We test-drive the latest version of Selenium using three different browsers, and automate the test case using the community edition of Visual Studio 2017 and C#.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Downloading Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition
- Creating a New Solution (and a Test Project)
- Creating a Test Case for Firefox Browser
- Adding Selenium/Firefox NuGet Packages
- Executing the Firefox Test Case
- Creating a Test Case for Chrome Browser
- Adding Selenium/Chrome Nuget Packages
- Executing the Chrome Test Case
- Creating a Test Case for Edge Browser
- Adding Selenium/Edge NuGet Packages
- Setting up the Edge Driver
- Executing the Edge Test Case
- Execute All Test Cases
- Conclusion
- History
In this article, we test-drive (no pun intendedJ) the latest version of Selenium (version 3.7.0 as of 11-30-2017) using the following browsers:
- Firefox
- Chrome
- MS Edge
For this exercise, we use the following test cases:
- Open Google homepage
- Enter a search term in the
textbox - Click the "Google Search" button
- Verify that the test results page is displayed
We automate the test case using the community edition of Visual Studio 2017 and C#. We write a separate test case for each of the browsers mentioned above. We purposely compartmentalized the instructions for creating the test cases, to experiment with them separately.
So, let us get started!
Downloading Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition
Download and install Visual Studio 2017 community edition (Skip ahead if you already have Visual Studio 2017 installed - any version will work).
Here is the link:
Creating a New Solution (and a Test Project)
Here are the steps for creating a test project.
- Open Visual Studio and create a new project. Click on ‘File’, select ‘New’, then select ‘Project…’
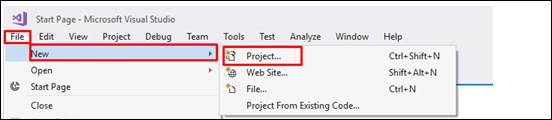
- From the “New Project” template, select ‘Visual C#’ on the left side of the pane, then select ‘Test’. On the right side, select “Unit Test project”.

- Select a name and location for your project and click “OK”.

Now that we created a ‘Test Project’, let us focus on creating a test case for Firefox.
- The unit test file is created with a default name “UnitTest1.cs”.

- Let us change the name to “GoogleSearch.cs”. The easiest way to rename the file is to right-click on “UnitTest1.cs” in solution explorer, and select rename.

- Click “Yes” for the dialog pop-up. This will rename both the file and the class. It is a best practice to give the same name to the class and the file containing it.

- Next, rename “
Method1” to “Should_Search_Using_Firefox”:

- After the rename, the method should look like the following:

Before we continue with the creation of the test case, let us add the required packages to the project:
Selenium.webdriverSelenium.SupportSelenium.Firefox.Webdriver
- Right-click on the project name in the solution explorer, then select ‘Manage NuGet Packages…’:

- From the NuGet window, make the following selections:
- Select “Browse".
- Type “selenium” in the search box.
- Select “Selenium.WebDriver” from the search results.
- Put a checkmark next to “Project’.
- Click “Install”.

- Follow the same process to install “Selenium.Support”:

- Again, follow the same process to install “
Selenium.Firefox.Webdriver”:

- Add a “
using” statement at the top of the test file, and create an instance of the Firefox driver, as shown below:

The complete code for the test case is shown below:
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Firefox;
namespace Selenium3_7_VisualStudio2017
{
[TestClass]
public class GoogleSearchEngineUsingFirefox
{
[TestMethod]
public void Shoud_Search_Using_Firefox()
{
using(var driver = new FirefoxDriver())
{
driver.Manage().Window.Maximize();
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("http://www.google.com");
var searchBox = driver.FindElementById("lst-ib");
searchBox.SendKeys("Automation using selenium 3.0 in C#");
var searchButton = driver.FindElementByName("btnK");
searchButton.Submit();
var searchResults = driver.FindElementById("resultStats");
}
}
}
}
Right-click on the test case in the test explorer, and select “Run Selected Tests”:
(You can also right-click inside the method itself, anywhere after line 13, for example):

Add a new test case, and give it a name: ‘Shoud_Search_Using_Chrome’.
Here is the complete code:
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
namespace Selenium3_7_VisualStudio2017
{
[TestClass]
public class GoogleSearchEngineUsingChrome
{
[TestMethod]
public void Shoud_Search_Using_Chrome()
{
using(var driver = new ChromeDriver())
{
driver.Manage().Window.Maximize();
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("http: //www.google.com");
var searchBox = driver.FindElementById("lst - ib");
searchBox.SendKeys("Automation using selenium 3.0 in C#");
var searchButton = driver.FindElementByName("btnK");
searchButton.Submit();
var searchResults = driver.FindElementById("resultStats");
}
}
}
}
The process for creating the test case for Chrome is very similar to that of Firefox. Basically, we use the NuGet manager to install the Chrome.Webdriver, and then we add a new test case. Here are the steps for installing the Chrome.Webdriver.
- Right-click on the project (or the solution)
- Select ‘Manage NuGet Packages for Solution…’
- Select ‘Browse’ from the NuGet window
- Enter ‘Selenium’ in the search box
- Select ‘Selenium.Chrome.Webdriver’ from the search results
- Click ‘Install’

Executing the Chrome Test Case
To execute the test case, right-click on the test case in the test explorer, then select “Run Selected Tests”. You can also right-click inside the method itself, anywhere after line 13, for example.
Add a new test case, and give it a name, such as ‘Shoud_Search_Using_EdgeBrowser’.
Here is the complete code for the test case:
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Edge;
namespace Selenium3_7_VisualStudio2017
{
[TestMethod]
public class GoogleSearchEngineUsingEdgeBrowser
{
string edgeDriverLocation = @ "C:\SeleniumEdgeDriver";
[TestMethod]
public void Shoud_Search_Using_EdgeBrowser()
{
using(var driver = new EdgeDriver(edgeDriverLocation))
{
driver.Manage().Window.Maximize();
driver.Navigate().GoToUrl("http://www.google.com");
driver.Manage().Timeouts().ImplicitWait = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10);
var searchBox = driver.FindElementById("lst-ib");
searchBox.SendKeys("Automation using selenium 3.0 in C#");
var searchButton = driver.FindElementByName("btnK");
searchButton.Submit();
var searchResults = driver.FindElementById("resultStats");
}
}
}
}
The process for creating the test case for Edge is very similar to that of Firefox and Chrome.
Basically, we start by using the NuGet manager to install the Edge.Webdriver. Here are the steps:
- Right-click on the project.
- Select ‘Manage NuGet Packages…’.
- Select ‘Browse’ from the NuGet window.
- Enter ‘Selenium’ in the search box.
- Select ‘Selenium.Webdriver.IEDriver’ from the search results.
- Click ‘Install’.

I run into 2 issues while creating the test case for the Edge browser.
- Installing the EdgeDriver
- Adding a timeout (10 seconds) just before locating the textbox (line 25 in the test case)
You may need to download the driver manually and place in a location that you need to reference in the test case. Here are the steps to get the edge driver to work correctly.
- Open the edge browser from your desktop.
- Click on the ellipses “…” at the top right of the browser.
- Click on “Settings”.

- Scroll to the bottom of the “Settings” window:

- Make note of the release number. In this case “
14393”. - Navigate to the following page: https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-edge/tools/webdriver/
- Note the release number, under the downloads section:

- Click on the “Release 14393” (i.e., select the correct release for the installed version of the browser).
- Save the “MicrosoftWebDriver.exe” to a location.
From the 'Test Explorer', right-click on the test case and select “Run Selected Tests”. You can also click inside the method itself, anywhere after line 13, for example.
If you implemented all test cases, right-click on the project name in the test explorer and select “Run Selected Tests”:

The results should look like the following. As a side note, notice that Edge execution is faster than Firefox and Chrome.

In this introductory article, we presented detailed steps for writing test cases for three browsers: Firefox, Chrome, and Edge. We used Selenium 3.7.0 and Visual Studio 2017 community edition/C# to write the test cases. We purposely provided separate instructions for each test case, to help beginners work through the process, one test case at a time.
- 30th November, 2017: Initial version
