What is Python?
- Python is an interpreted high-level programming language. It has advantages of both scripting and programming languages.
- It is very useful for rapid application development
- It is easy to learn when comparing with other programming languages and has a design philosophy that emphasizes code readability, mainly using indentation.
- The language was originally created by Guido van Rossum and first released on 1991.
- Python programming language has a wide range of applications from Web Development, scientific and mathematical computing.
- Nowadays, Python is gaining more attention as it's great for data analysis, artificial intelligence and scientific computing
- It does not need a compiler to run the application. It’s basically an interpreter language.
Few IDE for Python Development
- IDLE (Integrated Development Environment for Python)
- This is the default IDE available with Python installation. In this tutorial, I am running my example programs only on IDLE. There are other IDEs as well which have lots of features. I will give details about those IDEs in upcoming parts.
- Visual Studio
- PyCharm
- Anaconda
- Tkinter
Few Points to Remember
Similar to other programming languages, Python has some coding conventions. I will list a few of them. You can refer to the below link to get more details.
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/
- Indentation
The indentation is very important in Python code. We don’t use braces { } to define a block of code. Instead in python, we use 4 spaces per indentation level. The amount of indentation can be decided by the programmer, but it must be consistent throughout the block. - Identifiers in Python
- The python identifier is a name to identify a variable, function, class, module or any other object.
- It is case sensitive.
- Reserved keywords cannot be used as an identifier
- Special characters like @,! #,$,% cannot be used as an identifier
- There are some naming conventions similar to other programming languages
- Class name start with uppercase letter (For example:
Student) - Starting with single underscore indicates
protected (For example: _colour) - Starting with two underscores indicates
private (Ex: __colour)
How to Install/Configure Python in a Windows Machine
- You can download the latest version of python from the below URLs:
- Here, I am detailing about the installation and configuration in Windows 10 operating system.
- Execute Python-3.6.5.exe
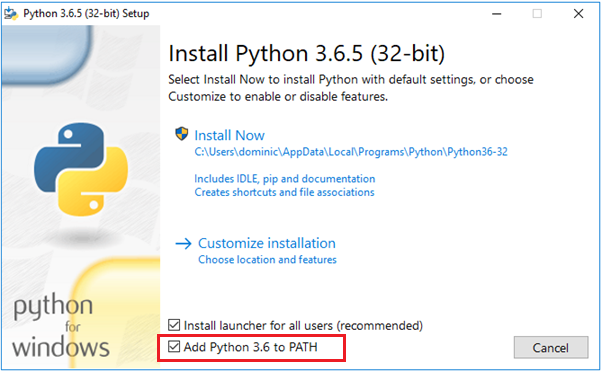
- By default, ‘Add Python 3.6 to Path’ check box is unchecked, but I suggest you check that box. This will set the environment variables automatically. So we can directly execute ‘Python’ from the windows command prompt.

Now open the windows command prompt:
Type ‘Python’ in command prompt and it will give you the python prompt where you can type and execute Python commands.
As you can see, I was able to print "Welcome to python programming".

If you want to install a different python package which is not available with the default python installation, you can use the ‘Pip’ command.

Now we can move on to the default IDE which is available with python installation.

‘Python 3.6.5 Shell’ will get opened and then click on ‘New File’

A new window will get opened and I saved it as ‘Prgoram1.py’ and here we can write programs. When we click on ‘F5’ or ‘Run -> Run Module’ window, the program will execute and provide the output in the output window.

Now let us directly dive into the sample programs.
Keywords in Python
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif',
'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal',
'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
To get the list of keywords, run the below code:
Input
|
| 
|
Output
|
| 
|
Here, we are importing the ‘keyword’ library file. We can see the list of library files in default Python installation location.

Arithmetic Operators
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Modulus - Divides left hand operand by right hand operand and returns remainder |
| ** | Exponent - Performs exponential (power) calculation on operators |
| // | Floor Division – The division of operands where the result is the quotient in which the digits after the decimal point are removed. |
Input
|
| 
|
Output
|
| 
|
There are few things to notice in the above example other than the use of operators.
For adding comments in the code, we use the hash (#) symbol. For multiline comments, we can use triple quotes, either ''' or " " ".
There are other operators available,
For example: Comparison Operators, Assignment Operators, Logical Operators, Bitwise Operators, Membership Operators and Identify Operators.
I am not going into the details of each of the operators, you can refer to the below link to get more information about the different operators:
To receive inputs from the key board, we can use ‘input’ keyword.
Input
|
| 
|
Output
|
| 
|
If statements
Input
|
| 
|
Output
|
| 
|
In the above examples, we can see there is colon ( : ) after each statement. Also make sure the indentation is the same. There is no elseif, instead in Python we are using ‘elif’ keyword.
If the indentation is not the same in the above code, it will throw the below error. So we should be very careful about these indentations while doing programming.

For loop
I will give some examples of ‘for loop’ in python. And we can read and understand the logic like plain English.
Example 1:
| Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
Example 2:
| Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
In this example, print () comes with a parameter called ‘end’. By default the value of this parameter is ‘\n’. But we can end a print statement with any character/string using the parameter ‘end’. Here I included a space at the end of the each print statement.
Example3:
| Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
In the above example, we are looping through a range of number. We can specify the start and end. It will print up to (n-1), if n is the upper range. Here all parameters in range () should be integers (either positive or negative).
Example 4:
| Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
Here the third parameter in range () function represents the stepping number. I.E In the above example, the difference of each number in the printed list is 2.
For loop - with else
| Python supports to have an else statement associated with a loop statement.
Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
| Input
|
| 
|
| Output
|
| 
|
If the else statement is used with a for loop, the else statement is executed when the loop has finished iterating the list.A break statement can be used to stop a for loop. In this case, the else part is ignored. Always make sure the indentation is correct otherwise it will give you unexpected results.
Data Types
Python has the following standard data types:
- Numbers
- String
- List
- Tuple
- Set
- Dictionary
Conclusion
I was trying to give you very basic information to start with. There are many other things to cover and it will be included in the next parts.
