How it Works
Let’s take a quick look at how the work is going to be done.
- Generating a customized token by each HTTP request.
- Pass it through request header (
x-access-token). - Server extracts the token from each request.
- Verify the custom token by regenerating in server.
- If token matches, then system checks the user permission from database.
- Otherwise, system will respond with status code of 403/404.
Prerequisites
It’s highly recommended to review these previous posts:
Let’s Get Started
Previously, we have created User table in database, now we need to create another table named ”UserAuthorization/Authorization”.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Authorization](
[Id] [int] NOT NULL,
[UserId] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[CanView] [bit] NULL,
[CanPost] [bit] NULL,
[CanPut] [bit] NULL,
[CanDelete] [bit] NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Authorization] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, _
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Add new Stored Procedure to validate user action.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[UserAuthorization]
@Userid NVarchar(250),
@Methodtype NVarchar(250)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT CASE WHEN result = 1 THEN 'true' ELSE 'false' END AS result FROM
(
SELECT CASE
WHEN @Methodtype = 'GET' THEN [CanView]
WHEN @Methodtype = 'POST' THEN [CanPost]
WHEN @Methodtype = 'PUT' THEN [CanPut]
WHEN @Methodtype = 'DELETE' THEN [CanDelete]
ELSE 0
END AS result
FROM [dbo].[Authorization] WHERE [UserId] = @Userid
)AUTH
END
GO
We are done with the database work. From our previous sample of application, we are going to start. Download it from GitHub, then open the application using Visual Studio 2017. In our application, we need to modify both client-side and server-side. First, we are going to modify in client-side.
Client-Side
Let’s get started with the client-side first. Here, we are going to generate the token based on several hash processes with HMAC SHA256 & Base64 encoding.
Here, HMAC is for Hash Message Authentication Code & SHA256 is the hash function.
Get more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMAC
Token Generation
We need to add these two libraries in our layout page to enable the hash/encoding process.
<script src="/javascripts/hmac-sha256.js"></script>
<script src="/javascripts/enc-base64-min.js"></script>
Below function is generating the token in client-side which is passed through each HTTP request header.
function generateSecurityToken(actionType, loggedUser) {
var model = {
username: loggedUser,
key: actionType,
userAgent: navigator.userAgent.replace(/ \.NET.+;/, '')
};
var message = [model.username, model.userAgent].join(':');
var hash = CryptoJS.HmacSHA256(message, model.key);
var token = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify(hash);
var tokenId = [model.username, model.key].join(':');
var tokenGenerated = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse([token, tokenId].join(':'));
return CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify(tokenGenerated);
};
Create a .js file in public/javascripts folder with the name of “authorization.js”, copy the code snippet then paste it.
Code Explanation
From token generation function, we can see the hash is generated by cryptographic hash function.
var hash = CryptoJS.HmacSHA256(message, model.key);
Here, the first argument is the message to hash & the second one is a secret key to authenticate the message. Get more at https://code.google.com/archive/p/crypto-js. Finally, the token is encoded by Base64 encoding type.
Layout.html
Now call the “authorization.js” file to layout page like below:
<!
<script src="/javascripts/hmac-sha256.js"></script>
<script src="/javascripts/enc-base64-min.js"></script>
<script src="/javascripts/authorization.js"></script>
AngularJS Controller
Let’s modify our existing “UserController” to add the token in request header with each HTTP method.
For GET Method
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('GET', $scope.loggedUser)}
For POST Method
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('POST', $scope.loggedUser)}
For PUT Method
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('PUT', $scope.loggedUser)}
For DELETE Method
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('DELETE', $scope.loggedUser) }
Finally the UserController
templatingApp.controller('UserController', ['$scope', '$http', function ($scope, $http) {
$scope.title = "All User";
$scope.loggedUser = 'Shashangka';
$scope.ListUser = null;
$scope.userModel = {};
$scope.userModel.Id = 0;
getallData();
function getallData() {
$http({
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/user/getAll/',
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('GET', $scope.loggedUser) }
}).then(function (response) {
$scope.ListUser = response.data;
}, function (error) {
showNotif(error.data.message);
console.log(error);
});
};
$scope.getUser = function (user) {
$http({
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/user/getUser/' + parseInt(user.Id),
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('GET', $scope.loggedUser) }
}).then(function (response) {
$scope.userModel = response.data[0];
}, function (error) {
showNotif(error.data.message);
console.log(error);
});
};
$scope.saveUser = function () {
$http({
method: 'POST',
url: '/api/user/setUser/',
data: $scope.userModel,
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('POST', $scope.loggedUser) }
}).then(function (response) {
showNotif("Data Saved")
$scope.reset();
getallData();
}, function (error) {
showNotif(error.data.message);
console.log(error);
});
};
$scope.updateUser = function () {
$http({
method: 'PUT',
url: '/api/user/putUser/',
data: $scope.userModel,
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('PUT', $scope.loggedUser) }
}).then(function (response) {
showNotif("Data Updated")
$scope.reset();
getallData();
}, function (error) {
showNotif(error.data.message);
console.log(error);
});
};
$scope.deleteUser = function (user) {
var IsConf = confirm('You are about to delete ' + user.Name + '. Are you sure?');
if (IsConf) {
$http({
method: 'DELETE',
url: '/api/user/deleteUser/' + parseInt(user.Id),
headers: { 'x-access-token': generateSecurityToken('DELETE', $scope.loggedUser) }
}).then(function (response) {
showNotif("Data Deleted")
$scope.reset();
getallData();
}, function (error) {
showNotif(error.data.message);
console.log(error);
});
}
};
$scope.loginUser = function () {
$http({
method: 'POST',
url: '/api/user/login/',
data: $scope.userModel
}).then(function (response) {
$scope.reset();
}, function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
};
$scope.reset = function () {
var msg = "Form Cleared";
$scope.userModel = {};
$scope.userModel.Id = 0;
showNotif(msg)
};
}]);
Server-Side
After completing the client-side token generation and sending it with the HTTP request, it’s time to work with server-end modifications.
We need to install utf8 npm packages to encode/decode our generated token.
- utf8 - UTF-8 encoder/decoder for Node.js
To install the package, right click on project Go to > Open Command Prompt Here then type “npm install utf8” command, press Enter.
Verify Token
Let’s create a .js file in data folder by naming it “verifyToken.js”. In this process Server extracts the token from each request, then performs two step validation.
- Comparing the custom token by regenerating in server and
- Validating the user permission from database on each request
Code Explanation
Extracting the token from request header
var token = req.headers['x-access-token'];
Regenerating Token in Server-side to compare
var message = [keymodel.userid, keymodel.useragent].join(':').toString();
var sec_key = keymodel.actionType;
var servertoken = crypto.createHmac(encConfig.hType.toString(),
sec_key).update(message).digest(encConfig.eType.toString());
Finally verifyToken.js
var utf8 = require('utf8');
var crypto = require('crypto');
var dbService = require('./dbService');
var encConfig = {
hType: "sha256",
eType: "base64",
cEnc: "ascii"
};
var validateToken = function (req, res, next) {
var token = req.headers['x-access-token'];
var userAgent = req.headers['user-agent'];
var key = utf8.encode(new Buffer(token, encConfig.eType.toString()).toString(encConfig.cEnc));
const parts = key.split(':');
var keymodel = {};
if (parts.length === 3) {
keymodel = {
clientToken: parts[0],
userid: parts[1],
actionType: parts[2],
useragent: userAgent
};
}
var message = [keymodel.userid, keymodel.useragent].join(':').toString();
var sec_key = keymodel.actionType;
var servertoken = crypto.createHmac(encConfig.hType.toString(),
sec_key).update(message).digest(encConfig.eType.toString());
if (keymodel.clientToken == servertoken) {
var query = "[UserAuthorization] '" + keymodel.userid + "', '" + keymodel.actionType + "'";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
var response = data.recordset[0].result;
if (response == 'true') {
next();
}
else {
return res.status(403).send
({ message: 'Authorization Failed!! You are not Permitted!!' });
}
}
});
}
else {
return res.status(404).send({ message: 'Invalid Token!!' });
}
}
module.exports = validateToken;
Secure APIs
Let’s include varifyToken module.
let verifyToken = require('../verifyToken');
Now we need to add verifyToken middleware as the second argument in express route to verify token.
router.get("/api/user/getAll", verifyToken, function (req, res)
router.get("/api/user/getUser/:id", verifyToken, function (req, res)
router.post("/api/user/setUser", verifyToken, function (req, res)
router.put("/api/user/putUser", verifyToken, function (req, res)
router.delete("/api/user/deleteUser/:id", verifyToken, function (req, res)
Get more at https://expressjs.com/en/guide/using-middleware.html.
Finally APIs
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
var dbService = require('../dbService');
let verifyToken = require('../verifyToken');
router.get("/api/user/getAll", verifyToken, function (req, res) {
var query = "GetUsers";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.send(data.recordset);
}
res.end();
});
});
router.get("/api/user/getUser/:id", verifyToken, function (req, res) {
var query = "[GetUserById] " + parseInt(req.params.id) + "";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.send(data.recordset);
}
res.end();
});
});
router.post("/api/user/setUser", verifyToken, function (req, res) {
var query = "[SetUser] '" + req.body.Name + "', '" + req.body.Email + "', '" + req.body.Phone + "'";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.send(data.recordset);
}
res.end();
});
});
router.put("/api/user/putUser", verifyToken, function (req, res) {
var query = "[PutUser] " + parseInt(req.body.Id) + ", '" +
req.body.Name + "','" + req.body.Email + "', '" + req.body.Phone + "'";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.send(data.recordset);
}
res.end();
});
});
router.delete("/api/user/deleteUser/:id", verifyToken, function (req, res) {
var query = "[DeleteUser] " + parseInt(req.params.id) + "";
dbService.executeQuery(query, function (data, err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.send(data.recordset);
}
res.end();
});
});
module.exports = router;
Publishing the App
Go to task explorer in Visual Studio as shown in the below image:
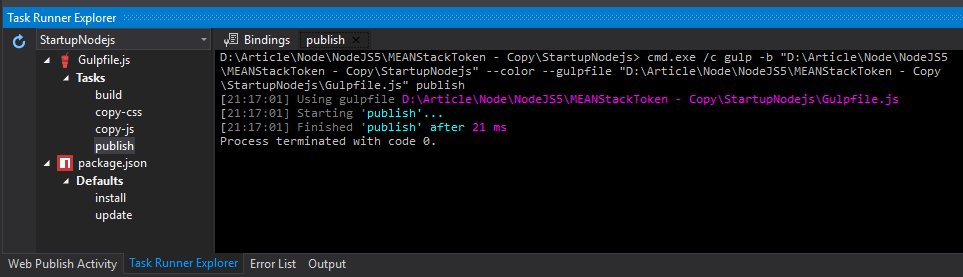
Run the task, this will copy all our application files to the published folder.

Open command prompt here (Shift + Right Mouse), then type “nodemon”. We are starting our application using nodemon. If we have any change in our application, nodemon will automatically restart the application.

Now open browser, type the URL: http://localhost:3000
Output
In the below table view as we can see, the access configuration is set by a particular user. Let’s test our application according to this configuration.

Delete Action
Here, we can see the request method “DELETE” is forbidden with the status code of 403.

Also, the custom response message is displayed in response tab.

Update Action
Here, we can see the request method “PUT” is executed successfully with the status code of 200.

Hope this will help. :)
References
- https://expressjs.com/en/guide/using-middleware.html
- https://code.google.com/archive/p/crypto-js
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMAC
- https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1110226/Authorization-Filters-in-ASP-NET-Web-API-Angular
