Introduction
In this tip, I'll tell you how to create a local server in C#.
Using the code
At the top of your code file, add this
using namespace statements:
using System.Net;
using System.Threading;
In the Program class, create a new instance of a HttpListener:
static HttpListener _httpListener = new HttpListener();
Then, create the Main(string[] args) method:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
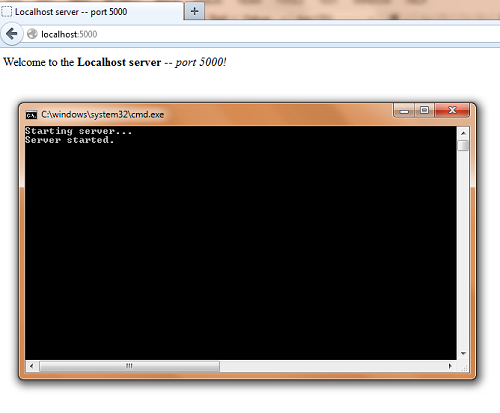
Console.WriteLine("Starting server...");
_httpListener.Prefixes.Add("http://localhost:5000/");
_httpListener.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Server started.");
Thread _responseThread = new Thread(ResponseThread);
_responseThread.Start();
}If you add a prefix, you need to terminate the prefix with a forward slash ("/"). You can add more then one prefix.
Before we can run the application, we need to create the ResponseThread method. And then, we must run the application as administrator.
The ResponseThread method:
static void ResponseThread()
{
while (true)
{
HttpListenerContext context = _httpListener.GetContext();
byte[] _responseArray = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("<html><head><title>Localhost server -- port 5000</title></head>" +
"<body>Welcome to the <strong>Localhost server</strong> -- <em>port 5000!</em></body></html>");
context.Response.OutputStream.Write(_responseArray, 0, _responseArray.Length);
context.Response.KeepAlive = false;
context.Response.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Respone given to a request.");
}
}First, you need to get a request (in the context). If you've a context, you'll find the request in context.Request. And context.Request.Url is the request URL. Then, you can write a response to context.Response.OutputStream. With Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes you can get the bytes of a string. The response must be HTML.
The name of the server
The name of the server can be:
- http://localhost/ (eventually with a port, such as http://localhost:5000/)
- http://[your local IP address]/ (eventually with a port, such as http://[your local IP address]:5000/)
- http://[IP from 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254]/ (eventually with a port, such as http://127.0.0.1:5000/)
