Introduction
This code was written to demonstrate the process of parsing vector SVG files in C/C++ application, working with Bezier curves, and saving the vector image to PDF. For ease of understanding, all processing in app only works in grayscale mode. The code was written for Windows, but has no Windows-only dependencies and can be easily ported to Linux or any embedded platform.
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is a 2D vector image format widely used in Web development. The SVG format is heavily based on XML standard. While the raster image (PNG, JPG, GIF, etc.) is composed of a fixed set of pixels, the vector SVG image is composed of a fixed set of shapes, like circles, lines, rectangles, Bezier curves, etc. The advantage of SVG format is that it can be easily scaled to any level without the loss of quality.
I have included a nice kitten here as a sample of SVG image:

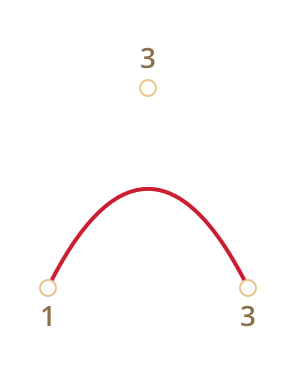
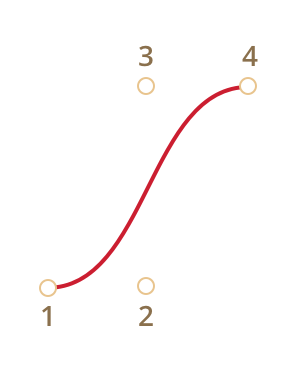
Bézier curve is a parametric curve which is used to model smooth curves that can be scaled indefinitely. Bezier curve can be represented as a set of control points. Quadratic and cubic Bezier curves are most common. Higher degree curves are more computationally expensive to evaluate. When more complex shapes are needed, low order Bezier curves are patched together, producing a composite Bezier curve. A composite Bezier curve is commonly referred to as a path.
| 
| 
|
| Quadratic Bézier curve
| Cubic Bézier curve
|
The Portable Document Format (PDF) is a file format to represent documents, including text formatting, raster images, vector graphics, etc. Vector graphics in PDF are constructed with paths too. Paths are usually composed of lines and cubic Bezier curves, but can also be constructed from the outlines of text. Paths in PDF can be stroked, filled, clipping. Strokes and fills can use any color set in the graphics state, including patterns.
Background
For the processing of SVG files, I used brilliant library called nanosvg. It is small and lightweight and can be used even in embedded development projects. To compose PDF files, I have used write-only libHaru library. Though not actively developed now (2018), it still can be used in C/C++ projects.
Using the Code
The SvgConverter class is a basic workhorse to convert SVG to PDF. The same object can be used multiple to convert other images. You just need to call a method that is responsible for loading the other file.
SvgConverter converter;
converter.loadFromFile(fileInput); converter.convertToPDF(fileOutput);
Class structure looks like this:
class SvgConverter {
private:
NSVGimage * g_image;
std::string fileName;
public:
SvgConverter(std::string fileName);
SvgConverter();
bool isLoaded();
bool loadFromFile(std::string fileName);
bool convertToPDF(std::string fileName);
~SvgConverter();
private:
float distPtSeg(float x, float y, float px, float py, float qx, float qy);
void pdfcubicBez(HPDF_Page page, float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,
float x3, float y3, float x4, float y4,
float tol, int level, Vector2f startPoint);
void pdfPath(HPDF_Page page, float* pts, int npts, char closed, float tol, bool bFilled,
Vector2f startPoint);
static void error_handler(HPDF_STATUS error_no,
HPDF_STATUS detail_no,
void *user_data);
};
To approximate Bezier curve and draw it, we will use one of the properties of such curves.
Any cubic Bezier curve B from beginning to end can be divided into two curves, which together will describe the same curve as B.
Converting and approximation method implementation, some code taken from nanosvg sample and adapted to PDF coordinate system:
bool SvgConverter::convertToPDF(std::string fileName) {
if (fileName.empty() || !isLoaded()) return false;
HPDF_Doc pdf = HPDF_New(error_handler, NULL);
if (!pdf) return false;
HPDF_Page page = HPDF_AddPage(pdf);
float width = this->g_image->width;
float height = this->g_image->height;
Vector2f startPoint = { 0, height};
HPDF_Page_SetWidth(page, width);
HPDF_Page_SetHeight(page, height);
HPDF_Page_SetLineWidth(page, 0.1f);
for (NSVGshape * shape = g_image->shapes; shape != NULL; shape = shape->next) {
if (!(shape->flags & NSVG_FLAGS_VISIBLE)) continue;
float r = (float)((shape->fill.color >> 16) & 0xFF) / 255.0f;
float g = (float)((shape->fill.color >> 8) & 0xFF) / 255.0f;
float b = (float)((shape->fill.color) & 0xFF) / 255.0f;
float gray = (r + g + b) / 3.0f;
gray = (gray < 0.5f) ? 0 : 1.0f;
HPDF_Page_SetGrayFill(page, gray);
for (NSVGpath * path = shape->paths; path != NULL; path = path->next ){
pdfPath(page, path->pts, path->npts, path->closed,
0.1f, shape->fill.type != NSVG_PAINT_NONE, startPoint);
}
if (shape->fill.type != NSVG_PAINT_NONE) {
if (shape->fillRule == NSVGfillRule::NSVG_FILLRULE_EVENODD)
HPDF_Page_EofillStroke(page); else HPDF_Page_FillStroke(page); }
else HPDF_Page_Stroke(page); }
HPDF_SaveToFile(pdf, fileName.c_str());
HPDF_Free(pdf);
return true;
}
float SvgConverter::distPtSeg(float x, float y, float px, float py, float qx, float qy)
{
float pqx, pqy, dx, dy, d, t;
pqx = qx - px;
pqy = qy - py;
dx = x - px;
dy = y - py;
d = pqx*pqx + pqy*pqy;
t = pqx*dx + pqy*dy;
if (d > 0) t /= d;
if (t < 0) t = 0;
else if (t > 1) t = 1;
dx = px + t*pqx - x;
dy = py + t*pqy - y;
return dx*dx + dy*dy;
}
void SvgConverter::pdfcubicBez(HPDF_Page page, float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,
float x3, float y3, float x4, float y4,
float tol, int level, Vector2f startPoint)
{
float x12, y12, x23, y23, x34, y34, x123, y123, x234, y234, x1234, y1234;
float d;
if (level > 12) return;
x12 = (x1 + x2)*0.5f;
y12 = (y1 + y2)*0.5f;
x23 = (x2 + x3)*0.5f;
y23 = (y2 + y3)*0.5f;
x34 = (x3 + x4)*0.5f;
y34 = (y3 + y4)*0.5f;
x123 = (x12 + x23)*0.5f;
y123 = (y12 + y23)*0.5f;
x234 = (x23 + x34)*0.5f;
y234 = (y23 + y34)*0.5f;
x1234 = (x123 + x234)*0.5f;
y1234 = (y123 + y234)*0.5f;
d = distPtSeg(x1234, y1234, x1, y1, x4, y4); if (d > tol * tol) {
pdfcubicBez(page, x1, y1, x12, y12, x123,
y123, x1234, y1234, tol, level + 1, startPoint); pdfcubicBez(page, x1234, y1234, x234, y234, x34,
y34, x4, y4, tol, level + 1, startPoint); }
else HPDF_Page_LineTo(page, startPoint.x + x4 / 3.0f,
startPoint.y - y4 / 3.0f); }
void SvgConverter::pdfPath(HPDF_Page page, float* pts, int npts, char closed,
float tol, bool bFilled, Vector2f startPoint)
{
HPDF_Page_MoveTo(page, startPoint.x + pts[0] / 3.0f,
startPoint.y - pts[1] / 3.0f);
for (int i = 0; i < npts - 1; i += 3) {
float* p = &pts[i * 2];
pdfcubicBez(page, p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4], p[5],
p[6], p[7], tol, 0, startPoint); }
if (closed) HPDF_Page_LineTo(page, startPoint.x + pts[0] / 3.0f, startPoint.y - pts[1] / 3.0f);
}
You can use an application from console to include in some batch processing. Application receives two command line arguments, where the first argument is SVG file path and the second is PDF file path.
For example:
./svgtopdf cat.svg cat.pdf
Points of Interest
While trying to link C library to C++ project, first you have to disable precompiled headers for C files. This can be done by selecting multiple C files first in Solution Explorer, right click, then go to "Precompiled Headers" tab and select "Not using Precompiled Headers".
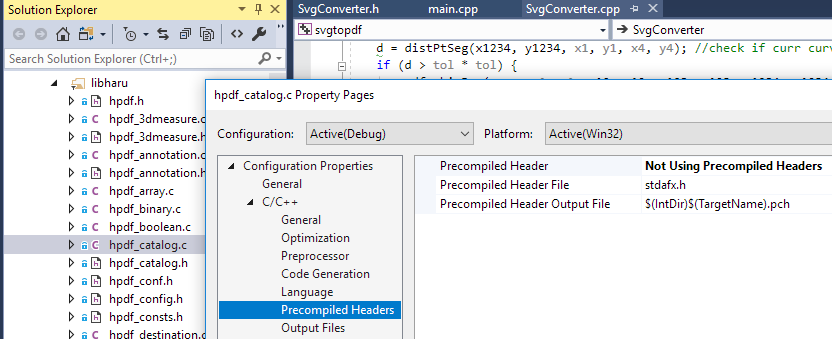
Also, you need to wrap the C include files in an extern "C" directive:
extern "C" {
#include "libharu\hpdf.h"
#include "libharu\hpdf_utils.h"
}
Conclusion
Feel free to send me any comments and suggestions. If you find this approach useful, feel free to upvote the article. If you find yourself wanting to improve the code, feel free to clone the github repository.
Good luck!
History
- 18th July, 2018 - First version
