is
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL .
Step 2 to 6 and 8 - Common part 
Follow the common steps:
step
2,
step
3,
step
4,
step
5,
step
6, and
step
8.
As you have used the ATL Wizard to generate your
project, it automatically added the command to register your server (in the
Project Settings window, in the tab of the
Custom build). However,
it does not do anything for the Proxy/Stub DLL, so you have to do it
yourself.
You also have to consider that generally the build machine is
different from the client or server machine.
Local In-process consideration
To register manually, in your build
machine, do like that (
in that order):
- To register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- type the command ">
regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL"
- To register the COM DLL server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL"
Remote consideration
In this case, you have to perform two
installations: one on the client machine and the other on the server machine.
Here are the instructions for both:
- On the client machine
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL)
using
the command line ">regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL".
- Register the remote server entries.
Generally we do not want (and we
do not need) to register the full Server component on the Client machine. In
that case, we need to create a registry file to add the necessary keys to
enable the remote access of our component on the Server machine. So, create
a new text file with the extension ".reg" (e.g.
registry_client_exe.reg) and add these lines to it: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{12345678-0000-0000-0000-abababababab}]
@="CoMacroTopo Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID\{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}]
@="MacroTopoServer_2dlls"
"RemoteServerName"="myservercomputer"
"myservercomputer" is the machine name where the COM Server is
installed.
If you have more than one COM Class object in your server
(here, you have only CoMacroTopo), you have to repeat the first 3 lines for
each CLSID value you have. However, keep with the same
value of AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU for the "AppID" key: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{<another COM Class ID>}]
@="CoAnother Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
...Now you have to register all this information on the registry. Using
Windows Explorer, double-click on your file. The registry will ask you if
you want to add this information to the current registry (if you have the
administrator rights) click "Yes" and that is it.
- On the server machine
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL)
by
using the command line ">regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL".
- Register the server entries stored in your server file
(MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL)
by using the command line
">regsvr32 MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL".
- Register the server entries indicating the use of the DLL surrogate
application.
You need to create a registry file to add the necessary keys
to enable the management of our component by the DLL Surrogate application.
So, create a new text file with the extension ".reg" (e.g.
registry_server_exe.reg) and add these lines to it: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{12345678-0000-0000-0000-abababababab}]
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID\{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}]
@="MacroTopoServer_2dlls"
"DllSurrogate"=""
The main point is to permit our COM DLL server to be launched using
the surrogate application. Here, the value is an empty field "" which
means that COM will use the default one provided with by the system (e.g.
the default surrogate application on Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 is
DLLHOST.EXE).
If you have more than one COM Class object in
your server (here, you have only CoMacroTopo), you have to repeat the first
3 lines for each CLSID you have. However, keep with the same
value for the "AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU" key: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{<another COM Class ID>}]
@="CoAnother Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
...Now you have to register all this information on the registry. Using
Windows Explorer, double-click on your file. The registry will ask you if
you want to add this information to the current registry (if you have the
administrator rights) click "Yes" and that is it.
The
"
AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU" value is a GUID. You have to generate it (e.g. use
the
GUIDGEN.EXE tools delivered with MS-Dev Studio). It must be the same
value used on both sides: Client and Server.
Local Surrogate consideration
You can as well look for a variant
configuration that uses your COM DLL Server on the same machine as your client
application but outside of the client process.
Nonetheless, a DLL can never
run without a parent process. COM provides a default DLL surrogate application
that can load your COM DLL Server and provide it a process
environment.
In order to do like that, you have just to do the same
things as explain on the section above (Remote Consideration) and follow the
instructions below "
On
the server machine".
Of course you have to execute them on the Server
machine, i.e. in this case the same as your Client machine (here we are
interested in the Local Surrogate consideration).
Now, you have to change
your client code and ask
explicitly for loading the COM DLL Server in a
separate process space (runs on the same machine but in a different process)
using the DLL Surrogate application.
To indicate to COM that you want to
create your object in the different process space you have to use the Flag
CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER (and only this flag) on the CoCreateInstance() call,
CoCreateInstanceEx() call or on the ATL Interface smart pointer constructor like
this:
...
IMacroTopoDispPtr pDisp(__uuidof(CoMacroTopo), NULL, CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER);
long lA(500), lB(114);
long lResultat = pDisp->Add(lA,lB);
...
A remark about the relation between a COM DLL server and a DLL surrogate
application. COM DLL servers are loaded, by default, into their own surrogate
process. If for some reasons, you need to load other COM DLL servers into an
existing surrogate process, so it supports more than one COM DLL servers, there
are two requirements:
- The COM DLL servers must have the same AppID value.
- The security context of the COM DLL servers must be the same. This means
that they have matching security identities.
If 2 COM DLL servers are
to be launched under different security identities, they must be in different
surrogate processes, regardless of whether or not their
AppID's match.
Local In-process consideration
To unregister manually do like that:
- Unregister the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- type the command ">
regsvr32 /u
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLLPS.DLL"
- Unregister the COM DLL server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory where is your registered file (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
regsvr32 /u
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLL_PSDLL.DLL"
Remote consideration
To unregister manually do like that:
Local Surrogate consideration
In order to do like that, you have just to
do the same things as explain on the section above (Remote Consideration) and
follow the instructions below "
On
the server machine".
Of course you have to execute them on the Server
machine, i.e. in this case the same as your Client machine (here we are
interested in the Local Surrogate consideration).
To build the COM Server as a single DLL, you have to follow
the steps define in the
General's
section (1 DLL).
To create the server, you have to follow the steps
below:
- Start the Visual C++ IDE and Select File, New and fill in
like below:

- You want to create a DLL Server with merging the Proxy/Stub code, so
choose Server type's option like that:
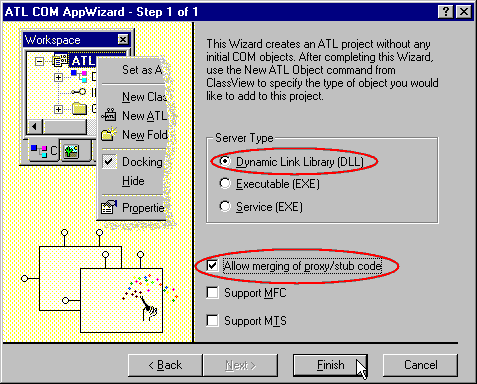
After that, the ATL COM wizard will create these files :
- Workspace:
macrotoposerver_dllmerged.dsw
- Project:
macrotoposerver_dllmerged.dsp
- Initialisation code in
macrotoposerver_dllmerged.cpp and
macrotoposerver_exe.h
- IDL source in
macrotoposerver_dllmerged.idl
- and files for the Proxy/Stub DLL:
macrotoposerver_dllmergedps.mk
macrotoposerver_dllmergedps.def
Now, I can
see in your eyes the question
"What do we get again a separated makefile for
the Proxy/Stub DLL file ?" rising. The answer is that in some cases it is
more at your convenience to have only 1 DLL to register than 2. However, this
convenience is just available when your component is to be used as an in-process
server. Otherwise, as an out-of-process server (Local or Remote) you still need
the Proxy/Stub code (more the Proxy than the Stub) insides the Client
application.
Therefore, although you have asked to have the Proxy/Stub code
merged you get the necessary code to build a Proxy/Stub DLL file.
The
final COM Server name is
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL .
You have to follow the general instructions at
Common
Step 2 - Edit project settings.
Although you have checked the
checkbox "allow merging of Proxy/Stub code", this is not enough to build your
COM DLL Server with the merged code.
So, In the project settings do as
follow:
- Choose "All configurations", be sure that the project node is selected.
- In the C++ tab:
- In the Pre-processor definitions go to the end, append a
comma and add _MERGE_PROXYSTUB
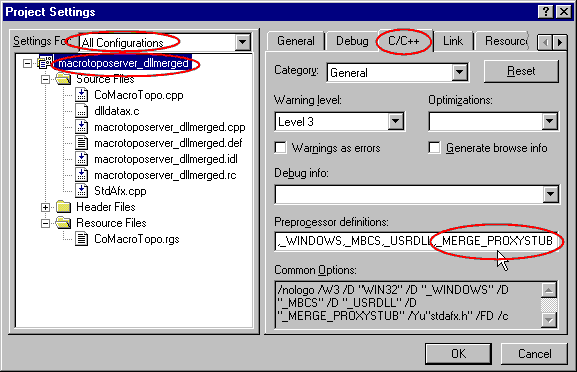
- Select the dlldatax.c file and always for All
configurations.
- In the General tab:
- Uncheck the Exclude file from build.
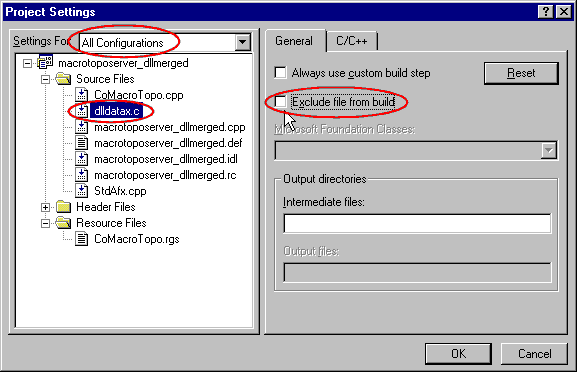
- Now, go to the C++ tab:
- Select Precompiled Headers in the Category drop down
list-box.
- Select the Not using precompiled headers choice.
- And press OK.
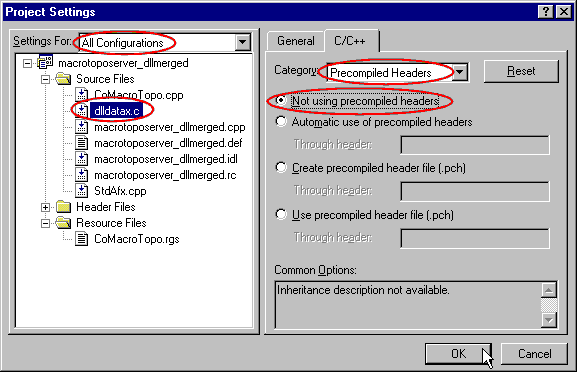
The file
dlldatax.c includes
dlldata.c and
file(s) called like "
your_idl_filename_p.c". The former contains
code for the necessary COM entry points for the COM DLL Server, such as
DllGetClassObject. The latter contains code to marshal (i.e. the Proxy/Stub
code) all Interfaces defined in the IDL file. These files are generated by the
MIDL compiler (Microsoft IDL compiler) deliver with the Win32 SDK.
Step 3 to 6 and 8 - Common part 
Follow the common steps:
step
3,
step
4,
step
5,
step
6, and
step
8.
As you have used the ATL Wizard to generate your
project, it automatically added the command to register your server (in the
Project Settings window, in the tab of the
Custom build). However,
it does not do anything for the Proxy/Stub DLL, so you have to do it
yourself.
You also have to consider that generally the build machine is
different from the client or server machine.
Local In-process consideration
To register manually, in your build
machine, do like that:
- To register the COM DLL server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL"
Here, the Proxy/Stub code
is register at the same time.
Remote consideration
In this case, you have to perform two
installations: one on the client machine and the other on the server machine.
Here are the instructions for both:
- On the client machine
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL)
using
the command line ">regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL".
- Register the remote server entries.
Generally we do not want (and we
do not need) to register the full Server component on the Client machine. In
that case, we need to create a registry file to add the necessary keys to
enable the remote access of our component on the Server machine. So, create
a new text file with the extension ".reg" (e.g.
registry_client_exe.reg) and add these lines to it: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{12345678-0000-0000-0000-abababababab}]
@="CoMacroTopo Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID\{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}]
@="MacroTopoServer_dllmerged"
"RemoteServerName"="myservercomputer"
"myservercomputer" is the machine name where the COM Server is
installed.
If you have more than one COM Class object in your server
(here, you have only CoMacroTopo), you have to repeat the first 3 lines for
each CLSID value you have. However, keep with the same
value of AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU for the "AppID" key: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{<another COM Class ID>}]
@="CoAnother Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
...Now you have to register all this information on the registry. Using
Windows Explorer, double-click on your file. The registry will ask you if
you want to add this information to the current registry (if you have the
administrator rights) click "Yes" and that is it.
- On the server machine (in that
order)
- Register the server entries stored in your server file
(MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL)
by using the command line
">regsvr32 MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL".
- Register the server entries indicating the use of the DLL surrogate
application.
You need to create a registry file to add the necessary keys
to enable the management of our component by the DLL Surrogate application.
So, create a new text file with the extension ".reg" (e.g.
registry_server_exe.reg) and add these lines to it: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{12345678-0000-0000-0000-abababababab}]
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AppID\{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}]
@="MacroTopoServer_dllmerged"
"DllSurrogate"=""
The main point is to permit our COM DLL server to be launched using
the surrogate application. Here, the value is an empty field "" which
means that COM will use the default one provided with by the system (e.g.
the default surrogate application on Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 is
DLLHOST.EXE).
If you have more than one COM Class object in
your server (here, you have only CoMacroTopo), you have to repeat the first
3 lines for each CLSID you have. However, keep with the same
value for the "AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU" key: [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{<another COM Class ID>}]
@="CoAnother Class"
"AppID"="{AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU}"
...Now you have to register all this information on the registry. Using
Windows Explorer, double-click on your file. The registry will ask you if
you want to add this information to the current registry (if you have the
administrator rights) click "Yes" and that is it.
The
"
AppID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU" value is a GUID. You have to generate it (e.g. use
the
GUIDGEN.EXE tools delivered with MS-Dev Studio). It must be the same
value used on both sides: Client and Server.
Local Surrogate consideration
You can as well look for a variant
configuration that uses your COM DLL Server on the same machine as your client
application but outside of the client process.
Nonetheless, a DLL can never
run without a parent process. COM provides a default DLL surrogate application
that can load your COM DLL Server and provide it a process
environment.
In order to do like that, you have just to do the same
things as explain on the section above (Remote Consideration) and follow the
instructions below "
On
the server machine".
Of course you have to execute them on the Server
machine, i.e. in this case the same as your Client machine (here we are
interested in the Local Surrogate consideration).
You have to register
the Proxy/Stub DLL file for your client application as well:
- Register the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL)
by
using the command line ">regsvr32
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL".
Now, you have to
change your client code and ask explicitly for loading the COM DLL Server
in a separate process space (runs on the same machine but in a different
process) using the DLL Surrogate application.
To indicate to COM that you
want to create your object in the different process space you have to use the
Flag CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER (and only this flag) on the CoCreateInstance()
call, CoCreateInstanceEx() call or on the ATL Interface smart pointer
constructor like this:
...
IMacroTopoDispPtr pDisp(__uuidof(CoMacroTopo), NULL, CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER);
long lA(500), lB(114);
long lResultat = pDisp->Add(lA,lB);
...
A remark about the relation between a COM DLL server and a DLL surrogate
application. COM DLL servers are loaded, by default, into their own surrogate
process. If for some reasons, you need to load other COM DLL servers into an
existing surrogate process, so it supports more than one COM DLL servers, there
are two requirements:
- The COM DLL servers must have the same AppID value.
- The security context of the COM DLL servers must be the same. This means
that they have matching security identities.
If 2 COM DLL servers are
to be launched under different security identities, they must be in different
surrogate processes, regardless of whether or not their
AppID's match.
Local In-process consideration
To unregister manually do like that:
- Unregister the COM DLL server file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL):
- Open a DOS-Command window and go to your project's directory,
- go to your built directory where is your registered file (e.g.
\Debug)
- type the command ">
regsvr32 /u
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGED.DLL"
To unregister manually
do like that:
Local Surrogate consideration
In order to do like that, you have just to
do the same things as explain on the section above (Remote Consideration) and
follow the instructions below "
On
the server machine".
Of course you have to execute them on the Server
machine, i.e. in this case the same as your Client machine (here we are
interested in the Local Surrogate consideration).
You have to unregister
the Proxy/Stub DLL file:
- Unregister the Proxy/Stub file (MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL)
by
using the command line ">regsvr32 /u
MACROTOPOSERVER_DLLMERGEDPS.DLL".
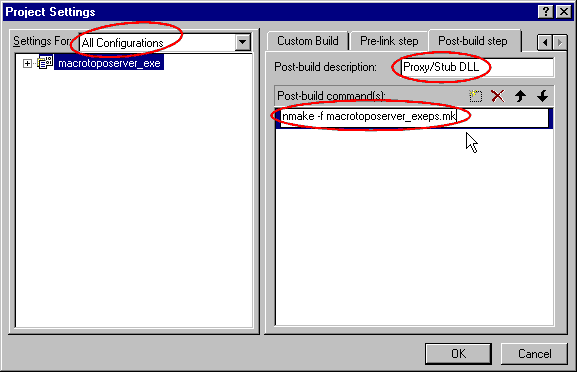
In the project settings, I generally do those changes in
order to avoid launching a makefile from the command line for the Proxy/Stub
DLL:
- Choose "All configurations",
- In the Post-build step's tab:
- Write a Post-build description,
- Create a new Post-build command as " nmake -f " + the Proxy/Stub
DLL makefile (e.g.
macrotoposerver_exeps.mk),
- And press OK.
Now lets insert our COM object and its Interface.
- Select Insert and New ATL Object :
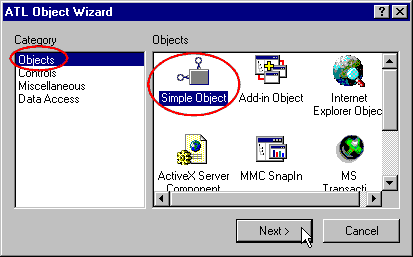
- Double click on simple object (or click on Next) and in the
Names' tab:
- Enter the Short Name as CoMacroTopo
- Enter the Interface name as IMacroTopoDisp
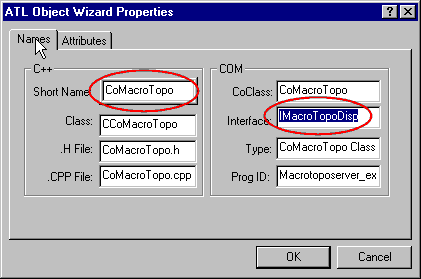
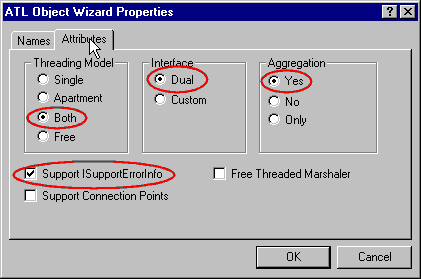
- In the Attributes' tab:
- Choose Both as value for Threading model,
- Dual (default) as value for Interface,
- Yes (default) as value for aggregation,
- Add Support ISupportErrorInfo,
- And press OK.
Now lets insert our methods.
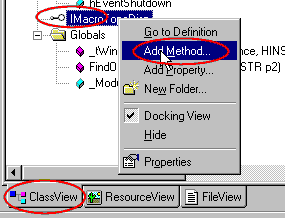
- Go to the ClassView's tab in the Workspace window,
- Select the
IMacrotTopDisp item (the one from the root node
and not from the CCoMacroTopo node),
- using the right click mouse button, select Add method... from the
popup menu.
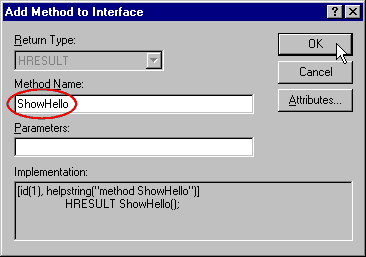
- Enter the Method Name as ShowHello
- And press OK.
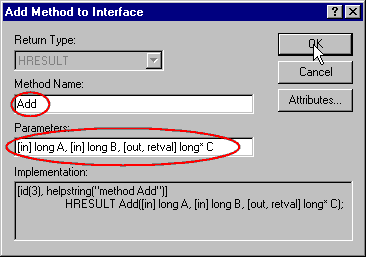
Let's do the same for the second method:
- do the same steps as before to open the "Add method dialog box",
- Enter the Method Name as Add
- Enter the Parameters as [in] long A, [in] long B, [out, retval]
long* C
- And press OK.
To edit the code implementation of those methods you have
to:
- Go to the ClassView's tab in the Workspace window,
- Open the
CCoMacroTopo node item,
- Open the
IMacrotTopDisp node item,
- Double-click on ShowHello() item.
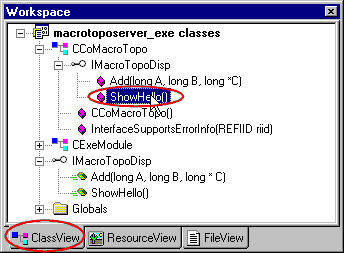
Write the function's body like that:
STDMETHODIMP CCoMacroTopo::ShowHello()
{
::MessageBox(NULL,
_T("Hello world ;~) - Dispatch"),
_T("CoMacroTopoServer - Executable"),
MB_OK);
return(S_OK);
}
Do the same for the <CODE>Add() method and write the function's body like that: STDMETHODIMP CCoMacroTopo::Add(long A, long B, long *C)
{
*C = A + B;
return(S_OK);
}
You will do it by hand as ATL wizard can not do it
(except if you want to create a new ATL CoCalss with a new Interface). The first
thing you must do is to edit the IDL file to add the new interface (For further
information look at "Learning DCOM" [Bi3]). The most relevant part of the IDL
file is:
...
[
object,
uuid(IID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU),
helpstring("IMacroTopoCustom Interface")
]
interface IMacroTopoCustom : IUnknown
{
};
...
coclass CoMacroTopo
{
[default] interface IMacroTopoDisp;
interface IMacroTopoCustom;
};
You must use the GUID Generator (
GUIDGEN.EXE) in order to
obtain your unique
IID_GUIDGEN_BY_YOU (Interface ID).
Just remember
you that a custom Interface can not be used from an Automated environment like
VBScript. Custom interface does not inherit from IDispatch.
Edit the
declaration file for the CCoMacroTopo class
(CoMacroTopo.h) and add the code in bold:
class ATL_NO_VTABLE CCoMacroTopo :
public CComObjectRootEx<CComMultiThreadModel>,
public CComCoClass<CCoMacroTopo, &CLSID_CoMacroTopo>,
public ISupportErrorInfo,
public IDispatchImpl<IMacroTopoDisp,
&IID_IMacroTopoDisp,
&LIBID_MACROTOPOSERVER_EXELib> ,
public IMacroTopoCustom
public:
CCoMacroTopo()
{
}
DECLARE_REGISTRY_RESOURCEID(IDR_COMACROTOPO)
DECLARE_PROTECT_FINAL_CONSTRUCT()
BEGIN_COM_MAP(CCoMacroTopo)
COM_INTERFACE_ENTRY(IMacroTopoDisp)
COM_INTERFACE_ENTRY(IDispatch)
COM_INTERFACE_ENTRY(ISupportErrorInfo)
COM_INTERFACE_ENTRY(IMacroTopoCustom)
END_COM_MAP()
...
};
Save the files (".idl" and ".h"). Visual will detect automatically
these changes and updates interfaces and CoCLass objects in the
ClassView's
tab in the workspace window. So, now repeat the step for
adding
methods to an Interface (as you have done for the
IMacroTopoDisp interface).
Be careful, remember to select
the Interface node item before.
Doing this, change the name of the methods
like that:
ShowHello() to ShowHelloCustom(),
Add() to AddCustom().
Implement them
with the same implementation as for
IMacroTopeDisp.
STDMETHODIMP CCoMacroTopo::ShowHelloCustom()
{
::MessageBox(NULL,
_T("Hello world ;~) - Custom"),
_T("CoMacroTopoServer - Executable"),
MB_OK);
return(S_OK);
}
STDMETHODIMP CCoMacroTopo::AddCustom(long A, long B, long *C)
{
*C = A + B;
return(S_OK);
}
Ok, now you can compile and link:
- our COM Server (e.g.
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXE.EXE)
- our Proxy/Stub DLL (e.g.
MACROTOPOSERVER_EXEPS.DLL)
At this stage Visual C++ has already registered your COM Server (DLL
or Executable) but not your Proxy/Stub (Look in the
Project Settings /
Custom Build tab).
Microsoft IDL compiler
Proxy/Stub DLL build
To build and test the COM Server describe in this
article you do not need to do anything if your are using them as Local servers
(in-process or out-of-process). However, if you are testing them as Remote
servers you need at least to enable them to run with the
Interactive user
account. This is due to display the Dialog box when you call
ShowHello().
To enable the COM Server to use the
Interactive
user for activation launch
DCOMCNFG.EXE application (you can use as
well
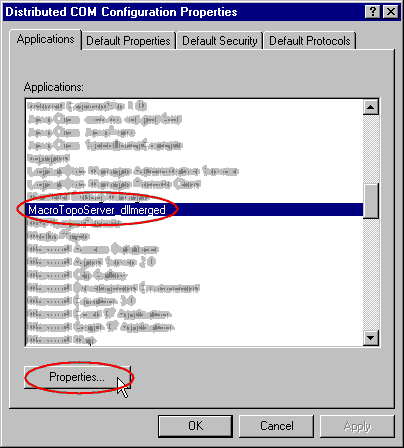
OLEVIEW.EXE):
- Scroll down the Applications list until finding your COM
application and select it (e.g.
MacroTopoServer_dllmerged).
- Click on Properties...
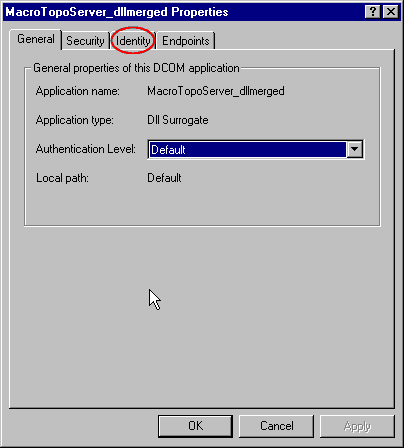
- In the user account radio buttons, choose the Interactive
User.
- Click on Ok and close the application.
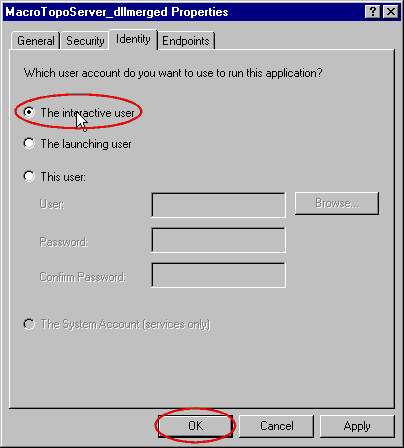
Now, your component will be launched with the
Interactive user account. This means also that if no one is connected,
your component can not be launched as well. However, here we just need an
account to test our component.
- CoClass and Interface name
CoClass and Interface (human
readable) names are the same for the 3 servers. COM documentation refers
these names at Logical name (e.g. IMacroTopoDisp).
However, each server has its own unique set of GUIDs (for Library ID,
Interface ID and CoClass ID) which are different. COM documentation refers
these names at Physical name (e.g.
{12345678-ABCD-FEDC-A1B2-F1F2F3F4F5D5}). For further information
about COM
GUIDs, click here.
To have the same logical name as another
Interface or CoClass might happen, but does not matter since you have
different Physical names, because COM will look after the Physical
names. There is an exception with the ProgID as COM will look for a
text name, but at the end, this logical name is coupled to a
physical name (i.e. a CLSID).
That is one of the main
concepts in COM: to be able to identify uniquely your coclasses and
interfaces.
- COM Server as a Windows NT Service
- Currently only a single instance of a Win32 service may be running at a
given time on a machine. COM services must therefore register their class
objects on launch using REGCLS_MULTIPLEUSE to support multiple
clients.
- A COM Server running as a service has some API restrictions such as: it
can not display dialog boxes or windows.
