This article is the second of eight parts introducing an advanced JSON form specification.
Chapters
Introduction
This chapter covers the parameters that define the following form screens:
- Information Output Screen
- Text Input Screen
- Integer Input Screen
- Number Input Screen
In order to understand the rest of this chapter, the reader is encouraged to download, unzip and copy the Input Widget Form to the Android device. Fill the form using the CCA Mobile app and then back up and inspect the text of the filled instance of this form as discussed here. The code block below shows an example of a completed instance of this form.
Information Output Screen
So far, the screens of a form have been consistently referred to as input screens but that term is not entirely correct. This is so because there is exactly one form screen called an Information screen which is an output screen. The primary purpose of such a screen is to display information that has relevance to the form as a whole. The Image below depicts an example of an Information screen.
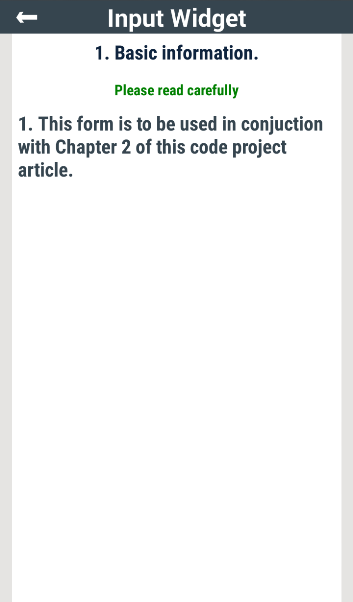
To see how the screen above is defined, take a look at the JSON code below:
Two parameters specific to an Information output screen are the screenwidgetType which is set to Info and the infoDisplayArray. The infoDisplayArray parameter is a JSON array that contains the text that conveys the information to be displayed. Just like the screenDisplayArray discussed in this section, the infoDisplayArray item is an object that consists of the localeCode and localeText which are both of type JSON string. The localeText content displayed to the user will be based on a match between the value of the localeCode parameter and the current language setting of the device displaying the form. See localeCode discussed here to get a better grip on the multi-language support feature of the advanced JSON forms.
The value of the inputRequired parameter for an Information output screen must always be set to false.
Text input screens as the name implies are screens that prompt the user for a text. The format and length of acceptable text inputs can be built into the form definition as is demonstrated in the input screens discussed in this section.

The image above shows the first of three text input screen.
The JSON definition for the screen above is contained in the code block below:
The three parameters relevant here are; screenwidgetType, inputRequired and widgetSchema. Notice that the widgetSchema says it expects a JSON string which will be called First Name. It can also be seen that this input is compulsory going by the value of the inputRequired parameter.

The Last Name text input screen shown above places a constraint on the length of the expected Last Name input string.
From the value widgetSchema parameter shown above, a valid Last Name input must have a length that is between 2 and 100 characters (inclusive).
Beyond text length, a text input screen can be defined such that for a text input to be considered valid, it must conform to a defined regular expression. This was the restriction that was placed on the input of the screen shown below:
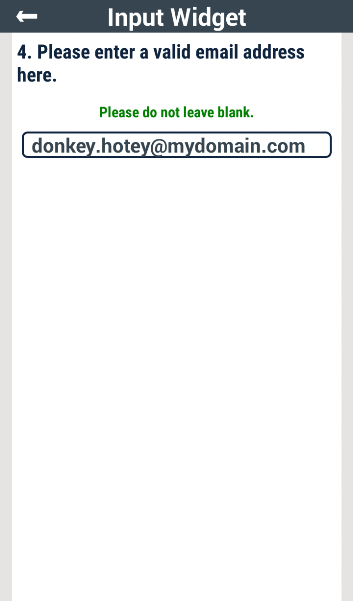
Notice the JSON escaped regular expression in the pattern variable of the widgetSchema in the code block below. This regular expression, i.e., [A-Z0-9a-z._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,6} ensures that the input text conforms to a valid email address.
Inputs to Integer input screens can be restricted to an integer range or multiple. For integer input screens, the screenwidgetType is always set to integerInput.
The input screen shown below prompts the user for an integer age value.

As can be seen in the widgetSchema parameter in the code block below, the Age JSON schema specifies that its value must be of JSON integer type and must be between 18 and 120, inclusive.
The hint in the screen shown below prompts the user to enter a value that is a multiple of 10.

The screen above is an example of restricting an integer input to a multiple of another integer, in this case 10. The code block below shows how this input screen definition uses the JSON schema specification to accomplish this.
Finally, it is possible to allow the integer input to assume any value as demonstrated in the input screen and code block that follows:

Number Input Screens
Number input screens are similar in structure to Integer input screens except that the screenwidgetType is always set to numberInput. This screen type accepts decimal as well as integer values.
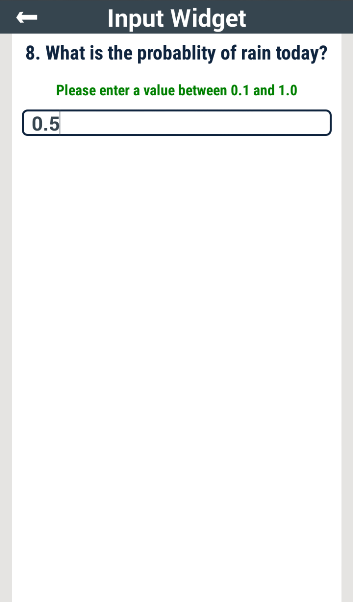
In the code block below, the widgetSchema parameter specifies that the Probability Rain value must be a JSON number type that is within the range of 0.1 and 1.0. Note that the multipleOf keyword shown in the last section also applies to numberInput screens.
Next Chapter
In the next chapter of this article, i.e., Chapter 3, a class of screens referred to as Input Lists is presented.
Point of Interest
The interested reader should follow the form design sections of these walkthroughs and use this GUI tool to learn more about designing forms based on a number of use case scenarios.
History
- 18th July, 2016: First version
- 3rd November, 2016: Made corrections to this work
