Topics to be Discussed
- Short Overview of .NET Framework
- What is .NET Core?
- What is ASP.NET Core?
- How to Start?
- Detailed Overview of Initial Sample Application
- Global.json
- Properties
- wwwroot
- Controller
- Views
- appsettings.json
- bower.json
- bundleconfig.json
- program.cs
- project.json
- startup.cs
- web.config
- Working with Data Using
- ASP.NET Core &
- Entity Framework-7 (Core)
- MVC-6 (Core)
Ok, let’s start with one topic at a time to clarify our thoughts on the magical world of .NET.
.NET Framework
The .NET Framework (pronounced dot net) is a software development platform developed by Microsoft. It provides tools and libraries that allow developers to develop applications. Microsoft started development on the .NET Framework in the late 1990s originally under the name of Next Generation Windows Services (NGWS). By late 2001, the first beta versions of .NET 1.0 were released.
.NET Framework Releases
Here, I have provided a short overview of .NET Framework Version evaluation that all we knew about, but it was just recapping for a better understand of .NET thinking & road-map.
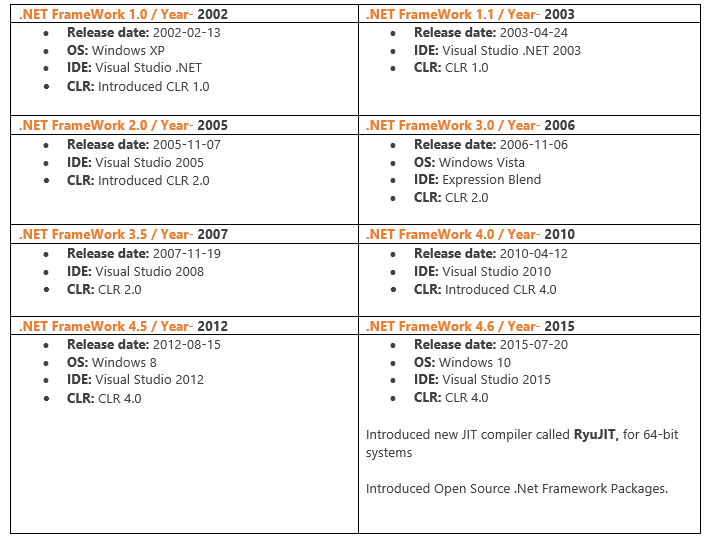
So far, we know all these releases, but what about the new announcement? Is .NET Core another framework? Ok, let’s just take it easy, Step by step, we will uncover all those issues.
.NET Today
Microsoft has announced a lots of exciting new innovations that are included with .NET in this year. Among them, the most powerful is open source cross-platform development (Any developer, Any app, Any platform). Learn more…

.NET Core
Simply .NET Core is modern, lightweight, high performance modular platform for creating web apps and RESTful APIs that run on Cross-Platform (Windows, Linux and Mac). It is a smaller set/sub-set of .NET Framework (Full), that is maintained by Microsoft & the .NET community on GitHub.
.NET Core Facilities
- Cross-platform that runs on Windows, macOS and Linux
- Open source
- Command-line tools that can be exercised at the command-line
- Compatible with .NET Framework, Xamarin and Mono, via the.NET Standard Library
- Flexible deployment
Learn more about .NET Core …
.NET Core Platform: The .NET Core platform is made up of several components:
- CoreFX - .NET Core foundational libraries
- CoreCLR - .NET Core runtime
- CLI - .NET Core command-line tools
- Roslyn - .NET Compiler Platform
Diagram of .NET Core vs .NET Framework

.NET Core Releases
- .NET Core 1.1 released on 11/16/2016
- .NET Core 1.0 Preview 1 released on 10/24/2016
- .NET Core 0.1 released on 9/13/2016
- .NET Core 0.0 released on 6/27/2016
- .NET Core RC2(Release Candidate) released on 5/16/2016
- .NET Core RC1(Release Candidate) released on 11/18/2015
Download the latest .NET Core SDK (Runtime + Command line Tool) or Only Runtime.
.NET Core Supports
Initially, .NET Core supports four types of application development, among them, we will focus on ASP.NET Core application development.
- NET Core web apps
- Command-line apps
- Libraries, and
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps
ASP.NET Core
ASP.NET Core is re-written new open source ASP.NET web framework for building web based application (web apps, IoT apps & mobile backends) that run on both full .NET Framework and .NET Core.
ASP.NET Core Facilities
- Developed and run on Cross Platform (Windows, Mac and Linux)
- Open Source
- Built on the .NET Core runtime & also on .NET Framework
- Facility of dynamic compilation
- Built in Dependency Injection (DI)
- MVC & Web API Controller are unified, Inherited from same base class
- New light-weight and modular HTTP request pipeline
- Ability to host on IIS or self-host in own process
- Ships entirely as NuGet packages
- Smart tooling like (Bower, Grunt & Gulp)
Learn more about ASP.NET Core.
How to Start?
Here is the quick installation guide for Windows.
Steps
- Install Visual Studio 2015 (provides a full-featured development environment)
- Make sure you have Visual Studio 2015 Update 3
- Install the .NET Core tools preview for Visual Studio
- Create a new .NET Core project
- Run the application
Learn more about how to get started…
Anatomy of ASP.NET Core Initial Application
Global.json
It is a JSON schema for the ASP.NET global configuration files, and contains the Solution information/metadata. In this file, we can configure the sdk with version, architecture or runtime that specifies which processor architecture to target, which runtime to target. Let’s get the properties in details.
- Projects: Specify the folders to search that contain the project
- Packages: Specify the package location
- Sdk: Specify information about the SDK
Here are our global.json properties by default.
{
"projects": [ "src", "test" ],
"sdk": {
"version": "1.0.0-preview2-003131"
}
}
To get other’s properties information details, go to > http://json.schemastore.org/global
"properties": {
"projects": {
"type": "array",
"description":
"A list of project folders relative to this file.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"packages": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The location to store packages"
},
"sdk": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Specify information about the SDK.",
"properties": {
"version": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The version of the SDK to use."
},
"architecture": {
"enum": [ "x64", "x86" ],
"description":
"Specify which processor architecture to target."
},
"runtime": {
"enum": [ "clr", "coreclr" ],
"description": "Chose which runtime to target."
}
}
}
}
Properties > launchSettings.json
JSON schema for the ASP.NET DebugSettings.json files. This is where we can configure our debug profile by using IDE interface, another way to set properties is launchSetting.json file. Right click on Project Properties > Debug.

Here’s the configuration properties by default in launchSetting.json.
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:17023/",
"sslPort": 0
}
},
"profiles": {
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
"CoreMVC": {
"commandName": "Project",
"launchBrowser": true,
"launchUrl": "http://localhost:5000",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
}
}
We can add another profile as production to the json file using the same command as IISExpress. Based on this environment profile, we can show hide HTML tags on different environment mood, which is known as working with multi environment. Later, we will discuss about it.
"IIS Production": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Production"
}
}
The new debug profile will appear like the below image:

Let’s get the properties in details:
commandLineArgs: The arguments to pass to the commandworkingDirectory: Sets the working directory of the commandlaunchBrowser: Set to true if the browser should be launchedlaunchUrl: The relative URL to launch in the browserenvironmentVariables: Set the environment variables as key/value pairssdkVersion: Sets the version of the SDK
To get other’s properties information details, go to > http://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.
"properties": {
"commandLineArgs": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The arguments to pass to the command.",
"default": ""
},
"workingDirectory": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Sets the working directory of the command."
},
"launchBrowser": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Set to true if the browser should be launched.",
"default": false
},
"launchUrl": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The relative URL to launch in the browser.",
"format": "uri"
},
"environmentVariables": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Set the environment variables as key/value pairs.",
"additionalProperties": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"sdkVersion": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Sets the version of the SDK."
}
}
wwwroot It’s all about serving static file directly to client. We need to serve static file. All we need to add is extension method UseStaticFiles() in startup class Configure method.

Then, resolve the dependency package "Microsoft.AspNetCore.StaticFiles": "1.0.0" for static file in project.json.

Controller
ASP.NET Core Controllers are now unified, there’s no difference between MVC Controllers (Controller base class) & WebAPI Controllers (ApiController base class). As you can see, I have put it side by side to show the difference between both MVC & WebAPI Controller, both controllers are being inherited from the same controller.

Views
ASP.NET Core MVC views are .cshtml files as we know earlier version of ASP.NET MVC views that use the Razor view engine to render views. Here, I have shown MVC folder structure and the related .cshtml files in our ASP.NET Core application.

Learn more about views & tag-helpers……
appsettings.json
This is the application configuration file that keeps the configuration value of Key/Value pair. Previously, this configuration was stored in web.config file.
{
"Logging": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Debug",
"System": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Information"
}
}
}
We can add the connection string to the appsetting file and then we have accessed the connection in startup.
"ConnectionStrings": {
"dbConn": "Server=DESKTOP-5B67SHH;
Database=TicketBooking;Trusted_Connection=True;
MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
In startup file, we added our service in ConfigureService method to enable the database connectivity through connection string.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
var connectionString = this.Configuration.GetConnectionString("dbConn");
services.AddDbContext<TicketBookingContext>
(options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
services.AddMvc();
}
var connectionString = this.Configuration.GetConnectionString("dbConn");
Here, GetConnectionString is an extension method that is passing the connection name “dbConn”.
bower.json
Bower is a Package manager that automatically adds/updates client side packages (like bootstrap, jquery, etc.) while we add/remove listed packages in json file.
{
"name": "asp.net",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"bootstrap": "3.3.6",
"jquery": "2.2.0",
"jquery-validation": "1.14.0",
"jquery-validation-unobtrusive": "3.2.6"
}
}
Here is the listed Client-side dependencies, there is another type of dependency called Server-side dependencies. Here private: true means it will refuse to publish, prevent accidental publication of private repositories.

To change bower installation location, open .bowerrc and change the directory value.

{
"directory": "wwwroot/lib"
}
Here, you can see the dependencies have installed in wwwroot/lib folder as initial value.

bundleconfig.json
Bundling and minifying JavaScript, CSS and HTML files in any project. Download BundlerMinifierVsix & install in Visual Studio 2015. Restart the IDE.

Task Runner Explorer will appear, to update all, right click > Update all files > Run.

Finally, the output file will be generated.

Here is how a bundleconfig.json looks like:
[
{
"outputFileName": "wwwroot/css/site.min.css",
"inputFiles": [
"wwwroot/css/site.css"
]
},
{
"outputFileName": "wwwroot/js/site.min.js",
"inputFiles": [
"wwwroot/js/site.js"
],
"minify": {
"enabled": true,
"renameLocals": true
},
"sourceMap": false
}
]
program.cs
This is the main point of any ASP.NET core application that prepares the host to run all configured services. Here is the program.cs code snippet.
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build();
host.Run();
}
}
In program.cs class, simply do the job of configuring & launching a host using WebHostBuilder. As we know, .NET Core application is a Console Application that needs to execute by host. WebHostBuilder is creating the host to bootstrap the server by UseKestrel() extension method, this means Kestrel server is going to host the application. There is another extension method UseIISIntegration() that is for IIS Server. Here's a diagram that clarifies the process between IIS and ASP.NET Core applications.

Source: ASP.NET Core Module overview By Tom Dykstra, Rick Strahl, and Chris Ross
The WebHostBuilder is responsible for creating the host that will bootstrap the server for the app. learn more about hosting… We can say that .NET Core Application needs a host to launch that defines which server is going to use, where to get the content files and specify the startup (middleware) services.
project.json
The project.json file stores the application information, dependencies, and compiler settings. It has several sections like Dependencies, Tools, Frameworks, Build Options and much more. Here, I have shown how the default project.json content looks like:
{
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.NETCore.App": {
"version": "1.0.1",
"type": "platform"
},
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc": "1.0.1",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Tools": {
"version": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"type": "build"
},
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing": "1.0.1",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.Kestrel": "1.0.1",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.StaticFiles": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.EnvironmentVariables": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Debug": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Options.ConfigurationExtensions": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.VisualStudio.Web.BrowserLink.Loader": "14.0.0"
},
"tools": {
"BundlerMinifier.Core": "2.0.238",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final"
},
"frameworks": {
"netcoreapp1.0": {
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8"
]
}
},
"buildOptions": {
"emitEntryPoint": true,
"preserveCompilationContext": true
},
"runtimeOptions": {
"configProperties": {
"System.GC.Server": true
}
},
"publishOptions": {
"include": [
"wwwroot",
"**/*.cshtml",
"appsettings.json",
"web.config"
]
},
"scripts": {
"prepublish": [ "bower install", "dotnet bundle" ],
"postpublish": [ "dotnet publish-iis
--publish-folder %publish:OutputPath% --framework %publish:FullTargetFramework%" ]
}
}
Let’s explorer the different sections in it step by step:
project.json > Dependencies
This section manages the project dependencies using key/value pair, we can add new dependencies if required, intellisense will help up to include with name & version.

As you can see from the upper image, I was adding three new packages for database service, intellisense was helping me by showing the version of that package. While I saved the changes, it automatically restored the required dependencies from NuGet.

project.json > Tools: This section manages & lists command line tools, we can see IISIntegration. Tools is added by default which is a tool that contains dotnet publish IIS command for publishing the application on IIS.
"tools": {
"BundlerMinifier.Core": "2.0.238",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final"
}
EntityFrameworkCore Tools (Command line tool for EF Core) Includes Commands
For Package Manager Console:
- Scaffold-DbContext
- Add-Migration
- Update-Database
For Command Window
- dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold
Both EF commands are show here, please take a close look at them. If we disable the EntityFrameworkCore Tools and run the command, it will show the below error in Package Manager Console:
 project.json > Frameworks
project.json > Frameworks
Define the framework that is supported in this application, we can use multiple frameworks by configuring in this section.
"frameworks": {
"netcoreapp1.0": {
"dependencies": {
},
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8"
]
}
}
Let’s clarify a bit more, in the framework section, we are targeting netcoreapp1.0 framework. By configuring import section, we can use several targeted packages/class libraries that are different from our application target version. Here "dotnet5.6" for older .NET Core preview versions, and "portable-net45+win8" for portable class library (PCL) profiles, that known as Target Framework Monikers (TFMs). We can use multiple frameworks by adding "net461": {} in the framework section.
"frameworks": {
"net461": {
"dependencies": {
}
},
"netcoreapp1.0": {
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.NETCore.App": {
"version": "1.0.1",
"type": "platform"
}
},
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8"
]
}
}
You may notice that we have to move our Microsoft.NETCore.App dependency from global dependencies to specific framework dependency section.

This is how we are using multiple frameworks/runtimes that support.
project.json > Build Options
Options that are passed to compiler while build application.
"buildOptions": {
"emitEntryPoint": true,
"preserveCompilationContext": true
}
project.json > RuntimeOptions
Manage server garbage collection at application runtime.
"runtimeOptions": {
"configProperties": {
"System.GC.Server": true
}
}
project.json > PublishOptions
This defines the file/folder to include/exclude to/from the output folder while publishing the application.
"publishOptions": {
"include": [
"wwwroot",
"**/*.cshtml",
"appsettings.json",
"web.config"
]
}
project.json > Scripts
Scripts is an object type which specifies which scripts to run during build or while publishing the application.
"scripts": {
"prepublish": [ "bower install", "dotnet bundle" ],
"postpublish": [ "dotnet publish-iis
--publish-folder %publish:OutputPath%
--framework %publish:FullTargetFramework%" ]
}
Learn more about project.json file...
startup.cs
This is the entry point of every ASP.NET Core application, provides services that application requires. Here’s a diagram that shows what happens at runtime when it is run for the first time.

In Startup class, there are several methods with different responsibilities. Here, I have separated them, the very first is the constructor of Startup class. In the constructor, IHostingEnvironment instance is passed as parameter to get the web hosting environment details.
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json",
optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json",
optional: true)
.AddEnvironmentVariables();
Configuration = builder.Build();
}

The instance of ConfigurationBuilder calls the extension methods of multiple configuration source, then chain calls together by order as a fluent API.

public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; } The IConfigurationRoot forces the configuration values to be reloaded while application is running & configuration data is changed. Next method is ConfigureServices that gets called before Configure method. In this section, we can configure our required service to use at runtime in our application. Instance of IServiceCollection has passed as parameter. IServiceCollection specifies collection of different services.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
var connectionString =
this.Configuration.GetConnectionString("dbConn");
services.AddDbContext<TicketBookingContext>
(options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
}
In Startup class, the Configure() method handles the HTTP request .
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app,
IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
}
The full startup looks like this:
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json",
optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json",
optional: true)
.AddEnvironmentVariables();
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app,
IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
loggerFactory.AddDebug();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseBrowserLink();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
web.config
In ASP.NET Core, the application configuration is now stored in appsettings.json file. Previously, this was stored in web.config file. Here is how the default web.config file looks like:
="1.0"="utf-8"
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<add name="aspNetCore" path="*"
verb="*" modules="AspNetCoreModule"
resourceType="Unspecified"/>
</handlers>
<aspNetCore processPath="%LAUNCHER_PATH%"
arguments="%LAUNCHER_ARGS%"
stdoutLogEnabled="false"
stdoutLogFile=".\logs\stdout"
forwardWindowsAuthToken="false"/>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Web.config is used only for configuration while hosting is done in IIS. In handler section, this is where IIS handles a request by passing it to ASP.NET Core Module.
<handlers>
<add name="aspNetCore" path="*"
verb="*" modules="AspNetCoreModule"
resourceType="Unspecified" />
</handlers>
We can specify environment through web.config in IIS.
<aspNetCore processPath="dotnet"
arguments=".\CoreMVC.dll" stdoutLogEnabled="false"
stdoutLogFile=".\logs\stdout"
forwardWindowsAuthToken="false">
<environmentVariables>
<environmentVariable name="ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT"
value="Development" />
</environmentVariables>
</aspNetCore>
Working with Data Using ASP.Net Core MVC (CRUD)
Database Creation
Create a new database using SSMS, name it “TicketBooking”. Copy the below query & run it using query editor of SSMS.
USE [TicketBooking]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Ticket](
[TicketID] [int] NOT NULL,
[DestinationFrom] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[DestinationTo] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[TicketDate] [datetime] NULL,
[TicketFee] [numeric](18, 2) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Ticket] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[TicketID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, _
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Reverse Engineer
Add Dependency Packages:
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer": "1.0.1",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools":"1.0.0-preview2-final",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Design": "1.0.1"
Add Tools:
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final"
Packages will automatically be restored by IDE.

Create the EF model from the existing database.
- Tools –> NuGet Package Manager –> Package Manager Console
- Run the following command:
Scaffold-DbContext "Server=DESKTOP-5B67SHH;
Database=TicketBooking;Trusted_Connection=True;"
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models

As you can see, models has created in Models folder. Rewrite Entity from Database with below Command if database has any changes.
Scaffold-DbContext "Server=DESKTOP-5B67SHH;
Database=TicketBooking;Trusted_Connection=True;"
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models -force
Context
using System;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata;
namespace CoreMVC.Models
{
public partial class TicketBookingContext : DbContext
{
public TicketBookingContext
(DbContextOptions<TicketBookingContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Ticket>(entity =>
{
entity.Property(e => e.TicketId).HasColumnName("TicketID");
entity.Property(e => e.DestinationFrom).HasMaxLength(50);
entity.Property(e => e.DestinationTo).HasMaxLength(50);
entity.Property(e => e.TicketDate).HasColumnType("datetime");
entity.Property(e => e.TicketFee).HasColumnType("numeric");
entity.Property(e => e.Vat)
.HasColumnName("VAT")
.HasColumnType("numeric");
});
}
public virtual DbSet<Ticket> Ticket { get; set; }
}
}
MVC Controller
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using CoreMVC.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace CoreMVC.Controllers
{
public class TicketsController : Controller
{
private TicketBookingContext _ctx = null;
public TicketsController(TicketBookingContext context)
{
_ctx = context;
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Index()
{
List<Ticket> tickets = null;
try
{
tickets = await _ctx.Ticket.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return View(tickets);
}
public IActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken, HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create(Ticket ticket)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
try
{
_ctx.Add(ticket);
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
}
return View(ticket);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Details(int? id)
{
object ticket = null;
try
{
if ((id != null) && (id > 0))
{
ticket = await _ctx.Ticket.SingleOrDefaultAsync(m => m.TicketId == id);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return View(ticket);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(int? id)
{
object ticket = null;
try
{
if ((id != null) && (id > 0))
{
ticket = await _ctx.Ticket.SingleOrDefaultAsync(m => m.TicketId == id);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return View(ticket);
}
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken, HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(int id, Ticket ticket)
{
if (id == ticket.TicketId)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
try
{
_ctx.Update(ticket);
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException dce)
{
if (!TicketExists(ticket.TicketId))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
dce.ToString();
}
}
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
return View(ticket);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(int? id)
{
object ticket = null;
try
{
if ((id != null) && (id > 0))
{
ticket = await _ctx.Ticket.SingleOrDefaultAsync(m => m.TicketId == id);
if (ticket == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return View(ticket);
}
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken, HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
try
{
var ticket = await _ctx.Ticket.SingleOrDefaultAsync(m => m.TicketId == id);
_ctx.Ticket.Remove(ticket);
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
private bool TicketExists(int id)
{
return _ctx.Ticket.Any(e => e.TicketId == id);
}
}
}
WebAPI Controller
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using CoreMVC.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace CoreMVC.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class TicketController : Controller
{
private TicketBookingContext _ctx = null;
public TicketController(TicketBookingContext context)
{
_ctx = context;
}
[HttpGet("GetTicket"), Produces("application/json")]
public async Task<object> GetTicket()
{
List<Ticket> Tickets = null;
object result = null;
try
{
using (_ctx)
{
Tickets = await _ctx.Ticket.ToListAsync();
result = new
{
Tickets
};
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return Tickets;
}
[HttpGet("GetTicketByID/{id}"),
Produces("application/json")]
public async Task<Ticket> GetTicketByID(int id)
{
Ticket contact = null;
try
{
using (_ctx)
{
contact = await _ctx.Ticket.FirstOrDefaultAsync
(x => x.TicketId == id);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ToString();
}
return contact;
}
[HttpPost, Route("PostTicket"),
Produces("application/json")]
public async Task<object> PostTicket([FromBody]Ticket model)
{
object result = null; string message = "";
if (model == null)
{
return BadRequest();
}
using (_ctx)
{
using (var _ctxTransaction = _ctx.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
_ctx.Ticket.Add(model);
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
_ctxTransaction.Commit();
message = "Saved Successfully";
}
catch (Exception e)
{
_ctxTransaction.Rollback();
e.ToString();
message = "Saved Error";
}
result = new
{
message
};
}
}
return result;
}
[HttpPut, Route("PutTicket/{id}")]
public async Task<object>
PutContact(int id, [FromBody]Ticket model)
{
object result = null; string message = "";
if (model == null)
{
return BadRequest();
}
using (_ctx)
{
using (var _ctxTransaction = _ctx.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
var entityUpdate = _ctx.Ticket.FirstOrDefault
(x => x.TicketId == id);
if (entityUpdate != null)
{
entityUpdate.DestinationFrom = model.DestinationFrom;
entityUpdate.DestinationTo = model.DestinationTo;
entityUpdate.TicketFee = model.TicketFee;
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
}
_ctxTransaction.Commit();
message = "Entry Updated";
}
catch (Exception e)
{
_ctxTransaction.Rollback(); e.ToString();
message = "Entry Update Failed!!";
}
result = new
{
message
};
}
}
return result;
}
[HttpDelete, Route("DeleteTicketByID/{id}")]
public async Task<object> DeleteContactByID(int id)
{
object result = null; string message = "";
using (_ctx)
{
using (var _ctxTransaction = _ctx.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
var idToRemove = _ctx.Ticket.SingleOrDefault(x => x.TicketId == id);
if (idToRemove != null)
{
_ctx.Ticket.Remove(idToRemove);
await _ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
}
_ctxTransaction.Commit();
message = "Deleted Successfully";
}
catch (Exception e)
{
_ctxTransaction.Rollback(); e.ToString();
message = "Error on Deleting!!";
}
result = new
{
message
};
}
}
return result;
}
}
}
Output

Hope this will help!
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/.NET_Framework
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/.NET_Framework_version_history
- https://dotnet.github.io
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core
- https://github.com/aspnet
- https://www.microsoft.com/net/core/platform
- https://github.com/dotnet/core
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/articles/core/index
- http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1115771/NET-CORE-MVC-ANGULARJS-STARTUP
- http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1118189/CRUD-USING-NET-CORE-ANGULARJS-WEBAPI
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core
