Probably you have read the article – Wrapping C/C++ Methods of Dynamsoft Barcode SDK for Python, which illustrates how to make Python extension on Windows. In this post, I’ll share how to make Python barcode extension on Ubuntu with Dynamsoft Barcode SDK for Linux.
Getting Started
Three Steps to Build Python Extension
Referring to the tutorial – Python Programming/Extending with C, you just need three steps to build a simple Python extension:
- Create a C source file:
#include <Python.h>
static PyObject*
show(PyObject* self, PyObject* args)
{
const char* content;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s", &content))
return NULL;
printf("%s!\n", content);
Py_RETURN_NONE;
}
static PyMethodDef Methods[] =
{
{"show", show, METH_VARARGS, "Print input"},
{NULL, NULL, 0, NULL}
};
PyMODINIT_FUNC
inithelloworld(void)
{
(void) Py_InitModule("helloworld", Methods);
}
- Create a Python file:
from distutils.core import setup, Extension
module_helloworld = Extension('helloworld', sources = ['helloworld.c'])
setup (name = 'Dynamsoft',
version = '1.0',
description = 'First module',
ext_modules = [module_helloworld])
- Make the extension with the following command:
python setup.py build
The module helloworld.so is generated under build/lib.linux-<version>. Change to the subdirectory and create a Python script:
from helloworld import *
show("My first Python module")
Run the script as follows:
$python test.py
My first Python module!
Wrapping C/C++ SDK for Python
Download Dynamsoft Barcode Reader for Linux.
Extract the package:
tar -xzf dbr-4.0.0-pre-alpha.tar.gz
Create a symbolic link for the shared library:
sudo ln -s $(DynamsoftBarcodeReader)/Redist/libDynamsoftBarcodeReaderx64.so
/usr/lib/libDynamsoftBarcodeReaderx64.so
Write C code to invoke Barcode APIs:
#include <Python.h>
#include "If_DBR.h"
#include "BarcodeFormat.h"
#include "BarcodeStructs.h"
#include "ErrorCode.h"
const char * GetFormatStr(__int64 format)
{
if (format == CODE_39)
return "CODE_39";
if (format == CODE_128)
return "CODE_128";
if (format == CODE_93)
return "CODE_93";
if (format == CODABAR)
return "CODABAR";
if (format == ITF)
return "ITF";
if (format == UPC_A)
return "UPC_A";
if (format == UPC_E)
return "UPC_E";
if (format == EAN_13)
return "EAN_13";
if (format == EAN_8)
return "EAN_8";
if (format == INDUSTRIAL_25)
return "INDUSTRIAL_25";
if (format == QR_CODE)
return "QR_CODE";
if (format == PDF417)
return "PDF417";
if (format == DATAMATRIX)
return "DATAMATRIX";
return "UNKNOWN";
}
static PyObject *
initLicense(PyObject *self, PyObject *args)
{
char *license;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s", &license)) {
return NULL;
}
printf("License: %s\n", license);
int ret = DBR_InitLicense(license);
return Py_BuildValue("i", ret);
}
static PyObject *
decodeFile(PyObject *self, PyObject *args)
{
char *pFileName;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s", &pFileName)) {
return NULL;
}
__int64 llFormat = (OneD | QR_CODE | PDF417 | DATAMATRIX);
int iMaxCount = 0x7FFFFFFF;
ReaderOptions ro = {0};
pBarcodeResultArray pResults = NULL;
ro.llBarcodeFormat = llFormat;
ro.iMaxBarcodesNumPerPage = iMaxCount;
int ret = DBR_DecodeFile(pFileName, &ro, &pResults);
printf("DecodeFile ret: %d\n", ret);
if (ret == DBR_OK) {
int count = pResults->iBarcodeCount;
pBarcodeResult* ppBarcodes = pResults->ppBarcodes;
pBarcodeResult tmp = NULL;
PyObject* list = PyList_New(count);
PyObject* result = NULL;
int i = 0;
for (; i < count; i++)
{
tmp = ppBarcodes[i];
result = PyString_FromString(tmp->pBarcodeData);
PyList_SetItem(list, i, Py_BuildValue("iN", (int)tmp->llFormat, result));
}
DBR_FreeBarcodeResults(&pResults);
return list;
}
return Py_None;
}
static PyMethodDef Methods[] =
{
{"initLicense", initLicense, METH_VARARGS, NULL},
{"decodeFile", decodeFile, METH_VARARGS, NULL},
{NULL, NULL, 0, NULL}
};
PyMODINIT_FUNC
initdbr(void)
{
(void) Py_InitModule("dbr", Methods);
}
Create setup.py:
from distutils.core import setup, Extension
module_dbr = Extension('dbr',
sources = ['dbr.c'],
include_dirs=['<Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK>/Include'],
library_dirs=['<Dynamsoft Barcode Reader SDK>/Redist'],
libraries=['DynamsoftBarcodeReaderx64'])
setup (name = 'DynamsoftBarcodeReader',
version = '1.0',
description = 'Python barcode extension',
ext_modules = [module_dbr])
Build the Python barcode extension dbr.so:
python setup.py build
If you want to clean the build files, you can use the following command:
python setup.py clean --all
Install the extension:
sudo python setup.py install
Write a Python script for testing:
import os.path
import sys
from dbr import *
formats = {
0x3FFL: "OneD",
0x1L : "CODE_39",
0x2L : "CODE_128",
0x4L : "CODE_93",
0x8L : "CODABAR",
0x10L : "ITF",
0x20L : "EAN_13",
0x40L : "EAN_8",
0x80L : "UPC_A",
0x100L: "UPC_E",
0x200L: "INDUSTRIAL_25",
0x2000000L: "PDF417",
0x8000000L: "DATAMATRIX",
0x4000000L: "QR_CODE"
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
license = open('license.txt', 'r')
license_content = license.readline().strip()
ret = initLicense(license_content)
if (ret != 0):
print "invalid license"
sys.exit(0)
barcode_image = raw_input("Enter the barcode file: ");
if not os.path.isfile(barcode_image):
print "It is not a valid file."
else:
results = decodeFile(barcode_image);
print "Total count: " + str(len(results))
for result in results:
print "barcode format: " + formats[result[0]]
print "barcode value: " + result[1] + "\n*************************"
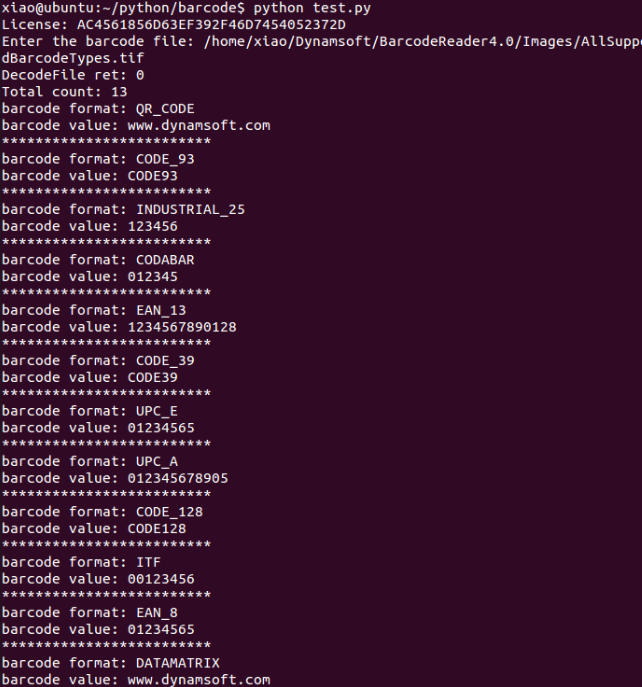
Run the script:
python test.py