Introduction
A Geographic Information System is a type of application which has a set of facilities to capture, store, retrieve, maintain, and display geographic data and information. GIS applications are developed to meet many purposes, from simple purposes like GIS data exploration to sophisticated purposes like watershed mapping. Different commercial libraries are available for developers to use and implement in their applications, like ArcObject from ESIR and Map Suite from ThinkGeo. Unfortunately, the cost of license for these libraries is usually high, which makes the GIS application development process not viable for free lance programmers and small firms. In this series of tutorials, I am going to describe in detail how to build a desktop GIS application using the Open Source MapWinGIS library and C#. MapWinGIS is an ActiveX control for GIS development, with built-in support for many Raster and Vector formats. MapWinGIS.ocx is the core of MapWindow GIS, the well known Open Source, multi-purpose, GIS desktop application. The first step in reading this tutorial is acquiring MapWinGIS.ocx from the MapWindow GIS Open Source project website, then installing it to your computer using the installation procedures provided by the project site.
Create Your Map
Preparation
In this tutorial, I am using .NET Framework 3.5 and Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 Professional Edition. Actually, you can use Visual Studio Express Edition without any problem. I am also using a set of GIS data in ESRI shapefile format, which I have provided above as a zipped file. I recommend you to download this data compressed file, decompress it, and place the file contents in an independent folder. Now, you are ready to go to the next step.
Create a Project and Add a Reference to MapWinGIS Components
Now, fire up your Visual Studio and create a new Windows Forms application. Point to the Project menu, then click Add Reference. In the Add Reference dialog box, point to COM tab, then select MapWinGIS Components from the Component Name list and click OK.
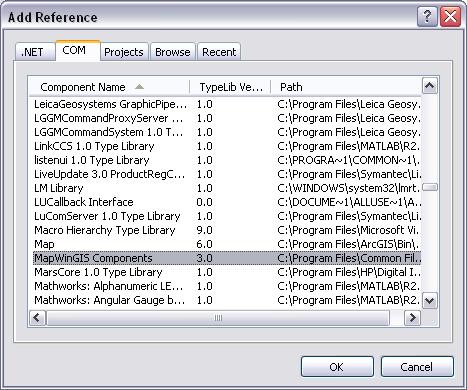
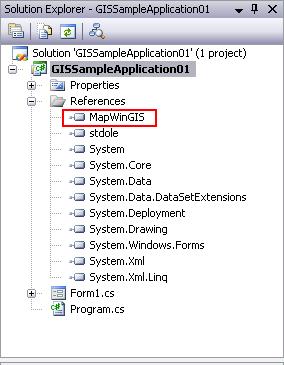
Now, you have a new reference in your project and you can show its name under References in the Solution Explorer.
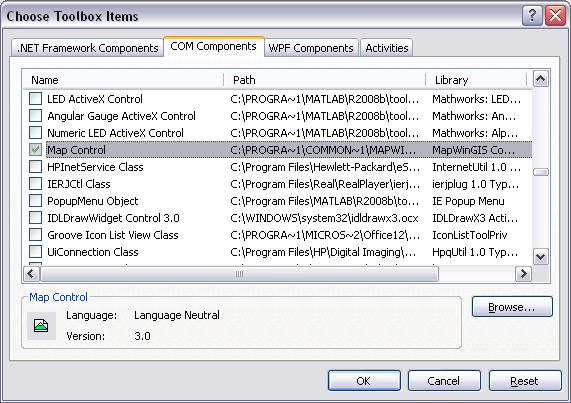
Now, we are going to add the Map control to our toolbox. The Map control is a control used as a container and interactive display area for geographic data. To add this control to the toolbox, point to the General tab in the toolbox and right click. Select Choose Item from the menu. The Choose Toolbox Item dialog box will appear. Select the COM Component tab and then select Map Control. To add it to the toolbox, click OK.
Now, you can see the Map Control icon in the toolbox contained by the General tab.
Time to Create Your GUI
Now, it's time to build your interface. Drag a ToolStrip control from the Menu & Toolbars tab in the toolbox and drop it to the form. Add five buttons to the ToolStrip, and name these buttons toolCursor, toolZoomExtent, toolZoomIn, toolZoomOut, and toolPan. You can also assign meaningful labels and images to the buttons (you can use the images that I have in my project resources). Drag the Map control from the toolbox and drop it to the form. In the Properties window, set the Dock property of the Map control to Fill and set the CursorMode property to cmNone.
Load your GIS data to the Application Pragmatically
Now, we will add two ESRI Shapefiles for our map. The ESRI Shapefile or simply a Shapefile is a popular geospatial vector data format for geographic information systems software. In the Form1_Load event, add the following code:
int intHandler1;
MapWinGIS.Shapefile shapefile1 = new MapWinGIS.Shapefile();
shapefile1.Open(@"D:\GISSampleData\base.shp", null );
intHandler1 = axMap1.AddLayer(shapefile1, true);
int intHandler2;
MapWinGIS.Shapefile shapefile2 = new MapWinGIS.Shapefile();
shapefile2.Open(@"D:\GISSampleData\nile.shp", null);
intHandler2 = axMap1.AddLayer(shapefile2, true);
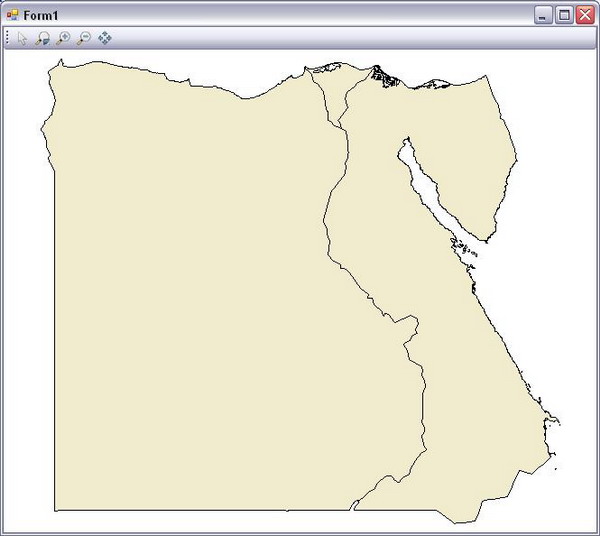
In the first line, we have created an integer variable (intHandler1). In the second line, we have created an instance (shapefile1) for the MapWinGIS.Shapefile class. MapWinGIS.Shapefile is a container for geometric entities that represent real world geographic features. In the third line, the data source for the new object (shapefile1) is defined. This data source is an ESRI Shapefile. This data source shows Egypt as a polygon. In the fourth line, we have added this new object to our map control (axMap1) and made it visible. The function AddLayer is used to add a geographic layer to the map control and return an integer indicating the layer handler. Lines 4 to 8 add the second Shapefile to the Map control and make it visible. It is now time to run your first GIS application; strike F5 in your key board to show Egypt's map in the map control.
Change Your Feature Symbol
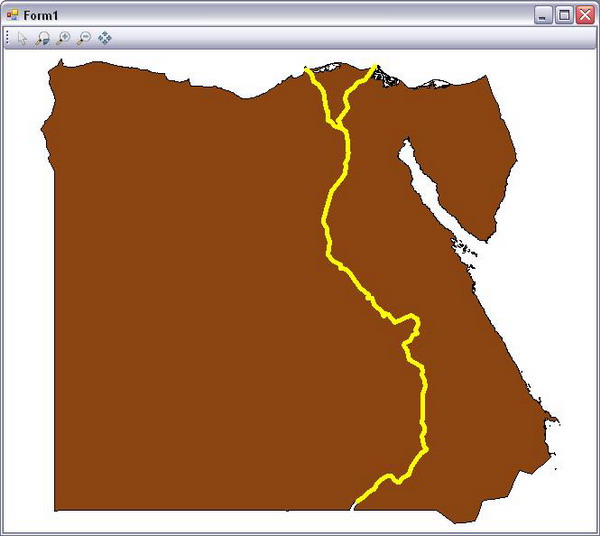
Customizing different symbology for different geographic features included in the map is one of the most important tasks for a GIS developer. In this lesson, I am going to present the easiest way to customize features symbology. Actually, MapWinGIS provides many advanced methods to symbolize GIS data, which I will discuss in an advanced lesson. Now, add the following code after the previous code in Form1_Load event:
axMap1.set_ShapeLayerFillColor(intHandler1,
(UInt32)(System.Drawing.ColorTranslator.ToOle
(System.Drawing.Color.SaddleBrown)));
axMap1 .set_ShapeLayerLineColor (intHandler2 ,
(UInt32)(System.Drawing.ColorTranslator.ToOle
(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow)));
axMap1.set_ShapeLayerLineWidth(intHandler2,5);
In the first line, we use the set_ShapeLayerFillColor method of the Map control (axMap1). This method uses the layer handler (intHandler1) and a color in UInt32 format to set the fill color for the defined layer. There are many other useful methods provided by the Map control to customize the layer symbology, like set_ShapeLayerFillStipple which defines the filling type of the layer, and set_ShapeLayerFillTransparency which defines the transparency level of the layer. In the second line, another method is used. This method - set_ShapeLayerLineColor - defines the color of line for line-geometry layers using the layer handler and the UInt32 format for color. In the third line, I have used the set_ShapeLayerLineWidth method to define the width of the line-geometry layer using this layer handler, and a float number denotes the line width. Run your application to see how it displays your map now.
Add Some Actions to Your Map
Sure, you want to add some amazing actions like zoom in, zoom out, and pan for your map. Adding such actions is a very simple task with MapWinGIS. The CursorMode property for the Map control provides these tasks in an easy to use way; you have to assign the mode that you want to this property to use it directly in your map. In the following code, I am going to play with the CursorMode property using the Click event for each button in my toolbar.
private void toolCursor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
axMap1.CursorMode = MapWinGIS.tkCursorMode.cmNone;
}
private void toolZoomIn_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
axMap1.CursorMode = MapWinGIS.tkCursorMode.cmZoomIn;
}
private void toolZoomOut_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
axMap1.CursorMode = MapWinGIS.tkCursorMode.cmZoomOut;
}
private void toolPan_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
axMap1.CursorMode = MapWinGIS.tkCursorMode.cmPan;
}
To set your map to the maximum map extent, you will use the ZoomToMaxExtents method of the Map control. Just call this method using the Click event as follows to display your map in the maximum extent:
private void toolZoomExtent_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
axMap1.ZoomToMaxExtents();
}
Time to test these new features; run your application, and check every button.
Conclusion
MapWinGIS is the most easy way to create GIS desktop applications. The above features show the principle tasks required by a GIS programmer. Future lessons in this series will look at many useful and advanced features of MapWinGIS.
History
- First version: July 12, 2009.
