Introduction
In this article I am going to discuss in detail on Value Types and Reference Types and about their memory allocation on Stack and Heap. Then later I will discuss on the use of Volatile keyword.
Table of Contents
Before diving into the details of memory allocation and other discussion, let’s have a look into the Built-in data types:
|
Data Type
|
Range
|
Type of Data Type
|
|
byte
|
0 .. 255
|
Value Type
|
|
sbyte
|
-128 .. 127
|
Value Type
|
|
short
|
-32,768 .. 32,767
|
Value Type
|
|
ushort
|
0 .. 65,535
|
Value Type
|
|
int
|
-2,147,483,648 .. 2,147,483,647
|
Value Type
|
|
uint
|
0 .. 4,294,967,295
|
Value Type
|
|
long
|
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 .. 9,223,372,036,854,775,807
|
Value Type
|
|
ulong
|
0 .. 18,446,744,073,709,551,615
|
Value Type
|
|
float
|
-3.402823e38 .. 3.402823e38
|
Value Type
|
|
double
|
-1.79769313486232e308 .. 1.79769313486232e308
|
Value Type
|
|
decimal
|
-79228162514264337593543950335 .. 79228162514264337593543950335
|
Value Type
|
|
char
|
A Unicode character.
|
Value Type
|
|
string
|
A string of Unicode characters.
|
Reference Type
|
|
bool
|
True or False.
|
Value Type
|
|
object
|
An object.
|
Reference Type
|
In .Net we have 2 types of data types: Value and Reference types. This is very important to know how CLR manages the data and memory for writing the optimized codes for better performance.
All the built-in data types given in the above table when used to declare a variable within a function or passed by parameters ( not by ref) then it will be a value type except for string and object data types which will be of reference types.
The value type data will be allocated on the Stack and the reference type data will be allocated on the Heap. But when the same value types declared as array or used as data members of a class then they will be stored on a Heap. Also when the value types used in the struct then they will be stored on the Stack.
For example:
class Program
{
public int intMember = 3; public bool flag = true; public void func1(int f, bool b, int[] intAry) {
int index = 5; string str = "string"; int[] ary = { 1, 2, 3 }; for (int i = 0; i < intAry.Length; i++)
{
intAry[i] = intAry[i] + 100;
}
f = 123;
b = true;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program obj = new Program();
int[] ary1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int intLocal = 5;
bool boolLocal = false;
obj.func1(intLocal, boolLocal, ary1);
for (int i = 0; i < ary1.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("ary1 [" + i + "]=" + ary1[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("intLocal=" + intLocal + ", boolLocal = " + boolLocal);
}
}
In the above sample code, when the object instance is created the value type member variables intMember and flag will be allocated on the Heap not on the stack. And in the Main function intLocal, boolLocal will be allocated on stack and integer array ary1 will be allocated on the heap. When we call the member function func1 then the parameter variables f, b and the local variable index will be stored on the Stack, whereas the string variable str and the integer array ary will be allocated on the Heap. It is important to note here that when any value types declared as array then they will be considered as reference type. If you use the above code and run then you can see the changes done to integer array in the func1 function are reflecting after the function returned whereas the local value type variables intLocal and boolLocal will not reflect the changes done in the called function func1.
Stack is always faster than heap. As memory for struct is allocated on the Stack, they are faster than compare to class for which memory is allocated on the Heap. But as the Stack has limited memory in size (max 1 MB), so we need to use struct only when we have small amount of data. If you need to store large amount of data in the memory e.g. a big struct, and you need to keep that variables for a long time, then it is better you should allocate it on the heap by using class instead of struct which is ideal for only small amount of data. If you are dealing with small variables that only need to persist as long as the function is using them, then you should use the stack.
Boxing is the process of converting a value type into a reference type, during which it creates a new reference variable of type object by allocating a memory on the Heap. Below is the sample code for Boxing:
int i = 67; object o = i;
Unboxing is the process of converting the reference type to a value type provided the value in the object (reference variable) is of value type, otherwise it will throw a runtime exception.
But this is a burden of converting the value type to reference type and vice versa, which impacts on the performance. So until it is very necessary we should avoid Boxing and Unboxing. Usually we use this process when we deal with classes which are designed to accept only values of type object. For example, When we store integers in the ArrayList which accepts only type object then it is boxed. When we retrieve and type caste the object value to its relevant data type then it is unboxed. Below is the sample code for Unboxing:
System.Collections.ArrayList list =
new System.Collections.ArrayList(); int n = 67; list.Add(n); n = (int)list[0];
When value type parameters are passed into methods, a copy of each parameter is created on the stack. If the parameter are of large data type, such as a user-defined structure with many elements, or the method is executed many times, this may have an impact on performance. In these situations it may be preferable to pass a reference to the type, using the ref keyword. The out keyword is similar to the ref keyword, the difference is when out is used, it tells the compiler that the method must assign a value to the parameter before returning otherwise a compilation error will occur.
In a multi-threaded application, each thread will have its own stack of around 1MB. But, all the different threads will share the heap memory. As heap memory will be shared among all the threads, this is where we have to be very careful and implement the thread synchronization by using locks or other .net synchronization techniques to avoid race conditions, dead locks etc. If we have non-volatile fields then the data updated in one thread will not be reflected in other threads. This is where the volatile keyword is useful.
In single threaded applications we will not be having any problem with data allocated on the heap memory. But in multi-threaded application, though the heap memory is been shared by all the threads, CLR internally optimizes and reorders the code due to which we may face data synchronization issues. For example, an object obj value is modified in a thread but the other thread reading its value will not get the updated value for obj. This problem can be solved by applying a volatile keyword to the fields. Let’s look into a sample code:
class MultiThreadingHeapIssue
{
bool stopLoop = true; public void Run()
{
new Thread(() => { Console.WriteLine("Loop started"); while (stopLoop);
Console.WriteLine("Loop ended");
}).Start();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
stopLoop = false;
Console.WriteLine("value set to false.");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MultiThreadingHeapIssue obj = new MultiThreadingHeapIssue();
obj.Run();
}
}
Result after running the above code in release mode with ctr+F5:
Result with bool stopLoop = true;
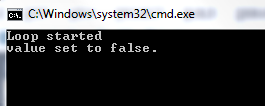
Result using volatile: volatile bool stopLoop = true;
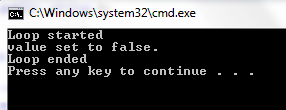
In the above code, the .Net JIT compiler might rewrite the while loop something like this because of using a non-volatile field stopLoop:
if (stopLoop) { while (true); }
It will be fine if the JIT compiler optimizing the code if it is a single-threaded application. But in multi-threaded application, if the stopLoop is set to false on another thread, the optimization may lead to an infinite loop. When we mark the stopLoop field as volatile then the JIT compiler will not optimize for the above code so the condition will remain same as in the original code.
Source Code
I have not attached any source code since the programs i have written to explain are very simple and can be copied as it is and executed to see the results.
Some good references worth reading for in detail knowledge on the topics i have covered
Below are the very good articles which are in depth with too many details and may confuse some of the readers. So I have tried to gather and explain only the necessary points to be aware of about these core .Net memory concetps.
