Introduction
Today, cities face several challenges. Traffic congestion control and pollution control are two of biggest challenges for any city. Various artificial intelligence systems and autonomous systems are being developed and deployed over the years to ease the traffic congestion as well as reducing the opollution level in a city. Often time, research and development of such products are tedious because product testing is expenssive.
A Simulation environment gives much needed flexibility for such large scale solution deployment.
It has been found in the past studies that overall pollution of a place is dependent on the industrial output in and around the place and the traffic. It is found that vehicles emit more Co2 while stationary with engines on. It is observed that the pollution at the junctions are more where vehicle wait with engine on for the lights to be turned green. In order to reduce such traffic volume, authorities have adopted flow based traffic light control where the traffic flow is being monitored throug either physical sensors or through machine vision techniques.
However, as the type of vehicles differs and as each vehicle type has their own pollution signature, density based traffic control has failed to reduce the pollution level. We therefore need more intelligent system that can actually take into account of the pollution level while controlling the traffic light timer.
As City traffic is interconnected from one traffic junction to another, it would require immense resource to deploy physical sensors across all parts of a jusnction, to observe traffic flow, pollution and then take light timing decisions.
We want to reduce this cumbersome and difficult process by providing a framework that readily integrates IoT with a realistic city traffic and vehicle flow simulation. A physical sensor is integrated into the simulation environment such that the solution can be tested against real city jucntion even while in simulation mode.
So, our solution offers:
- A realistic traffic simulation using VANET Open source simulator
- An Intel Edison based Co2 sensing device
- A Mqtt gateway based integration of the sensing data to the simulation environment
- A ThingSpeak based gateway to mitigate the data into cloud for further analysis
- An intelligent object to attach the Co2 monitoring data with one of the traffic junctions of the simulation environment and then finally controlling the traffic light timing of that particular junction.
This is a high end simulation of a adhoc based traffic system which shows how co2 consumption happens in the way of increasinh vehicles.The condition blends in both of virtual and real world scenario in a map.
This simulation works in a full indepth research that has happened in the field of traffic based system.We have taken data from various considerations and broken it in a map of small pocket where we can intensely classify the demographic of a vehicle.Keepin key considerations in mind such as the vehicle and their types plus they
velocity amount of fuel burnt more of a carbon footprint of the vehicle and the causes of it.Here we measure the CO2 emission of the vehicles present the densely populated with different vehicles how it works.
The project is an adoptation and improvement of the concepts presented in this paper
The Physical world
The physical world comprises of an Intel Edison board with Grove shield where a Mq7 sensor is connected with one of the analog ports.
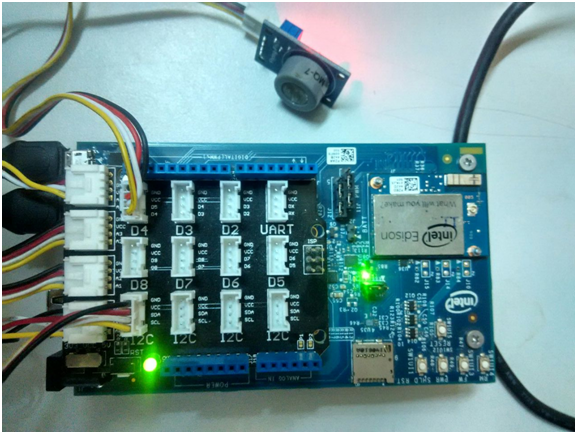

Fig. Intel Edison board with Mq7 Sensor
The arrangement measure the gas in the environment and analog value varies accordingly. This 10 bit precision analog value needs to be mapped to the actual Co2 value in PPM which is done in following way:

Methodology
- Create a realistic city traffic simulation using VanetSim (a java based open source vanet simulator).
- Implement a real time pollution sensing device using Intel Edison and Mq7 sensor.
- Mitigate the observe pollution level (CO2 level) to the simulation environment using high quality of service, low latency Mqtt protocol.
- Create a dependency graph between traffic flow and congestion level.
- Control city traffic light based on the vehicle flow.
- Integrate the pollution level into traffic light control system.
- To observe the performance of variation of the traffic light behavior in accordance to change in the pollution level at specific junction.
- To validate that such a system can ensure realistic results through huge number of vehicles and by incorporating movement of the vehicles through multiple junctions.
- The correlation of the monitored Co2 value with the traffic light is shown in following equation:

Where 400 is the normal Co2 value in PPM, ParameterValue is the simulation object representing the actual pollution ( Co2 level) assigned to it through Mqtt by Intel Edison. 10 is the factor by which the green light phase is increased in the mapped junction
System Design

The main thing is to push the values to the simulation and at the same time keep the values into cloud. The iot.eclipse.org provides a cloud service but we want a real time visualization at large area by pushing the values into cloud analytic service called ThingSpeak.
Simulation Overview

Fig. Way points in the open street map

Fig. nodes (vehicles) moving through junction
Coding
Co2 Sensing and Publishing over ioT
var mqtt = require('mqtt');
var client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://iot.eclipse.org');
In unix, push the data into any open websites like curl (command line URL).From javascript, access the curl command which is Unix base command. Then push data into the cloud calling http get method.The thingspeak use the JavaScript id. So thingspeak need http protocol, we call http protocol using curl command. Here node js doesn’t have http directives, so we can access Unix system commands from node js to use Unix as Unix http features to push the data into thingspeak http API. To do this process using the library function called ‘sys’.
var sys = require('sys')
It is Unix system library which means all APIs like word count,ls commands etc are access using ‘sys’ library.
var exec = require('child_process').exec;
Here,’exe’ is a process, we take a JavaScript module by child process. We create a background process while we do network related operations, such that it doesn’t block the main process. The node js doesn’t create any thread and node.js is a system which runs a single thread. But the problem is that it cannot access the Unix command system because those are kernel level commands. The js runs a single thread which cannot run kernel command from the user a command. So we take a node module called child process, which allows node js system to fork a child process. If we can fork a child process. Then we can access kernel level program and id doesn’t run in the user level. The ‘exe’ is a variable of child process.
function puts(error, stdout, stderr) { sys.puts(stdout) }
The ‘puts’ is a function which puts all the results coming from the child process.When we execute a any linux command like ls,wc etc.Then we get setup results.We want to put its results into the actual command prompts.So ‘put’ command going to put all error,stdout into current command.
The node js a program which of two types of libraries:
- Core library
- User defined library
There are some set of function which is already available with node js and there are some other functions which are not available with node js.The functions which are not to be available with node js are to be installed by npm (node package manager).Once we install the npm package by saying npm-install.Now we can access any number of libraries.
var mraa=require('mraa');
The ‘mraa’ is a library.This node js library used to access the hardware.Because we want to access digital pin called GPIO pin, hence we using the ‘mraa’ library.In javascript use the ‘require’ function to use the modules.There are two types of modules which are one is core module and another is use module.The javascript support some core modules including anything for example math library etc.
//var LCD = require('jsupm_i2clcd');
//var myLCD = new LCD.Jhd1313m1(6, 0x3E, 0x62);
var a0=new mraa.Aio(3);
The pollution sensor connected to analog port which is pin 3(Aio(3)).The analog pin3 used to reads the analog value of amount of CO2 emitted by vehicles coming from Mq7 sensor.It will measure the analog value.
The formula is computed for calculating the ppm value.
According to formulae that is ppm=a*(Rs/R0)^b,
var a=116.602;
var b=-5.96;
var In=4.5/3.34e+4;
var R0=41000;
These are the default resistance values.First we read the analog value from a0 pin where pollution sensor is connected.Then we go through all conversions in order to get the pollution value.The pollution will be in ppm.The CO2 level will be measure in the ppm’s.
var Rs=v1/In;
var v2=Rs/R0;
v2=Math.pow(v2,b);
var ppm=179.73*v2;
console.log("x="+val+" vo="+vo+" Rs="+Rs+" ppm"+ppm);
if(ppm<420)
{
}
else
{
}
The ppm value will be less than 420 then it display the value in display as green or else display the value in display as red color.
s="curl \"http://api.thingspeak.com/update?api_key=3ZXPXW3SPPDEC1HU&field1="+ppm+ "\"";
exec(s);
client.publish('rupam/Simulator', ""+ppm);
setTimeout(Loop,10000);
}
The ‘curl’ command used to call the thingspeak.com where the value are updated.The thingspeak.com/update is a API key,along with this API key only one field thingspeak.In thingspeak channel,we can push the eight sensors together.So we can pass upto 8 sensors.In our project using only one sensor in the field1 to display the ppm value.
At the same time, we pushing this value to the simulator.So we need to publish the data in a channel using Mqtt protocol.
The Simulation Part
This is an adoptation of Open Source VANET Simulator Project where we have integrated our physical sensing model and embedded intelligence to control the traffic light based on environmental Co2 value. As the traffic gets congested at a specific road leading to a junction, the pollution increases. Now, the pollution level also depends upon several other factors like type of vehicles ( generally bikes and trucks will emit more co2 than cars). Normally modern traffic flow doesn't take into consideration of these factors and traffic lights at best adopts a density based control model where highly densed roads are given more priority and high timer value for the green light in order to clear the traffic in that road.
But as we elaborated at the top, that approch not always result in most optimum pollution control. We argue that instead of controlling the traffic through traffic lights, the authorities must adopt more intelligent solution and must integrate the environmental parameters like Co2 into traffic control.
We have adopted a realistic city traffic scenerio with VANET simulator that can not only simulate the traffic lights, junctions, but also many important aspects of a realistic city traffic scenerio like accidents, pot holes, inter vehicular communication and so on.

We have been through how the process works now it is important on how the data and the simulation works.The entire code is written in java.We have used netbeans ide to write the programs.OpenStreetMap allows the file which you want to work on to be loaded.It generates a *.osn file for our usage.Now that file is uploaded in the vanet simulator and can be worked upon.The starting point of the code is shown below.The buttons in the code are for exact choices of what we are doing.
package vanetsim;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import vanetsim.localization.Messages;
public class VanetSimStarter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length < 3) SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new VanetSimStart());
else SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new ConsoleStart(args[0], args[1], args[2]));
}
public static void restartWithLanguage(String language){
String[] buttons = {Messages.getString("VanetSimStarter.Yes", language), Messages.getString("VanetSimStarter.No", language)};
if(JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null, Messages.getString("VanetSimStarter.WarningMessage", language), "", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE, 0, null, buttons, buttons[1]) == 0){
Messages.setLanguage(language);
VanetSimStart.getMainFrame().dispose();
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new VanetSimStart());
}
}
}
</http:>
Now for the mqtt part where communication occurs in Intel Edison the code is as shown below.
var mqtt = require('mqtt');
var client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://iot.eclipse.org');
var sys = require('sys')
var exec = require('child_process').exec;
function puts(error, stdout, stderr) { sys.puts(stdout) }
var mraa=require('mraa');
var a0=new mraa.Aio(3);
var a=116.602;
var b=-5.96;
var In=4.5/3.34e+4;
var R0=41000;
Loop();
function Loop()
{
var val=a0.read();
var vo=val*5/1000;
var v1=5-vo;
var Rs=v1/In;
var v2=Rs/R0;
v2=Math.pow(v2,b);
var ppm=179.73*v2;
console.log("x="+val+" vo="+vo+" Rs="+Rs+" ppm"+ppm);
if(ppm<420)
{
}
else
{
}
s="curl \"http://api.thingspeak.com/update?api_key=3ZXPXW3SPPDEC1HU&field1="+ppm+ "\"";
exec(s);
client.publish('rupam/Simulator', ""+ppm);
setTimeout(Loop,10000);
}
Breaking down the code
Now we will work on the scenario of the vanet simulator as soon as the osm file is uploaded we can generate the map of our area.It helps in replicating the best scenario for which we can consider amount of traffic load at time and place when it is at peak and when it is less.We can test the extremes of the traffic and the CO2 emission rate at a particular place.
Getting the important things done
The Intel edison board which will feed the data and communicate to internet and other services should be kept at the junction point that too for the first traffic light of the junction.This will help in creating the simulation environment starting point.
Let's get in to the code
package vanetsim;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttDeliveryToken;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttCallback;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttConnectOptions;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttException;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.persist.MemoryPersistence;
public class IoTSimulatorInterface extends javax.swing.JFrame implements MqttCallback {
public IoTSimulatorInterface() {
initComponents();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void initComponents() {
jLabel1 = new javax.swing.JLabel();
jLabel2 = new javax.swing.JLabel();
jtfBrokerUrl = new javax.swing.JTextField();
jButton1 = new javax.swing.JButton();
jlChart = new javax.swing.JLabel();
jlConnectionStatus = new javax.swing.JLabel();
jButton2 = new javax.swing.JButton();
setDefaultCloseOperation(javax.swing.WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
jLabel1.setText("Connect IoT Module With Simulator Using MqTT Protocol");
jLabel2.setText("Server URL:");
jtfBrokerUrl.setText("tcp://iot.eclipse.org:1883");
jButton1.setText("Connect Simulation With IoT");
jButton1.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
jButton1ActionPerformed(evt);
}
});
jlChart.setText("jLabel3");
jlConnectionStatus.setText("Not Connected");
jButton2.setText("Run Simulator");
jButton2.setEnabled(false);
jButton2.addActionListener(new java.awt.event.ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
jButton2ActionPerformed(evt);
}
});
javax.swing.GroupLayout layout = new javax.swing.GroupLayout(getContentPane());
getContentPane().setLayout(layout);
layout.setHorizontalGroup(
layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING)
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING)
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
.addGap(55, 55, 55)
.addComponent(jlChart, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE, 848, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE))
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
.addGap(178, 178, 178)
.addComponent(jLabel2)
.addPreferredGap(javax.swing.LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.UNRELATED)
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING)
.addComponent(jLabel1)
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING, false)
.addComponent(jButton1, javax.swing.GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, 198, Short.MAX_VALUE)
.addComponent(jtfBrokerUrl))
.addPreferredGap(javax.swing.LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED)
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING)
.addComponent(jlConnectionStatus)
.addComponent(jButton2, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE, 145, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE))))))
.addContainerGap(85, Short.MAX_VALUE))
);
layout.setVerticalGroup(
layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.LEADING)
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
.addGap(24, 24, 24)
.addComponent(jLabel1)
.addGap(18, 18, 18)
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.BASELINE)
.addComponent(jLabel2)
.addComponent(jtfBrokerUrl, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE, javax.swing.GroupLayout.DEFAULT_SIZE, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE)
.addComponent(jlConnectionStatus))
.addPreferredGap(javax.swing.LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED)
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.BASELINE)
.addComponent(jButton1)
.addComponent(jButton2))
.addPreferredGap(javax.swing.LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.UNRELATED)
.addComponent(jlChart, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE, 427, javax.swing.GroupLayout.PREFERRED_SIZE)
.addContainerGap(41, Short.MAX_VALUE))
);
pack();
}
String topic = "rupam/Simulator";
String content = "Message from MqttPublishSample";
int qos = 2;
String broker = "tcp://iot.eclipse.org:1883";
String clientId = "RUPAM";
MemoryPersistence persistence = new MemoryPersistence();
MqttClient sampleClient=null;
public static double ParameterValue=-1.0;
private void jButton1ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
broker=jtfBrokerUrl.getText().trim();
try {
sampleClient = new MqttClient(broker, clientId, persistence);
MqttConnectOptions connOpts = new MqttConnectOptions();
connOpts.setCleanSession(true);
System.out.println("Connecting to broker: "+broker);
sampleClient.connect(connOpts);
System.out.println("Connected");
System.out.println("Publishing message: "+content);
if(sampleClient.isConnected())
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,"Connected");
jlConnectionStatus.setText("Connected");
sampleClient.subscribe(topic);
sampleClient.setCallback(this );
jButton2.setEnabled(true);
ds=new DataSet();
ds.colNames=new Object[]{"Co2 Emission"};
data=new ArrayList<>();
}
else
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,"Not Connected");
}
}
catch(MqttException me) {
System.out.println("reason "+me.getReasonCode());
System.out.println("msg "+me.getMessage());
System.out.println("loc "+me.getLocalizedMessage());
System.out.println("cause "+me.getCause());
System.out.println("excep "+me);
me.printStackTrace();
}
}
VanetSimStarter vss=null;
DataSet ds=null;
ArrayList<double> data;
private void jButton2ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
vss=new VanetSimStarter();
vss.Main();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
for (javax.swing.UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo info : javax.swing.UIManager.getInstalledLookAndFeels()) {
if ("Nimbus".equals(info.getName())) {
javax.swing.UIManager.setLookAndFeel(info.getClassName());
break;
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(IoTSimulatorInterface.class.getName()).log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(IoTSimulatorInterface.class.getName()).log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(IoTSimulatorInterface.class.getName()).log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
} catch (javax.swing.UnsupportedLookAndFeelException ex) {
java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(IoTSimulatorInterface.class.getName()).log(java.util.logging.Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
java.awt.EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
new IoTSimulatorInterface().setVisible(true);
}
});
}
private javax.swing.JButton jButton1;
private javax.swing.JButton jButton2;
private javax.swing.JLabel jLabel1;
private javax.swing.JLabel jLabel2;
private javax.swing.JLabel jlChart;
private javax.swing.JLabel jlConnectionStatus;
private javax.swing.JTextField jtfBrokerUrl;
@Override
public void connectionLost(Throwable thrwbl) {
}
@Override
public void messageArrived(String string, MqttMessage mm) throws Exception {
String para=new String(mm.getPayload());
System.out.println();
try
{
ParameterValue=Double.parseDouble(para);
data.add(ParameterValue);
ds.numericData=new double[1][data.size()];
for(int i=0;i<data.size();i++)>
</data.size();i++)></double>
At the first part it links to iot.eclipse.org where bothe the vanet simulator as well as the Intel edison communicate between each other.The mqtt message exchange works as in this case the contact between edison and vanet simulator. Let's put a particular stress on message arrived function.The key here is the declaration of the variable ParameterValue which fetches the CO2 values. Now in the next code block we will see as the ParameterValue increases the greenlight phase value too increases.
package vanetsim.map;
public class TrafficLight {
private static final double[] DEFAULT_SWITCH_INTERVALS = new double[] {5000, 1000, 5000};
private static final double JUNCTION_FREE_TIME = 2000;
private double redPhaseLength_;
private double yellowPhaseLength_;
private double greenPhaseLength_;
private int state = 0;
private Street[] streets_;
private boolean[] streetIsPriority_;
private double timer_;
private Junction junction_;
private boolean switcher = true;
public TrafficLight(Junction junction) {
junction_ = junction;
junction_.getNode().setTrafficLight_(this);
redPhaseLength_ = DEFAULT_SWITCH_INTERVALS[0];
yellowPhaseLength_ = DEFAULT_SWITCH_INTERVALS[1];
greenPhaseLength_ = DEFAULT_SWITCH_INTERVALS[2];
initialiseTrafficLight();
}
public TrafficLight(double redPhaseLength, double yellowPhaseLength, double greenPhaseLength, Junction junction) {
junction_ = junction;
junction_.getNode().setTrafficLight_(this);
redPhaseLength_ = redPhaseLength;
yellowPhaseLength_ = yellowPhaseLength;
greenPhaseLength_ = greenPhaseLength;
initialiseTrafficLight();
}
private void initialiseTrafficLight(){
streetIsPriority_ = new boolean[junction_.getNode().getCrossingStreetsCount()];
if(!junction_.getNode().hasNonDefaultSettings()){
junction_.getNode().setStreetHasException_(new int[junction_.getNode().getCrossingStreetsCount()]);
for(int m = 0; m < junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_().length; m++) junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_()[m] = 1;
}
streets_ = junction_.getNode().getCrossingStreets();
Street[] tmpPriorityStreets = junction_.getPriorityStreets();
boolean isOneway = false;
for(int i = 0; i < streets_.length; i++){
streetIsPriority_[i] = false;
for(int j = 0; j < tmpPriorityStreets.length; j++){
if(streets_[i] == tmpPriorityStreets[j]) streetIsPriority_[i] = true;
}
if(streets_[i].isOneway() && streets_[i].getStartNode() == junction_.getNode()) isOneway = true;
if(!isOneway){
if(streetIsPriority_[i]){
if(junction_.getNode() == streets_[i].getStartNode()){
streets_[i].setStartNodeTrafficLightState(0);
if(junction_.getNode().hasNonDefaultSettings()){
streets_[i].setStartNodeTrafficLightState(junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_()[i]);
}
streets_[i].setPriorityOnStartNode(true);
}
else{
streets_[i].setEndNodeTrafficLightState(0);
if(junction_.getNode().hasNonDefaultSettings()){
streets_[i].setEndNodeTrafficLightState(junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_()[i]);
}
streets_[i].setPriorityOnEndNode(true);
}
}
else{
if(junction_.getNode() == streets_[i].getStartNode()){
streets_[i].setStartNodeTrafficLightState(4);
if(junction_.getNode().hasNonDefaultSettings()){
streets_[i].setStartNodeTrafficLightState(junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_()[i]);
}
}
else {
streets_[i].setEndNodeTrafficLightState(4);
if(junction_.getNode().hasNonDefaultSettings()){
streets_[i].setEndNodeTrafficLightState(junction_.getNode().getStreetHasException_()[i]);
}
}
}
}
isOneway = false;
calculateTrafficLightPosition(streets_[i]);
}
timer_ = greenPhaseLength_;
junction_.getNode().setHasTrafficSignal_(true);
}
public void changePhases(int timePerStep){
if(timer_ < timePerStep){
state = (state +1) % 4;
greenPhaseLength_=1000*(vanetsim.IoTSimulatorInterface.ParameterValue-400)/10;
System.out.println("Green Light Period="+greenPhaseLength_+" red light period="+redPhaseLength_+" yellow time period= "+yellowPhaseLength_);
if(state == 1) timer_ = yellowPhaseLength_;
else if(state == 2)timer_ = JUNCTION_FREE_TIME;
else if(state == 0 && switcher)
{
if(vanetsim.IoTSimulatorInterface.ParameterValue>0.0)
{
timer_ = greenPhaseLength_;
}
else
{
timer_ = greenPhaseLength_;
}
}
else if(state == 0 && !switcher)timer_ = redPhaseLength_;
else if(state == 3)timer_ = yellowPhaseLength_;
switcher = !switcher;
for(int i = 0; i < streets_.length; i++){
if(streets_[i].getStartNode() == junction_.getNode() && streets_[i].getStartNodeTrafficLightState() != -1){
streets_[i].updateStartNodeTrafficLightState();
}
else if(streets_[i].getEndNode() == junction_.getNode() && streets_[i].getEndNodeTrafficLightState() != -1){
streets_[i].updateEndNodeTrafficLightState();
}
}
}
else timer_ = timer_ - timePerStep;
}
public void calculateTrafficLightPosition(Street tmpStreet){
double junctionX = junction_.getNode().getX();
double junctionY = junction_.getNode().getY();
double nodeX;
double nodeY;
if(junction_.getNode().equals(tmpStreet.getStartNode())){
nodeX = tmpStreet.getEndNode().getX();
nodeY = tmpStreet.getEndNode().getY();
}
else{
nodeX = tmpStreet.getStartNode().getX();
nodeY = tmpStreet.getStartNode().getY();
}
double m = (nodeY-junctionY)/(nodeX-junctionX);
double n = nodeY - m*nodeX;
double a = 1 + (m * m);
double b = (2 * m * n) - (2 * m * junctionY) - (2 * junctionX);
double c = (n * n) - (2 * n * junctionY) + (junctionY * junctionY) - (700 * 700) + (junctionX * junctionX);
if(junction_.getNode().equals(tmpStreet.getStartNode())){
if(nodeX < junctionX){
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightStartX_((int)Math.round((-b - Math.sqrt((b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a)));
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightStartY_((int)Math.round((m * tmpStreet.getTrafficLightStartX_()) + n));
}
else{
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightStartX_((int)Math.round((-b + Math.sqrt((b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a)));
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightStartY_((int)Math.round((m * tmpStreet.getTrafficLightStartX_()) + n));
}
}
else{
if(nodeX < junctionX){
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightEndX_((int)Math.round((-b - Math.sqrt((b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a)));
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightEndY_((int)Math.round((m * tmpStreet.getTrafficLightEndX_()) + n));
}
else{
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightEndX_((int)Math.round((-b + Math.sqrt((b*b) - (4*a*c))) / (2*a)));
tmpStreet.setTrafficLightEndY_((int)Math.round((m * tmpStreet.getTrafficLightEndX_()) + n));
}
}
}
public double getGreenPhaseLength() {
return greenPhaseLength_;
}
public void setGreenPhaseLength(double greenPhaseLength) {
this.greenPhaseLength_ = greenPhaseLength;
}
public void setYellowPhaseLength(double yellowPhaseLength) {
this.yellowPhaseLength_ = yellowPhaseLength;
}
public double getYellowPhaseLength() {
return yellowPhaseLength_;
}
public void setRedPhaseLength(double redPhaseLength) {
this.redPhaseLength_ = redPhaseLength;
}
public double getRedPhaseLength() {
return redPhaseLength_;
}
public void setState(int state) {
this.state = state;
}
public int getState() {
return state;
}
public Street[] getStreets_() {
return streets_;
}
public void setStreets_(Street[] streets_) {
this.streets_ = streets_;
}
}
</http:>
Results
The Intel Edison board has two ports: one is closer to switch called power port. It directly get power from pc. The other one is serial port, from serial port pc can send commands to the board.Once board put into wi fi network, We can program the board remotely.The board is connected with pc using USB port.Once connected,the LED is glowing in the board,which means board is powered.Once USB puts,right click on my computer.Click on properties as shown below:

Fig. connecting the serial port.
Next click on device manager,next click on COM&LPT ports to select the USB serial port for communication purpose where computer communicate with this serial port communication.

Fig. selecting the COM and LPT port.
To check the port number,then use a serial communication software called putty.Putty is very popular serial communication software.Next step is to just open the putty software.It has two connections,one SSH and another one is serial.Here board is connected using serial connection so click on serial from device manager and see which poet is configured.Its depend on pc’s,here my computer configured with COM18.In putty,click on serial tap then press 18 infront COM and this board has got a bit data rate is 115200.The speed change into 115200 and this number of bits per second.Now once we enter the value and say open then pc can communicate with this board.The black screen appear.

Fig. enters the serial line and bit rate
We should enter, once entered. We should login with root and enter the password.First take Edison board into our wi-fi network.The board get connected with internet through our local network that is our wi-fi network.The command used is configure_edison --wifi.Once run this command.

Fig. login to putty and configure the wi-fi.
It configure all the wifi networks available in the surrounding area as shown in below.Here my modem number is 4.It will ask for network SSID and make sure that oue network Id by entering Yes.Then enter the our network password.

Fig. Configuring the Edison wifi connection.
Once enter the password,the Edison board get connected with our local network.Then it will shown the IP-address.It may have different IP-addresses for different pc’s,it using SSH connection.The ls command used to see our program.

My pogram is PollutionSim.js.It can run by entering node PollutionSim.js.It will display x value where x is analog value.The analog value sensed by the sensor which sense the CO2 level from vehicles.The CO2 value display in ppm.

Fig. Run the program to get ppm value.
Next part is to run the project VanetSimulatorIoT:
The VanetSimulatorIoT package has source packages to run the simulation such as IoTSimulatorInterface.java package.Here right click on IoTSimulatorInterface.java package and debug the file to connect the server.

Fig. Connecting simulation with IoT
Once debug the IoTSimulatorInterface.java package,we are going to connect the Mqtt server.Mqtt is a machine to machine communication protocol which is pub-sub based service.The channel is created to store the data into channel and retrieve the data from channel.Here the channel is created for message exchange is rupam/simulator.We can create our own channel in Mqtt server.
First we connecting the Mqtt broker.If broker is connected.The msg is displayed as broker is connected as shown in above figure. The Mqtt has two servers such as, iot.eclipse.org and test.mosquitto.org.
Our aim to show the local plot on the simulator which one already plotting in thingspeak at the same time.We want to show in local plot of variations of the CO2 level.In order to show the simulation result,we taking the array of data where we are storing the data.The simulation result shown below.

Before running the simulator, first connect the IoT device to system and login through putty software using COM18 serial port.The node PollutionSim.js is a javascript program to get the current ppm value.Then pinging to the google.com.Once pings to google then asure that the ppm value is updated.Run the project,at the same time open the thingspeak channel for real time visualization of simulation value.The channel is thingspeak.com/channels/105527 as shown in below figure.

Fig. Thingspeak updated result
Once we get connected with IoT.Run the simulation.During this observe that traffic light value do not hit the break points because we aren’t reset the map.
Next step is to edit section of open street map.

Fig. Edit section for taking the open street map.

Fig. The map creation process using values

Fig.Open street map of Gulbarga city
Let starts the edit section by opening the open street map of any city. We are taking the Gulbarga’s open street map as gulbarga3.osm file.

Fig. Selecting the particular junction
Then enable the edit mode to put the traffic light at the junction and vehicles.

Fig. Selecting traffic light at the junction
After enabling the edit mode.Select the particular junction in open street map to put the traffic light and vehicles.Next go into the settings, select the one traffic light for one junction.

Fig.Putting one traffic light at specific junction
Next, selecting the number of vehicles from setting section only.

Fig.Selecting the vehicle option from setting
After selecting the option as vehicle, we are going to put the number of vehicles.

Fig. Selecting the by click option
Here, we use the by click option.By click we are selecting and adding the number of vehicles in the street map.

Fig. Adding the selected no. of vehicles
Once we selected the number of vehicles for example consider the 30 vehicle.The vehiclesmove from source point to destination point with 10sec difference.We have to set the waypoint for the vehicles that is source and destination point for selected no. of vehicles and which must pass through the specified junction where traffic light is placed.

Fig.Selecting Road side units

Fig. Putting the Road side units
The road side unit option selecting by clicking on setting.Then select the road side units and put on roads on the open street map.The road side units are extended the communication range between vehicles.

Fig. Selecting the event action
Now, let place the some events.The option event selecting from the settings only.

Fig. Selecting particular event spots
The events are nothing but hospitals, damaged road. schoolzone etc. We are selecting here damaged road as an eventspot.

Fig. placing the damaged road eventspot
After selecting damaged road.This event placed on the roads.While vehicles move from one place to another place, the vehicle get the information about damaged road before reaching to that road,when vehicles are nearer to damaged road slow down the vehicles to avoid the accidents.

Fig. Selecting the disable mode
After completion of editing section, we disable the editing section by using disable mode (statistics).

Fig. Run the simulation part
Finally, run the simulation. Once simulation will start the vehicles are pass through the particular junction where traffic light is placed.

Once simulation will start, the green light timing display on the IoTSimulatorInterface.java interface of console based on CO2 level and traffic congestion.When CO2 level and traffic congestion increases the green light timing increases.So that the number of vehicle pass smoothly through the junction.
Simulation-Real World Mapping
simulation point when there is greater consumption of CO2 occurs.
Let's check on how we did the simulation again
The first figure shows how we started working on the code at netbeans.

The second figure highlights with a red tick where green phase length is calculated.

The third figures portrays how the traffic simulation have started and the traffic lights showing co2 consumption.

The fourth figure also shows the same and depicts from where the traffic is arriving.

The sigificant green light shows that how the green light has been created.So with the entire pictures we have shown how the simulation happens.
Simulation results show that by controlling the traffic
Conclusion
Often City traffic planning and management needs good simulation Engines. VANET Simulator is one such realistic simulator where any city's traffic scenerio can be projected with the aid of OpenStreet map. One of the toughest challenges that the cities phases these days is to reduce pollution. Even though simulation engines are good at developing functional algorithm for traffic planning and management, validating them against real world scenerio is difficult. In this work we have shown how a single pollution sensing physical node can be integrated into the simulation environment and how the data acquired through physical device can be used as a variable in simulation environment. This work can be used as a framework, the devices can be considered as assets deployed over different known geospatial positions, broadcasting their position and pollution data simultansously. By adding an asset discovery interface with the code, these real time assests can be imported into simulation environment and multi-junction poluution data can be used to develop better traffic planning scenerios. Also vehicles using Android phones if broadcasts their GPS data, entire traffic flow of real traffic can be observed on the map. In such scenerios a hybrid of simulation and real time data can be used with a collaborative context to develop more roboust city traffic planning scenerios.
History
Keep a running update of any changes or improvements you've made here.
