Background
Nowadays continious integration is the important part of the agile software development life cycle. There is a number of tools on the market: Atlassian Bamboo, Jenkins, Jetbrains TeamCity. In my opinion Jenkins has the most optimal product community and set of really useful plugins that suits most of your software projects: you can build software, deploy software,
websites, portals to various places, including AWS, DigitalOcean, bare metal servers or to run unit tests. It can be integrated with communication tools of your choice, like Slack, HipChat or email.
If you haven't had a chance to try Jenkins earlier, feel free to use tutorial below to start.
Manual installation
In order to install Jenkins, we will need:
- Unix system. I would recommend debian based, like ubuntu server LTS
- Java runtime environment installed. I usually use Java 8
- Get base Jenkins setup
- Install necessary plugins
-
Put behind web server.
Install Java
Easist way to install Java, is using apt-get package manager
sudo apt-get install python-software-properties
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update
Once you added ppa above, you can install java with the following command:
sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
Get base Jenkins setup
You will need to execut series of the commands, namely: add jenkins signing key, register jenkins apt sources, update package lists, and install Jenkins package.
wget -q -O - http:
sudo echo deb http:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
By default, it will install base Jenkins setup, which is insecure. You will need to go to the host were your Jenkins is installed, for example: http://jenkins-host:8080/. Navigate to Manage Jenkins (on the left) and choose "Configure Global Security" item on the page loaded. 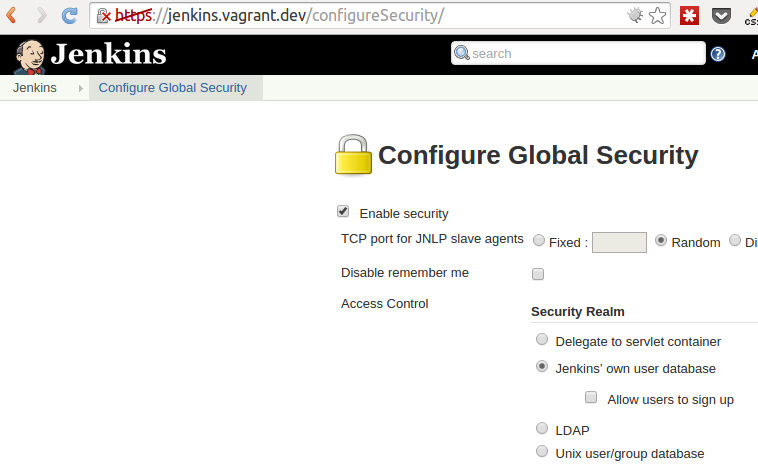
Now look below on the Matrix based security (select it, if it is not selected previously), and make sure Anonymous only has the Read right under the View group. Click save at the bottom of the page. After the page load, you'll see a login form, simply ignore that, go to the home page (like, for example, http://jenkins-host:8080/). You'll see this sign up form, the first signed up account will be the administrator.
Power of plugins.
Jenkins would not be so powerful without plugins. Usually I install next plugins by default:
-
bitbucket BitBucket plugin is designed to offer integration between BitBucket and Jenkins. BitBucket offer a Jenkins hook, but this one just trigger a build for a specific job on commit, nothing more. BitBucket plugin, like GitHub plugin already did, use the POST hook payload to check which job has to get triggered based on changed repository/branch.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/BitBucket+Plugin
-
bitbucket-pullrequest-builder This plugin builds pull requests from Bitbucket.org. Must have plugin, if you perfor QA deploy of each pull request submitted.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Bitbucket+pullrequest+builder+plugin
-
build-pipeline-plugin This plugin provides a Build Pipeline View of upstream and downstream connected jobs that typically form a build pipeline. In addition, it offers the ability to define manual triggers for jobs that require intervention prior to execution, e.g. an approval process outside of Jenkins. Provides nice visualization of the pathes & flows.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Build+Pipeline+Plugin
-
copyartifact Adds a build step to copy artifacts from another project. The plugin lets you specify which build to copy artifacts from (e.g. the last successful/stable build, by build number, or by a build parameter). You can also control the copying process by filtering the files being copied, specifying a destination directory within the target project, etc.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Copy+Artifact+Plugin
- credentials Adds a build step to copy artifacts from another project. The plugin lets you specify which build to copy artifacts from (e.g. the last successful/stable build, by build number, or by a build parameter). You can also control the copying process by filtering the files being copied, specifying a destination directory within the target project, etc.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Credentials+Plugin - delivery-pipeline-plugin Visualisation of Delivery/Build Pipelines, renders pipelines based on upstream/downstream jobs. When using Jenkins as a build server it is now possible with the Delivery Pipeline Plugin to visualise one or more Delivery Pipelines in the same view even in full screen.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Delivery+Pipeline+Plugin - environment-script Environment Script Plugin allows you to have a script run after SCM checkout, before the build. If the script fails (exit code isn't zero), the build is marked as failed. Any output on standard out is parsed as environment variables that are applied to the build. It supports "override syntax" to append paths to PATH-like variables.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Environment+Script+Plugin - git Supports popular git version control system
- ghprb This plugin builds pull requests in github. Must have, if your software development life cycle includes deploying pull requests to PR environment to test.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/GitHub+pull+request+builder+plugin -
greenballs The most funny plugin - changes Jenkins to use green balls instead of blue for successful builds.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Green+Balls
-
hipchat This plugin allows your team to setup build notifications to be sent to HipChat rooms.To enable notifications add "HipChat Notifications" as a post-build step.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/HipChat+Plugin
- junit Allows JUnit-format test results to be published. Note: number of tools, including Karma, PhpUNIT & other tools allow to publish test results in a JUnit format. Thus this is must have plugin for unit test flows.
Plugin page:https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/JUnit+Plugin - matrix-auth Offers matrix-based security authorization strategies (global and per-project). Good, if you have shared build server across several teams,
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Matrix+Authorization+Strategy+Plugin - parameterized-trigger This plugin lets you trigger new builds when your build has completed, with various ways of specifying parameters for the new build. You can add multiple configurations: each has a list of projects to trigger, a condition for when to trigger them (based on the result of the current build), and a parameters section.
Plugin page:https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Parameterized+Trigger+Plugin - rebuild Plays nice the with previous one: this plug-in allows the user to rebuild a parametrized build without entering the parameters again.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Rebuild+Plugin - ssh You can use the SSH Plugin to run shell commands on a remote machine via ssh.
Plugin page:https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/SSH+plugin - s3 allows uploading artifacts to S3 with multiple options.
Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/S3+Plugin - throttle-concurrents This plugin allows for throttling the number of concurrent builds of a project running per node or globally. Unfortunately, this is must have plugin for Node (0.10-0.12) projects with NPM - two concurrent npm install will fail often. Plugin page: https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Throttle+Concurrent+Builds+Plugin
Plugins are installed using Plugin manager on a Manage Jenkins Section. 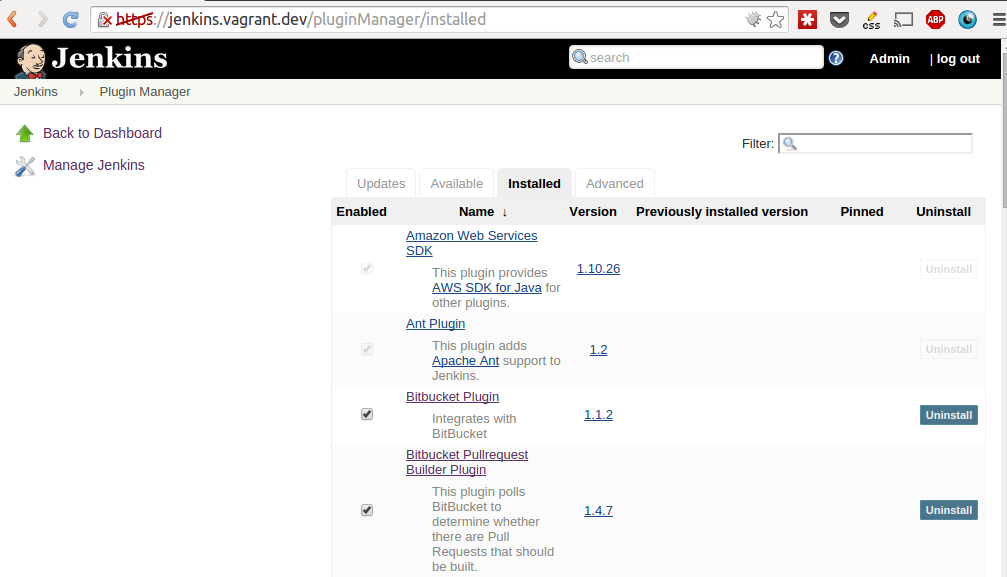
Put behind web server
Usually I hide Jenkins behind nginx. Typical configuration looks like the one below
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name jenkins.vagrant.dev;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/jenkins_selfsigned.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/jenkins_selfsigned.key;
location / {
proxy_pass http:
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_connect_timeout 150;
proxy_send_timeout 100;
proxy_read_timeout 100;
}
...
}
Automated installation
Do I install Jenkins manually each time? Of course not, I do it often for my customers. With ansible, and sa-box-jenkins role new Jenkins installation can be deployed while you drink the coffee.
Let's prepare basic bootstrap project, that can be used by you in the future. It includes following files:
- bootstrap.sh - installs ansible alongside with dependences.
- init.sh - initializes 3rd party dependencies
- .projmodules - fully compatible with .gitmodules git syntax, specifies list of the dependencies that will be used by the playbook. In particular, it includes ansible- by default developer_recipes (repository with set of handy deployment recipes) and ansible role called sa-box-bootstrap responsible for box securing steps (assuming you plan to put Jenkins on a remote hosts).
[submodule "public/ansible_developer_recipes"]
path = public/ansible_developer_recipes
url = git@github.com:Voronenko/ansible-developer_recipes.git
[submodule "roles/sa-box-bootstrap"]
path = roles/sa-box-bootstrap
url = git@github.com:softasap/sa-box-bootstrap.git
[submodule "roles/sa-box-jenkins"]
path = roles/sa-box-jenkins
url = git@github.com:softasap/sa-box-jenkins.git
- *hosts* - list here the initial box credentials, that were provided to you for the server. Note: jenkins-bootstrap assumes, you have the fresh box with the root access only. If your box already secured, adjust credentials appropriately
[jenkins-bootstrap]
jenkins_bootstrap ansible_ssh_host=192.168.0.17 ansible_ssh_user=yourrootuser ansible_ssh_pass=yourpassword
[jenkins]
jenkins ansible_ssh_host=192.168.0.17 ansible_ssh_user=jenkins
- jenkins_vars.yml - set here specific environment overrides, like your preferred deploy user name and keys.
- jenkins_bootstrap.yml - First step - box securing. Creates jenkins user, and secures the box using sa-box-bootstrap role. See more details about the sa-box-bootstrap role In order, to override params for sa-box-bootstrap - pass the parameters like in example below.
- hosts: all
vars_files:
- ./jenkins_vars.yml
roles:
- {
role: "sa-box-bootstrap",
root_dir: "{{playbook_dir}}/public/ansible_developer_recipes",
deploy_user: "{{jenkins_user}}",
deploy_user_keys: "{{jenkins_authorized_keys}}"
}
- *jenkins.yml* provisioning script that configures jenkins with set of plugins and users. - *jenkins_vars.yml* configuration options for jenkins deployment. - *setup_jenkins.sh* shell script that invokes deployment in two steps: initial box bootstraping & jenkins setup
ansible-playbook jenkins_bootstrap.yml --limit jenkins_bootstrap
ansible-playbook jenkins.yml --limit jenkins
Configuration options for automated installation
You need to override:
- jenkins_authorized_keys (this is list of the keys, that allow you to login to Jenkins box under jenkins)
- jenkins_domain - your agency domain
- jenkins_host - name of the jenkins host (Site will be binded to jenkins_host.jenkins_domain)
- java_version - your Java choice (6,7,8 supported)
jenkins_user: jenkins
jenkins_authorized_keys:
- "{{playbook_dir}}/components/files/ssh/vyacheslav.pub"
jenkins_domain: "vagrant.dev"
jenkins_host: "jenkins"
java_version: 8
-jenkins_users list of users with passwords to create. Admin and deploy are required users. Admin is used to manage instance, deploy is used to access the artifacts via deployment scripts. If you won't override passwords, default one will be used (per role), which is not the best, for public deployments.
jenkins_users:
- {
name: "Admin",
password: "AAAdmin",
email: "no-reply@localhost"
}
- {
name: "deploy",
password: "DeDeDeDeploy",
email: "no-reply@localhost"
}
- jenkins_plugins Your choice of plugins to install. By default:
jenkins_plugins:
- bitbucket # https:
- bitbucket-pullrequest-builder
- build-pipeline-plugin
- copyartifact # https:
- credentials # https:
- delivery-pipeline-plugin # https:
- environment-script # https:
- git
- ghprb # https:
- greenballs # https:
- hipchat # https:
- junit # https:
- matrix-auth # https:
- matrix-project #https:
- parameterized-trigger #https:
- rebuild # https:
- ssh
- s3 # https:
- throttle-concurrents #https:
Code in action
Code can be downloaded from repository https://github.com/Voronenko/devops-jenkins-box-template In order to use it - fork it, adjust parameters to your needs, and use.
Running is as simple as
./bootstrap.sh
./init.sh
./setup_jenkins.sh
Welcome to the world of continious integration & deployment.
