Introduction
Application internationalization mostly uses resx file to store the various strings that need to be translated. This tool helps you to ensure that your resx file within a Visual Studio project are correctly filled with a comment value for each entry.
Here is a screenshot of the result.
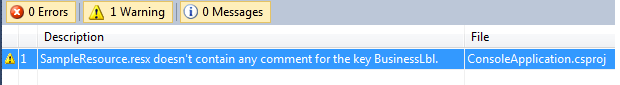
How Does It Work ?
This tool uses two namespaces from MSBuild:
In order to implement a custom MSBuild task, all you need to do is to create a class that extends the Microsoft.Build.Utilities.Task abstract class and implement the task logic in the Execute method. The return value will indicate if the task failed or succeeded.
In this tool, all we want is just to add one warning by missing entry, so we will always return true.
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.IO;
using System.Resources;
using Microsoft.Build.Framework;
using Microsoft.Build.Utilities;
namespace MSBuild.Tools.Tasks {
public class ResXCommentCheck : Task {
public override bool Execute() {
foreach (string file in Directory.GetFiles(Environment.CurrentDirectory,
"*.resx", SearchOption.AllDirectories)) {
using (ResXResourceReader reader = new ResXResourceReader(file)) {
reader.UseResXDataNodes = true;
foreach (DictionaryEntry entry in reader) {
ResXDataNode node = (ResXDataNode)entry.Value;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(node.Comment)) {
Log.LogWarning(
"{0} doesn't contain any comment for the key {1}.",
Path.GetFileName(file), node.Name);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
MSBuild Integration
The MSBuild integration has to be made within the Visual Studio project (.vbproj, .csproj file) with the help of the UsingTask node that helps you to load a specific task by its taskname (i.e. class FullName) and its location :
AssemblyFile attribute means a local reference AssemblyName attribute means Global Assembly Cache
<Project ToolsVersion="4.0" DefaultTargets="Build"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/developer/msbuild/2003">
<UsingTask TaskName="MSBuild.Tools.Tasks.ResXCommentCheck"
AssemblyFile="c:\MSBuild.Tools.Tasks.dll" />
</Project>
The custom task can be called in the AfterBuild target.
<Target Name="AfterBuild">
<UsingTask TaskName="MSBuild.Tools.Tasks.ResXCommentCheck"
AssemblyFile="C:\MSBuild.Tools.Tasks.dll" />
</Target>
Points of Interest
This tool was my first experience with custom MSBuild tasks. As you can see, the API is very easy to use and it offers many possibilities to help developers to check their code.
History
- 25th August, 2010: Initial post
