Introduction
In this article, I would discuss Flutter Navigation, Navigation or movement among pages is important business requirement of any application, for example almost every application requires a login page or option page, where various options could be set based on user input.
In simpler terms, it means leaving one page and loading a new page. Based on code, page may persist in memory or be simply deleted from stack. So at most, care should be taken by Developer/Architect while developing an application, what should be kept in memory and what shouldn't.
Background
If you happen to read my article, Flutter Getting Started: Tutorial 2 - StateFulWidget, we will build on the same application. Let me summarize what I have done in that article - I have provided a TextField which is similar to TextBox in C#, and on press of Save button, it gets added to list which also presents the same page.
Now, we destroy that application and create two pages out of it, one which will display the list of cities added and the other page provides options for adding the cities. So this would be the final result once the application is completed.
Add City new UI design
|
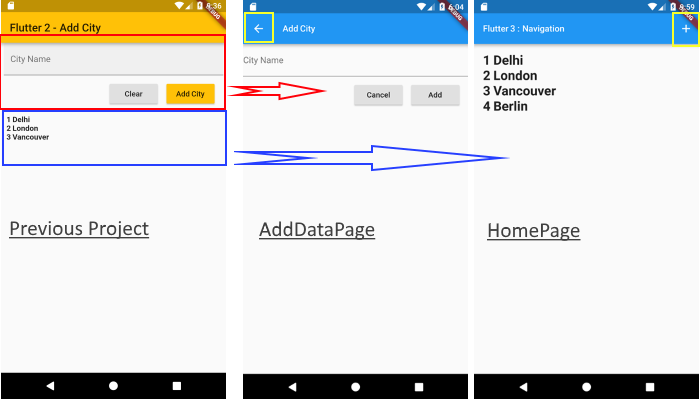 |
| Here, as mentioned above, form portion going into AddDataPage file and Listview which kept list of data, added by user would become part of home page. I marked two new additions with yellow squares, one for invoking AddDataPage and another for going back to HomePage.
|
Aim of the Tutorial
As mentioned earlier in this article, I will be building an application based on my previous article. I will be creating two pages application and in the end, I will be adding additional pages to showcase removing of multiple pages.
- There would be two pages:
- Page #1:
Homepage would contain ListView, where all the user input city would be displayed - Page #2:
AddDataPage would contain TextField from where you can add data to list (it contains TextField, Cancel and Add RaisedButton )
- Task #1: Basic Navigation, when we navigate between pages using known page object
- Task #2: Sending data using
Navigation object - Task #3: Using named route for navigation instead of page object
- Bonus Task#4: Additional page would be added to show navigation stack, and how pages persist between navigation
Overall, application would contain two pages, one would show all the text entered by user and the other page would provide form to enter data.
Using the Code
- Let's start by creating a new flutter project in Android Studio, Give it name
Flutter3_navigation. In case you don't know how to create Flutter project, please read here. - Create a package in lib directory by name pages and add two DART files:
adddatapage.dart: Add AddDataPage class which extend Statelesswidgethomepage.dart: Add HomePage class which extend StateFulWidget (if you don't know about StateFulWidget, read here), also add _HomePageState which extends state<HomePage>
- Delete all code from
main.dart, the entry point of Mobile Application, and replace with this code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter3_navigation/pages/homepage.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: new ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue
),
home: new HomePage(title: 'Flutter 3 : Navigation'),
);
}
}
Explanation of Code
- Here,
MyApp is our entry class for mobile application, here we return MaterialApp object. This will provide skeleton for our app. - I set home object to
HomePage object, which means it would be loaded when application starts running.
- Put the following code in
HomePage.dart, the following control has been added:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter3_navigation/pages/adddatapage.dart';
class HomePage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
HomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
@override
_HomePageState createState() => new _HomePageState();
}
class _HomePageState extends State<HomePage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(
widget.title,
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 16.0),
),
actions: <Widget>[
new IconButton(
icon: new Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: () {
print("Add button clicked");
})
],
),
);
}}
- Here, we create page
Scaffold and create AppBar inside it. - Here is a new addition in App Bar, I have added
IconButton with display of Icons.add. This is a placeholder for navigating to AddDataPage, currently we are not doing anything:

- Now, before I show you code for
AddDataPage.dart, let me give you a small overview of Navigator Class. We generally use the following function (definition taken from Flutter website):
Navigator.push - Push the given route onto the navigator that most tightly encloses the given contextNavigator.pop - Pop the top-most route off the navigator that most tightly encloses the given contextNavigator.pushNamed - Push a named route onto the navigator that most tightly encloses the given context. We are going to use it in Task#3.Navigator.pushNamedAndRemoveUntil - Push the route with the given name onto the navigator that most tightly encloses the given context, and then remove all the previous routes until the predicate returns true. We are going to use in Task#4.
- Now, add function
void _onAddCityButtonPressed(BuildContext context) in HomePage.dart file and call that from Add IconButton:
void _onAddCityButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => AddDataPage())
) }
Explanation of Code
- As mentioned in step 5, I am using
Navigator.Push to push new page on stack, here we need to use current BuildContext and Push AddDataPage, when person clicks on + button in AppBar.
- Now it's the turn of AddDataPage.dart. Add the following code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class AddDataPage extends StatelessWidget {
final TextEditingController _CityNameController = new TextEditingController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(
"Add City",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 16.0),
),
),
body: new SafeArea(
child: new Container(
child: new Column(children: <Widget>[
new TextField(
decoration: new InputDecoration(
labelText: "City Name",
),
controller: _CityNameController,
),
new ButtonBar(
alignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: <Widget>[
new RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pop(context);
},
child: new Text("Cancel"),
),
new RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pop(context,_CityNameController.text);
},
child: new Text("Add"),
)
],
)
]),
),
));
}
}
Explanation of Code
- Here in this page, I have added a
TextField, a ButtonBar with two button Cancel (which will pop the current page) and Add (which will return whatever data is entered in TextField). - For returning data when unloading page, you can use the second parameter with whatever data you want to return. In our case,
CityName.

Here, we come to the end of Task#1. - Now we are sending the data, but we haven't written code to catch whatever is coming from the other page, the answer lies in
Future class, its type of object which keeps track of object coming in future and lets you catch its linked function. I would be writing a full-fledged article using async function and Future in Dart language. It is similar to Observable/ Promises in Angular. Here is how we going to catch CityName sent by AddDataPage to HomePage. Here is a modified function that looks like:
void _onAddCityButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => AddDataPage())
)
.then((Object result){
print("result from addpage ${result.toString()}");
});
}
Explanation of Code
then function is part of Future class, this function will be anchor to page you navigate to, and bring you data whatever sent from there.- There are various ways to achieve this (gathering of data), I am showing only one way here, as it's not fruitful to tell them before letting you know how
async works in DART.
- Now I modified code to include
ListView in the HomePage and adding data received from AddDataPage, all explanation of the below code is available in my previous article here.
final List<Text> _lstCities = new List<Text>();
Widget _getListViewFromBuilder() {
return ListView.builder(
itemCount: _lstCities.length,
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
itemBuilder: getListItems,
);
}
Widget getListItems(BuildContext context, int index) {
return _lstCities[index];
}
void _onAddCityButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
Navigator
.push(context, MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => AddDataPage()))
.then((Object result) {
if (result == null) return;
setState(() {
_lstCities.add(new Text(
"${_lstCities.length + 1} ${result.toString()}",
textAlign: TextAlign.justify,
style: new TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,fontSize: 24.0),
));
});
});
}

Here, we come to end of Task#2.
- Now the problem with the above code, the routing is fixed, i.e., since we are navigating through providing new object for page we want to load, this creates a problem if we want to have dynamic routes and avoid references of pages in a different project (you need to
import class file, before providing page object). - Now you have to modify the
Main.dart with the following changes, home property needs to be commented out, as we are relying completely on routing now:
routes: {
'/' : (BuildContext build)=> new HomePage(title: 'Flutter 3 : Navigation'),
'/adddata':(BuildContext build)=> new AddDataPage(),
},
initialRoute: "/"
Explanation of Code
Here, we come to the end of Task#3. - Now for the bonus part, here we would be adding a new page by name
EndPage and I would include bottom bar in both AddDataPage and EndPage.
AddDataPage bottom bar would contain forward navigation to end, which will use Navigator.pushNamed to reach EndPage EndPage bottom bar would have one home button, which navigates to home page using pushNamedAndRemoveUntil and backward button to move HomePage
- Now modified
AddDataPage looks like, inside page container add bottomNavigationBar and new function _getBottomNavigationBarWidget():
bottomNavigationBar: _getbottomNavigationBarWidget(context),
New function needs to be added at the bottom of class, don't forget to route definition for EndPage in main.dart, as mentioned in Step 11.
Widget _getbottomNavigationBarWidget(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
color: Colors.black87,
child: new ButtonBar(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
alignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: <Widget>[
new IconButton(icon: new Icon
(Icons.arrow_forward,size: 24.0,color: Colors.white,), onPressed: (){
Navigator.pushNamed(context, "/endpage");
})
],
),
);
}
Here, we added an IconButton in bottombar, on pressing the button, we navigate to endpage:

- Add a new dart file in pages folder by
endpage.dart, and add EndPage class to it, since we are not managing any state inside it, we can safely derived it from StatelessWidget, code would look like this:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class EndPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text(
"End Page",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 16.0),
),
),
body: new Center(
child: new Text("Welcome to End Page",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 24.0,fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),),
),
bottomNavigationBar: _getbottomNavigationBarWidget(context),
);
}
Widget _getbottomNavigationBarWidget(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
color: Colors.black87,
child: new ButtonBar(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
alignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: <Widget>[
new IconButton(icon: new Icon
(Icons.arrow_back,size: 24.0,color: Colors.white,), onPressed: (){
Navigator.pop(context);
}),
new IconButton(icon: new Icon
(Icons.home,size: 24.0,color: Colors.white,), onPressed: (){
Navigator.pushNamedAndRemoveUntil(context, "/",
(Route<dynamic> route){ return false;});
})
],
),
);
}
}
Here, we have two buttons in BottomNavigationBar, on pressing backward button, we pop current page and move to AddDataPage. On pressing Home button, we remove all pages till we show HomePage.

Here, we come to the end of Task#4.
- Here is a GIF file of final output.

Though there are a lot of things left, like Page Animation during transition, etc. Hopefully, I have covered all basic maneuvering in this article. Please don't hesitate to ask any question or comment.
Points of Interest
Please go through these articles. It might give you a headway, where the wind is actually flowing:
- Flutter — 5 reasons why you may love it
- What’s Revolutionary about Flutter
- Why Flutter Uses Dart
- Github: https://github.com/thatsalok/FlutterExample/tree/master/flutter3_navigation
Flutter Tutorial
- Flutter Getting Started: Tutorial 1 Basics
- Flutter Getting Started: Tutorial 2 - StateFulWidget
Dart Tutorial
- DART2 Prima Plus - Tutorial 1
- DART2 Prima Plus - Tutorial 2 - LIST
History
- 12th July, 2018: First version
