Introduction
Design and implement architecture for enterprise applications it's a big challenge, there is a common question in this point: What is the the best way following the best practices according to selected technology in our company.
This guide uses .NET Core, so We'll work with Entity Framework Core, but these concepts apply for another technologies like Dapper or another ORM.
In fact, We'll take a look at the common requirements to design enterprise architect in this article.
The sample database provided in this guide represents an online store.
This is the stack for this solution:
Entity Framework CoreASP.NET CorexUnit for unit testsxUnit for integration testsIdentity Server 4
Payment Gateway
Online Store needs to receive payments through payment service, for this case I created a payment gateway named Rothschild House, you can found source code in this link.
Rothschild House allows to receive payments with credit cards.
This payment gateway is for demonstration purposes only.
Running Payment Gateway
Run RothschildHouse solution, solution has these projects:
| Project | Runs on port |
RothschildHouse | 18000 |
RothschildHouse.IdentityServer | 19000 |
The above output is the configuration for Identity Server, RothschildHouse.IdentityServer provides authentication and authorization to receive payments.
Credentials for Online Store
| User name | Password |
| administrator@onlinestore.com | onlinestore1 |
These credentials are provided by Rothschild House to clients.
Payment Schema
RothschildHouse project contains PaymentDbContext class, this class provides the model to process payments.
Entities:
PersonCreditCardPaymentMethodPaymentTransaction
Payment Data
PaymentDbContext accepts these customers:
| User name | Password | Card holder name | Issuing network | Card number | Expiration Date | CVV |
| jameslogan@walla.com | wolverine | James Logan | Visa | 4024007164051145 | 6/1/2024 | 987 |
| ororo_munroe@yahoo.com | storm | Ororo Munroe | MasterCard | 5473913699329307 | 1/1/2023 | 147 |
Background
According to my experience, enterprise applications should have the following levels:
- Database: Is the relational database management system
- Common: Contains common objects for layers (e.g. Loggers, Mappers, Extensions)
- Core: Contains objects related to business logic and database access
- Testing: Contains tests for back-end (units and integration)
- External Services (optional): Contains invocations for external services (ASMX, WCF, RESTful)
- Security: Is an API that provides authentication and authorization
- Presentation: Is the user interface
Architecture: Big Picture
| DATABASE | SQL Server | DATABASE |
| COMMON | Extensions, Helpers (Loggers and Mappers) | BACK-END |
| CORE | Services, Exceptions, DbContext, Entities, Configurations and Data Contracts | BACK-END |
| TESTING | Unit tests and Integration tests | BACK-END |
| EXTERNAL SERVICES | ASMX, WCF, RESTful | BACK-END |
| SECURITY | Authentication and Authorization (Identity Server | Others) | BACK-END |
| PRESENTATION | UI Frameworks (Angular | ReactJS | Vue.js | Others) | FRONT-END |
Prerequisites
Skills
Before to continuing, keep in mind we need to have the folllowing skills in order to understand this guide:
- Object Oriented Programming
- Aspect Oriented Programming
- Object Relational Mapping
- Design Patterns
Software
- .NET Core
- Visual Studio 2017
- SQL Server instance (local or remote)
- SQL Server Management Studio
- Using the Code
- Code improvements
- Points of Interest
- Related Links
Using the Code
Chapter 01 - Database
Take a look for sample database to understand each component in architecture. In this database there are 4 schemas:
- Dbo
- HumanResources
- Sales
- Warehouse
Each schema represents a division for online store company, keep this in mind because all code is designed following this aspect; at this moment this code only implements features for Warehouse and Sales schemas.
All tables have a primary key with one column and have columns for creation, last update and concurrency token.
Tables
| Schema | Name |
dbo | ChangeLog |
dbo | ChangeLogExclusion |
dbo | Country |
dbo | CountryCurrency |
dbo | Currency |
dbo | EventLog |
HumanResources | Employee |
HumanResources | EmployeeAddress |
HumanResources | EmployeeEmail |
Sales | Customer |
Sales | OrderDetail |
Sales | OrderHeader |
Sales | OrderStatus |
Sales | PaymentMethod |
Sales | Shipper |
Warehouse | Location |
Warehouse | Product |
Warehouse | ProductCategory |
Warehouse | ProductInventory |
You can found the scripts for database in this link: Online Store Database Scripts on GitHub.
Please remember: This is a sample database, only for demonstration of concepts.
Chapter 02 - Core Project
Core project represents the core for solution, in this guide Core project includes docmain and business logic.
Online Store works with .NET Core, the naming convention is .NET naming convention, so it's very useful to define a naming convention table to show how to set names in code, something like this:
| Identifier | Case | Example |
| Namespace | PascalCase | Store |
| Class | PascalCase | Product |
| Interface | I prefix + PascalCase | ISalesRepository |
| Method | Verb in PascalCase + Noun in PascalCase | GetProducts |
| Async Method | Verb in PascalCase + Noun in PascalCase + Async sufix | GetOrdersAsync |
| Property | PascalCase | Description |
| Parameter | camelCase | connectionString |
This convention is important because it defines the naming guidelines for architecture.
This is the structure for OnlineStore.Core project:
DomainDomain\ConfigurationsDomain\DataContractsBusinessBusiness\ContractsBusiness\Responses
Inside of Domain We'll place all entities, in this context, entity means a
class that represents a table or view from database, sometimes entity is named POCO (Plain Old Common language runtime Object) than means a class with only properties not methods nor other things (events); according to wkempf feedback it's necessary to be clear about POCOs, POCOs can have methods and events and other members but it's not common to add those members in POCOs.
For Domain\Configurations, There are object definitions related to mapping classes for database.
Inside of Domain and Domain\Configurations, there is one directory per schema.
Inside of Business, There are interfaces and implementations for services, in this case, the services will contain the methods according to use cases (or something like that) and those methods must perform validations and handle exceptions related to business.
For Business\Responses, These are the responses definitions: single, list and paged to represent the results from services.
We'll inspect the code to understand these concepts but the review would be with one object per level because the remaining code is similar.
Domain
Please take a look at POCOs, We're using nullable types instead of native types because nullable are easy to evaluate if property has value or not, that's more similar to database model.
In Domain there are two interfaces: IEntity and IAuditEntity, IEntity represents all entities in our application and IAuditEntity represents all entities that allows to save audit information: create and last update; as special point if we have mapping for views, those classes do not implement IAuditEntity because a view doesn't allow insert, update and delete operations.
OrderHeader class:
using System;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Dbo;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.HumanResources;
namespace OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales
{
public class OrderHeader : IAuditableEntity
{
public OrderHeader()
{
}
public OrderHeader(long? id)
{
ID = id;
}
public long? ID { get; set; }
public short? OrderStatusID { get; set; }
public DateTime? OrderDate { get; set; }
public int? CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public int? ShipperID { get; set; }
public decimal? Total { get; set; }
public string CurrencyID { get; set; }
public Guid? PaymentMethodID { get; set; }
public int? DetailsCount { get; set; }
public long? ReferenceOrderID { get; set; }
public string Comments { get; set; }
public string CreationUser { get; set; }
public DateTime? CreationDateTime { get; set; }
public string LastUpdateUser { get; set; }
public DateTime? LastUpdateDateTime { get; set; }
public byte[] Timestamp { get; set; }
public virtual OrderStatus OrderStatusFk { get; set; }
public virtual Customer CustomerFk { get; set; }
public virtual Employee EmployeeFk { get; set; }
public virtual Shipper ShipperFk { get; set; }
public virtual Currency CurrencyFk { get; set; }
public virtual PaymentMethod PaymentMethodFk { get; set; }
public virtual Collection<OrderDetail> OrderDetails { get; set; }
}
}
Keys
Also there is an important aspect for Entity Layer, all entities that allow create operation have the key property as nullable type, this is related to philosophy in software develoment.
Lets take a look on this, We'll use the Product entity as sample:
public class Product
{
public int? ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
Lets create an instance of Product class:
var entity = new Product();
Now lets create a new Product in database:
using (var ctx = new OnlineStore())
{
var newProduct = new Product
{
Name = "Product sample"
};
ctx.Products.Add(newProduct);
await ctx.SaveChangesAsync();
}
So, now change the type for ID property from int? to int, the property value will be initialized with 0 value, 0 it's an integer, please consider if in some cases there are ID that can be negatives , so isn't enough to validate if property value is greather than zero.
This explanation makes sense?, let me know in comments :)
Data Layer
This solution doesn't work with Repository pattern anymore, later I'll add an explanation why.
We're working with Entity Framework Core in this guide, so We need to have a DbContext and objects that allow mapping database objects like tables and views.
Naming Issue
Repository versus DbHelper versus Data Access Object.
This issue is related to naming objects, some years ago I used DataAccessObject as suffix to class that contain database operatios (select, insert, update, delete, etc). Other developers used DbHelper as suffix to represent this kind of objects, at my beggining in EF I learned about repository design pattern, so from my point of view I prefer to use Repository suffix to name the object that contains database operations.
OnlineStoreDbContext class:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations.Dbo;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations.HumanResources;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations.Sales;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations.Warehouse;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Dbo;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.HumanResources;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Warehouse;
namespace OnlineStore.Core.Domain
{
public class OnlineStoreDbContext : DbContext
{
public OnlineStoreDbContext(DbContextOptions<OnlineStoreDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<ChangeLog> ChangeLogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<ChangeLogExclusion> ChangeLogExclusions { get; set; }
public DbSet<CountryCurrency> CountryCurrencies { get; set; }
public DbSet<Country> Countries { get; set; }
public DbSet<Currency> Currencies { get; set; }
public DbSet<EventLog> EventLogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public DbSet<EmployeeAddress> EmployeeAddresses { get; set; }
public DbSet<EmployeeEmail> EmployeeEmails { get; set; }
public DbSet<ProductCategory> ProductCategories { get; set; }
public DbSet<ProductInventory> ProductInventories { get; set; }
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
public DbSet<ProductUnitPriceHistory> ProductUnitPriceHistories { get; set; }
public DbSet<Location> Locations { get; set; }
public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderDetail> OrderDetails { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderHeader> OrderHeaders { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderStatus> OrderStatuses { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrderSummary> OrderSummaries { get; set; }
public DbSet<PaymentMethod> PaymentMethods { get; set; }
public DbSet<Shipper> Shippers { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder
.ApplyConfiguration(new ChangeLogConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new ChangeLogExclusionConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new CountryCurrencyConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new CountryConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new CurrencyConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new EventLogConfiguration())
;
modelBuilder
.ApplyConfiguration(new EmployeeConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new EmployeeAddressConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new EmployeeEmailConfiguration())
;
modelBuilder
.ApplyConfiguration(new ProductCategoryConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new ProductConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new ProductUnitPriceHistoryConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new ProductInventoryConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new LocationConfiguration())
;
modelBuilder
.ApplyConfiguration(new CustomerConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new OrderDetailConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new OrderHeaderConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new OrderStatusConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new OrderSummaryConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new PaymentMethodConfiguration())
.ApplyConfiguration(new ShipperConfiguration())
;
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
OrderHeaderConfiguration class:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales;
namespace OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Configurations.Sales
{
public class OrderHeaderConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<OrderHeader>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<OrderHeader> builder)
{
builder.ToTable("OrderHeader", "Sales");
builder.HasKey(p => p.ID);
builder.Property(p => p.ID).UseSqlServerIdentityColumn();
builder.Property(p => p.OrderStatusID).HasColumnType("smallint").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.OrderDate).HasColumnType("datetime").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.CustomerID).HasColumnType("int").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.EmployeeID).HasColumnType("int");
builder.Property(p => p.ShipperID).HasColumnType("int");
builder.Property(p => p.Total).HasColumnType("decimal(12, 4)").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.CurrencyID).HasColumnType("varchar(10)");
builder.Property(p => p.PaymentMethodID).HasColumnType("uniqueidentifier");
builder.Property(p => p.DetailsCount).HasColumnType("int").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.ReferenceOrderID).HasColumnType("bigint");
builder.Property(p => p.Comments).HasColumnType("varchar(max)");
builder.Property(p => p.CreationUser).HasColumnType("varchar(25)").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.CreationDateTime).HasColumnType("datetime").IsRequired();
builder.Property(p => p.LastUpdateUser).HasColumnType("varchar(25)");
builder.Property(p => p.LastUpdateDateTime).HasColumnType("datetime");
builder.Property(p => p.Timestamp).ValueGeneratedOnAddOrUpdate().IsConcurrencyToken();
builder
.HasOne(p => p.OrderStatusFk)
.WithMany(b => b.Orders)
.HasForeignKey(p => p.OrderStatusID);
builder
.HasOne(p => p.CustomerFk)
.WithMany(b => b.Orders)
.HasForeignKey(p => p.CustomerID);
builder
.HasOne(p => p.ShipperFk)
.WithMany(b => b.Orders)
.HasForeignKey(p => p.ShipperID);
}
}
}
How about Unit of Work? in EF 6.x was usually create a repository class and unit of work class: repository provided operations for database access and unit of work provided operations to save changes in database; but in EF Core it's a common practice to have only repositories and no unit of work; anyway for this code we have added two methods in Repository class: CommitChanges and CommitChangesAsync, so just to make sure that inside of all data writing mehotds in repositories call CommitChanges or CommitChangesAsync and with that design we have two definitions working on our architecture.
How about async operations? In previous versions of this post I said We'll implement async operations in the last level: REST API, but I was wrong about that because .NET Core it's more about async programming, so the best decision is handle all database operations in async way using the Async methods that Entity Framework Core provides.
For the last version of this article, We have a payment gateway named Rothschild House, this API provides payment authorization, this API below to external services layer.
Later, I'll add a section to explain about payment gateway.
Stored Procedures versus LINQ Queries
In data layer, there is a very interesting point: How we can use stored procedures? For the current version of EF Core, there isn't support for stored procedures, so we can't use them in a native way, inside of DbSet, there is a method to execute a query but that works for stored procedures not return a result set (columns), we can add some extension methods and add packages to use classic ADO.NET, so in that case we need to handle the dynamic creation of objects to represent the stored procedure result; that makes sense? if we consume a procedure with name GetOrdersByMonth and that procedure returns a select with 7 columns, to handle all results in the same way, we'll need to define objects to represent those results, that objects must define inside of DataLayer\DataContracts namespace according to our naming convention.
Inside of enterprise environment, a common discussion is about LINQ queries or stored procedures. According to my experience, I think the best way to solve that question is: review design conventions with architect and database administrator; nowadays, it's more common to use LINQ queries in async mode instead of stored procedures but sometimes some companies have restrict conventions and do not allow to use LINQ queries, so it's required to use stored procedure and we need to make our architecture flexible because we don't say to developer manager "the business logic will be rewrite because Entity Framework Core doesn't allow to invoke stored procedures"
As We can see until now, assuming We have the extension methods for EF Core to invoke stored procedures and data contracts to represent results from stored procedures invocations, Where do we place those methods? It's preferable to use the same convention so we'll add those methods inside of contracts and repositories; just to be clear if we have procedures named Sales.GetCustomerOrdersHistory and HumanResources.DisableEmployee; we must to place methods inside of Sales and HumanResources repositories.
You can also read more about this point in this link.
Just to be clear: STAY AWAY FROM STORED PROCEDURES!
The previous concept applies in the same way for views in database. In addition, we only need to check that repositories do not allow add, update and delete operations for views.
Change Tracking
Inside of OnLineStoreDbContextExtensions class there is a method with name GetChanges, that method get all changes from DbContext through ChangeTracker and returns all changes, so those values are saved in ChangeLog table in CommitChanges method. You can update one existing entity with business object, later you can check your ChangeLog table:
ChangeLogID ClassName PropertyName Key OriginalValue CurrentValue UserName ChangeDate
----------- ------------ -------------- ---- ---------------------- ---------------------- ---------- -----------------------
1 Employee FirstName 1 John John III admin 2017-02-19 21:49:51.347
2 Employee MiddleName 1 Smith III admin 2017-02-19 21:49:51.347
3 Employee LastName 1 Doe Doe III admin 2017-02-19 21:49:51.347
(3 row(s) affected)
As We can see all changes made in entities will be saved on this table, as a future improvement we'll need to add exclusions for this change log. In this guide we're working with SQL Server, as I know there is a way to enable change tracking from database side but in this post I'm showing to you how you can implement this feature from back-end; if this feature is on back-end or database side will be a decision from your leader. In the timeline we can check on this table all changes in entities, some entities have audit properties but those properties only reflect the user and date for creation and last update but do not provide full details about how data change.
Business
Naming Issue
Controller versus Service versus Business Object
There is a common issue in this point, How we must to name the object that represents business operations: for first versions of this article I named this object as BusinessObject, that can be confusing for some developers, some developers do not name this as business object because the controller in Web API represents business logic, but Service is another name used by developers, so from my point of view is more clear to use Service as sufix for this object. If we have a Web API that implements business logic in controller we can ommit to have services, but if there is business layer it is more useful to have services, these classes must to implement logic business and controllers must invoke service's methods.
Business Layer: Handle Related Aspects To Business
- Logging: We need to have a logger object, that means an object that logs on text file, database, email, etc. all events in our architecture; we can create our own logger implementation or choose an existing log. We have added logging with package
Microsoft.Extensions.Logging, in this way we're using the default log system in .NET Core, we can use another log mechanism but at this moment we'll use this logger, inside of every method in controllers and business objects, there is a code line like this: Logger?.LogInformation("{0} has been invoked", nameof(GetOrdersAsync));, in this way we make sure invoke logger if is a valid instance and ths using of nameof operator to retrieve the name of member without use magic strings, after we'll add code to save all logs into database. - Business exceptions: The best way to handle messaging to user is with custom exceptions, inside of business layer, We'll add definitions for exceptions to represent all handle errors in architecture.
- Transactions: as We can see inside of
Sales business object, we have implemented transaction to handle multiple changes in our database; inside of CreateOrderAsync method, we invoke methods from repositories, inside of repositories we don't have any transactions because the service is the responsible for transactional process, also we added logic to handle exceptions related to business with custom messages because we need to provide a friendly message to the end-user. - There is a
CloneOrderAsync method, this method provides a copy from existing order, this is a common requirement on ERP because it's more easy create a new order but adding some modifications instead of create the whole order there are cases where the sales agent create a new order but removing 1 or 2 lines from details or adding 1 or 2 details, anyway never let to front-end developer to add this logic in UI, the API must to provide this feature. GetPostOrderModelAsync method in SalesService provides the required information to create an order, information from foreign keys: products and anothers. With this method We are providing a model that contains the list for foreign keys and in that way We reduce the work from front-end to know how to create create order operation.
Service class:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain;
namespace OnlineStore.Core.Business
{
public abstract class Service : IService
{
protected bool Disposed;
protected readonly ILogger Logger;
public Service(ILogger logger, OnlineStoreDbContext dbContext, IUserInfo userInfo)
{
Logger = logger;
DbContext = dbContext;
UserInfo = userInfo;
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (Disposed)
return;
DbContext?.Dispose();
Disposed = true;
}
public OnlineStoreDbContext DbContext { get; }
public IUserInfo UserInfo { get; set; }
}
}
SalesService class:
using System;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Requests;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Responses;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Dbo;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Repositories;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Warehouse;
namespace OnlineStore.Core.Business
{
public class SalesService : Service, ISalesService
{
public SalesService(ILogger<SalesService> logger, OnlineStoreDbContext dbContext, IUserInfo userInfo)
: base(logger, dbContext, userInfo)
{
}
public async Task<IPagedResponse<Customer>> GetCustomersAsync(int pageSize = 10, int pageNumber = 1)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetCustomersAsync));
var response = new PagedResponse<Customer>();
try
{
var query = DbContext.Customers;
response.PageSize = pageSize;
response.PageNumber = pageNumber;
response.ItemsCount = await query.CountAsync();
response.Model = await query
.Paging(pageSize, pageNumber)
.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetCustomersAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<IPagedResponse<Shipper>> GetShippersAsync(int pageSize = 10, int pageNumber = 1)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetShippersAsync));
var response = new PagedResponse<Shipper>();
try
{
var query = DbContext.Shippers;
response.PageSize = pageSize;
response.PageNumber = pageNumber;
response.ItemsCount = await query.CountAsync();
response.Model = await query
.Paging(pageSize, pageNumber)
.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetShippersAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<IPagedResponse<Currency>> GetCurrenciesAsync(int pageSize = 10, int pageNumber = 1)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetCurrenciesAsync));
var response = new PagedResponse<Currency>();
try
{
var query = DbContext.Currencies;
response.PageSize = pageSize;
response.PageNumber = pageNumber;
response.ItemsCount = await query.CountAsync();
response.Model = await query
.Paging(pageSize, pageNumber)
.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetCurrenciesAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<IPagedResponse<PaymentMethod>> GetPaymentMethodsAsync(int pageSize = 10, int pageNumber = 1)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetPaymentMethodsAsync));
var response = new PagedResponse<PaymentMethod>();
try
{
var query = DbContext.PaymentMethods;
response.PageSize = pageSize;
response.PageNumber = pageNumber;
response.ItemsCount = await query.CountAsync();
response.Model = await query
.Paging(pageSize, pageNumber)
.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetPaymentMethodsAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<IPagedResponse<OrderInfo>> GetOrdersAsync(int? pageSize, int? pageNumber, short? orderStatusID, int? customerID, int? employeeID, int? shipperID, string currencyID, Guid? paymentMethodID)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetOrdersAsync));
var response = new PagedResponse<OrderInfo>();
try
{
var query = DbContext
.GetOrders(orderStatusID, customerID, employeeID, shipperID, currencyID, paymentMethodID);
response.PageSize = (int)pageSize;
response.PageNumber = (int)pageNumber;
response.ItemsCount = await query.CountAsync();
response.Model = await query
.Paging((int)pageSize, (int)pageNumber)
.ToListAsync();
response.Message = string.Format("Page {0} of {1}, Total of rows: {2}", response.PageNumber, response.PageCount, response.ItemsCount);
Logger?.LogInformation(response.Message);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetOrdersAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>> GetOrderAsync(long id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetOrderAsync));
var response = new SingleResponse<OrderHeader>();
try
{
response.Model = await DbContext.GetOrderAsync(new OrderHeader(id));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetOrderAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<ISingleResponse<CreateOrderRequest>> GetCreateOrderRequestAsync()
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(GetCreateOrderRequestAsync));
var response = new SingleResponse<CreateOrderRequest>();
try
{
response.Model.Products = await DbContext.GetProducts().ToListAsync();
response.Model.Customers = await DbContext.Customers.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(GetCreateOrderRequestAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>> CreateOrderAsync(OrderHeader header, OrderDetail[] details)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(CreateOrderAsync));
var response = new SingleResponse<OrderHeader>();
using (var transaction = await DbContext.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
try
{
var warehouses = await DbContext.Locations.ToListAsync();
foreach (var detail in details)
{
var product = await DbContext.GetProductAsync(new Product(detail.ProductID));
if (product == null)
throw new NonExistingProductException(string.Format(SalesDisplays.NonExistingProductExceptionMessage, detail.ProductID));
if (product.Discontinued == true)
throw new AddOrderWithDiscontinuedProductException(string.Format(SalesDisplays.AddOrderWithDiscontinuedProductExceptionMessage, product.ID));
if (detail.Quantity <= 0)
throw new InvalidQuantityException(string.Format(SalesDisplays.InvalidQuantityExceptionMessage, product.ID));
detail.ProductName = product.ProductName;
detail.UnitPrice = product.UnitPrice;
detail.Total = product.UnitPrice * detail.Quantity;
}
if (!header.OrderDate.HasValue)
header.OrderDate = DateTime.Now;
header.OrderStatusID = 100;
header.Total = details.Sum(item => item.Total);
header.DetailsCount = details.Count();
DbContext.Add(header, UserInfo);
await DbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
foreach (var detail in details)
{
detail.OrderHeaderID = header.ID;
detail.CreationUser = header.CreationUser;
DbContext.Add(detail, UserInfo);
await DbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
var productInventory = new ProductInventory
{
ProductID = detail.ProductID,
LocationID = warehouses.First().ID,
OrderDetailID = detail.ID,
Quantity = detail.Quantity * -1,
CreationUser = header.CreationUser,
CreationDateTime = DateTime.Now
};
DbContext.Add(productInventory);
}
await DbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
response.Model = header;
transaction.Commit();
Logger.LogInformation(SalesDisplays.CreateOrderMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(CreateOrderAsync), ex);
}
}
return response;
}
public async Task<ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>> CloneOrderAsync(long id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(CloneOrderAsync));
var response = new SingleResponse<OrderHeader>();
try
{
var entity = await DbContext.GetOrderAsync(new OrderHeader(id));
if (entity == null)
return response;
response.Model = new OrderHeader
{
ID = entity.ID,
OrderDate = entity.OrderDate,
CustomerID = entity.CustomerID,
EmployeeID = entity.EmployeeID,
ShipperID = entity.ShipperID,
Total = entity.Total,
Comments = entity.Comments
};
if (entity.OrderDetails?.Count > 0)
{
response.Model.OrderDetails = new Collection<OrderDetail>();
foreach (var detail in entity.OrderDetails)
{
response.Model.OrderDetails.Add(new OrderDetail
{
ProductID = detail.ProductID,
ProductName = detail.ProductName,
UnitPrice = detail.UnitPrice,
Quantity = detail.Quantity,
Total = detail.Total
});
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(CloneOrderAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
public async Task<IResponse> CancelOrderAsync(long id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(CancelOrderAsync));
var response = new Response();
try
{
var entity = await DbContext.GetOrderAsync(new OrderHeader(id));
if (entity == null)
return response;
if (entity.OrderDetails.Count > 0)
throw new ForeignKeyDependencyException(string.Format(SalesDisplays.RemoveOrderExceptionMessage, id));
DbContext.Remove(entity);
await DbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
Logger?.LogInformation(SalesDisplays.DeleteOrderMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
response.SetError(Logger, nameof(CancelOrderAsync), ex);
}
return response;
}
}
}
In Business it's better to have custom exceptions for represent errors instead of send simple string messages to client, obviously the custom exception must have a message but in logger there will be a reference about custom exception. For this architecture these are the custom exceptions:
Business Exceptions | Name | Description |
AddOrderWithDiscontinuedProductException | Represents an exception adding order with a discontinued product |
ForeignKeyDependencyException | Represents an exception deleting an order with detail rows |
DuplicatedProductNameException | Represents an exception adding product with existing name |
NonExistingProductException | Represents an exception adding order with non existing product |
Chapter 03 - Putting All Code Together
We need to create a OnlineStoreDbContext instance, that instance works with SQL Server, in OnModelCreating method, all configurations are applied to ModelBuilder instance.
Later, there is an instance of SalesService created with a valid instance of OnlineStoreDbContext to get access for service's operations.
Get All
This is an example to retrieve orders:
var logger = LoggingHelper.GetLogger<ISalesService>();
var userInfo = new UserInfo();
var options = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<OnlineStoreDbContext>()
.UseSqlServer("YourConnectionStringHere")
.Options;
using (var service = new SalesService(logger, userInfo, new OnlineStoreDbContext(options)))
{
var pageSize = 10;
var pageNumber = 1;
var response = await service.GetOrderHeadersAsync(pageSize, pageNumber);
var valid = !response.DidError;
}
GetOrderHeadersAsync method in SalesService retrieves rows from Sales.OrderHeader table as a generic list.
Get by Key
This is an example to retrieve an entity by key:
var logger = LoggingHelper.GetLogger<ISalesService>();
var userInfo = new UserInfo();
var options = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<OnlineStoreDbContext>()
.UseSqlServer("YourConnectionStringHere")
.Options;
using (var service = new SalesService(logger, userInfo, new OnlineStoreDbContext(options)))
{
var id = 1;
var response = await service.GetOrderHeaderAsync(id);
var valid = !response.DidError;
var entity = response.Model;
}
For incoming versions of this article, there will be samples for another operations.
Chapter 04 - Mocker
Mocker it's a project that allows to create rows in Sales.OrderHeader, Sales.OrderDetail and Warehouse.ProductInventory tables for a range of dates, by default Mocker creates rows for one year.
Program class:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using OnlineStore.Common.Helpers;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales;
namespace OnlineStore.Mocker
{
public class Program
{
static readonly ILogger Logger;
static Program()
{
Logger = LoggingHelper.GetLogger<Program>();
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
=> MainAsync(args).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
static async Task MainAsync(string[] args)
{
var year = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1).Year;
var ordersLimitPerDay = 3;
foreach (var arg in args)
{
if (arg.StartsWith("/year:"))
year = Convert.ToInt32(arg.Replace("/year:", string.Empty));
else if (arg.StartsWith("/ordersLimitPerDay:"))
ordersLimitPerDay = Convert.ToInt32(arg.Replace("/ordersLimitPerDay:", string.Empty));
}
var start = new DateTime(year, 1, 1);
var end = new DateTime(year, 12, DateTime.DaysInMonth(year, 12));
if (start.DayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.Sunday)
start = start.AddDays(1);
do
{
if (start.DayOfWeek != DayOfWeek.Sunday)
{
await CreateDataAsync(start, ordersLimitPerDay);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
start = start.AddDays(1);
}
while (start <= end);
}
static async Task CreateDataAsync(DateTime date, int ordersLimitPerDay)
{
var random = new Random();
var warehouseService = ServiceMocker.GetWarehouseService();
var salesService = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService();
var customers = (await salesService.GetCustomersAsync()).Model.ToList();
var currencies = (await salesService.GetCurrenciesAsync()).Model.ToList();
var paymentMethods = (await salesService.GetPaymentMethodsAsync()).Model.ToList();
var products = (await warehouseService.GetProductsAsync(10, 1)).Model.ToList();
Logger.LogInformation("Creating orders for {0}", date);
for (var i = 0; i < ordersLimitPerDay; i++)
{
var header = new OrderHeader
{
OrderDate = date,
CreationDateTime = date
};
var selectedCustomer = random.Next(0, customers.Count - 1);
var selectedCurrency = random.Next(0, currencies.Count - 1);
var selectedPaymentMethod = random.Next(0, paymentMethods.Count - 1);
header.CustomerID = customers[selectedCustomer].ID;
header.CurrencyID = currencies[selectedCurrency].ID;
header.PaymentMethodID = paymentMethods[selectedPaymentMethod].ID;
var details = new List<OrderDetail>();
var detailsCount = random.Next(1, 5);
for (var j = 0; j < detailsCount; j++)
{
var detail = new OrderDetail
{
ProductID = products[random.Next(0, products.Count - 1)].ID,
Quantity = (short)random.Next(1, 5)
};
if (details.Count > 0 && details.Count(item => item.ProductID == detail.ProductID) == 1)
continue;
details.Add(detail);
}
await salesService.CreateOrderAsync(header, details.ToArray());
Logger.LogInformation("Date: {0}", date);
}
warehouseService.Dispose();
salesService.Dispose();
}
}
}
Now in the same window terminal, we need to run the following command: dotnet run and if everything works fine, We can check the data in database for OrderHeader, OrderDetail and ProductInventory tables.
How Mocker works? set a range for dates and a limit of orders per day, then iterates all days in date range except sundays because We're assuming create order process is not allowed on sundays; then create the instance of DbContext and Services, arranges data using a random index to get elements from products, customers, currencies and payment methods; then invokes the CreateOrderAsync method.
You can adjust the range for dates and orders per day to mock data according to your requirements, once the Mocker has finished you can check the data on your database.
Chapter 05 - Payment Gateway
The payment gateway implements Identity Server as authentication and authorization API.
Payment Gateway has two projects:
RothschildHouse.IdentityServerRothschildHouse
RothschildHouse.IdentityServer
Payment gateway implements in-memory configuration for Identity Server.
Identity Server API for Payment Gateway runs on port 18000.
In browser, open http://localhost:18000/.well-known/openid-configuration url:
{
"issuer":"http://localhost:18000",
"jwks_uri":"http://localhost:18000/.well-known/openid-configuration/jwks",
"authorization_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/authorize",
"token_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/token",
"userinfo_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/userinfo",
"end_session_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/endsession",
"check_session_iframe":"http://localhost:18000/connect/checksession",
"revocation_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/revocation",
"introspection_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/introspect",
"device_authorization_endpoint":"http://localhost:18000/connect/deviceauthorization",
"frontchannel_logout_supported":true,
"frontchannel_logout_session_supported":true,
"backchannel_logout_supported":true,
"backchannel_logout_session_supported":true,
"scopes_supported":[
"RothschildHouseApi",
"offline_access"
],
"claims_supported":[
],
"grant_types_supported":[
"authorization_code",
"client_credentials",
"refresh_token",
"implicit",
"password",
"urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:device_code"
],
"response_types_supported":[
"code",
"token",
"id_token",
"id_token token",
"code id_token",
"code token",
"code id_token token"
],
"response_modes_supported":[
"form_post",
"query",
"fragment"
],
"token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported":[
"client_secret_basic",
"client_secret_post"
],
"subject_types_supported":[
"public"
],
"id_token_signing_alg_values_supported":[
"RS256"
],
"code_challenge_methods_supported":[
"plain",
"S256"
]
}
In order to allow connections, We need to add configuration for API resources and clients, this configuration is in Config class:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Security.Claims;
using IdentityModel;
using IdentityServer4.Models;
namespace RothschildHouse.IdentityServer
{
public static class Config
{
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources()
=> new List<ApiResource>
{
new ApiResource("RothschildHouseAPI", "Rothschild House API")
};
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients()
=> new List<Client>
{
new Client
{
ClientId = "onlinestoreclient",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword,
ClientSecrets =
{
new Secret("onlinestoreclientsecret1".Sha256())
},
AllowedScopes =
{
"RothschildHouseAPI"
},
Claims =
{
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Customer")
}
}
};
}
}
Let's take a look in Startup code:
using IdentityServer4.Services;
using IdentityServer4.Validation;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RothschildHouse.IdentityServer.Domain;
using RothschildHouse.IdentityServer.Services;
using RothschildHouse.IdentityServer.Validation;
namespace RothschildHouse.IdentityServer
{
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<AuthDbContext>(options => options.UseInMemoryDatabase("Auth"));
services
.AddTransient<IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator, ResourceOwnerPasswordValidator>()
.AddTransient<IProfileService, ProfileService>();
services
.AddIdentityServer()
.AddDeveloperSigningCredential()
.AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources())
.AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients());
services
.AddAuthentication()
.AddIdentityServerAuthentication();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
var authDbContext = app
.ApplicationServices
.CreateScope()
.ServiceProvider
.GetService<AuthDbContext>();
authDbContext.SeedInMemory();
app.UseIdentityServer();
}
}
}
RothschildHouse
RothschildHouse implements in-memory configuration for Identity Server.
RothschildHouse runs on port 19000.
Configuration for Startup class:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Reflection;
using IdentityServer4.AccessTokenValidation;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using RothschildHouse.Controllers;
using RothschildHouse.Domain;
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;
namespace RothschildHouse
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1);
services.AddTransient<ILogger<TransactionController>, Logger<TransactionController>>();
services.AddDbContext<PaymentDbContext>(options =>
{
options
.UseInMemoryDatabase("Payment")
.ConfigureWarnings(w => w.Ignore(InMemoryEventId.TransactionIgnoredWarning));
});
services
.AddAuthentication("Bearer")
.AddIdentityServerAuthentication(options =>
{
var settings = new IdentityServerAuthenticationOptions();
Configuration.Bind("IdentityServerSettings", settings);
options.Authority = settings.Authority;
options.RequireHttpsMetadata = settings.RequireHttpsMetadata;
options.ApiName = settings.ApiName;
options.ApiSecret = settings.ApiSecret;
});
services.AddSwaggerGen(options =>
{
options.SwaggerDoc("v1", new Info { Title = "RothschildHouse API", Version = "v1" });
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
options.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
var paymentDbContext = app
.ApplicationServices
.CreateScope()
.ServiceProvider
.GetService<PaymentDbContext>();
paymentDbContext.SeedInMemory();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(options =>
{
options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "RothschildHouse API V1");
});
app.UseMvc();
}
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
}
Code for TransactionController class:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using RothschildHouse.Domain;
using RothschildHouse.Requests;
using RothschildHouse.Responses;
namespace RothschildHouse.Controllers
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
[Route("api/v1/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
[Authorize]
public class TransactionController : ControllerBase
{
readonly ILogger<TransactionController> Logger;
readonly PaymentDbContext DbContext;
public TransactionController(ILogger<TransactionController> logger, PaymentDbContext dbContext)
{
Logger = logger;
DbContext = dbContext;
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
[HttpPost("Payment")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PostPaymentAsync([FromBody]PostPaymentRequest request)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("'{0}' has been invoked", nameof(PostPaymentAsync));
var creditCards = await DbContext.GetCreditCardByCardHolderName(request.CardHolderName).ToListAsync();
var creditCard = default(CreditCard);
var last4Digits = request.CardNumber.Substring(request.CardNumber.Length - 4);
if (creditCards.Count > 1)
creditCard = creditCards.FirstOrDefault(item => item.CardNumber == request.CardNumber);
else if (creditCards.Count == 1)
creditCard = creditCards.First();
if (creditCard == null)
return BadRequest(string.Format("There is not record for credit card with last 4 digits: {0}.", last4Digits));
if (!creditCard.IsValid(request))
return BadRequest(string.Format("Invalid information for card payment."));
if (!creditCard.HasFounds(request))
return BadRequest(string.Format("There are no founds to approve the payment."));
using (var txn = await DbContext.Database.BeginTransactionAsync())
{
try
{
var paymentTxn = new PaymentTransaction
{
PaymentTransactionID = Guid.NewGuid(),
CreditCardID = creditCard.CreditCardID,
ConfirmationID = Guid.NewGuid(),
Amount = request.Amount,
PaymentDateTime = DateTime.Now
};
DbContext.PaymentTransactions.Add(paymentTxn);
creditCard.AvailableFounds -= request.Amount;
await DbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
txn.Commit();
Logger?.LogInformation("The payment for card with last 4 digits: '{0}' was successfully. Confirmation #: {1}", last4Digits, paymentTxn.ConfirmationID);
var response = new PaymentResponse
{
ConfirmationID = paymentTxn.ConfirmationID,
PaymentDateTime = paymentTxn.PaymentDateTime,
Last4Digits = creditCard.Last4Digits
};
return Ok(response);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger?.LogCritical("There was an error on '{0}': {1}", nameof(PostPaymentAsync), ex);
txn.Rollback();
return new ObjectResult(ex.Message)
{
StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError
};
}
}
}
}
}
Payment request:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace RothschildHouse.Requests
{
public class PostPaymentRequest
{
public PostPaymentRequest()
{
}
[Required]
[StringLength(30)]
public string CardHolderName { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(20)]
public string IssuingNetwork { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(20)]
public string CardNumber { get; set; }
[Required]
public DateTime? ExpirationDate { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(4)]
public string Cvv { get; set; }
[Required]
[Range(0.0, 10000.0)]
public decimal? Amount { get; set; }
}
}
Chapter 06 - Online Store Identity
This solution implements Identity Server as authentication and authorization API.
This guide implements in-memory configuration for Identity Server.
This implementation for Identity Server doesn't have any value in real life, if do You want to apply Identity Server in real life, remove in-memory configuration and replace it with database store.
Identity API for Online Store runs on port 56000.
In order to allow connections, We need to add configuration for API resources and clients, this configuration is in Config class:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Security.Claims;
using IdentityModel;
using IdentityServer4.Models;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Identity
{
public static class Config
{
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources()
=> new List<ApiResource>
{
new ApiResource("OnlineStoreAPI", "Online Store API")
{
ApiSecrets =
{
new Secret("Secret1")
}
}
};
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients()
=> new List<Client>
{
new Client
{
ClientId = "OnlineStoreAPI.Client",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword,
ClientSecrets =
{
new Secret("OnlineStoreAPIClientSecret1".Sha256())
},
AllowedScopes =
{
"OnlineStoreAPI"
},
Claims =
{
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Administrator"),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Customer"),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "WarehouseManager"),
new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Role, "WarehouseOperator")
}
}
};
}
}
Also We need to add the configuration for services in Identity Server API Startup class:
using IdentityServer4.Services;
using IdentityServer4.Validation;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using OnlineStore.API.Identity.Domain;
using OnlineStore.API.Identity.Services;
using OnlineStore.API.Identity.Validation;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Identity
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc()
.SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
services
.AddDbContext<IdentityDbContext>(options => options.UseInMemoryDatabase("Identity"));
services
.AddTransient<IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator, ResourceOwnerPasswordValidator>()
.AddTransient<IProfileService, ProfileService>();
services
.AddIdentityServer()
.AddDeveloperSigningCredential()
.AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources())
.AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients());
services
.AddAuthentication()
.AddIdentityServerAuthentication();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
var authDbContext = app
.ApplicationServices
.CreateScope()
.ServiceProvider
.GetService<IdentityDbContext>();
authDbContext.SeedInMemory();
app.UseIdentityServer();
}
}
}
As You know, We're working with in-memory configurations, these configurations apply for DbContext.
To handle authentication and autorization, there are two entities: User and UserClaim.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Identity.Domain
{
public class IdentityDbContext : DbContext
{
public IdentityDbContext(DbContextOptions<IdentityDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; }
public DbSet<UserClaim> UserClaims { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder
.Entity<User>(builder => builder.HasKey(e => e.UserID));
modelBuilder
.Entity<UserClaim>(builder => builder.HasKey(e => e.UserClaimID));
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
OnlineStore doesn't use Repository and Unit of Work design patterns anymore, the replacement for these design patterns is to have extension methods for DbContext class, later I'll explain this point with examples.
This is the code for AuthDbContextExtentions class:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using IdentityModel;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Identity.Domain
{
public static class IdentityDbContextExtentions
{
public static bool ValidatePassword(this IdentityDbContext dbContext, string userName, string password)
{
var user = dbContext.Users.FirstOrDefault(item => item.Email == userName);
if (user == null)
return false;
if (user.Password == password.ToSha256())
return true;
return false;
}
public static User GetUserByUserName(this IdentityDbContext dbContext, string userName)
=> dbContext.Users.FirstOrDefault(item => item.Email == userName);
public static User GetUserByID(this IdentityDbContext dbContext, string id)
=> dbContext.Users.FirstOrDefault(item => item.UserID == id);
public static IEnumerable<UserClaim> GetUserClaimsByUserID(this IdentityDbContext dbContext, string userID)
=> dbContext.UserClaims.Where(item => item.UserID == userID);
public static void SeedInMemory(this IdentityDbContext dbContext)
{
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("1000", "erik.lehnsherr@outlook.com", "magneto".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "1000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "eriklehnsherr"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Administrator"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "erik.lehnsherr@outlook.com"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.GivenName, "Erik"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.MiddleName, "M"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "1000", JwtClaimTypes.FamilyName, "Lehnsherr")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("2000", "charlesxavier@gmail.com", "professorx".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "2000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "charlesxavier"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Administrator"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "charlesxavier@gmail.com"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.GivenName, "Charles"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.MiddleName, "F"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "2000", JwtClaimTypes.FamilyName, "Xavier")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("3000", "jameslogan@walla.com", "wolverine".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "3000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "jameslogan"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Customer"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "jameslogan@walla.com"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.GivenName, "James"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.MiddleName, ""),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "3000", JwtClaimTypes.FamilyName, "Logan")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("4000", "ororo_munroe@yahoo.com", "storm".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "4000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "ororo_munroe"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "Customer"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "ororo_munroe@yahoo.com"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.GivenName, "Ororo"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.MiddleName, ""),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "4000", JwtClaimTypes.FamilyName, "Munroe")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("5000", "warehousemanager1@onlinestore.com", "password1".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "5000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "5000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "5000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "warehousemanager1"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "5000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "WarehouseManager"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "5000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "warehousemanager1@onlinestore.com")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
dbContext.Users.Add(new User("6000", "warehouseoperator1@onlinestore.com", "password1".ToSha256(), true));
dbContext.UserClaims.AddRange(
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "6000", JwtClaimTypes.Subject, "6000"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "6000", JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, "warehouseoperator1"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "6000", JwtClaimTypes.Role, "WarehouseOperator"),
new UserClaim(Guid.NewGuid(), "6000", JwtClaimTypes.Email, "warehouseoperator1@onlinestore.com")
);
dbContext.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
All actions in OnlineStore APIs need to get token from Identity API.
Chapter 07 - APIs
There are three projects:
OnlineStore.API.CommonOnlineStore.API.SalesOnlineStore.API.Warehouse
All of these projects contain a reference to OnlineStore.Core project.
Clients for Payment Gateway
Payment Gateway provides two APIs, one for authentication and other for payment, in order to perform payment requests there are two clients for Rothschild House.
Code for RothschildHouseIdentityClient class:
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityModel.Client;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Contracts;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
public class RothschildHouseIdentityClient : IRothschildHouseIdentityClient
{
private readonly RothschildHouseIdentitySettings Settings;
public RothschildHouseIdentityClient(IOptions<RothschildHouseIdentitySettings> settings)
{
Settings = settings.Value;
}
public async Task<TokenResponse> GetRothschildHouseTokenAsync()
{
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
var disco = await client.GetDiscoveryDocumentAsync(Settings.Url);
return await client.RequestPasswordTokenAsync(new PasswordTokenRequest
{
Address = disco.TokenEndpoint,
ClientId = Settings.ClientId,
ClientSecret = Settings.ClientSecret,
UserName = Settings.UserName,
Password = Settings.Password
});
}
}
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
}
Code for RothschildHousePaymentClient class:
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using IdentityModel.Client;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Models;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
public class RothschildHousePaymentClient : IRothschildHousePaymentClient
{
private readonly RothschildHousePaymentSettings Settings;
private readonly ApiUrl apiUrl;
public RothschildHousePaymentClient(IOptions<RothschildHousePaymentSettings> settings)
{
Settings = settings.Value;
apiUrl = new ApiUrl(baseUrl: Settings.Url);
}
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> PostPaymentAsync(TokenResponse token, PostPaymentRequest request)
{
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
return await client.PostAsync(
apiUrl.Controller("Transaction").Action("Payment").ToString(),
request.GetStringContent()
);
}
}
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
}
Sales API
Let's take a look on SalesController class:
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Models;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Controllers;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Filters;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Responses;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.Requests;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.Security;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Contracts;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Sales.Controllers
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
[Route("api/v1/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class SalesController : OnlineStoreController
{
readonly ILogger Logger;
readonly IRothschildHouseIdentityClient RothschildHouseIdentityClient;
readonly IRothschildHousePaymentClient RothschildHousePaymentClient;
readonly ISalesService SalesService;
public SalesController(ILogger<SalesController> logger, IRothschildHouseIdentityClient rothschildHouseIdentityClient, IRothschildHousePaymentClient rothschildHousePaymentClient, ISalesService salesService)
: base()
{
Logger = logger;
RothschildHouseIdentityClient = rothschildHouseIdentityClient;
RothschildHousePaymentClient = rothschildHousePaymentClient;
SalesService = salesService;
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
[HttpGet("order")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetOrdersAsync([FromQuery]GetOrdersRequest request)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(GetOrdersAsync));
var response = await SalesService
.GetOrdersAsync(request.PageSize, request.PageNumber, request.OrderStatusID, request.CustomerID, request.EmployeeID, request.ShipperID, request.CurrencyID, request.PaymentMethodID);
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
[HttpGet("order/{id}")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(404)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetOrderAsync(long id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(GetOrderAsync));
var response = await SalesService.GetOrderAsync(id);
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
[HttpGet("order-model")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
[Authorize(Policy = Policies.CustomerPolicy)]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetPostOrderModelAsync()
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(GetPostOrderModelAsync));
var response = await SalesService.GetCreateOrderRequestAsync();
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
[HttpPost("order")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(400)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
[Authorize(Policy = Policies.CustomerPolicy)]
public async Task<IActionResult> PostOrderAsync([FromBody]PostOrderRequest request)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(PostOrderAsync));
var token = await RothschildHouseIdentityClient
.GetRothschildHouseTokenAsync();
if (token.IsError)
return Unauthorized();
var paymentRequest = request.GetPostPaymentRequest();
var paymentHttpResponse = await RothschildHousePaymentClient
.PostPaymentAsync(token, paymentRequest);
if (!paymentHttpResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode)
return BadRequest();
var paymentResponse = await paymentHttpResponse
.GetPaymentResponseAsync();
var entity = request.GetHeader();
entity.CreationUser = UserInfo.UserName;
var response = await SalesService
.CreateOrderAsync(entity, request.GetDetails().ToArray());
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
[HttpGet("order/{id}/clone")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
[Authorize(Policy = Policies.CustomerPolicy)]
public async Task<IActionResult> CloneOrderAsync(int id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(CloneOrderAsync));
var response = await SalesService.CloneOrderAsync(id);
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
[HttpDelete("order/{id}")]
[ProducesResponseType(200)]
[ProducesResponseType(401)]
[ProducesResponseType(403)]
[ProducesResponseType(404)]
[ProducesResponseType(500)]
[OnlineStoreActionFilter]
[Authorize(Policy = Policies.CustomerPolicy)]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteOrderAsync(int id)
{
Logger?.LogDebug("{0} has been invoked", nameof(DeleteOrderAsync));
var response = await SalesService.CancelOrderAsync(id);
return response.ToHttpResult();
}
}
}
ViewModel versus Request
ViewModel is an object that contains behavior, request is the action related to invoke a Web API method, this is the misunderstood: ViewModel is an object linked to a view, contains behavior to handle changes and sync up with view; usually the parameter for Web API method is an object with properties, so this definition is named Request; MVC is not MVVM, the life's cycle for model is different in those patterns, this definition doesn't keep state between UI and API, also the process to set properties values in request from query string is handled by a model binder.
Settings
To provide settings for API, first We need to define configurations in appsettings.json file:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"OnlineStore": "server=(local);database=OnlineStore;integrated security=yes;MultipleActiveResultSets=True;"
},
"IdentityServerSettings": {
"Authority": "http://localhost:5100",
"RequireHttpsMetadata": false,
"ApiName": "OnlineStoreAPI",
"ApiSecret": "Secret1"
},
"OnlineStoreIdentityClientSettings": {
"Url": "http://localhost:5100",
"ClientId": "OnlineStoreAPI.Client",
"ClientSecret": "OnlineStoreAPIClientSecret1",
"UserName": "",
"Password": ""
},
"RothschildHouseIdentitySettings": {
"Url": "http://localhost:18000",
"ClientId": "onlinestoreclient",
"ClientSecret": "onlinestoreclientsecret1",
"UserName": "administrator@onlinestore.com",
"Password": "onlinestore1"
},
"RothschildHousePaymentSettings": {
"Url": "http://localhost:19000"
}
}
Then take a look on Startup.cs class:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Reflection;
using IdentityServer4.AccessTokenValidation;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.Clients.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.PolicyRequirements;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.Security;
using OnlineStore.Core;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Contracts;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain;
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Sales
{
#pragma warning disable CS1591
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services
.AddMvc()
.SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2)
.AddJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.SerializerSettings.ReferenceLoopHandling = ReferenceLoopHandling.Ignore;
});
services.AddDbContext<OnlineStoreDbContext>(builder =>builder.UseSqlServer(Configuration["ConnectionStrings:OnlineStore"]));
services.AddScoped<IUserInfo, UserInfo>();
services.AddScoped<ILogger, Logger<Service>>();
services.Configure<RothschildHouseIdentitySettings>(Configuration.GetSection("RothschildHouseIdentitySettings"));
services.AddSingleton<RothschildHouseIdentitySettings>();
services.Configure<RothschildHousePaymentSettings>(Configuration.GetSection("RothschildHousePaymentSettings"));
services.AddSingleton<RothschildHousePaymentSettings>();
services.AddScoped<IRothschildHouseIdentityClient, RothschildHouseIdentityClient>();
services.AddScoped<IRothschildHousePaymentClient, RothschildHousePaymentClient>();
services.AddScoped<ISalesService, SalesService>();
services
.AddMvcCore()
.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy(Policies.CustomerPolicy, builder =>
{
builder.Requirements.Add(new CustomerPolicyRequirement());
});
});
services
.AddAuthentication("Bearer")
.AddIdentityServerAuthentication(options =>
{
var settings = new IdentityServerAuthenticationOptions();
Configuration.Bind("IdentityServerSettings", settings);
options.Authority = settings.Authority;
options.RequireHttpsMetadata = settings.RequireHttpsMetadata;
options.ApiName = settings.ApiName;
options.ApiSecret = settings.ApiSecret;
});
services.AddSwaggerGen(options =>
{
options.SwaggerDoc("v1", new Info { Title = "Online Store Sales API", Version = "v1" });
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
options.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseCors(builder =>
{
builder
.WithOrigins("http://localhost:4200")
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowAnyMethod()
;
});
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(options => options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "Online Store Sales API"));
app.UseMvc();
}
}
#pragma warning restore CS1591
}
This class it's the configuration point for Web API project, in this class there is the configuration for dependency injection, API's configuration and another settings.
For API project, these are the routes for controllers:
| Verb | Route | Description |
| GET | api/v1/Sales/order | Gets orders |
| GET | api/v1/Sales/order/5 | Gets an order by id |
| GET | api/v1/Sales/order-model | Gets model to create order |
| GET | api/v1/Sales/order/5/clone | Clones an existing order |
| POST | api/v1/Sales/order | Creates a new order |
| DELETE | api/v1/Sales/order/5 | Deletes an existing order |
There is a v1 in each route, this is because the version for API is 1 and that value is defined in Route attribute for controllers in API project.
Chapter 08 - Help Page for API
API uses Swagger to show a help page.
The following package is required to show a help page with Swagger:
The configuration for Swagger is located in Startup class, addition for Swagger is in ConfigureServices method:
services.AddSwaggerGen(options =>
{
options.SwaggerDoc("v1", new Info { Title = "Online Store Sales API", Version = "v1" });
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
options.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
});
The configuration for endpoint is in Configure method:
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(options => options.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "Online Store Sales API"));
Swagger allows to show description for actions in controllers, these descriptions are taken from xml comments.
Help Page:
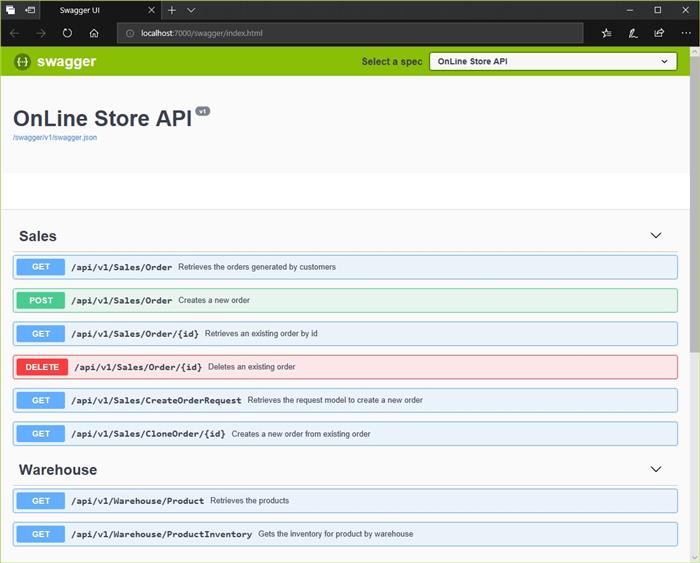
Models Section in Help Page:

Help Page for API it's a good practice, because provides information about API for clients.
Chapter 09 - Unit Tests for API
Now We proceed to explain unit tests for API project, these tests work with in-memory database, what is the difference between unit tests and integration tests? for unit tests We simulate all dependencies for Web API project and for integration tests We run a process that simulates Web API execution. I mean a simulation of Web API (accept Http requests), obviously there is more information about unit tests and integration tests but at this point this basic idea is enough.
What is TDD? Testing is important in these days, because with unit tests it's easy to performing tests for features before to publish, Test Driven Development is the way to define tests and validate the behavior in code.
Another concept linked to TDD is AAA: Arrange, Act and Assert is a pattern for arranging and formatting code in test methods.
- Arrange: is the block for creation of objects
- Act: is the block to place all invocations for methods
- Assert: is the block to validate the results from methods invocation
Let's take a look for SalesControllerTests class:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.UnitTests.Mocks;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.Controllers;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.Requests;
using OnlineStore.API.Sales.UnitTests.Mocks;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Requests;
using OnlineStore.Core.Business.Responses;
using OnlineStore.Core.Domain.Sales;
using Xunit;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Sales.UnitTests
{
public class SalesControllerTests
{
[Fact]
public async Task TestSearchOrdersAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestSearchOrdersAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var request = new GetOrdersRequest();
var response = await controller.GetOrdersAsync(request) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as IPagedResponse<OrderInfo>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestSearchOrdersByCurrencyAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestSearchOrdersByCurrencyAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var request = new GetOrdersRequest
{
CurrencyID = "USD"
};
var response = await controller.GetOrdersAsync(request) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as IPagedResponse<OrderInfo>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
Assert.True(value.Model.Count(item => item.CurrencyID == request.CurrencyID) == value.Model.Count());
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestSearchOrdersByCustomerAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestSearchOrdersByCustomerAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var request = new GetOrdersRequest
{
CustomerID = 1
};
var response = await controller.GetOrdersAsync(request) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as IPagedResponse<OrderInfo>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
Assert.True(value.Model.Count(item => item.CustomerID == request.CustomerID) == value.Model.Count());
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestSearchOrdersByEmployeeAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestSearchOrdersByEmployeeAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var request = new GetOrdersRequest
{
EmployeeID = 1
};
var response = await controller.GetOrdersAsync(request) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as IPagedResponse<OrderInfo>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
Assert.True(value.Model.Count(item => item.EmployeeID == request.EmployeeID) == value.Model.Count());
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestGetOrderAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestGetOrderAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var id = 1;
var response = await controller.GetOrderAsync(id) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestGetNonExistingOrderAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestGetNonExistingOrderAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var id = 0;
var response = await controller.GetOrderAsync(id) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestGetCreateOrderRequestAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestGetCreateOrderRequestAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var response = await controller.GetPostOrderModelAsync() as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as ISingleResponse<CreateOrderRequest>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestPostOrderAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestPostOrderAsync), true);
var identityClient = new MockedRothschildHouseIdentityClient();
var paymentClient = new MockedRothschildHousePaymentClient();
var controller = new SalesController(null, identityClient, paymentClient, service);
var request = new PostOrderRequest
{
ID = 2,
CustomerID = 1,
PaymentMethodID = new Guid("7671A4F7-A735-4CB7-AAB4-CF47AE20171D"),
CurrencyID = "USD",
Comments = "Order from unit tests",
Details = new List<OrderDetailRequest>
{
new OrderDetailRequest
{
ID = 2,
ProductID = 1,
Quantity = 1
}
}
};
var response = await controller.PostOrderAsync(request) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
Assert.True(value.Model.ID.HasValue);
}
[Fact]
public async Task TestCloneOrderAsync()
{
var userInfo = IdentityMocker.GetCustomerIdentity().GetUserInfo();
var service = ServiceMocker.GetSalesService(userInfo, nameof(TestCloneOrderAsync), true);
var controller = new SalesController(null, null, null, service);
var id = 1;
var response = await controller.CloneOrderAsync(id) as ObjectResult;
var value = response.Value as ISingleResponse<OrderHeader>;
Assert.False(value.DidError);
}
}
}
IdentityMocker class provides user identities, GetUserInfo extension method returns an implementation of IUserInfo interface that contains information for authenticated user.
Chapter 10 - Integration Tests for API
As We did with unit tests, integration tests should be created according to Web API, so let's choose SalesController to explain the model for integration tests.
Now, this is the code for SalesTests class:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.IntegrationTests;
using OnlineStore.API.Common.IntegrationTests.Helpers;
using Xunit;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Sales.IntegrationTests
{
public class SalesTests : IClassFixture<TestFixture<Startup>>
{
readonly HttpClient Client;
public SalesTests(TestFixture<Startup> fixture)
{
Client = fixture.Client;
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetOrdersAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order?pageSize=10&pageNumber=1"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetOrdersByCurrencyAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order?pageSize=10&pageNumber=1¤cyID=1"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task SearchOrdersByCustomerAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetOrdersByEmployeeAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order?employeeId=1"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetOrderByIdAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order/1"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetOrderByNonExistingIdAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order/0"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
Assert.True(response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetPostOrderRequestAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order-model"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task GetPlaceOrderRequestAsWarehouseOperatorAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWarehouseOperatorAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order-model"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
Assert.True(response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Forbidden);
}
[Fact]
public async Task PlaceOrderAsCustomerAsync()
{
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order",
Body = new
{
UserName = "jameslogan@walla.com",
Password = "wolverine",
CardHolderName = "James Logan",
IssuingNetwork = "Visa",
CardNumber = "4024007164051145",
ExpirationDate = new DateTime(2024, 6, 1),
Cvv = "987",
Total = 29.99m,
CustomerID = 1,
CurrencyID = "USD",
PaymentMethodID = new Guid("7671A4F7-A735-4CB7-AAB4-CF47AE20171D"),
Comments = "Order from integration tests",
Details = new[]
{
new
{
ProductID = 1,
Quantity = 1
}
}
}
};
var token = await TokenHelper
.GetOnlineStoreTokenAsync(request.Body.UserName, request.Body.Password);
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client
.PostAsync(request.Url, ContentHelper.GetStringContent(request.Body));
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
[Fact]
public async Task CloneOrderAsCustomerAsync()
{
var token = await TokenHelper.GetTokenForWolverineAsync();
var request = new
{
Url = "/api/v1/Sales/order/1/clone"
};
Client.SetBearerToken(token.AccessToken);
var response = await Client.GetAsync(request.Url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
}
}
}
IdentityServerHelper class provides static methods to retrieve valid tokens.
SetBearerToken is an extension method that allows to set an authorization header with a bearer token.
As We can see those methods perform tests for Urls in Web API project, please note that all tests are async methods.
Don't forget We can have more tests, We have another project to have tests for Warehouse API.
To run integration tests, We need to run the following APIs: payment gateway, identity and Online store APIs.
In order to work with integration tests, We need to create a class to provide a Web Host to performing Http behavior, this class it will be TestFixture and to represent Http requests for Web API, there is a class with name SalesTests, this class will contains all requests for defined actions in SalesController class, but using a mocked Http client.
Code for TestFixture class:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Reflection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationParts;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Controllers;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ViewComponents;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.TestHost;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace OnlineStore.API.Common.IntegrationTests
{
public class TestFixture<TStartup> : IDisposable
{
public static string GetProjectPath(string projectRelativePath, Assembly startupAssembly)
{
var projectName = startupAssembly.GetName().Name;
var applicationBasePath = AppContext.BaseDirectory;
var directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(applicationBasePath);
do
{
directoryInfo = directoryInfo.Parent;
var projectDirectoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(Path.Combine(directoryInfo.FullName, projectRelativePath));
if (projectDirectoryInfo.Exists)
if (new FileInfo(Path.Combine(projectDirectoryInfo.FullName, projectName, $"{projectName}.csproj")).Exists)
return Path.Combine(projectDirectoryInfo.FullName, projectName);
}
while (directoryInfo.Parent != null);
throw new Exception($"Project root could not be located using the application root {applicationBasePath}.");
}
private TestServer Server;
public TestFixture()
: this(Path.Combine(""))
{
}
public HttpClient Client { get; }
public void Dispose()
{
Client.Dispose();
Server.Dispose();
}
protected virtual void InitializeServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
var startupAssembly = typeof(TStartup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
var manager = new ApplicationPartManager
{
ApplicationParts =
{
new AssemblyPart(startupAssembly)
},
FeatureProviders =
{
new ControllerFeatureProvider(),
new ViewComponentFeatureProvider()
}
};
services.AddSingleton(manager);
}
protected TestFixture(string relativeTargetProjectParentDir)
{
var startupAssembly = typeof(TStartup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
var contentRoot = GetProjectPath(relativeTargetProjectParentDir, startupAssembly);
var configurationBuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(contentRoot)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json");
var webHostBuilder = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseContentRoot(contentRoot)
.ConfigureServices(InitializeServices)
.UseConfiguration(configurationBuilder.Build())
.UseEnvironment("Development")
.UseStartup(typeof(TStartup));
Server = new TestServer(webHostBuilder);
Client = Server.CreateClient();
Client.BaseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:5001");
Client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();
Client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
}
}
}
Code Improvements
- Save logs to text file
- Implement Money Pattern to represent money in application
- Add a section to explain why this solution doesn't implement Repository and Unit of Work design patterns
Related Links
Points of Interest
- In this article, We're working with
Entity Framework Core. Entity Framework Core has in-memory database.- Extension methods for
OnLineStoreDbContext class allow to us expose specific operations, in some cases We don't want to have GetAll, Add, Update or Remove operations. - Help page for Web API has been built with
Swagger. - Unit tests perform testing for Assemblies.
- Integration tests perform testing for Web Server.
- Unit and integration tests have been built with
xUnit framework. - Mocker is an object that creates an instance of object in testing.
History
- 12th December, 2016: Initial version
- 13th December, 2016: Addition of Business Layer
- 15th December, 2016: Addition of Mocker
- 31th December, 2016: Addition of Web API
- 5th January, 2017: Addition of Unit Tests for Web API
- 22th January, 2017: Addition of Change Log
- 4th February, 2017: Addition of Async Operations
- 15th May, 2017: Addition of Logs
- 29th October, 2017: Code Refactor, using of Service in Business Layer
- 10th February, 2018: Addition of exclusions for Change Log
- 28th May, 2018: Addition of Integration Tests for Web API
- 2nd October, 2018: Addition of in memory database for Unit Tests
- 25th November, 2018: Addition of Help Page for Web API
- 27th November, 2018: Addition of Related Links section
- 16th January, 2019: Addition of Identity Server
- 23th January, 2019: Addition of Payment Gateway
- 10th February, 2019: Addition of Clients for Payment Gateway
- 9th February, 2020: Addition of microservices architecture
