Introduction
This article presents and explains how to gain access to SAM file while Windows 7 system is running. The goal here is not to give a method to hack Windows systems, but this solution is designed to help system administrators in detecting the SAM file corruption.
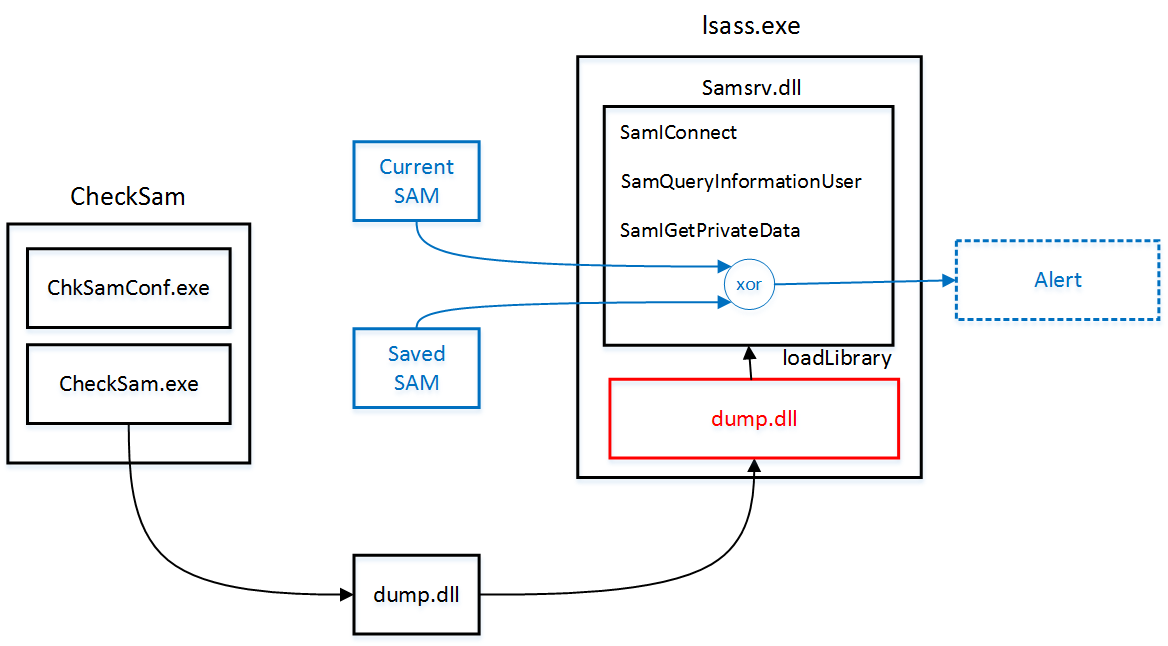
Several approaches exist to extract user credentials from SAM file either under a running system or when the system is turned off. In this article, we have opted for the first approach. Indeed, for our purpose, we need the most recent credentials in order to compare them to the previously saved one and emit an alert if the comparison fails.
This approach works by performing DLL injection inside the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process (better known as lsass.exe). It is a way that malware uses to run a DLL inside another process, thereby providing that DLL with all of the privileges of that process. Hash dumping tools often target lsass.exe because it has the necessary privilege level as well as access to many useful API functions.
When the DLL was injected, it uses undocumented API functions like SamIConnect, SamQueryInformationUser and SamIGetPrivateData to extract hashes from SAM file.
Once the hashes were dumped, they are compared to the previously saved ones. If the comparison fails, the system emits an alert.
Background
Our application, developed under Visual Studio 2013 is composed of three programs:
- CheckSam.exe: contains a Windows service that injects a DLL inside the
lsass process. Our choice of using a Windows service is motivated by the introduction since Vista of 'Session Separation' protection. ‘Session Separation' ensures that core system processes including services always run in session 0 while all user process's run in different sessions. As a result, any process running in user session fails to inject DLL into system process as "CreateRemoteThread" did not work across session boundaries. In addition, services run in the security context of the local system account. This account is the same account in which core Windows user-mode operating system components run, including Smss.exe, Csrss.exe, Lsass.exe, and so on. - ChkSamConfig.exe: This program proposes a user console interface to start, stop and delete a CheckSam service.
- The dump.dll DLL: This DLL contains a code responsible for extracting the credential hashes from a SAM file.
ChkSamConfig.exe
Writing a Service Program's Main Function
The main function of CheckSam.exe calls the "StartServiceCtrlDispatcher" function to connect to the service control manager (SCM) and start the control dispatcher thread. The dispatcher thread loops, waiting for incoming control requests for the services specified in the dispatch table, namely "SvcMain".
#pragma comment(lib, "advapi32.lib")
#define SVCNAME TEXT("checkSam")
void __cdecl _tmain(int argc, TCHAR *argv[])
{
if (lstrcmpi(argv[1], TEXT("install")) == 0)
{
InstallSvc();
return;
}
SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY DispatchTable[] =
{
{ SVCNAME, (LPSERVICE_MAIN_FUNCTION)SvcMain },
{ NULL, NULL }
};
if (!StartServiceCtrlDispatcher(DispatchTable))
{
return;
}
}
Writing a ServiceMain Function
The "SvcMain" function first calls the "RegisterServiceCtrlHandler" function to register the "CtrlHandler" function as the service's Handler function and begin initialization.
Next, the "SvcMain" function calls the "ReportSvcStatus" function to indicate that its initial status is SERVICE_START_PENDING. While the service is in this state, no controls are accepted. To simplify the logic of the service, it is recommended that the service doesn't accept any controls while it is performing its initialization.
Finally, the "SvcMain" function calls the "SvcInit" function to perform the service-specific initialization and begin the work to be performed by the service.
SERVICE_STATUS gSvcStatus;
SERVICE_STATUS_HANDLE gSvcStatusHandle;
VOID WINAPI SvcMain(DWORD dwArgc, LPTSTR *lpszArgv)
{
gSvcStatusHandle = RegisterServiceCtrlHandler( SVCNAME, CtrlHandler);
if (!gSvcStatusHandle)
{
return;
}
gSvcStatus.dwServiceType = SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS;
gSvcStatus.dwServiceSpecificExitCode = 0;
ReportSvcStatus(SERVICE_START_PENDING, NO_ERROR, 3000);
SvcInit(dwArgc, lpszArgv);
}
Writing a SvcInit Function
This function reports the running state to SCM, launches a thread that executes the "Thread" function, waits for its end thanks to "WaitForSingleObject" function and finally calls "ReportSvcStatus" function to indicate that the service has entered the SERVICE_STOPPED state, and returns.
VOID SvcInit(DWORD dwArgc, LPTSTR *lpszArgv)
{
ReportSvcStatus(SERVICE_RUNNING, NO_ERROR, 0);
HANDLE hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, Thread, NULL, 0, NULL);
WaitForSingleObject(hThread, INFINITE);
ReportSvcStatus(SERVICE_STOPPED, NO_ERROR, 0);
}
Once the thread was launched, it executes the "Thread" function that calls, in its turn, the injection code.
The "injection( )" function starts by calling "LsassId()" function in order to get the PID of lsass process. The PID is passed to "OpenProcess" to obtain the handle of lsass process. Using this handle, "VirtualAllocEx" and "WriteProcessMemory" then respectively allocate space and write the name of the DLL (the string "dump.dll") into the victim process. Next, "GetProcAddress" is used to get the address to "LoadLibrary". Finally, "CreateRemoteThread" is called with three important parameters: the handle to lsass process (hp), the address of LoadLibrary (loadLibAddr), and a pointer to the DLL name previously written inside lsass process (baseAdd). "CreateRemoteThread" allows a process to execute a thread inside a remote process when it has the appropriate privileges.
#define DLLTOINJECT "C:\\dump.dll"
#define LOGFILE "C:\\checkSam.log
VOID injection()
{
FILE * log;
DWORD pid;
HANDLE hp = NULL;
LPSTR baseAdd = NULL;
fopen_s(&log, LOGFILE, "w");
pid = LsassId();
if (pid == 0){
fprintf(log, "Can't find the pid of lsass process\n");
fclose(log);
return;
}
hp = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, pid);
if (hp == NULL){
fprintf(log, "ERROR: (%d) while trying to
open lsass process (PID: %d)\n", GetLastError(), pid);
fclose(log);
return;
}
baseAdd = (LPSTR)VirtualAllocEx(hp, NULL,
strlen(DLLTOINJECT), MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
if (baseAdd == NULL)
{
fprintf(log, "ERROR: (%d) while creating a vitual memory address
space inside lsass process (PID: %d)\n", GetLastError(), pid);
fclose(log);
return;
}
fprintf(log, "The base address inside lsass of %s is : %p\n", DLLTOINJECT, baseAdd);
if (!WriteProcessMemory(hp, baseAdd, DLLTOINJECT, strlen(DLLTOINJECT), NULL)){
fprintf(log, "ERROR : (%d) while trying to write inside
the committed address space in lsass process (PID: %d)\n", GetLastError(), pid);
fclose(log);
return;
};
PTHREAD_START_ROUTINE loadLibAddr = (PTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)GetProcAddress
(GetModuleHandle(TEXT("Kernel32")), "LoadLibraryA");
if (loadLibAddr == NULL) {
fprintf(log, "ERROR : (%d) while loading the loadLibrary function \n", GetLastError());
fclose(log);
return;
}
fprintf(log, "loadLibrary function is loaded at %p\n", loadLibAddr);
if (!CreateRemoteThread(hp, NULL, 0, loadLibAddr, baseAdd, 0, NULL)){
fprintf(log, "ERROR: (%d) occurred when attempting
to launch a thread in lsass process", GetLastError());
fclose(log);
return;
}
fprintf(log, "The DLL has been successfully injected in the lsass process...\n");
fclose(log);
return;
}
DWORD LsassId(){
DWORD ProcessList[1024];
DWORD cbNeeded;
DWORD cProcesses;
TCHAR szProcessName[MAX_PATH] = TEXT("<unknown>");
if (!EnumProcesses(ProcessList, sizeof(ProcessList), &cbNeeded))
{
return 0;
}
cProcesses = cbNeeded / sizeof(DWORD);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cProcesses; i++)
{
if (ProcessList[i] != 0)
{
HANDLE hProcess = OpenProcess(PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ,
FALSE,
ProcessList[i]);
if (NULL != hProcess)
{
HMODULE hMod;
DWORD cbNeeded;
if (EnumProcessModules(hProcess, &hMod, sizeof(hMod),
&cbNeeded))
{
GetModuleBaseName(hProcess, hMod, szProcessName,
sizeof(szProcessName) / sizeof(TCHAR));
}
}
if (lstrcmp(szProcessName, TEXT("lsass.exe")) == 0)
{
CloseHandle(hProcess);
return ProcessList[i];
}
}
}
return 0;
}
ChkSamConfig.exe
This console program allows a user to start and delete the checkSam service.
The install, start and delete functions share the same starting code. They first call "OpenSCManager" to open and get a handle to SCM, then they get a handle to the desired service.
SC_HANDLE schSCManager;
SC_HANDLE schService;
SERVICE_STATUS ssStatus;
schSCManager = OpenSCManager(
NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_ALL_ACCESS);
if (NULL == schSCManager)
{
printf("OpenSCManager failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return;
}
schService = OpenService(
schSCManager, SvcName, DELETE);
if (schService == NULL)
{
printf("OpenService failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
CloseServiceHandle(schSCManager);
return;
}
CloseServiceHandle(schService);
CloseServiceHandle(schSCManager);
Install Service Function
It starts by obtaining the path to the service image. For this purpose, we use "GetModuleFileName" function with NULL as first parameter. This indicates that "GetModuleFileName" retrieves the path of the executable file of the current process. Indeed, To keep the code as simple as possible, we have included the code of install function in the checkSam program.
...
TCHAR ServicePath[MAX_PATH];
if (!GetModuleFileName(NULL, ServicePath, MAX_PATH))
{
printf("Cannot install service (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return;
}
...
schService = CreateService(
schSCManager, SVCNAME, SVCNAME, SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS, SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS, SERVICE_DEMAND_START, SERVICE_ERROR_NORMAL, ServicePath, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (schService == NULL)
{
printf("CreateService failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
CloseServiceHandle(schSCManager);
return;
}
else printf("Service installed successfully\n");
...
Start Service Function
After getting a handle to the service, we check the status of the service. If the service is in running state, the program returns. Otherwise, we wait until the service exits its "SERVICE_STOP_PENDING state" and then we call the "StartService" function to start the service.
if (!StartService(
schService, 0, NULL)) {
printf("StartService failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
CloseServiceHandle(schService);
CloseServiceHandle(schSCManager);
return;
}
else printf("Service start pending...\n");
Delete Service Function
To delete a service, we just need to obtain a handle to a concerned service and call the "DeleteService" Windows function.
if (!DeleteService(schService))
{
printf("DeleteService failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
}
else printf("Service deleted successfully\n");
Conclusion
In this first part of the article, we showed how to inject a DLL to lsass process. In the second part of the article, we will present how to create dump.dll, how to extract the hashes from SAM file and how the detection works.
References
-
Windows Internals, Sixth Edition, Part 1, Mark Russinovich, David A. Solomon, Alex Ionescu, Microsoft Press, 2012
-
Practical Malware Analysis, The Hands-On Guide to Dissecting Malicious Software, Michael Sikorski and Andrew Honig, William Pollock, 2012
-
The Art of Memory Forensics Detecting Malware and Threats in Windows, Linux, and Mac Memory, Michael Hale Ligh Andrew Case Jamie Levy AAron Walters, Wiley, 2014
- https://developer.microsoft.com/fr-fr/windows/desktop/develop
