In this tip, you will see how to use the mathnet.numerics library to compute a 2D FFT. You will also learn how to use a mathnet complex32 array to return amplitude and phase of the complex numbers and aggregate functions.
Introduction
This tip shows how to perform a 2D FFT in VB.NET for arbitrary image sizes using the freely available mathnet.numerics library.
Background
The nuget package "mathnet.numerics" for VB.NET provides a 1D Fourier Transform, but no multidimensional FFT. However, the 1D transform can be used to compute a 2D Fourier transform for processing image data by transforming first the rows and then the columns using the 1D FFT (or the other way round). I have shown how to read/write the image data of a bitmap in a separate article.
Using the Code
- Import the nuget package mathnet.numerics
- Define a
complex32 array from the mathnet numerics library - Fill the array with image data,
- For all rows: read out the ith row using "
in_row = arr.Row(i).ToArray" - Perform the 1D FFT for the ith row
- Write the result back into the row using "
arr.SetRow(in_row)" - For all columns: read out the jth column using "
in_col = arr.Column(i).ToArray" - Perform the 1D FFT for the jth column
- Write the result back into the column using "
arr.SetColumn(in_col)"
Imports mnum = MathNet.Numerics
Dim arr As New mnum.LinearAlgebra.Complex32.DenseMatrix(Height, Width)
For i = 0 To Height - 1
For j = 0 To Width - 1
arr(i, j) = New mnum.Complex32(value, 0.0)
next
next
For i = 0 To Height - 1
in_row = arr.Row(i).ToArray
mnum.IntegralTransforms.Fourier.Forward(in_row)
arr.SetRow(i, in_row)
Next
For j = 0 To Width - 1
in_col = arr.Column(j).ToArray
mnum.IntegralTransforms.Fourier.Forward(in_col)
arr.SetColumn(j, in_col)
Next
Dim magnitude as double
magnitude = arr(i, j).Magnitude
maxval = arr.Enumerate().Max(Function(x) mnum.Complex32.Abs(x))
Dim phase as double
phase = arr(i, j).Phase
maxval = arr.Enumerate().Max(Function(x As mnum.Complex32) Math.Abs(x.Phase))
When it comes to displaying the 2D FFT data (amplitude and phase) there are two things to note:
- the amplitudes should be scaled with a dynamic range compression or otherwise the image will appear completely black. In my case I used the function f(x) = log(1+x)/log(1+max(x))*255, where 255 is the intensity range of a color channel for one pixel. You could also use other concave functions, such as sqrt(x), sqrt(1+x) or log(1+log(1+x)) for dynamic range compression.
- the quadrants should be swapped so that zero frequency is at the center of the image. I used the following vb.net function:
Function FFTShift(FFTmat As mnum.LinearAlgebra.Matrix(Of mnum.Complex32)) As mnum.LinearAlgebra.Matrix(Of mnum.Complex32)
Dim i, j As Integer
Dim i_shift, j_shift As Integer
Dim i_max, j_max As Integer
i_shift = FFTmat.RowCount
If isEven(i_shift) Then
i_shift = i_shift / 2
Else
i_shift = i_shift \ 2 + 1
End If
i_max = FFTmat.RowCount \ 2
j_shift = FFTmat.ColumnCount
If isEven(j_shift) Then
j_shift = j_shift / 2
Else
j_shift = j_shift \ 2 + 1
End If
j_max = FFTmat.ColumnCount \ 2
Dim FFTShifted As New mnum.LinearAlgebra.Complex32.DenseMatrix(FFTmat.RowCount, FFTmat.ColumnCount)
For i = 0 To i_max - 1
For j = 0 To j_max - 1
FFTShifted(i + i_shift, j + j_shift) = FFTmat(i, j)
FFTShifted(i, j) = FFTmat(i + i_shift, j + j_shift)
FFTShifted(i + i_shift, j) = FFTmat(i, j + j_shift)
FFTShifted(i, j + j_shift) = FFTmat(i + i_shift, j)
Next
Next
Return FFTShifted
End Function
For the well known "cameraman" picture, the ampitude and phase of the 2D FFT would look like this:
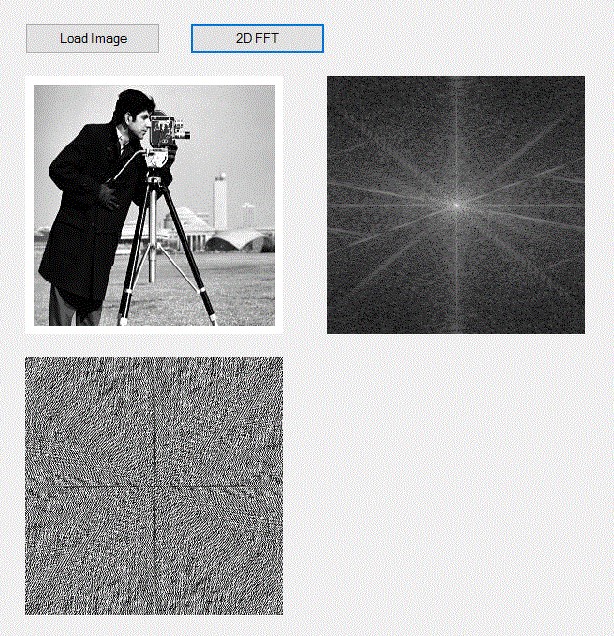
Points of Interest
The FFT from mathnet numerics is not limited to data with a height and width equal to a power of two. Rather, it can be used to process images of arbitrary sizes (up to a maximum size). The possibility to slice the data by accessing the rows and columns of a mathnet array is useful in this context. Even though the image data are usually real numbers, the data must be supplied as complex numbers to the FFT function. Another interesting point to note is that a mathnet.numerics array can return an enumerator which can be used to calculate an aggregate function, such as max, min, median, average, etc. The aggregate is supplied as a lambda function. In VB.NET, the lambda function takes the syntax "Function(x As Datatype) function body".
History
- 1st March, 2021: Initial version
