Introduction
This tip introduces a simple HTTP server class which you may incorporate into your own projects and it can work either locally or processing limited concurrent requests.
Background
An Http Server is bound to an IP address and port number and listens for incoming requests and returns responses to clients. Simple http server is flexible to be added into complex projects for rendering Html elements or serving as a backend server, or even deployed in the client side to drive specific devices. If you are looking for a solution to create a simple HTTP server which can be easily embedded to your projects and process limited web requests, this tip meets your need.
Here is the structure of Http Server implementation:
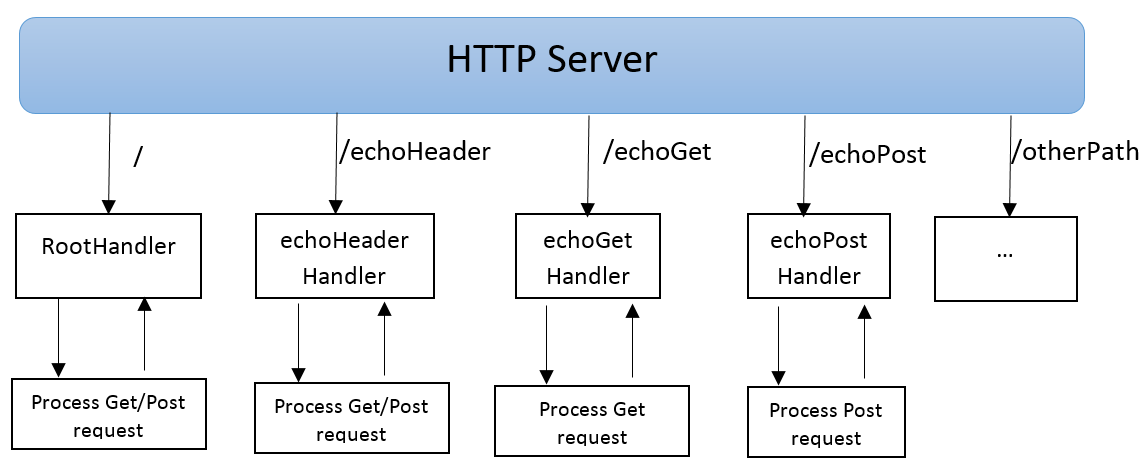
Using the Code
Since Java 1.6, there's a built-in HTTP server included with the J2EE SDK. It can be downloaded at:
A simple HTTP server can be added to a Java program using four steps:
- Construct an HTTP server object
- Attach one or more HTTP handler objects to the HTTP server object
- Implement HTTP handler to process
GET/POST requests and generate responses - Start the HTTP server
1. Create a http Server
The HttpServer class provides a simple high-level Http server API, which can be used to build embedded HTTP servers.
int port = 9000;
HttpServer server = HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress(port), 0);
System.out.println("server started at " + port);
server.createContext("/", new RootHandler());
server.createContext("/echoHeader", new EchoHeaderHandler());
server.createContext("/echoGet", new EchoGetHandler());
server.createContext("/echoPost", new EchoPostHandler());
server.setExecutor(null);
server.start();
2. Create http Handler
Http Handlers are associated with http server in order to process requests. Each HttpHandler is registered with a context path which represents the location of service on this server. Requests for a defined URI path is mapped to the right http handler. Any request for which no handler can be found is rejected with a 404 response.
Create root handler to display server status:
public class RootHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange he) throws IOException {
String response = "<h1>Server start success
if you see this message</h1>" + "<h1>Port: " + port + "</h1>";
he.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = he.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
Declare echoHeader handler to display request header information:
public class EchoHeaderHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange he) throws IOException {
Headers headers = he.getRequestHeaders();
Set<Map.Entry<String, List<String>>> entries = headers.entrySet();
String response = "";
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : entries)
response += entry.toString() + "\n";
he.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = he.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.toString().getBytes());
os.close();
}}
3. Process Get and Post Requests
There are two common methods for a request-response between a client and server through HTTP protocol:
GET - Requests data from specified resourcesPOST - Submits data to be processed to identified resources
Here, you create two handlers to process GET/POST methods respectively.
Declare echoGet handler to process Get request:
public class EchoGetHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange he) throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> parameters = new HashMap<String, Object>();
URI requestedUri = he.getRequestURI();
String query = requestedUri.getRawQuery();
parseQuery(query, parameters);
String response = "";
for (String key : parameters.keySet())
response += key + " = " + parameters.get(key) + "\n";
he.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = he.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.toString().getBytes());
s.close();
}
}
Declare echoPost handler to process Post request:
public class EchoPostHandler implements HttpHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange he) throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> parameters = new HashMap<String, Object>();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(he.getRequestBody(), "utf-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String query = br.readLine();
parseQuery(query, parameters);
String response = "";
for (String key : parameters.keySet())
response += key + " = " + parameters.get(key) + "\n";
he.sendResponseHeaders(200, response.length());
OutputStream os = he.getResponseBody();
os.write(response.toString().getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
Here, you declare a static parseQuery() method to parse request parameters:
public static void parseQuery(String query, Map<String,
Object> parameters) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (query != null) {
String pairs[] = query.split("[&]");
for (String pair : pairs) {
String param[] = pair.split("[=]");
String key = null;
String value = null;
if (param.length > 0) {
key = URLDecoder.decode(param[0],
System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
}
if (param.length > 1) {
value = URLDecoder.decode(param[1],
System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
}
if (parameters.containsKey(key)) {
Object obj = parameters.get(key);
if (obj instanceof List<?>) {
List<String> values = (List<String>) obj;
values.add(value);
} else if (obj instanceof String) {
List<String> values = new ArrayList<String>();
values.add((String) obj);
values.add(value);
parameters.put(key, values);
}
} else {
parameters.put(key, value);
}
}
}
}
4. Test http Server
/ display server status, processed by RootHandler

/echoHeader displays header information, processed by EchoHeaderHandler.

/echoGet processed by EchoGetHandler:


/echoPost processed by EchoPostHandler.


History
- October 15, 2015: Initial version posted
- October 19, 2015: Added server tests
- October 23, 2015: Updated source code
