Introduction
Mule is one of the popular middlewares in the market. It is built using Java and supports on-premise and cloud based deployments with the same application code. Development, testing and deployment of Mule based applications can be done in an automated and effective way which shall allow bigger projects with multiple developers working on them to be updated and deployed without much hassle. We will now explore the tools used for different activities and the best practices to be followed in Mule development for an enhanced development and deployment experience.
Following tools are recommended to be used in different stages of our Mule projects:
- Maven for building the projects
- Maven repository for the dependencies
- Source code repository in Git
- Nexus repository for shared dependencies
- Jenkins for continuous integration/deployment
- Mule unit testing for automated testing
We’ll explore each of the above items and how they can be used for Mule projects.
Maven for Building the Projects
Maven should be installed in the machine where we are developing the application. The maven directory should be specified in the Anypoint studio.
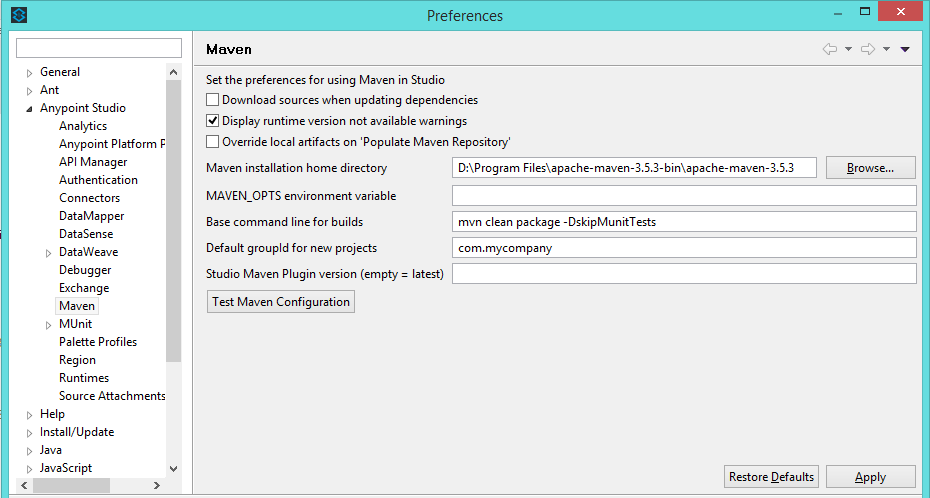
Go to Windows -> Preferences. In that, under Anypoint Studio -> Maven, set the following properties:
Maven Installation home directory. Leave the other properties as it is. Refer to the below screenshot.
When we are building a new project, we need to check ‘Use Maven’ and specify the Group Id, Artifact Id, and Version, which will get added in the POM file.

Maven Repository for the Dependencies
The repositories element specifies in the POM the location and manner in which Maven may download remote artifacts for use by the current project. Refer to this link for more information on POM file structure. We specify the repository from where the dependencies need to be downloaded when the project is built. See the below structure of dependencies and repositories.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mulesoft.muleesb</groupId>
<artifactId>mule-core-ee</artifactId>
<version>${mule.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>Central</id>
<name>Central</name>
<url>http://repo1.maven.org/maven2/</url>
<layout>default</layout>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>mulesoft-releases</id>
<name>MuleSoft Releases Repository</name>
<url>http://repository.mulesoft.org/releases/</url>
<layout>default</layout>
</repository>
</repositories>
Source Code Repository in Git
The mule projects are stored in GitHub repository, for which we can use egit plugin for Any point Studio. This can be used for syncing the code in GitHub.

Installing the Git Plugin, Saving the Studio Project to Git and Importing a Git Project into Studio are explained in this link.
Nexus Repository for Shared Dependencies
Nexus is a repository manager, and acts as a staging repository which "intercepts" artifacts uploaded by mvn deploy. Nexus can be used with Maven in the following cases:
- Maintaining and referencing the libraries used by the Maven application
- Uploading the maven project library to Nexus for reference by other applications
Maintaining and Referencing the Libraries used by the Maven Application
For maven applications referencing the Nexus repository, the nexus repository has to be added in the Settings.xml file as below. We have added 2 repositories, nexus and stc where the artifacts will be downloaded from.

The dependent jar should be added to the Nexus repository and then can be specified in the dependencies in the project POM file. If we do it, during build, the dependent jar will be downloaded from the Nexus repository and the project will be built successfully.

Once upon the successful completion of maven build, you could see the dependency jar in the following location:
C:\Users\<username>\.m2\repository\com\microsoft\sqlserver\sqljdbc4\4.0\....jar
Uploading the Maven Project Library to Nexus for Reference by Other Applications
Distribution Management manages the distribution of the artifact and supporting files generated throughout the build process. The repositories element specifies in the POM the location and manner in which Maven may download remote artifacts for use by the current project, distributionManagement specifies where (and how) this project will get to a remote repository when it is deployed. The repository elements will be used for snapshot distribution if the snapshotRepository is not defined. Refer here for more details.
<code>="1.0"="UTF-8"
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
...
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<uniqueVersion>false</uniqueVersion>
<id>nexus</id>
<name>Nexus Repository</name>
<url>http://localhost:8091/nexus/content/repositories/nexus</url>
<layout>default</layout>
</repository>
<snapshotRepository>
<uniqueVersion>true</uniqueVersion>
<id>propSnap</id>
<name>Propellors Snapshots</name>
<url>sftp://propellers.net/maven</url>
<layout>legacy</layout>
</snapshotRepository>
...
</distributionManagement>
...
</project>
</code>
The above POM file settings will cause the project to be deployed in Nexus repository during each build.
Jenkins for Continuous Integration/Deployment
Jenkins can be used for doing an automated build from Git, which requires to install 'Git Plugin'. Also Maven related plug-ins need to be installed as below which will enable us to create Maven project so that we can execute maven commands during the build process.

Go to Manage Jenkins -> Global tool configuration
In the JDK section, uncheck the 'Install automatically' checkbox and set the JAVA_HOME (your jdk location)
In the Git section, check 'Install automatically'.
In the Maven section, click maven installations. Click add MAVEN, uncheck the 'Install automatically' checkbox and set the maven home. (For example: D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.2)
In the POM.xml, add this plugin element after the existing plugin elements inside the plugins element. This is necessary for Cloudhub deployment.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mule.tools.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>mule-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<configuration>
<deploymentType>cloudhub</deploymentType>
<muleVersion>3.8.4</muleVersion>
<redeploy>true</redeploy>
<workerType>Micro</workerType>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>deploy</id>
<phase>deploy</phase>
<goals>
<goal>deploy</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
For building and deploying the Mule project, enter the following maven command in Goals & Options:
-X -Dmaven.repo.local="Path\to\your\local\maven\repository"
--settings "Path\to\the\settings.xml\in\your\local\maven\repository"
package mule:deploy -Danypoint.username=anypoint_username
-Danypoint.password=anypoint_password -Danypoint.environment=Sandbox
Your local maven repository is located in C:\Users\YourName mostly.
For example:
-X -Dmaven.repo.local="C:\Users\<username>\.m2\repository"
--settings "C:\Users\<username>\.m2\settings.xml" package mule:deploy
-Danypoint.username=jenkins1 -Danypoint.password=<password> -Danypoint.environment=Sandbox
Now building the Jenkins project using ‘Build Now’ should take the mule source code from Git and build it and deploy it into the Cloud hub.
Mule Unit Testing for Automated Testing
MUnit is a Mule application testing framework which enables us to build automated tests for the Mule integrations and APIs. MUnit is integrated with Anypoint Studio. It has to be used after installing the MUnit from Help -> Install New Software…
To create test cases, we need to create a munit test suite for the flow and add Munit library to classpath. Refer to this document for more information on MUnit.
="1.0"="UTF-8"
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:munit="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/munit"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:core="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/munit
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/munit/current/mule-munit.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd">
<munit:config name="munit" doc:name="MUnit configuration"/>
<spring:beans>
<spring:import resource="classpath:message-demo-filter.xml"/>
</spring:beans>
<munit:test name="message-demo-filter-test-suite-message-demo-filterFlowTest" description="Test">
<set-payload value="#['The cat is brown and clever']" doc:name="Set Payload"/>
<flow-ref name="message-demo-filterFlow" doc:name="Flow-ref to message-demo-filterFlow"/>
<munit:assert-payload-equals message=
"Output message is not matching expected value #[payload]"
expectedValue="#[payload]" doc:name="Assert Payload"/>
</munit:test>
</mule>
The test cases can be executed when building the project from Jenkins as well.
Conclusion
We have gone through the different tools to be used with Mule applications for executing in different stages of Mule application development. This shall be beneficial when building a CI/CD architecture and build process for Mule applications.
