In this article, we are going to learn how we can call Web API using HttpClient. Normally, we call a Web API either from a jQuery Ajax or from Angular JS right? Recently, I came across a need of calling our Web API from server side itself. Here, I am going to use two Visual Studio application. One is our normal Web API application in which I have a Web API controller and actions, another one is a console application where I consume my Web API. Sounds good? I am using Visual Studio 2015. You can always get the tips/tricks/blogs about these mentioned technologies from the links given below:
Now we will go and create our application. I hope you will like this.
Background
We all use Web API in our application to implement Http services. Http services are much simpler than ever if we use Web API. But the fact is, the benefits of a Web API is not limited to that. Previously, we used WCF services instead of Web API, where we were working with endpoints and all. Here, I am going to explain an important feature of a Web API that we can call Web API from our server itself instead of using an Ajax Call. That is pretty cool right? Now we will create our application.
First, we will create our Web API application.
Creating Web API Application
Click File-> New-> Project, then select MVC application. From the following pop up, we will select the template as empty and select the core references and folders for MVC.
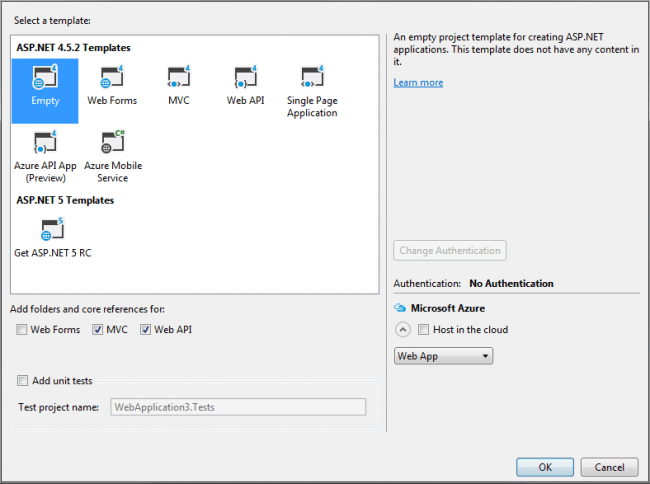
Empty Template With MVC And Web API Folders
Once you click OK, a project with MVC like folder structure with core references will be created for you.

Folder Structure And References For Empty MVC Project
Using the Code
We will set up our database first so that we can create Entity Model for our application later.
Create a Database
The following query can be used to create a database in your SQL Server.
USE [master]
GO
Now we will create the table we needed. As of now, I am going to create the table tblTags.
Create Tables in Database
Below is the query to create the table tblTags.
USE [TrialsDB]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[tblTags](
[tagId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[tagName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
[tagDescription] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_tblTags] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[tagId] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, _
IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Can we insert some data to the tables now?
Insert Data to Table
You can use the below query to insert the data to the table tblTags.
USE [TrialsDB]
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[tblTags]
([tagName]
,[tagDescription])
VALUES
(<tagName, nvarchar(50),>
,<tagDescription, nvarchar(max),>)
GO
Next thing we are going to do is create a ADO.NET Entity Data Model.
Create Entity Data Model
Right click on your model folder and click new, select ADO.NET Entity Data Model. Follow the steps given. Once you have done the processes, you can see the edmx file and other files in your model folder. Here, I gave Dashboard for our Entity data model name. Now you can see a file with edmx extension has been created.
Now we will create our Web API controller.
Create Web API Controller
To create a Web API controller, just right click on your controller folder and click Add -> Controller -> Select Web API 2 controller with actions, using Entity Framework.

Web API 2 Controller With Actions Using Entity Framework
Now select tblTag (WebAPIWithHttpClient.Models) as our Model class and TrialsDBEntities (WebAPIWithHttpClient.Models) as data context class. This time, we will select controller with async actions.

Web API Controller With Async Actions
As you can see, it has been given the name of our controller as tblTags. Here, I am not going to change that, if you wish to change, you can do that.
Now, you will be given the following codes in our new Web API controller.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web.Http;
using System.Web.Http.Description;
using WebAPIWithHttpClient.Models;
namespace WebAPIWithHttpClient.Controllers
{
public class tblTagsController : ApiController
{
private TrialsDBEntities db = new TrialsDBEntities();
public IQueryable<tblTag> GettblTags()
{
return db.tblTags;
}
[ResponseType(typeof(tblTag))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> GettblTag(int id)
{
tblTag tblTag = await db.tblTags.FindAsync(id);
if (tblTag == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(tblTag);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> PuttblTag(int id, tblTag tblTag)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (id != tblTag.tagId)
{
return BadRequest();
}
db.Entry(tblTag).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!tblTagExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return StatusCode(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(tblTag))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> PosttblTag(tblTag tblTag)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.tblTags.Add(tblTag);
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = tblTag.tagId }, tblTag);
}
[ResponseType(typeof(tblTag))]
public async Task<IHttpActionResult> DeletetblTag(int id)
{
tblTag tblTag = await db.tblTags.FindAsync(id);
if (tblTag == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.tblTags.Remove(tblTag);
await db.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(tblTag);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
db.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private bool tblTagExists(int id)
{
return db.tblTags.Count(e => e.tagId == id) > 0;
}
}
}
As you can see, we have actions for:
So the coding part to fetch the data from database is ready, now we need to check whether our Web API is ready for action!. To check that, you just need to run the URL http://localhost:7967/api/tbltags. Here, tblTags is our Web API controller name. I hope you get the data as a result.

Web_API_Result
As of now, our Web API application is ready, and we have just tested whether it is working or not. Now we can move on to create a console application where we can consume this Web API with the help of HttpClient. So shall we do that?
Create Console Application To Consume Web API
To create a console application, Click File -> New -> Click Windows -> Select Console application -> Name your application -> OK

Console Application
I hope now you have a class called Program.cs with the below code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace WebAPIWithHttpClientConsumer
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
Now we will start our coding. We will create a class called tblTag with some properties so that we can use those when we need.
public class tblTag
{
public int tagId { get; set; }
public string tagName { get; set; }
public string tagDescription { get; set; }
}
To get started using the class HttpClient, you must import the namespace as follows:
using System.Net.Http;
Once you have imported the namespaces, we will set our HttpClient and the properties as follows:
HttpClient cons = new HttpClient();
cons.BaseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:7967/");
cons.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();
cons.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add
(new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
As you can see, we are just giving the base address of our API and setting the response header. Now we will create an async action to get the data from our database by calling our Web API.
Get Operation Using HttpClient
MyAPIGet(cons).Wait();
Following is the definition of MyAPIGet function.
static async Task MyAPIGet(HttpClient cons)
{
using (cons)
{
HttpResponseMessage res = await cons.GetAsync("api/tblTags/2");
res.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
if (res.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
tblTag tag = await res.Content.ReadAsAsync<tblTag>();
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("---------------------Calling Get Operation------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("tagId tagName tagDescription");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}\t\t{2}", tag.tagId, tag.tagName, tag.tagDescription);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Here, res.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); ensures that it throws errors if we get any. If you don’t need to throw the errors, please remove this line of code. If the async call is success, the value in IsSuccessStatusCode will be true.
Now when you run the above code, there are chances to get an error as follows:
Error CS1061 ‘HttpContent’ does not contain a definition for ‘ReadAsAsync’ and no extension method ‘ReadAsAsync’ accepting a first argument of type ‘HttpContent’ could be found (are you missing a using directive or an assembly reference?)
This is just because of the ReadAsAsync is a part of System.Net.Http.Formatting.dll which we have not added to our application as a reference yet. Now we will do that? Sounds OK?
Just right click on the references and click add reference -> Click browse -> search for System.Net.Http.Formatting.dll – Click OK

Add References
Please add Newtonsoft.Json also. Now let us run our project and see our output.

Web_API_Consumer_Get_Output
Now shall we create a function for updating the record? Yes, we are going to create a function with ‘Put’ request. Please copy and paste the preceding code for that.
Put Operation Using HttpClient
static async Task MyAPIPut(HttpClient cons)
{
using (cons)
{
HttpResponseMessage res = await cons.GetAsync("api/tblTags/2");
res.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
if (res.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
tblTag tag = await res.Content.ReadAsAsync<tblTag>();
tag.tagName = "New Tag";
res = await cons.PutAsJsonAsync("api/tblTags/2", tag);
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("------------------Calling Put Operation--------------------");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("tagId tagName tagDescription");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}\t\t{2}", tag.tagId, tag.tagName, tag.tagDescription);
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
As you can see, we are just updating the record as below once we get the response from await cons.GetAsync(“api/tblTags/2”).
tag.tagName = "New Tag";
res = await cons.PutAsJsonAsync("api/tblTags/2", tag);
Now again run your application, and check whether the tag name has been changed to ‘New Tag’.

Web_API_Consumer_Put_Output
Now, did you see that your tag name has been changed? If yes, we are ready to go for our next operation. Are you ready?
Delete Operation Using HttpClient
We will follow the same procedure for delete operation too. Please see the code for delete operation below.
async Task MyAPIDelete(HttpClient cons)
{
using (cons)
{
HttpResponseMessage res = await cons.GetAsync("api/tblTags/2");
res.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
if (res.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
res = await cons.DeleteAsync("api/tblTags/2");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("------------------Calling Delete Operation--------------------");
Console.WriteLine("------------------Deleted-------------------");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
To delete a record, we uses res = await cons.DeleteAsync(“api/tblTags/2”); method. Now run your application and see the result.

Web_API_Consumer_Delete_Output
What action is pending now? Yes, it is Post.
Post Operation Using HttpClient
Please add the below function to your project for the post operation.
static async Task MyAPIPost(HttpClient cons)
{
using (cons)
{
var tag = new tblTag { tagName = "jQuery", tagDescription = "This tag is all about jQuery" };
HttpResponseMessage res = await cons.PostAsJsonAsync("api/tblTags", tag);
res.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
if (res.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("------------------Calling Post Operation--------------------");
Console.WriteLine("------------------Created Successfully--------------------");
}
}
}
We are just creating a new tblTag and assign some values, once the object is ready, we are calling the method PostAsJsonAsync as follows:
var tag = new tblTag { tagName = "jQuery", tagDescription = "This tag is all about jQuery" };
HttpResponseMessage res = await cons.PostAsJsonAsync("api/tblTags", tag);
As you have noticed, I have not provided the tagId in the object, do yo know why? I have already set Identity Specification with Identity Increment 1 in my table tblTags in SQL database.
Now we will see the output. Shall we?

Web_API_Consumer_Post_Output
We have done everything! That’s fantastic right? Have a happy coding.
You can always use WebClient also for this requirement, that I will share in an another article.
Conclusion
Did I miss anything that you may think is needed? Did you try Web API yet? Have you ever wanted to call a Web API from server itself or from any console application? Could you find this post useful? I hope you liked this article. Please share your valuable suggestions and feedback.
Your Turn. What Do You Think?
A blog isn’t a blog without comments, but do try to stay on topic. If you have a question unrelated to this post, you’re better off posting it on C# Corner, Code Project, Stack Overflow, ASP.NET Forum instead of commenting here. Tweet or email me a link to your question there and I’ll definitely try to help if I can.
