Introduction
The attached .NET library UziSecureSmtpClient allows you to send secure email from your .NET application. The class library is written in C# for .NET framework. This library was developed for MM Interplast. MM Interplast is a Myanmar based manufacturer providing customized PET preforms, HDPE closures and containers for the food, beverage and consumer industry produced on state of the art equipment. The library was developed because the current Microsoft Visual Studio SmtpClient class does not support implicit SSL connection security. It is important to note that using implicit SSL to communicate with the mail server implies that everything including the plain text password is encrypted between your computer and the mail server provider. The library was tested by sending mail messages using the following email server provides: Gmail, Yahoo, ATT, Rogers, HostGator and Network Solutions.
Version 2.0 supports subject line with non ASCII characters.
The class library supports three types of outgoing email servers.
- Gmail: Connection security is SSL/TLS. Authentication method is OAuth2. For GMAIL, the outgoing host server is smtp.gmail.com and outgoing port is 465.
- Servers such as Yahoo, ATT and Rogers: Connection security is SSL/TLS. The authentication method is plain text password. However, the password is encrypted as all other parts of the email message by SSL. Outgoing port number is normally is 465.
- Servers with no connection security and plain text password. Outgoing port number is 587.
Authentication method OAuth2 was only tested with Gmail. In order to use OAuth2, one needs to create a refresh token file. Step 2 below describes the creation process for Gmail. I do not know if other providers of OAuth2 authentication outgoing email use the same process. I suspect that GmailRefreshToken program will have to be modified or rewritten.
Email message format is described in Wikipedia MIME entry. MIME is specified in six linked RFC memoranda: RFC 2045, RFC 2046, RFC 2047, RFC 4288, RFC 4289 and RFC 2049; with the integration with SMTP email specified in detail in RFC 1521 and RFC 1522.
Step 1- Email Account
Create an email account for your outgoing mail. Add it to your email program and make sure you can send and receive emails. Make note of the outgoing server settings:
- Host or server name
- Port
- User name
- User password
- Authentication method
- Connection Security
Step 2- Demo Folder
Create a new folder for testing the software. Extract the five files from the demo zip file into this folder.
- GMailRefreshToken.exe
- UziSecureSmtpClient.dll
- TestSecureSmtpClient.exe
- EmailImage.png
- Rfc2045.pdf
Step 3- Create Authentication Refresh Token File (Only for Gmail)
If your email provider is not Gmail, skip this step.
Step 3A- Create a Client ID Token File
- Go to the link: https://console.developers.google.com/apis/
- If you are not logged into Google, it will ask you to login. Login with your Gmail account.
- Select on the left the API manager Library tab.
- Select Gmail API under Google Apps APIs.
- Select on the left Credentials under API Manager.
- Click on Create credentials combo-box.
- Select OAuth Client ID.
- Under Application type, select Other.
- Change the Name to your email application.
- Click on Create.
- You will see OAuth Client box with Client ID and Client Secret random text data.
- Click OK.
- You will see a one line table with your OAuth 2.0 client ID.
- At the end of this line, there is a down arrow icon. If you put the cursor on the icon, it will say Download JSON.
- Click on this icon.
- The browser will let you save a JSON file. Save the file to the demo folder from step 2. The default name is very long. You can change the name to a shorter name (i.e., SecureSmtpClientIDToken.json).
Step 3B- Create Refresh Token File
- Run the GMailRefreshToken.exe program.
- Click on the Browse button.
- Find the JSON file that you saved in the demo folder (step 3A above). Click Open. The name will be displayed in the Gmail API Client ID text box.
- Type the user email address into the Email address box.
- Press Create Refresh Token button.
- You will see a message box on the screen Email Authorization. Click OK.
- Your default browser will open or a new tab will be added to your open browser.
- You will need to log into your email account.
- After login, you will see a message asking permission to View and manage your email.
- Click Allow.
- The browser screen will turn blue and will ask you to close the tab. And at the same time, you will get a Save Refresh Token File dialog box.
- Save the SecureSmtpRefreshToken.xml file to your demo folder.
Step 4- Run the Demo Program
I strongly recommend running the demo program TestSecureSmtpClient.exe before starting programming. You want to be sure that the class library will work with your email service. The demo program will send an email consisting of two alternate views, plain text and HTML and two attachments. One attachment is a file for the recipient of the email and the other is inline image to be part of the HTML view. The two attachments are part of your demo folder. The email content can be viewed in the TestSecureSmtpClient.cs source. The text was taken out of one of the RFC documents associated with the MIME standard.
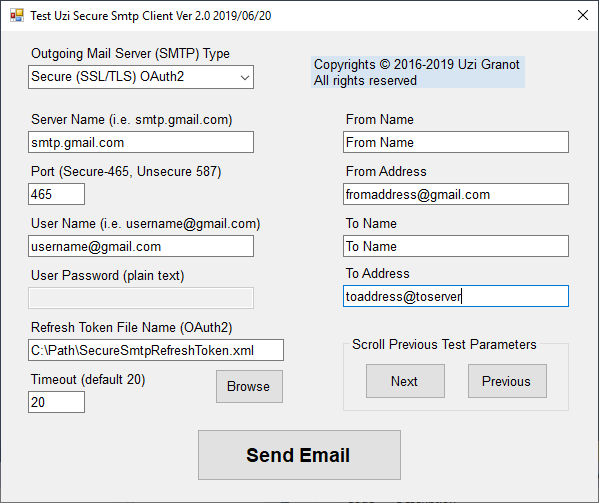
To run the demo program, start TestSecureSmtpClient.exe. Select the type of email server. Fill the relevant information. For Gmail, browse to the demo folder and select the SecureSmtpRefreshToken.xml file. And press Send Email. If the mail was sent, you will see "Email was successfully sent". Otherwise you will see an error message.
If there is a problem, load the source to Visual Studio and run it in debug mode. The process is being traced in the output view pane.
If you are successful, you are ready to integrate the class library to your code.
Step 5- Send Email From Your .NET Application
To use the library, you need to add a reference to the attached UziSecureSmtpClient.dll class library file. In each source file that references the library, you need to add a using UziSecureSmtpClient statement. The library UziSecureSmtpClient.dll must be included with your distribution. Alternatively, you can include the source code of the library with your application and avoid the need to distribute a separate data link library (dll) file. The software was developed with Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2013. The target .NET Framework was set to 4.5.
A typical email message has a subject line, from address and a list of to, cc or bcc addresses and a message body. Message body is made of parts. The parts are organized as a tree. Plain text content, HTML content and attachments are leaf nodes. If there is more than one part, the parts are divided by boundaries. This library supports three types of boundaries: mixed, alternate and related. The Wikipedia MIME entry describes these boundaries. Boundaries are parts. Boundaries can have children. Example three below shows how to create all of these parts and link them together to create a message tree.
The SecureSmtpClient class object is reusable. It is an advantage for an application sending multiple emails using GMail. The Gmail refresh token file never expires. When a SecureSmtpClient class object is being created, the software creates internally an authorization token that is valid for one hour. If the SecureSmtpClient object is reused for a long time, the software will request a new authorization token once an hour. All of this is transparent to your application. The advantage to you is a small gain in performance. If you create a new SecureSmtpClient for each mail, the software has to request a new authorization token for each mail message. If you reuse the SecureSmtpClient for sending multiple mail messages, there is only one request for authorization per hour.
Below, you will find three examples of sending email.
Example One: Unsecure Network Connection and Plain Text Password
private void ExampleUnsecurePlainText
(
string Host,
string UserName,
string UserPassword,
string FromName,
string FromAddress,
string ToName,
string ToAddress,
string MessageSubject,
string MessageText
)
{
try
{
if(ConnectionUnsecurePlain == null) ConnectionUnsecurePlain =
new SecureSmtpClient(ConnectMethod.Secure, Host, UserName, UserPassword);
SecureSmtpMessage Message = new SecureSmtpMessage();
Message.Subject = MessageSubject;
Message.From = new MailAddress(FromAddress, FromName);
Message.To.Add(new MailAddress(ToAddress, ToName));
SecureSmtpContent PlainTextContent =
new SecureSmtpContent(ContentType.Plain, MessageText);
Message.RootPart = PlainTextContent;
ConnectionUnsecurePlain.SendMail(Message);
MessageBox.Show("Email was successfully sent");
}
catch (Exception Exp)
{
MessageBox.Show(Exp.Message);
}
return;
}
Example Two: Secure Network Connection and No Authentication
private void ExampleSecureHtml
(
string Host,
string UserName,
string UserPassword,
string FromName,
string FromAddress,
string ToName,
string ToAddress,
string MessageSubject,
string MessageHtml
)
{
try
{
if(ConnectionSecureHtml == null) ConnectionSecureHtml =
new SecureSmtpClient(ConnectMethod.Secure, Host, UserName, UserPassword);
SecureSmtpMessage Message = new SecureSmtpMessage();
Message.Subject = MessageSubject;
Message.From = new MailAddress(FromAddress, FromName);
Message.To.Add(new MailAddress(ToAddress, ToName));
SecureSmtpMultipart Related = new SecureSmtpMultipart(MultipartType.Related);
Message.RootPart = Related;
SecureSmtpContent HtmlContent = new SecureSmtpContent(ContentType.Html, MessageHtml);
Related.AddPart(HtmlContent);
SecureSmtpAttachment ImageAttachment =
new SecureSmtpAttachment(AttachmentType.Inline, "EmailImage.png", "IMAGE001");
ImageAttachment.MediaType = "image/png";
Related.AddPart(ImageAttachment);
ConnectionSecureHtml.SendMail(Message);
MessageBox.Show("Email was successfully sent");
}
catch (Exception Exp)
{
MessageBox.Show(Exp.Message);
}
return;
}
Example Three GMail: Secure Network Connection and Oauth2 Authentication
private void ExampleGMail
(
string Host,
string UserName,
string RefreshToken,
string FromName,
string FromAddress,
string ToName,
string ToAddress,
string MessageSubject,
string MessageHtml
)
{
try
{
if(ConnectionGMail == null) ConnectionGMail =
new SecureSmtpClient(Host, UserName, new SecureSmtpOAuth2(RefreshToken));
SecureSmtpMessage Message = new SecureSmtpMessage();
Message.Subject = MessageSubject;
Message.From = new MailAddress(FromAddress, FromName);
Message.To.Add(new MailAddress(ToAddress, ToName));
SecureSmtpMultipart Mixed = new SecureSmtpMultipart(MultipartType.Mixed);
Message.RootPart = Mixed;
SecureSmtpMultipart Alternative = new SecureSmtpMultipart(MultipartType.Alternative);
Mixed.AddPart(Alternative);
SecureSmtpContent PlainTextContent =
new SecureSmtpContent(ContentType.Plain, PlainTextView);
Alternative.AddPart(PlainTextContent);
SecureSmtpMultipart Related = new SecureSmtpMultipart(MultipartType.Related);
Alternative.AddPart(Related);
SecureSmtpContent HtmlContent = new SecureSmtpContent(ContentType.Html, HtmlView);
Related.AddPart(HtmlContent);
SecureSmtpAttachment ImageAttachment =
new SecureSmtpAttachment(AttachmentType.Inline, "EmailImage.png", "IMAGE001");
ImageAttachment.MediaType = "image/png";
Related.AddPart(ImageAttachment);
SecureSmtpAttachment PdfAttachment =
new SecureSmtpAttachment(AttachmentType.Attachment, "rfc2045.pdf");
Mixed.AddPart(PdfAttachment);
ConnectionGMail.SendMail(Message);
MessageBox.Show("Email was successfully sent");
}
catch (Exception Exp)
{
MessageBox.Show(Exp.Message);
}
return;
}
History
- 2017/03/01: Version 1.0 Original version
- 2019/06/20: Version 2.0 Support for subject line with non ASCII characters
