Introduction
In the past, there were not much choices to embed media (video and audio) into the Web. Adobe Flash was probably the only choice.
Now with the support of HTML5, it's more enjoyable to work with Web's media. In this project, I'm building an audio player with playlist of mp3 tracks, with these basic functionalities:
- Pick a track and play, pause, resume.
- Advance to next, or go back to previous one
- Repeat, either the whole playlist, a single track, or randomly
Although HTML has built-in support for Audio, but different browsers implement differently. For more details, you can have a look at w3schools and developer.mozilla.org. Also, in this project, I don't care to handle fallbacks for older browser. And mp3 is my only format to use. So, let's have a look:
AUD on Chrome:
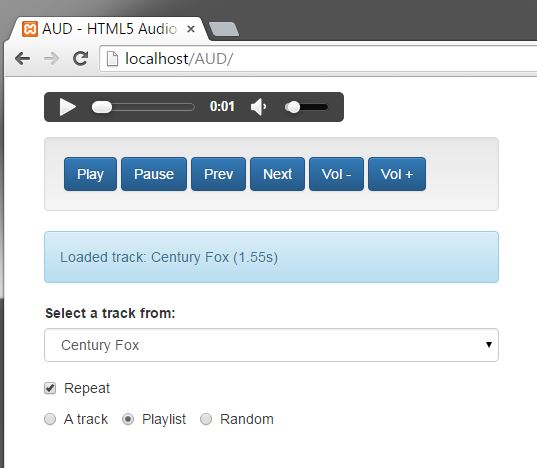
AUD on FireFox

AUD on IE 10

Now let's get started!
Preparation
Since we take advantage of Bootstrap CSS framework, so download it and set up the project as below.

HTML structure
The HTML structure should be thought of first. It is the one that dictates how every other script and style will be. JavaScript and CSS can change frequently without problem. But when HTML structure changes, it will affect and can break up everything!
<div id="myDiv">
<audio id="myAudio" controls="controls" preload="metadata">
<source src="audio/Horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the <code>audio</code> tag.
</audio>
<div id="myAudioControllers" class="well">
<button type="button" id="playBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Play</button>
<button type="button" id="pauseBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Pause</button>
<button type="button" id="prevBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Prev</button>
<button type="button" id="nextBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Next</button>
<button type="button" id="decreaseVolBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Vol -</button>
<button type="button" id="increaseVolBtn" class="btn btn-primary">Vol +</button>
</div>
<div id="myAudioStatus" class="alert alert-info">
<p></p>
</div>
<form role="form">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="myAudioPlaylist">Select a track from:</label>
<select id="myAudioPlaylist" class="form-control">
<option value="audio/CenturyFox.mp3">Century Fox</option>
<option value="audio/Helicopter.mp3">Helicopter</option>
<option value="audio/UniversalStudios.mp3">Universal Studio</option>
<option value="audio/Horse.mp3">Horse</option>
<option value="audio/Army.mp3">Army</option>
<option value="audio/BabyCry.mp3">Baby Cry</option>
<option value="audio/BraveHeart.mp3">BraveHeart</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="checkbox" id="repeatCheckBox">
<label class="checkbox-inline">
<input id="isRepeat" type="checkbox" value="yesRepeat">
Repeat
</label>
</div>
<div class="radio" id="repeatOptions">
<label class="radio-inline">
<input type="radio" name="repeatOptions" id="optionTrack" value="track" checked>
A track
</label>
<label class="radio-inline">
<input type="radio" name="repeatOptions" id="optionPlaylist" value="playlist">
Playlist
</label>
<label class="radio-inline">
<input type="radio" name="repeatOptions" id="optionRandom" value="random">
Random
</label>
</div>
</form>
</div> <!--
The HTML Audio element with ID of myAudio is our player. We will load mp3 track into it programmatically by modifying the src attribute of the source of myAudio:
<audio id="myAudio" controls="controls" preload="metadata">
<source src="audio/Horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the <code>audio</code> tag.
</audio>
You can choose to display the list of tracks by either ul/ol lis or as. I use drop-down option lists for this project (with ID myAudioPlaylist) because it is more compact.
The div#myAudioStatus is a place to display status info (paused, playing, metadata such as duration, etc.). Other elements are self-explanatory by their names.
JavaScript
With the HTML structure has been set. We can customize the appearance by CSS. But all the work here is with the script.js now.
Set up AUD
var AUD = {
player: $("#myAudio")[0],
currentPosition: 0,
totalTracks: 0,
init: function () {
AUD.player.volume = 0.1;
AUD.totalTracks = $('#myAudioPlaylist option').length;
... set initial appropriate values
... listen and handle interested events
},
... more functions
};
By that, we have a single AUD object/variable and the ability to avoid anonymous callback functions if we want.
The item $("#myAudio")[0] (equals to $("#myAudio").get(0)) is a native DOM object (document.getElementById("myAudio")). All three of them are the same. They are NOT jQuery wrapped DOM element object.
jQuery objects have many useful and easy-to-use functions, such as text(), append(), html(), etc. but don't have audio related functions, properties, and events. That is the reason we use DOM object.
Responde to user's select
var AUD = {
player: $("#myAudio")[0],
currentPosition: 0,
totalTracks: 0,
init: function () {
AUD.player.volume = 0.1;
AUD.totalTracks = $('#myAudioPlaylist option').length;
$("#myAudioPlaylist").on("change", function () {
AUD.currentPosition = $("#myAudioPlaylist option:selected").index();
AUD.playTrack();
});
...
},
setTrack: function () {
$('#myAudioPlaylist option').eq(AUD.currentPosition).prop('selected', true);
var trackLink = $("#myAudioPlaylist").val();
$("#myAudio source").attr("src", trackLink);
},
playTrack: function () {
AUD.setTrack();
AUD.player.load();
AUD.player.play();
},
...
};
The program starts with init() function, where we set reasonable starting value, such as volume, or auto play/repeat or not. Selecting a track (initially by us, and then by the user) comes in mind first. So we handle the change event when the use select a track from the provided list.
The crucial, most important here is to keep track of current position index of the selected/playing/pause track in the list via the currentPosition variable.
Most of the code were written in init(), then I refactor to separate setTrack() and playTrack() to reduce the complexity, and to make it more beautiful :)
Handle repeat options
var AUD = {
init: function () {
...
AUD.player.addEventListener("ended", AUD.repeat);
...
},
repeat: function () {
if (!$("#isRepeat").prop("checked")) {
} else {
if ($("#optionTrack").prop("checked")) {
AUD.playTrack();
} else if ($("#optionPlaylist").prop("checked")) {
AUD.currentPosition++;
if (AUD.currentPosition >= AUD.totalTracks) {
AUD.currentPosition = 0;
}
AUD.playTrack();
} else {
AUD.currentPosition = Math.floor(Math.random() * (AUD.totalTracks - 1));
AUD.playTrack();
}
}
},
...
};
We handle the repeat options by listening to the ended event (when a track has been done playing). Then based on the option (repeat a single track, the whole playlist, or randomly), we can decide which track to play next.
Handle user controls
Similar to and simpler than the repeating, for example, when the user clicks 'next' button, we advance the currentPosition++ and play at that position.
Others
There are several other functions in init(), such astoggleRepeatUI() is to handle the repeat option HTML UI. listenToAudioEvents() to update the status info.
Complete script.js
var AUD = {
player: $("#myAudio")[0],
currentPosition: 0,
totalTracks: 0,
init: function () {
AUD.player.volume = 0.1;
AUD.totalTracks = $('#myAudioPlaylist option').length;
$("#myAudioPlaylist").on("change", function () {
AUD.currentPosition = $("#myAudioPlaylist option:selected").index();
AUD.playTrack();
});
AUD.player.addEventListener("ended", AUD.repeat);
AUD.toggleRepeatUI();
AUD.listenToControllers();
AUD.listenToAudioEvents();
},
toggleRepeatUI: function () {
$("#repeatOptions").hide();
$("#isRepeat").on("change", function () {
if ($("#isRepeat").prop("checked")) {
$("#repeatOptions").show();
} else {
$("#repeatOptions").hide();
}
});
},
listenToControllers: function () {
$("#playBtn").on("click", function () {
if (AUD.player.paused) {
AUD.player.play();
}
});
$("#pauseBtn").on("click", function () {
AUD.player.pause();
});
$("#prevBtn").on("click", function () {
AUD.currentPosition--;
if (AUD.currentPosition < 0) {
AUD.currentPosition = 0;
}
AUD.playTrack();
});
$("#nextBtn").on("click", function () {
AUD.currentPosition++;
if (AUD.currentPosition >= AUD.totalTracks) {
AUD.currentPosition = AUD.totalTracks - 1;
}
AUD.playTrack();
});
$("#decreaseVolBtn").on("click", function () {
AUD.player.volume -= 0.1;
if (AUD.player.volume <= 0) {
AUD.player.volume = 0;
}
});
$("#increaseVolBtn").on("click", function () {
AUD.player.volume += 0.1;
if (AUD.player.volume >= 1) {
AUD.player.volume = 1;
}
});
},
setTrack: function () {
$('#myAudioPlaylist option').eq(AUD.currentPosition).prop('selected', true);
var trackLink = $("#myAudioPlaylist").val();
$("#myAudio source").attr("src", trackLink);
},
playTrack: function () {
AUD.setTrack();
AUD.player.load();
AUD.player.play();
},
repeat: function () {
if (!$("#isRepeat").prop("checked")) {
} else {
if ($("#optionTrack").prop("checked")) {
AUD.playTrack();
} else if ($("#optionPlaylist").prop("checked")) {
AUD.currentPosition++;
if (AUD.currentPosition >= AUD.totalTracks) {
AUD.currentPosition = 0;
}
AUD.playTrack();
} else {
AUD.currentPosition = Math.floor(Math.random() * (AUD.totalTracks - 1));
AUD.playTrack();
}
}
},
listenToAudioEvents: function () {
AUD.player.addEventListener("loadedmetadata", function () {
var trackName = $("#myAudioPlaylist option:selected").text();
var trackDuration = AUD.player.duration.toFixed(2);
var info = trackName + " (" + trackDuration + "s)";
$("#myAudioStatus p").text("Loaded track: " + info);
});
AUD.player.addEventListener("pause", function () {
var trackName = $("#myAudioPlaylist option:selected").text();
$("#myAudioStatus p").text("Ready: " + trackName);
});
AUD.player.addEventListener("playing", function () {
var trackName = $("#myAudioPlaylist option:selected").text();
$("#myAudioStatus p").text("Now playing: " + trackName);
});
}
};
