Introduction
Have you ever wanted to pass a DataTable, or array, containing tens or tens of thousands (or even millions) of records, into a SQL Server2000 stored procedure in just one database call? Ever wanted to pass a list of IDs of records to select or delete into a SP? Then read on.
The trick is to convert lists of data into byte arrays, which are then passed as Image type parameters into the stored procedure, then in the SP the image is transformed into a table variable containing the original data. The following SQL server function is one of a number of functions I have written to easily transform an Image parameter into a variable table. This one creates a table of varchars.
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.GetTableVarchar(@Data image)
RETURNS @DataTable TABLE (RowID int primary key IDENTITY ,
Value Varchar(8000))
AS
BEGIN
IF(dbo.ValidateExpectedType(103, @Data)<>1) RETURN
DECLARE @Ptr int, @Length int,
@VarcharLength smallint, @Value Varchar(8000)
SELECT @Length = DataLength(@Data), @Ptr = 2
WHILE(@Ptr<@Length)
BEGIN
SET @VarcharLength = SUBSTRING(@Data, @ptr, 2)
SET @Ptr = @Ptr + 2
IF(@VarcharLength<0)
SET @Value = NULL
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @Value = SUBSTRING(@Data, @ptr, @VarcharLength)
SET @Ptr = @Ptr + @VarcharLength
END
INSERT INTO @DataTable (Value) VALUES(@Value)
END
RETURN
END
I have also created a number of C# classes for creating byte arrays from collects of different types of data.
Calls to the database, in the following examples, use SQLHelper from the Microsoft Application Blocks, as these hide most of the dull plumbing required to call a SP. MSDN Website.
Please bear with my humble snail farm examples; I couldn�t bring myself to use customer/orders examples.
We�ll start off with a simple case for the first example.
Passing a list of integer IDs to select records with
Code to take the checked items in a checked list box and pass their IDs in to a stored procedure. The SP then returns a result set containing the details for each selected ID.
private DataSet GetSelectedSnailDetails()
{
SQLIntListCreator snailIDs = new SQLIntListCreator();
foreach(Snail aSnail in mySelectionCheckedListBox.CheckedItems)
snailIDs.AddValue(aSnail.SnailID);
return SQLHelper.ExecuteDataset(CONN_STRING,
"GetSnailDetails", snailIDs.GetList());
}
Stored procedure to take a list of ints in the form of an image (byte array), convert it to a table variable of ints which is then joined on the SnailID column of the Snails table to return details for each selected snail.
CREATE PROCEDURE GetSnailDetails
@SnailIDs image
AS
SELECT Snail.*
FROM dbo.GetTableInt(@SnailIDs) SIDs
INNER JOIN Snails ON SIDs.Value = Snails.SnailID
GO
Stored procedure to delete all the snails in the @Snails image list..
CREATE PROCEDURE DeleteSnails
@SnailIDs image
AS
DELETE Snail
FROM dbo.GetTableInt(@SnailIDs) SIDs
INNER JOIN Snails ON SIDs.Value = Snails.SnailID
GO
Passing a collection of snail statuses to a SP for updating
private void UpdateSnailStatuses(Snail[] snails)
{
SQLIntListCreator snailIDs = new SQLIntListCreator();
SQLVarcharListCreator statuses =
new SQLVarcharListCreator();
SQLRowversionListCreator rowVersions=
new SQLRowversionListCreator();
foreach(Snail aSnail in snails)
{
snailIDs.AddValue(aSnail.SnailID);
statuses.AddValue(aSnail.Status);
rowVersions.AddValue(aSnail.RowVersion);
}
SQLHelper.ExecuteNonquery(CONN_STRING,
"UpdateSnailStatuses", snailIDs.GetList(),
statuses.GetList(), rowVersions.GetList());
}
Stored procedure to update the statuses of snails while also checking for the correct timestamp rowversion.
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.UpdateSnailStatuses
@SnailIDs image,
@Statuses image,
@RowVersions image
AS
UPDATE Snail
SET Snail.Status = Statuses.Value
FROM Snail
INNER JOIN GetTableInt(@SnailIDs) SnailIDs
ON Snail.SnailID = SnailIDs.Value
INNER JOIN GetTableVarchar(@Statuses) Statuses
ON SnailIDs.RowID = Statuses.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableRowversion(@RowVersions) RowVersions
ON Statuses.RowID = RowVersions.RowID
WHERE TSEQUAL(Snail.RowVersion, RowVersions.Value)
RETURN @@ERROR
Passing a DataTable to a SP for insertion into a table
Code to convert the data in a DataTable into 5 byte arrays, which are then passed to the AddSnails stored procedure to be inserted into the Snail table.
private void AddSnails(DataTable snails)
{
SQLVarcharListCreator species = new SQLVarcharListCreator();
SQLDatetimeListCreator dOB = new SQLDatetimeListCreator();
SQLNvarcharListCreator location = new SQLNvarcharListCreator();
SQLBitListCreator isMale = new SQLBitListCreator();
SQLMoneyListCreator value = new SQLMoneyListCreator();
foreach(DataRow row in snails.Rows)
{
species.AddValue(row["Species"]);
dOB.AddValue(row["DOB"]);
location.AddValue(row["Location"]);
isMale.AddValue(row["IsMale"]);
value.AddValue(row["Value"]);
}
using(SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection(CONN_STRING))
{
cnn.Open();
SqlCommand comInst = new SqlCommand("AddSnails", cnn);
comInst.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
comInst.CommandTimeout = 10000;
comInst.Parameters.Add("@Species", species.GetListAndReset());
comInst.Parameters.Add("@DOB", dOB.GetListAndReset());
comInst.Parameters.Add("@Location", location.GetListAndReset());
comInst.Parameters.Add("@IsMale", isMale.GetListAndReset());
comInst.Parameters.Add("@Value", value.GetListAndReset());
comInst.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
Stored procedure to convert the images into table variables, join them together and insert the resulting data into the Snail table.
ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.AddSnails
(
@Species image,
@DOB image,
@Location image,
@IsMale image,
@Value image
)
AS
INSERT INTO Snail (Species, DOB, Location, IsMale, Value)
SELECT Species.Value, DOB.Value,
Location.Value, IsMale.Value, Value.Value
FROM GetTableMoney(@value) Value
INNER JOIN GetTableBit(@isMale) IsMale ON Value.RowID = IsMale.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableVarchar(@species) Species
ON IsMale.RowID = Species.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableDateTime(@dOB) DOB ON Species.RowID = DOB.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableNvarchar(@location) Location
ON DOB.RowID = Location.RowID
RETURN @@ERROR
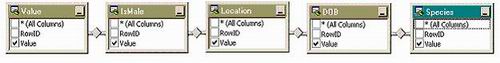
Design view of the join across all the table variables.
Performance
I ran a performance comparison between inserting snail records using the above stored procedure and a standard 1 record insert stored procedure called many times. These are the results I got.
| Records Inserted |
Standard one stored procedure call per record (msec) |
One stored procedure call for all records (msec) |
| 1 |
2 |
10 |
| 10 |
22 |
14 |
| 100 |
219 |
60 |
| 1000 |
2 259 |
505 |
| 10 000 |
22 593 |
4 083 |
| 100 000 |
301 368 |
44 645 |
| 1 000 000 |
3 094 385 |
571 020 |
The comparison was done on a PC running a P4 1.8 GHz processor with 512 MB RAM. This is a very crude comparison as network speed, table structure and other things will greatly influence the speed of both methods. In this example both the SQL Server and the client where running on the same machine resulting in a very fast network. Inserts into the snail table are fast as it has only one index (clustered).
Points of interest
- Strong Type checking: Each
SQLListCreator object prefixes the byte array it produces with a data type byte e.g. 107 for the SQLMoneyListCreator. The SQL function then checks this first byte and throws an error if it is of the wrong data type. As RAISERROR cannot be called from within a SQL function, the following work around is used. An attempt to convert the error message to an int is made; this results in an error being returned like this - 'Syntax error converting the varchar value'. The real error is: 'Function expected a list of Int types but was given a list of Money types.' to a column of data type int. Not the most elegant message but it points you in the right direction.
- ToString:
ToString() returns a hex version of the list, this can be useful during development/debugging when you may want to paste lists into Query Analyzer. E.g. SELECT C.Value, PV.Value, EC.Value, TS.Value,
P.Value, PV.Value/TS.Value
FROM GetTableVarchar
(0x670007416C20476F7265000E47656F726765
20572E2042757368000B52616C7068204E61646572) C
INNER JOIN GetTableInt(0x65030A32590301E5C2002BFD8B)
PV ON C.RowID = PV.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableInt(0x650000010A0000010F00000000) EC ON
PV.RowID = EC.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableMoney
(0x6B00000117782C6150000001B0E20FACF00000001217F259D0)
TS ON EC.RowID = TS.RowID
INNER JOIN GetTableBit(0x6C9B) P ON TS.RowID = P.RowID
- Data Types: I have implemented SQL functions and C# classes for
BigInt, Int, Bit, Datetime, Money, RowVersion, Uniqueidentifier, Varchar and Nvarchar. Most other data types could be implemented without too much difficulty, the exceptions are ntext, text and image. These data types can contain more that 8000 bytes and as such the SQL Substring function can not be used to strip the individual items from a list of items contained in an image.
- Nulls: Null values can be added into a list with the
AddNull() method, also the AddValue(object value) overload will accept DBNull and any object that implements INullable and returns true for IsNull().
- Packet size: The database connection packet size can be set to a larger size than the default in the connection string. This may give additional performance improvements when sending large amounts of data to the database in single calls, but will degrade performance for smaller calls.
