In this article, we will see how to perform specific and multiple column searches, sorting, dynamic page sizing, be non-database specific, handle very large data, have elegant code structure, least coding effort and most of all performance features in a single, easy to code and easy to manage solution without degrading the performance aspect.
Introduction
There was a need for a plausible data grid, capable of performing specific and multiple column searches, sorting, dynamic page sizing, should be non-database specific (at least we had tested with MSSQL and MySQL), handles very large data (over a million records), had elegant code structure, least coding effort and most of all performance. Intention is to amalgamate these features in a single, easy to code and easy to manage solution without degrading the performance aspect.
Pre-requisites
In order to follow this article, you need to have some understanding of MVC Framework. If you think you have sufficient expertise, then you are good to further read through this article.
Abstraction
The solution is a blend of DataTables and LINQKit tools, DataTables is used on client side, it handles display grid data and provider searching and ordering UI feature and sends user search query to the server. At server end, LINQKit is used to build up flexible and high performance query. For further explanation, the code is broken up into two, client side and server side code.
Client Side Code
At client side, DataTables is king, here we are using its server-side processing feature. Before going further, DataTables is a plug-in for the jQuery Javascript library. It is a highly flexible tool, based upon the foundations of progressive enhancement, and will add advanced interaction controls to any HTML table. It handles and performs our demanded functionality from our client side. Most importantly, it invokes Ajax request to the server for each draw of the information on the grid or page (i.e., when paging, ordering, searching, etc.). it sends a number of variables to the server (its DataTables build in feature) to allow server side to process this Ajax request and return's JSON data. You can download DataTables plugin from here or just add up the coming line to your page.
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/r/dt/dt-1.10.9/datatables.min.css"
rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<script type="text/javascript"
src="https://cdn.datatables.net/r/dt/dt-1.10.9/datatables.min.js"></script>
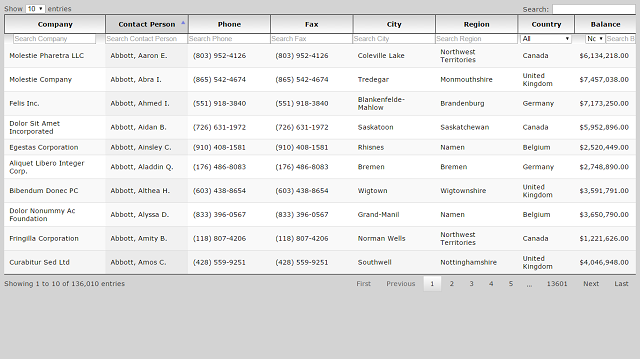
DataTables Table Structure
Here is an example of table structure for DataTables plugin to use, you can see that we have defined two headers for the table, the first header contains the column name while the next header is a placeholder for our search controls.
<table cellspacing="0" class="display"
id="grid" style="font-size: small;" width="100%">
<thead>
<tr>
<th width="20%">Company</th>
<th width="10%">Contact Person</th>
<th width="10%">Phone</th>
<th width="10%">Fax</th>
<th width="10%">City</th>
<th width="10%">Region</th>
<th width="10%">Country</th>
<th width="10%">Balance</th>
</tr>
<tr id="filterrow">
<th width="20%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
<th width="10%"> </th>
</tr>
</thead>
</table>
DataTables Table's Initialization
Before going into the initialization step, let me explain the variable _columnFilterMannifest, it holds manifest and data for all the column search control which will reside on the second header row as discussed previously. This variable is set during our default action method call. On page ready function, call setGridFilter('grid',_columnFilterManifest) function is invoked, this function is present in our Grid.js to encapsulate functionalities, to make it short, first parameter is the id of our structure table and second is the manifest which we had discussed not long ago. Now our created table structure is initialize from DataTables plugin, you can go through it manual here.
At the end, initGridFilter() method is called which is again in Grid.js, and encapsulated. Its core purpose is to assign trigger search feature to all the grid's columns search controls.
var _columnFilterManifest =
JSON.parse( @Html.Raw(Json.Encode( ViewData["columnFilterManifest"].ToString() ) ));
$(document).ready(function () {
setGridFilters('grid',_columnFilterManifest);
var table = $('#grid').DataTable({
"order": [[1, "asc"]],
"orderCellsTop": true,
"pagingType": "full_numbers",
"scrollCollapse": true,
"processing": true,
"serverSide": true,
"lengthMenu": [[10,15,25, 50], [10,15,25, 50]],
"ajax": "/Customer/GetPage",
"columns": [
{ "data": "company" },
{ "data": "contactPerson" },
{ "data": "phone" },
{ "data": "fax" },
{ "data": "city" },
{ "data": "region" },
{ "data": "country" },
{ "data": "balance" },
],
"columnDefs": [
{
"render": function (data, type, row) {
return accounting.formatMoney(data);
},
"targets": 7
}
],
"initComplete": function () {
var api = this.api();
api.$('td').click(function () {
api.search(this.innerHTML).draw();
});
},
"autoWidth": false,
});
initGridFilter(table,'grid');
});
Server Side
On server side, we have LINQKit to make our aspiration possible. One of its controller action method set _columnFilterManifest variable for the client side which is used to initiate and populate the column search controls which we had discussed earlier in our client side code discussion.
public ActionResult Index()
{
BusinessLogic.Entity.Customer objCust = new BusinessLogic.Entity.Customer();
ViewData["columnFilterManifest"] =
new JavaScriptSerializer().Serialize(objCust.GetColumnFilterManifest());
return View("list");
}
DataTables shall call GetPage() controller Action method to get paginated data here you can see it calling Business Logic layer entity to get entity array result which send back to the client in JSON format. Its return JSON object contain properties such as data (which contains entity array), recordsTotal (entity array size), recordsFiltered (entity array size) and draw (its used by DataTables to ensure that the Ajax returns from server-side processing requests are drawn in sequence by DataTable).
public JsonResult GetPage()
{
int draw = Convert.ToInt32(Request["draw"]);
BusinessLogic.Entity.Customer objCust = new BusinessLogic.Entity.Customer();
CustomerGrid[] customers = objCust.Search(this);
return Json(new
{
data = customers,
recordsTotal = base.GetGridTotalRows(),
recordsFiltered = base.GetGridTotalRows(),
draw = draw
},
"application/json", Encoding.UTF8, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
Now moving on to the entity business logic layer which got invoke from controller action method, which we have just discussed that is Search(IBaseController iBaseController), it performs all of our pagination activities in this Business Logic layer entity method that filter by clause and order by clause shall be added to the query dynamically according to DataTables query.
public Common.Entity.Customer.CustomerGrid[] Search
(Common.Generic.IBaseController iBaseController)
{
GridParameterCollector gridParamCollet =
iBaseController.GenerateGridParameterCollector();
AccessLayer.DataTableEntities obj = new AccessLayer.DataTableEntities();
records = from cus in obj.customers
join count in obj.countries on cus.countryId equals count.countryId
select new CustomerGrid
{
id = cus.customerID,
idStr =
SqlFunctions.StringConvert((double?)
cus.customerID, 20, 0).Trim(),
company = cus.company ,
contactPerson = cus.contactPerson,
phone = cus.phone,
fax = cus.phone,
city = cus.city,
region = cus.region,
country = count.country1,
countryId = cus.countryId.Value,
balance = cus.balance.Value
};
genericSearchText = gridParamCollet.searchText.Trim();
foreach (ColumnParameterCollector column in gridParamCollet.columnCollector)
{
searchColumnText = column.columnSearchText.Trim();
switch (column.dataName)
{
case "email":
string emailColumnText = searchColumnText;
string emailGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.email.StartsWith(emailColumnText),
x => x.email.StartsWith(emailGenericText),
x => x.email
);
break;
case "company":
string companyColumnText = searchColumnText;
string companyGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.company.StartsWith(companyColumnText),
x => x.company.StartsWith(companyGenericText),
x => x.company
);
break;
case "contactPerson":
string contactPersonColumnText = searchColumnText;
string contactPersonGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.contactPerson.StartsWith(contactPersonColumnText),
x => x.contactPerson.StartsWith(contactPersonGenericText),
x => x.contactPerson
);
break;
case "phone":
string phoneColumnText = searchColumnText;
string phoneGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.phone.StartsWith(phoneColumnText),
x => x.phone.StartsWith(phoneGenericText),
x => x.phone
);
break;
case "fax":
string faxColumnText = searchColumnText;
string faxGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.fax.StartsWith(faxColumnText),
x => x.fax.StartsWith(faxGenericText),
x => x.fax
);
break;
case "city":
string cityColumnText = searchColumnText;
string cityGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.city.StartsWith(cityColumnText),
x => x.city.StartsWith(cityGenericText),
x => x.city
);
break;
case "region":
string regionColumnText = searchColumnText;
string regionGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.region.StartsWith(regionColumnText),
x => x.region.StartsWith(regionGenericText),
x => x.region
);
break;
case "country":
string countryColumnText = searchColumnText;
string countryGenericText = genericSearchText;
Expression<func<customergrid, bool="">> countryFilterExpression = null;
if ( searchColumnText.Length != 0 && searchColumnText != "0")
{
int countryId = int.Parse(countryColumnText);
countryFilterExpression = x => x.countryId == countryId;
}
EvaluateFilter(column,
countryFilterExpression,
x => x.country.StartsWith(countryGenericText),
x => x.country
);
break;
case "id":
string idColumnText = searchColumnText;
string idGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.idStr.StartsWith( idColumnText ),
x => x.idStr.StartsWith( idGenericText ),
x => x.id
);
break;
case "balance":
string balanceColumnText = searchColumnText;
EvaluateNumericComparisonFilter(column,
balanceColumnText,
"balance",
x => x.balance
);
break;
}
}
return ForgeGridData(iBaseController, gridParamCollet, x => x.id);
}<customergrid,>
<summary>
In the first part of the above entity search method, GenerateGridParameterCollector() method is called which makes DataTables Ajax calls querystring into desire object, in this case, its turned into GridParameterCollector object definition of which is as under. I belief that only comments shall do the job here.
public class GridParameterCollector
{
public int start{ get; set; }
public int length{ get; set; }
public string searchText { get; set; }
public bool isSearchRegex { get; set; }
public List<ColumnParameterCollector> columnCollector { get; set; }
}
public class ColumnParameterCollector
{
public int columnIndex { get; set; }
public string orderDirection { get; set; }
public string dataName { get; set; }
public string columnName { get; set; }
public bool isColumnSearchable { get; set; }
public bool isColumnOrderable { get; set; }
public string columnSearchText { get; set; }
public bool isColumnSearchRegex { get; set; }
}
The next step is to pass Entity Framework's query to entity IQueryable object, keep in mind during and after assigning query to object records no database call is made to the server unless you are working in EF 4 (so no high performance query in this case when EF 4 is used). In a subsequent step, gridParamCollect objects iteratable property columnCollector is iterated to append where clause to the query. Now in the next step, we shall discuss the search column filter evaluation method that would build up the predicate, functionality of which is encapsulated in business logic layer entity base class.
case "email":
string emailColumnText = searchColumnText;
string emailGenericText = genericSearchText;
EvaluateFilter(column,
x => x.email.StartsWith(emailColumnText),
x => x.email.StartsWith(emailGenericText),
x => x.email
);
break;
When dealing with column text search or select option (sometime), then EvaluteFilter method is called which has its definition in base class. It takes four parameters, first parameter is current iteration ColumnParameterCollector object which provides info regarding current iterated column, second one is lamda expression for column search only, for instance lamda expression x => x.email.StartWtih("codeproject") shall generate where clause equivalent to '%codeproject'. The third parameter is for generic search, it consumes value from the upper right search textbox of DataTables grid. The fourth parameter is lamda expression as well but with different purpose, it defines order by clause for the query. e.g x => x.email then query will embedded with order by email clause.
case "country":
string countryColumnText = searchColumnText;
string countryGenericText = genericSearchText;
Expression<Func<CustomerGrid, bool>> countryFilterExpression = null;
if ( searchColumnText.Length != 0 && searchColumnText != "0")
{
int countryId = int.Parse(countryColumnText);
countryFilterExpression = x => x.countryId == countryId;
}
EvaluateFilter(column,
countryFilterExpression,
x => x.country.StartsWith(countryGenericText),
x => x.country
);
break;
For select option, column search approach is slightly difference, only from second parameter in which lamda expression is dynamic defined in if condition rest are exactly same as the last explanation.
case "balance":
string balanceColumnText = searchColumnText;
EvaluateNumericComparisonFilter(column,
balanceColumnText,
"balance",
x => x.balance
);
break;
Numerical comparison is different from previous one as dynamic binary tree expression is involved here, this functionality is performed by EvaluateNumericComparisionFilter() method, its second parameter is column search value, the third column is concerned with entity object field name, and last one is lamda expression for order by clause.
ForgeGridData(iBaseController, gridParamCollet, x => x.id);
At the end of iteration, ForgeGridData() method is called which assembles the query with predicates and regenerates the query and executes it to return entity array.
History
- 7th November, 2015: Initial version
