Introduction
This is a VB.NET class which updates WebBrowser control to use the latest version of the installed browser (Internet Explorer, Edge).
Background
If you need to load a webpage in your VB.NET WinForm or WPF app you have to use a WebBrowser control. The WebBrowser Control is - by default - stuck in IE 7 rendering mode . This happens whether you’re using the WebBrowser control in a WPF application or a WinForms app. You will notice that when your app loads a webpage and page does not look like what you expected! Another case is when you get a message that wants you to update your web browser (IE).
There are a couple of ways to override the default rendering behavior:
- Using the IE X-UA-Compatible Meta header
- Using Application specific FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION Registry Keys
If you control the content of the web page, the easiest way to provide latest versions of the IE rendering engine is by using the IE Edge mode header. This is when you apply option 1:
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
You can also specify version of IE:
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=10" />
I will show you how to apply the second method by using a VB.NET calss ( WebBrowserUpdater ) in your code.
Using the code
Public Class WebBrowserUpdater
Shared is64BitProcess As Boolean = (IntPtr.Size = 8)
Shared is64BitOperatingSystem As Boolean = is64BitProcess OrElse InternalCheckIsWow64()
<dllimport("kernel32.dll", callingconvention:="CallingConvention.Winapi)" setlasterror:="True,">_
Private Shared Function IsWow64Process(<[In]()> ByVal hProcess As IntPtr, <out()> ByRef wow64Process As Boolean) As <marshalas(unmanagedtype.bool)> Boolean
End Function
Public Shared Function InternalCheckIsWow64() As Boolean
If (Environment.OSVersion.Version.Major = 5 AndAlso Environment.OSVersion.Version.Minor >= 1) OrElse Environment.OSVersion.Version.Major >= 6 Then
Using p As Process = Process.GetCurrentProcess()
Dim retVal As Boolean
If Not IsWow64Process(p.Handle, retVal) Then
Return False
End If
Return retVal
End Using
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
Public Shared Function GetEmbVersion() As Integer
Dim ieVer As Integer = GetBrowserVersion()
If ieVer > 9 Then
Return ieVer * 1000 + 1
End If
If ieVer > 7 Then
Return ieVer * 1111
End If
Return 7000
End Function
Public Shared Sub FixBrowserVersion()
Dim appName As String = System.IO.Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location)
FixBrowserVersion(appName)
End Sub
Public Shared Sub FixBrowserVersion(ByVal appName As String)
FixBrowserVersion(appName, GetEmbVersion())
End Sub
Public Shared Sub FixBrowserVersion(ByVal appName As String, ByVal ieVer As Integer)
FixBrowserVersion_Internal("HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE", appName & Convert.ToString(".exe"), ieVer)
FixBrowserVersion_Internal("HKEY_CURRENT_USER", appName & Convert.ToString(".exe"), ieVer)
FixBrowserVersion_Internal("HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE", appName & Convert.ToString(".vshost.exe"), ieVer)
FixBrowserVersion_Internal("HKEY_CURRENT_USER", appName & Convert.ToString(".vshost.exe"), ieVer)
End Sub
Private Shared Sub FixBrowserVersion_Internal(ByVal root As String, ByVal appName As String, ByVal ieVer As Integer)
Try
If InternalCheckIsWow64() Then
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.SetValue(root & Convert.ToString("\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION"), appName, ieVer)
Else
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.SetValue(root & Convert.ToString("\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION"), appName, ieVer)
End If
Catch generatedExceptionName As Exception
MessageBox.Show("You have to be administrator to run start this process. Please close the software. Right click on the iGiftCard icon and select RUN AS ADMINISTRATOR .", "Administrator", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information, MessageBoxDefaultButton.Button1)
End Try
End Sub
Public Shared Function GetBrowserVersion() As Integer
Dim strKeyPath As String = "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer"
Dim ls As String() = New String() {"svcVersion", "svcUpdateVersion", "Version", "W2kVersion"}
Dim maxVer As Integer = 0
For i As Integer = 0 To ls.Length - 1
Dim objVal As Object = Microsoft.Win32.Registry.GetValue(strKeyPath, ls(i), "0")
Dim strVal As String = System.Convert.ToString(objVal)
If strVal IsNot Nothing Then
Dim iPos As Integer = strVal.IndexOf("."c)
If iPos > 0 Then
strVal = strVal.Substring(0, iPos)
End If
Dim res As Integer = 0
If Integer.TryParse(strVal, res) Then
maxVer = Math.Max(maxVer, res)
End If
End If
Next
Return maxVer
End Function
Since IE 8 Microsoft introduced registry entries that control browser behavior when a WebBrowser Control is embedded into applications. Many applications on your system use these registry values:
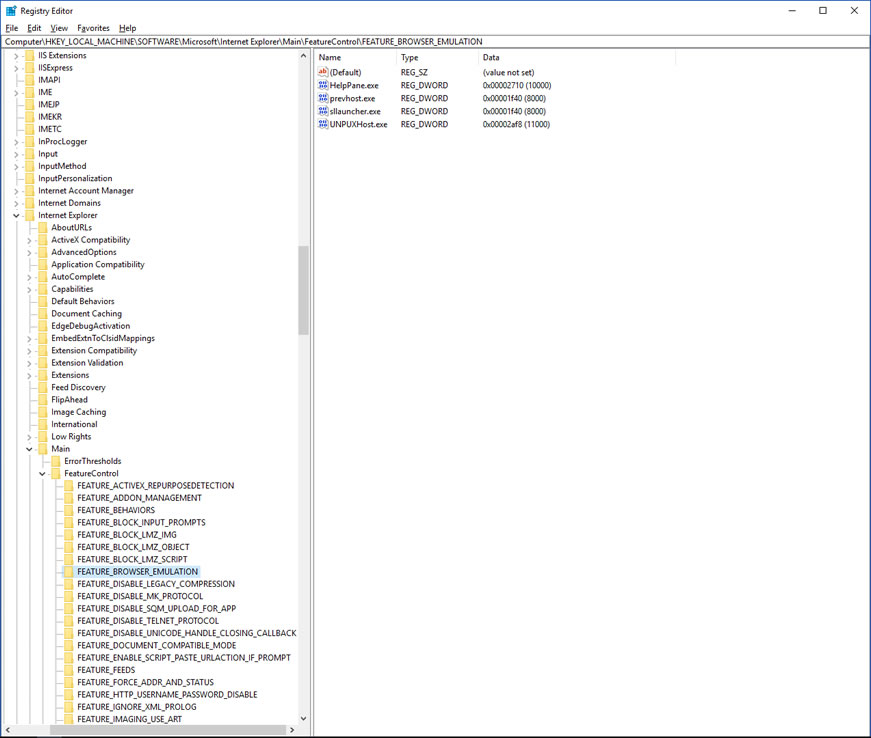
You can specify a registry with the name of your executable and specify the version of IE that you would like to load. The numbers are specified as 11000, 10000, 9000, 8000 and 7000.
The value specifies the IE version as follows:
The value to set this key to is (taken from MSDN) as decimal values:
11001 (0x2AF9)
Internet Explorer 11. Webpages are displayed in IE11 Standards mode, regardless of the !DOCTYPE directive.
11000 (0x2AF8)
Internet Explorer 11. Webpages containing standards-based !DOCTYPE directives are displayed in IE9 mode.
10001 (0x2AF7)
Internet Explorer 10. Webpages are displayed in IE10 Standards mode, regardless of the !DOCTYPE directive.
10000 (0x2710)
Internet Explorer 10. Webpages containing standards-based !DOCTYPE directives are displayed in IE9 mode.
9999 (0x270F)
Internet Explorer 9. Webpages are displayed in IE9 Standards mode, regardless of the !DOCTYPE directive.
9000 (0x2328)
Internet Explorer 9. Webpages containing standards-based !DOCTYPE directives are displayed in IE9 mode.
8888 (0x22B8)
Webpages are displayed in IE8 Standards mode, regardless of the !DOCTYPE directive.
8000 (0x1F40)
Webpages containing standards-based !DOCTYPE directives are displayed in IE8 mode.
7000 (0x1B58)
Webpages containing standards-based !DOCTYPE directives are displayed in IE7 Standards mode. This mode is kind of pointless since it's the default.
Setting these keys enables your applications to use the latest Internet Explorer versions on the host machine.
WebBrowserUpdater class does what you need in order to run your app by using the latest version of installed IE.
Points of Interest
WebBrowserUpdater has to figure out whether it's dealing with a 32-bit or a 64-bit app. This task is done by the following method:
Public Shared Function InternalCheckIsWow64() As Boolean
If (Environment.OSVersion.Version.Major = 5 AndAlso Environment.OSVersion.Version.Minor >= 1) OrElse Environment.OSVersion.Version.Major >= 6 Then
Using p As Process = Process.GetCurrentProcess()
Dim retVal As Boolean
If Not IsWow64Process(p.Handle, retVal) Then
Return False
End If
Return retVal
End Using
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION
And value setting is done here:
Private Shared Sub FixBrowserVersion_Internal(ByVal root As String, ByVal appName As String, ByVal ieVer As Integer)
Try
If InternalCheckIsWow64() Then
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.SetValue(root & Convert.ToString("\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION"), appName, ieVer)
Else
Microsoft.Win32.Registry.SetValue(root & Convert.ToString("\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION"), appName, ieVer)
End If
Catch generatedExceptionName As Exception
MessageBox.Show("You have to be administrator to run start this process. Please close the software. Right click on the iGiftCard icon and select RUN AS ADMINISTRATOR .", "Administrator", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information, MessageBoxDefaultButton.Button1)
End Try
End Sub
Use this class as shown below:
WebBrowserUpdater.FixBrowserVersion()
WebBrowserUpdater.FixBrowserVersion("AppName")
WebBrowserUpdater.FixBrowserVersion("AppName",IEVer)
Remember that IEVer must be one of the allowed values that I show you before.
Last by not the least. Since we set a registery value, and to avoid any errors, you will need to have elevated privileges in order to apply the changes. Add the following to your app manifist:
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
This code is compatible with .NET 2 through .NET 4.5. If you only use newest versions of .NET in your app then it is possible to shorten the process.
History
