Introduction
React-Native allows you to create native mobile applications using JavaScript and React, it follows the same design as React, this means that lets you create components and compose those components from other components.
React Native offers you already components that results on native mobile components such as UITextView in iOS or TextView in Android. This is important because we will not have a web application inside our mobile app, but rather we will have a native application.
React Native Architecture
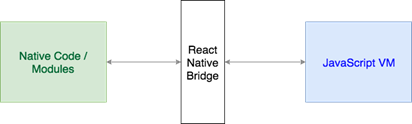
The architecture of react native is composed by 3 main components:
- Native Code / Modules, this elements are the native code written on Java (Android) or Objective C (iOS).
- React Native Bridge is the responsible for the communication between the native and JavaScript thread.
- JavaScript VM is the Virtual Machine that runs all of our JavaScript code and finally.
Technology stack
Before we start coding we must give a brief explanation about some of the tools needed to build our application:
Node.js is an OpenSource platform to develop applications, which is focused in real time. It is very useful for applications that have high concurrency. It uses JavaScript as programming language and asynchronous and object-oriented programming patterns.
Npm Package manager that allows us to install dependencies / packages that we need.
ES6 As any language, Javascript also has versions named ECMAScript (short for ES). Is the new JavaScript standard.
Babel Is a JS transpiler that converts new JS code into old ones. A tool that transforms and compiles our code. This means that it allows us to write in a code with the latest features of EcmaScript that transforms it compatible with any browser
Redux "is a predictable state container for JavaScript apps", that means that the complete state of the application is stored in the "Store".
Components in Redux
Store: It is the center and the truth of everything, with methods to update, obtain and listen to data.
Actions: These are blocks of information that send data from the application to the store.
Reducers: Are functions that specify how the actions change the status of the application.
Creating react-native project: First steps
This point is fun because we must bear in mind that we will have different environments: Development OS: macOS, Windows, Linux.
Target OS: iOS, Android.
Only from Mac we will be able to work with iOS and Android.
From Windows and Linux we are going to configure the environment to work with Android Studio.
So let's prepare the environment to be able to make our application, starting with iOS.
Install Xcode
To simulate the iOS application, we will need Apple's development software, Xcode. The easiest way to install it is through the Mac App Store. Installing Xcode will also install all the necessary tools to build our iOS app. https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/xcode/id497799835?mt=12
Install Node
On Mac you can easily install using Homebrew without having to manually download it and install it, since this last procedure sometimes gives problems. The command to install node would be:

Install React Native
Once we have a node installed on our computer we can install React Native by launching the following command:

Creating a new app
Use the React Native command line interface to generate a new React Native project called "imageGallery":

Honestly the best guide is in the official documentation: https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/getting-started.html
Project structure: Structure of files and folders.
After having created and initialized the project we can see that React Native has created a main folder that contains all the necessary files to develop the app.
Let's pay attention to the structure of project files:

The folders of android and iOS, are the folders that contain the "native" files of our app in each one of the platforms. The different libraries that we will use for our app are saved in the node_modules directory.
App design: Flow chart

Creating a component
The components are the main part of React they have properties, status, life cycle, etc. The main components will be views, texts and images.
As we mentioned before the App.js is the main component that was already created by the react-init.

With the tag <View/> we are going to replace those that were <div/> in the html.
In the case of <Text/> it replaces the paragraphs, titles, etc.
And with <Image/> we can include the images.

In React Native we will have the emulator in place of the browser to see the content.

Well, we must say that to give the dimension to our image we need to import and call the component StyleSheet. This allows us to create an object in which we will write the styles and that we can add to our components through its attribute style.

Load data from API: Flickr
To start pulling the information from the page of flickr we need:
Step 1: enter to https://www.flickr.com/services/api/ and click in Sign up.

Step 2: register our information and then an email will arrive with a password.

Step 3: Once flickr welcomes us we will go to create an App and then Get your API Key in Request an API Key.
Step 4: for this step you have to define how to choose the API "commercial" or "Non commercial", in this case I choose Non commercial.

Step 5: Register the information of your app, accept and the terms and submit.

Ready! Right away he gives us the Key and our secret key.
Keep them close because we will use them later.
Flow diagram

Working with images
First thing we want to do is to retrieve the data from the server, for that we will use a library called "axios" (https://github.com/axios/axios). In order to install axios we will type the following command on our project:
$ npm install axios
The output will be something like:

Now we need to import axios into our App component. For that we will write a new import statement bellow our current import statements:

The next thing to do is we need to call to an endpoint, in this case Flickr we will use the following endpoint: https://www.flickr.com/services/api/flickr.photos.search.html
For this endpoint we need to provide an API_KEY, this process was describe above. Also we will include some other parameters to complete our search.
We will add a new const bellow of our import statements with the API Key we obtain from Flickr
const API_KEY = 'TypeYourAPIKeyHere'
We will define a new method called imageSearch that will receive a text as an argument, this will be the method that calls the server and returns the images. So first we need to know the address we want to call, second we will get the information from the server and finally we will display the images on the screen.
imageSearch(text) {
const urlEndpoint = `https:
${text}&nojsoncallback=true&per_page=20&extras=url_s`
.then((response) => { console.log(response)
}).catch((error) => { console.log(error)
})
}
If you debug your application using the CMD+D option on chrome you can see something like this. CMD + D

On chome open developer tools:

It is important to notice that "axios" returns an object that contains a property called "data" this property is the one that contains the information that we need, in this case photos, we can also check "stat" to determine if the request has an error.
We will change the styles for our App in order to present a "FlatList" component remove the items that are not required:
const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#F3F3F3',
},
image: {
width: (Dimensions.get('window').width / 2) - 20,
height: 150,
margin: 10,
},
flatListStyle: { flex: 1,
}
});
Now we are using Dimensions, this is object comes from react-native name space that provides the width of the screen.
If you run the app it would look like:

As you can see the image is on the top left corner and is over the status bar, to avoid this we have another class available on react-native namespace "SafeAreaView" like this:
render() {
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View>
<Image
source={{uri:'https://s3.amazonaws.com/crisoforo.com/flowers.jpg'}}
style={styles.image} />
</View>
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
This will fix the issue and the image will be position correctly.

We will change the content of the render method of our App, to include a FlatList:
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.container}>
<FlatList style={styles.flatListStyle} data={this.state.images} numColumns={2} renderItem={({item})=>{ return (
<View>
<Image style={styles.image} source={{uri: item.url_s}} />
</View>
)}
} />
</View>
</SafeAreaView>
As you can see we have define the attribute of the FlatList data as this.state.images, this is the component state we must define this our constructor in order to have the property set, otherwise we will get undefined as the value.
constructor(props) { super(props)
images: []
}
}
In the constructor we have define the images array as empty but we need to refresh the component once we get the images from the server, we will do that using the setState method, we just to invoke this method in the then function that we have on axios
imageSearch(text) {
const urlEndpoint = `https:
.then((response) => { console.log(response) this.setState({
images: response.data.photos.photo
})
}).catch((error) => { console.log(error)
})
}
If we run now the app we will have something like this:

The user should be able to search images, we will add a TextInput on our render:
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.container}>
<TextInput style={styles.search} placeholder={'Search'} value={this.state.searchTerm} onChangeText={(text)=> { this.setState({
searchTerm: text
})
this.imageSearch(text) }} />
<FlatList style={styles.flatListStyle} data={this.state.images} numColumns={2} renderItem={({item})=>{ return (
<View>
<Image style={styles.image} source={{uri: item.url_s}} />
</View>
)}
} />
</View>
Is important to notice that we are using a state.searchTerm but we haven't define it, so we need to declare this on the constructor like this:
constructor(props) { super(props)
images: [], searchTerm: ''
}
}
Also the styles for the TextInput were added to the end of the StyleSheet.create
const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#F3F3F3',
},
image: {
width: (Dimensions.get('window').width / 2) - 20,
height: 150,
margin: 10,
},
flatListStyle: { flex: 1,
},
search: { height: 30,
marginLeft: 10,
marginRight: 10,
fontSize: 20,
marginTop: 10
}
});
If we refresh the app we have something like this:

Code location
You can find the code in:
https://gitlab.itexico.com/groups/blogposts
Conclusions
We have built a gallery of images using react-native, we define some stacks, we use the flickr API and we run the app in our emulator.
