Introduction
The Ring programming language is an innovative and practical general-purpose programming language. Using Ring we can develop Desktop, Web and Mobile Applications. The language is free open source and multi-paradigm (Imperative, Procedural, Object-Oriented, Functional, Declarative and Natural).
In this article we will use the Ring language to develop an Android application for storing the weight information (Date, Time and Weight). The application is an example about using Ring for Android Apps development based on the Qt framework through RingQt.
Note: The same code that we will write will work also on Desktop (Windows, Linux and MacOS X) and other Mobile platforms.
Background
You can download Ring, Also you can check the next articles about the language
(1) The Ring Programming Language
(2) Syntax Flexibility in the Ring Programming Language
Using the code
At first we will create new file for our application. The file name will be weighthistory.ring
In the start of our application we will load the guilib.ring
This library provide us with the GUI classes that we can use to create the user interface of our application.
The 'Load' command is used for loading libraries
Then we will create a new object from the qApp class, the object name is MyApp
Each GUI application must contains an application object.
After creating the object we will define a global variable $ApplicationObject contains the object name that we will use later for our application when we call events.
Then we create an object from our class (App). This object name is oApp
After that we call the exec() method to give the control to the GUI event loop.
In the end we will call the method closedatabase()
Load "guilib.ring"
MyApp = new qApp
{
$ApplicationObject = "oApp" # To be used when calling events
oApp = new App
exec()
oApp.CloseDatabase()
}
Now we will start defining our class, The App class.
After the class name, In the class region where we define the class attributes, We will have
cDir : Attribute for the current directory
oCon : Connection object to the database
aIDs : List contains records IDs
win1 : object from the qWidget() class
Also we have other attributes for the user interface like layoutButtons, label1, text1, btnAdd, btnDelete, LayoutData, Table1, LayoutClose and LayoutMain
Then we will call the OpenDatabase() Method and the ShowRecords() Method.
class App
cDir = currentdir() + "/"
oCon
aIDs = []
win1 = new qWidget()
{
setWindowTitle("Weight History")
resize(600,600)
layoutButtons = new qhboxlayout()
{
label1 = new qLabel(win1) { setText("Weight") }
text1 = new qlineedit(win1)
btnAdd = new qpushbutton(win1) {
setText("Add")
setClickEvent($ApplicationObject+".AddWeight()")
}
btnDelete = new qpushbutton(win1) {
setText("Delete")
setClickEvent($ApplicationObject+".Deleteweight()")
}
addwidget(label1)
addwidget(text1)
addwidget(btnAdd)
addwidget(btnDelete)
}
layoutData = new qhboxlayout()
{
Table1 = new qTableWidget(win1) {
setrowcount(0)
setcolumncount(3)
setselectionbehavior(QAbstractItemView_SelectRows)
setHorizontalHeaderItem(0, new QTableWidgetItem("Date"))
setHorizontalHeaderItem(1, new QTableWidgetItem("Time"))
setHorizontalHeaderItem(2, new QTableWidgetItem("Weight"))
setitemChangedEvent($ApplicationObject+".ItemChanged()")
setAlternatingRowColors(true)
horizontalHeader().setStyleSheet("color: blue")
verticalHeader().setStyleSheet("color: red")
}
addWidget(Table1)
}
layoutClose = new qhboxlayout()
{
btnclose = new qpushbutton(win1) { setText("Close") setClickEvent("MyApp.Quit()") }
addwidget(btnClose)
}
layoutMain = new qvboxlayout()
{
addlayout(layoutButtons)
addLayout(LayoutData)
addLayout(layoutClose)
}
setlayout(layoutMain)
self.OpenDatabase()
self.ShowRecords()
show()
}
Then we have the openDatabase() method as in the next code
The method check the SQLite database file (weighthistory.db) if it's found it will be opened
If the database file is not found, it will be created using the Create Table command.
Func OpenDatabase
lCreate = False
if not fexists(cDir + "weighthistory.db")
lCreate = True
ok
new QSqlDatabase() {
this.oCon = addDatabase("QSQLITE") {
setDatabaseName("weighthistory.db")
Open()
}
}
if lCreate
new QSqlQuery( ) {
exec("create table weighthistory (id integer primary key, f_date varchar(10), f_time varchar(8), f_weight varchar(8) );")
delete()
}
ok
Then we have the CloseDatabase() method
This method use the connection object (oCon) and call the Close() method.
Func CloseDatabase
oCon.Close()
Then we have Addweight() and DeleteWeight() Methods
The Addweight() method get the text from the textbox then pass it to the AddRecord() method.
The DeleteWeight() method check the current record in the Table then execute the SQL command (Delete) after getting the record ID from the aIDs list
Func AddWeight
cWeight = text1.text()
AddRecord(cWeight)
Func DeleteWeight
Table1 {
nRow = CurrentRow()
if nRow >= 0
nID = this.aIDs[nROW+1]
new QSqlQuery( ) {
exec("delete from weighthistory where id = " + nID )
}
Del(this.aIDs,nRow+1)
removerow(nRow)
selectrow(nRow)
ok
}
The next code present the AddRecord() and the ShowRecords() methods.
The AddRecord() method will get the weight as parameter then execute the SQL command (Insert Into)
The ShowRecords() method will execute the SQL command ("select * from weighthistory") to get the records data
Then display the data in the Table.
Func AddRecord cWeight
new QSqlQuery( ) {
cStr = "insert into weighthistory (f_date,f_time,f_weight) values ('%f1','%f2','%f3')"
cDate = Date()
cTime = Time()
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f1",cDate)
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f2",cTime)
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f3",cWeight)
exec(cStr)
delete()
}
ShowRecords()
Table1.selectrow(table1.rowcount()-1)
Func ShowRecords
table1.setitemChangedEvent("")
aIDs = []
query = new QSqlQuery() {
exec("select * from weighthistory")
nRows = 0
this.Table1.setrowcount(0)
while movenext()
this.table1 {
insertRow(nRows)
this.aIDs + query.value(0).tostring()
for x = 1 to 3
cStr = query.value(x).tostring()
item = new qTableWidgetItem(cStr)
setItem(nRows,x-1,item)
next
}
nRows++
end
delete()
}
table1.setitemChangedEvent($ApplicationObject+".ItemChanged()")
In the end we have the itemChanged() method
Using the next method we update the table in the database after updating the data in the table widget through the User Interface.
The method execute the SQL command (Update).
Func ItemChanged
nRow = table1.currentrow()
if nRow >= 0
myitem = Table1.item(table1.currentrow(),0)
cDate = myitem.text()
myitem = Table1.item(table1.currentrow(),1)
cTime = myitem.text()
myitem = Table1.item(table1.currentrow(),2)
cWeight = myitem.text()
new QSqlQuery( ) {
cStr = "update weighthistory set f_date ='%f1' , f_time = '%f2' , f_weight ='%f3' where id = " + this.aIDs[nROW+1]
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f1",cDate)
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f2",cTime)
cStr = substr(cStr,"%f3",cWeight)
exec(cStr)
delete()
}
ok
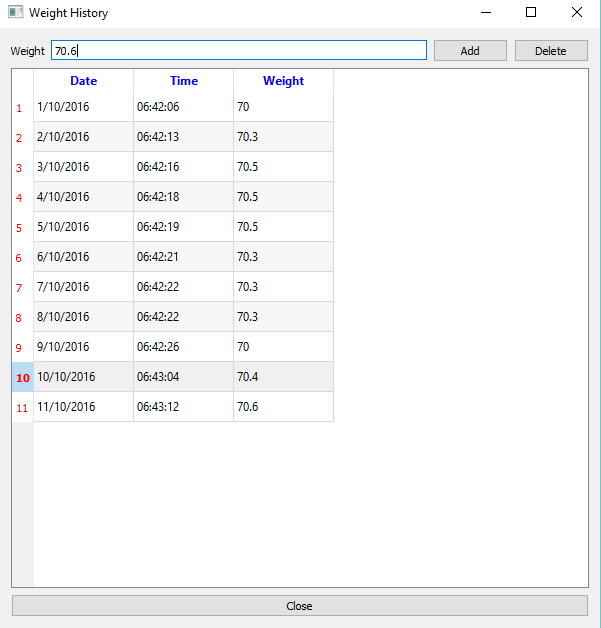
The next screen shot presents the application in windows
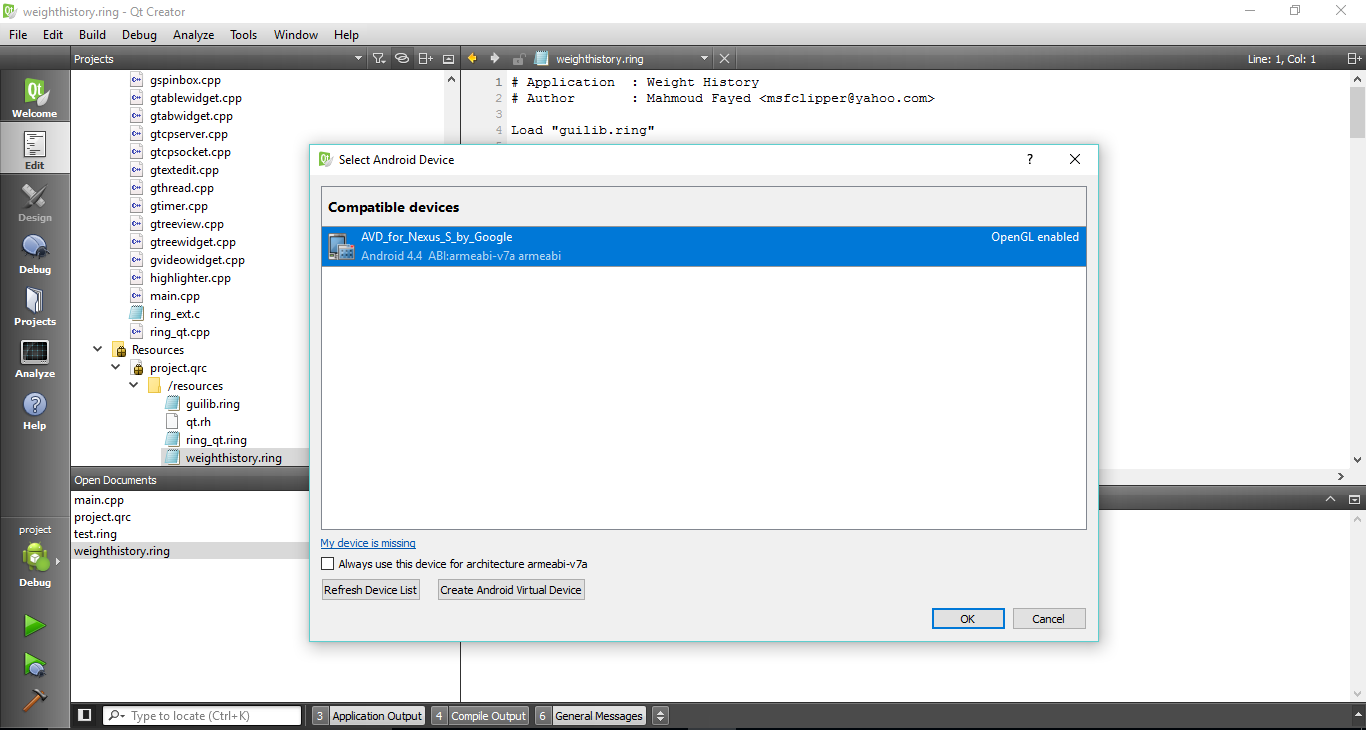
To build the application for Android, Using Qt Creator open the Qt project and click build
To know about downloading Qt, Android SDK, and the required tools check this link
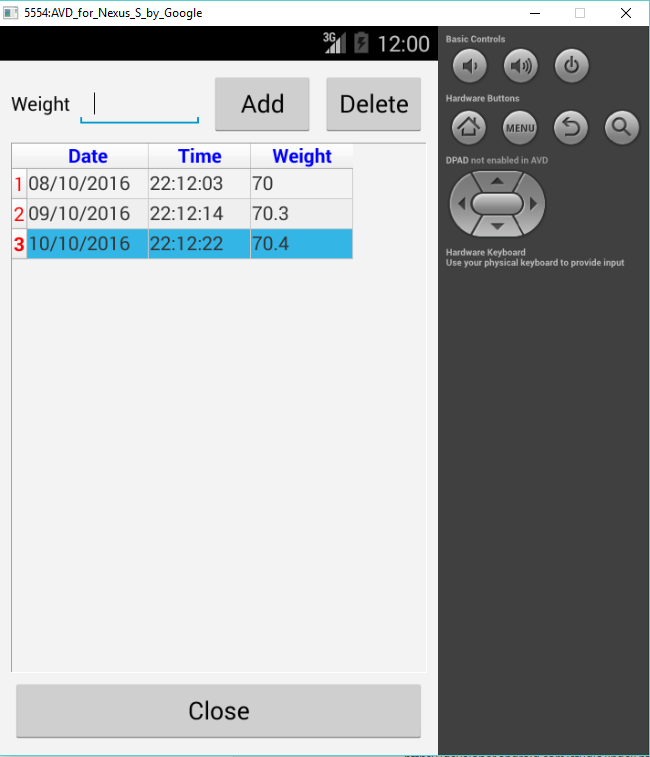
The next screen shot for the application on an Android Virtual Device
Points of Interest
It is very simple to develop and test the application as desktop application then create a package for Android and get the same results. Also using Ring reduce the development time, Thanks to Dynamic Typing, Object-Oriented, Nice Qt interface through RingQt and using braces { } to quickly access the object attributes and methods.
History
The Ring programming language version 1.0 is released on 2016.01.25
The Ring programming language version 1.1 is released on 2016.10.06
This application in this article uses Ring version 1.1 and Qt 5.5
