Introduction
Nowadays, having real time web applications as two way connection is necessary in all kind of fields. JavaScript is a good solution, but it just works on the client side while there are some scenarios for which we really need to have solutions which work on the server side. For instance, storing data on database or processing data on server side. There are two popular technologies, one is SignalR and other Node.js.
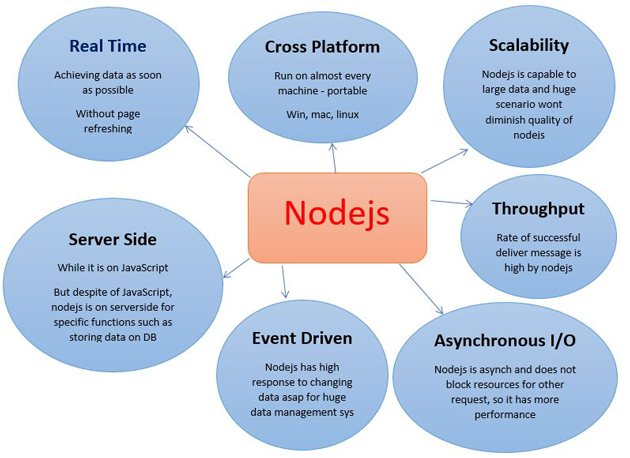
Why Do We Use Node.js?
First and formost, it is because we need a real time solution for our web application in two way client to server and server to client side, so data can be shared between both sides. Another good advantage of Node.js is that it is cross platform and does not need complex preparation and installation before using it. It is well established for I/O and last but not the least, the probability of missing data is too rare.
While the architecture of Node.js is drawn as below picture to flow data between client and server, it is possible to have connection with database by using some solutions which I have described as follows:

There are some situations which we need to keep on .NET platform and just use benefits from node.js. In such case, I have written this code with the help of WCF to communicate with MS SQL Server instead of installing drivers such as node-ts, node-sqlserver, mssqlhelper, mssqlx, edge.js.

Background
I strongly recommend you read this article in order to know how trigger node.js works on .NET platform.
Using the Code
- File -> New Project ->
WebApplication - Solution -> Right Click -> Add New Project -> Class Library -> DAL
- Add New Item-> Class -> DataAccess.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
namespace DAL
{
public abstract class DataAccess
{
public string ConnectionString
{
get
{
return "Data Source =DESKTOP-EVM02NE\\MAHSA;
Initial Catalog = NodeByWCF; Integrated Security=true ";
}
}
protected Int32 ExecuteNonQuery(DbCommand cmd)
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
protected IDataReader ExecuteReader(DbCommand cmd)
{
return ExecuteReader(cmd, CommandBehavior.Default);
}
protected IDataReader ExecuteReader(DbCommand cmd, CommandBehavior behavior)
{
return cmd.ExecuteReader(behavior);
}
protected object ExecuteScalar(DbCommand cmd)
{
return cmd.ExecuteScalar();
}
}
}
- Add New Item-> Class -> CustomerDAL.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DAL
{
public class CustomerDAL : DataAccess
{
public CustomerDAL()
{
}
public IEnumerable<customer> Load()
{
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
SqlDataAdapter dAd = new SqlDataAdapter("select * from Customer", conn);
dAd.SelectCommand.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
try
{
dAd.Fill(dt);
foreach (DataRow row in dt.Rows)
{
yield return new Customer
{
ID = Convert.ToInt32(row["ID"]),
Name = (row["Name"]).ToString()
};
}
}
finally
{
dAd.Dispose();
conn.Close();
conn.Dispose();
}
}
}
}
- Add New Item-> Class -> Customer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DAL
{
public class Customer
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
- Solution -> Right Click -> Add New Project -> Class Library -> BAL
- Add New Item-> Class -> CustomerBAL.cs:
using DAL;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace BAL
{
public class CustomerBAL
{
public IEnumerable<dal.customer> Load()
{
CustomerDAL customer = new CustomerDAL();
try
{
return customer.Load();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
finally
{
customer = null;
}
}
}
}
- Solution -> Right Click -> Add New Project ->
WebApplication - Add New Item-> WCF Service (Ajax-enabled)-> MyService.svc
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Activation;
using System.ServiceModel.Web;
using System.Text;
using BAL;
using DAL;
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
namespace WebApplication
{
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "")]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
public class MyService
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet()]
public string GetCustomer()
{
CustomerBAL _Cust = new CustomerBAL();
try
{
var customers = _Cust.Load();
string json = new JavaScriptSerializer().Serialize(customers);
return json;
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
finally
{
}
}
}
}

- Solution -> Right Click -> Add New Project ->Javascript -> Blank Node.js Web Application

- Server.js:
var http = require("http");
var url = require('url');
var fs = require('fs');
var io = require('socket.io');
var port = process.env.port || 1337;
var server = http.createServer(function (request, response) {
var path = url.parse(request.url).pathname;
switch (path) {
case '/':
response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' });
response.write('hello world');
response.end();
break;
case '/Index.html':
fs.readFile(__dirname + path, function (error, data) {
if (error) {
response.writeHead(404);
response.write("page doesn't exist - 404");
response.end();
}
else {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/html" });
response.write(data, "utf8");
response.end();
}
});
break;
default:
response.writeHead(404);
response.write("page this doesn't exist - 404");
response.end();
break;
}
});
server.listen(port);
var listener = io.listen(server);
listener.sockets.on('connection', function (socket) {
socket.emit('message', { 'message': 'Hello this message is from Server' });
socket.on('client_data', function (data) {
socket.emit('message', { 'message': data.name });
socket.broadcast.emit('message', { 'message': data.name });
process.stdout.write(data.name);
console.log(data.name);
});
});
- Index.html:
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.socket.io/socket.io-1.4.5.js"></script>
<script src="http://localhost:8080/server.js"></script>
<script src="/server.js"></script>
<script>
var socket = io.connect();
socket.on('message', function (data) {
$('#conversation').append('
' + data.message);
});
$(document).ready(function () {
$('#send').click(function () {
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "http://localhost:28448/MyService.svc/GetCustomer",
contentType: "application/json; charset=utf-8",
dataType: "text",
processdata: true,
success: function (msg) {
var obj = JSON.parse(msg);
var t = obj.d.length;
var completeMsg = "";
for (var i = 0; i < t; i++) {
completeMsg = completeMsg + " " + obj.d[i].Name;
}
alert(completeMsg);
socket.emit('client_data', { 'name': completeMsg });
}
});
})
});
</script>
<input id="text" type="text" /><button id="send">send</button>
This is our conversation.
Test and Run
Type: Localhost:1337/Index.html
Click on "send" button, Data will come from DB on Node.js.

References
History
- 4th July, 2016: First version
