Introduction
The first part of this article discussed the Microservice Architecture (MSA) in detail and tried to explain the basic terminology of MSA and its concepts. This part will discuss OWIN Framework and will try to give a glance into their usage in the building of MSA based services. Before you start reading this part, I suggest you to read the Part I, if you do not have any background about MSA.
Read Part I: Dive-into-Microservices-Architecture-Part-I
Background
Before Open Web Server Interface for .NET (OWIN) standard, web servers like IIS, Apache Tomcat, or even HTTP.sys (in the case of stand-alone applications) was the connection between web applications and the HTTP protocol. This means any kind of web-oriented software like web services or web applications were using one of the mentioned web servers with no standard interface to communicate over HTTP protocol.
There were several problems involved in this way but the most dramatic problem was platform dependency, means that an IIS based application would not be able to run over Apache server or would be extremely expensive to make it work. For example, consider running an ASP.NET application on Apache or in the case of stand-alone applications like a self-hosted web service (a web service hosted by windows service), a direct communication through HTTP.sys was bringing some limitations such as the number of concurrent connections which was limited to 1000 (have a look at the HttpServerQueueLengthProperty).
Windows Communication Function (WCF) was the first attempt to fix these problems by adding extra layer (in this case a framework) between web servers and applications (in this case services).
WCF was allowing you to send data as asynchronous messages from one service endpoint to another over HTTP or TCP protocols. It was also introducing several new concepts to make SOA implementation easier, such as ABC (Address, Binding, Contract) and etc. But, soon after realising this framework software engineers have noticed that WCF is suffering from unnecessary complexities that often came by the WCF Architecture.
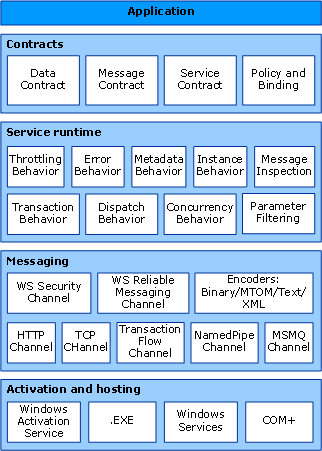
Windows Communication Foundation Architecture (Referenced from the Microsoft`s official website)
Drawbacks of WCF can be summarized as following:
- Complexity - Difficult to understand for many of software developers
- Interoperability - Since WCF is a Microsoft implementation of SOA it makes all parts of this framework highly dependent on Microsoft licensing and this decrease the interoperability of the technology
- Expensive - It requires more hardware resources to run
- Less Flexible - Developing RESTful service with WCF is just pain in the bottom
- More Effort - Development speed in WCF is much more slow than NancyFx with OWIN
Why Microsoft OWIN?
Microsoft OWIN targets exactly these problems and tries to solve them by defining standard interfaces between web servers and web applications. The OWIN Framework developed by Microsoft and distributed as a NuGet Package defines an interface between the web server and the web application and removes dependency to System.Web which this by itself allows you to host your web application independently from the web servers, in other word it allows you to host your service on IIS, Apache, as a stand-alone Windows Service or even in a console application. The below figure shows what I already explained in a graphical way.
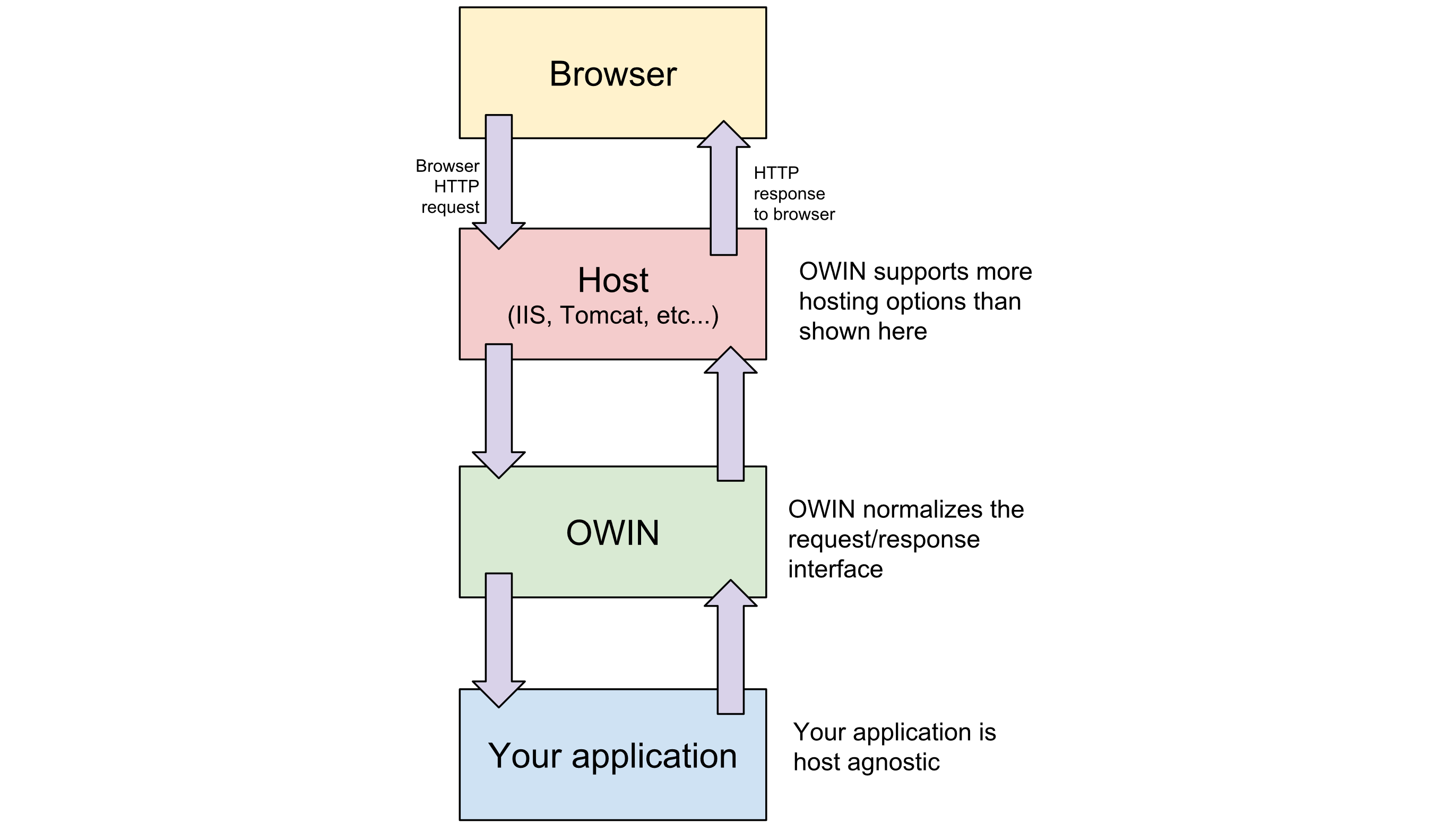
Microsoft OWIN is also middleware oriented, this means it allows the application to have a pipeline of middleware components chained through Func<Task> references. Middleware is software for software, means that software layers that are chained to each other through a mechanism that allows each piece in the chain to hand over data and control of sequence to the next piece by a calling method.
In other word, each piece would have its own lifetime and will act independently as a function or a class (read more about middleware in ASP.NET Core in here).
Of course, when we are talking about middleware, we also expect some mechanism that allows developers to add their own middleware. The Microsoft OWIN provides AppBuilder class which is a concrete implementation of IAppBuilder and allows developers to add middleware into a chain by calling a set of Use extension methods defined in IAppBuilder interface.
using Microsoft.Owin;
using Owin;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ClinetOwinNancy
{
public class CustomMiddleware
{
public void Build(IAppBuilder app)
{
app.Use(Invoke);
}
private Task Invoke(IOwinContext context, Func<Task> next)
{
return next();
}
}
}
Microsoft OWIN Hello World
Now it is time to put hands on OWIN Framework and see how to use it. Before downloading the source from the repository, you need to bear in mind that the following NuGet Packages need to be restored/re-installed on the project after opening it (usually, Visual Studio should take care of this part).
Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.Client {5.2.6}
Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.Core {5.2.6}
Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.Owin {5.2.6}
Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.OwinSelf {5.2.6}
Microsoft.Owin {2.0.2}
Microsoft.Owin.Host.HttpListener {2.0.2}
Microsoft.Owin.Hosting {2.0.2}
Newtonsoft.Json {6.0.4}
Owin {1.0}
Otherwise, you can simply install them by using the following PM command.
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.OwinSelfHost
Using the Code
The following part will explain the use of three prominent classes called Startup, ApiController, and Program, that are involved in keeping the service up and running over the OWIN Framework. For simplicity, please let me call the OWIN Framework, OwinFx from now.
Configure Web API for Self-Host
The AppBuilder (implementor of the IAppBuilder interface) needs to be configured on Self-Hosting mode via HttpConfiguration class. The following code is presenting the steps of such a configuration.
using Owin;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace OwinFxMicroservice
{
public class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder appBuilder)
{
var config = new HttpConfiguration();
CreateHttpConfig(config);
appBuilder.UseWebApi(config);
}
private static void CreateHttpConfig(HttpConfiguration config)
{
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
}
The IAppBuilder is a key interface of Owin.dll that provides a concrete interface for AppBuilder classes which will provide you a Use method to inject the custom middleware in the OWIN pipeline and it looks like the above code:
public interface IAppBuilder
{
IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
object Build(Type returnType);
IAppBuilder New();
IAppBuilder Use(object middleware, params object[] args);
}
Add a Web API Controller
Your custom Web API Controller need to be derived from the abstract class called ApiController which implements two interfaces, IHttpController and IDisposable. This class will, in fact, handle DELETE, GET, POST, PUT requests. In some other frameworks, this class called routs or modules.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace OwinFxMicroservice
{
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
public IEnumerable<string> Get() => new string[] { "Hello", "World", "...!" };
public string Get(int id) => (id == 1) ? "Hello" : (id == 2) ?
"World" : (id == 3) ? "...!" : "No world found... ;-)";
public void Post([FromBody]string value) =>
Console.WriteLine($"The received value is {value}");
public void Put(int id, [FromBody]string value)
{
}
public void Delete(int id)
{
}
}
}
How to Call Your Service?
So far, we developed a very simple service (assume that this service has a Microservice granularity) and now, it is time to see how to use the service. Basically, in this stage, I would like to show you two ways, first, call service from the code, and second, call it via a third party app like Postman which is very useful and handy to test and debug your service before the final publish.
Call Service via HttpClient
.NET allows you to create a new instance of the HttpClient class and pass your Uri (the base address of service plus the route) then use Get, Post, Delete, Put, asynchronously. See the below code:
var client = new HttpClient();
var response = client.GetAsync(new Uri(baseAddress + "api/values")).Result;
this will be the way that we will use to call our developed service from the code. The following part represents the code inside of Program.cs class.
using Microsoft.Owin.Hosting;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
namespace OwinFxMicroservice
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string baseAddress = "http://localhost:9000/";
using (WebApp.Start<Startup>(url: baseAddress))
{
var client = new HttpClient();
#region GET
Console.WriteLine
("///////////////////////// GET HAS BEEN SENT ///////////////////////////////////////");
var response = client.GetAsync(new Uri(baseAddress + "api/values")).Result;
Console.WriteLine(response);
Console.WriteLine(response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result);
#endregion
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue with the POST message.");
Console.ReadLine();
#region POST
Console.WriteLine
("///////////////////////// POST HAS BEEN SENT ///////////////////////////////////");
var stringContent = new StringContent(JsonConvert.SerializeObject("Hello World...!"),
Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
response = client.PostAsync
(new Uri(baseAddress + "api/values"), stringContent).Result;
Console.WriteLine(response);
Console.WriteLine(response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result);
#endregion
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit or call Postman for more tests.");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}
Call Service via Postman
Postman is an API Development Environment which allows you to call invoke HTTP requests from via range of endpoints and at the same time, keep track of the requests and responses. To know more about Postman, I would like to redirect you to the following article from the postman official website.
Send a Get request:
To see how our developed service works with Postman, run the service and create a Get request via Postman (see the following picture) and invoke localhost:9000/api/values route. I assume after this step, you should see the below response on the response body.
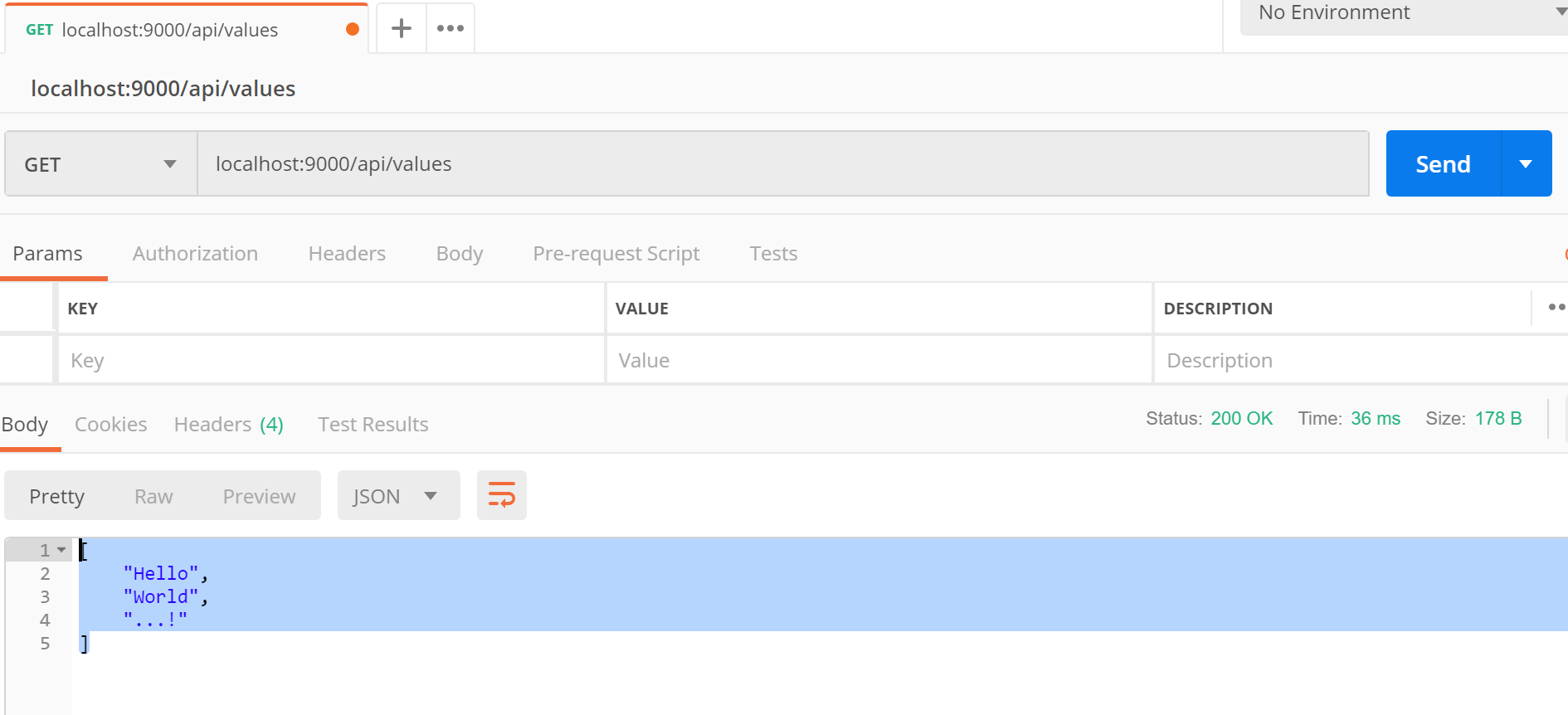
To create a Get request, select the GET method from the combo box and insert the endpoint (localhost:9000/api/values) then hit the Send blue button.
If you try the localhost:9000/api/values/1 then you will get only the "Hello" as result. Note that the type of messages by default are JSON.
Send a Post request
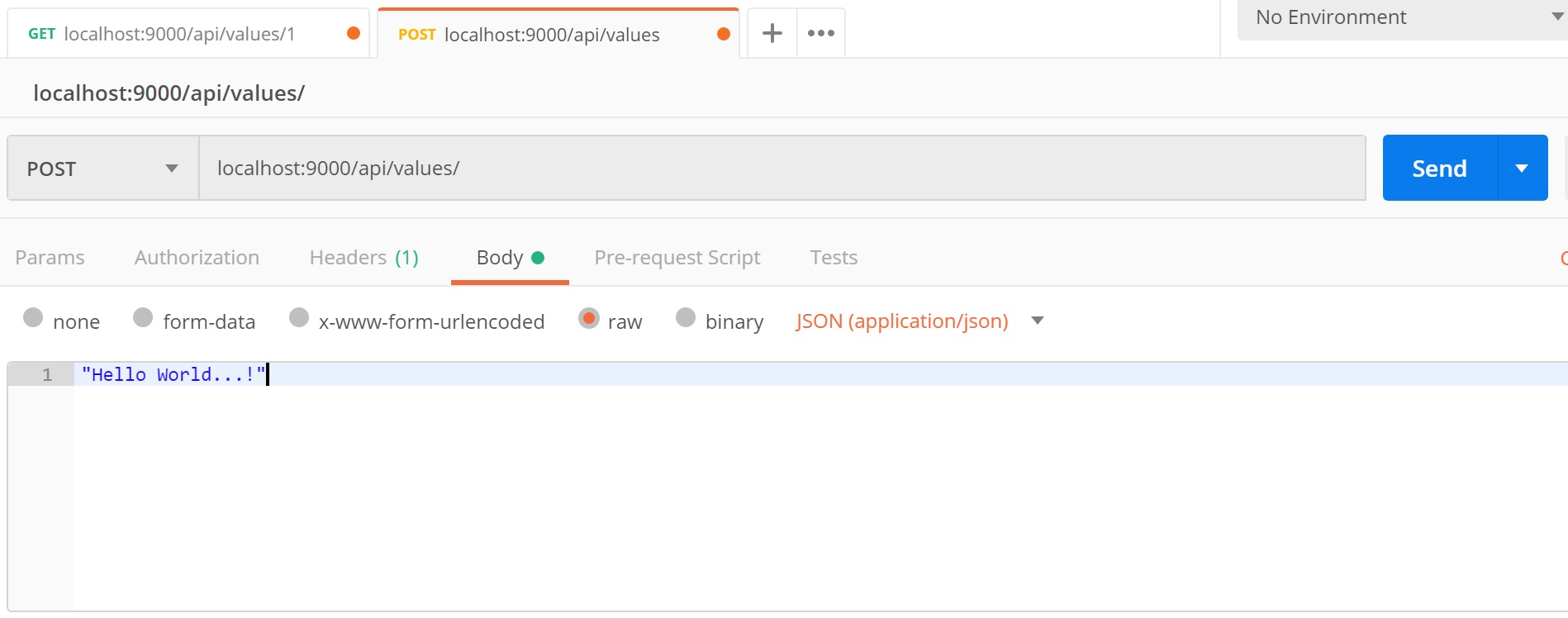
To create a Post request, select the POST method from the combo box and insert the endpoint (localhost:9000/api/values) then go to the Body section and select Raw and set type to JSON and write "Hello World ...!" in the body and hit the Send blue button
Now if you put a breakpoint on the Post method you should be able to debug and see what you got on the service side.
public void Post([FromBody]string value) => Console.WriteLine($"The received value is {value}");
Why NancyFx?
Developers of Nancy says that "Nancy is a lightweight, low-ceremony, framework for building HTTP based services on .NET and Mono. The goal of the framework is to stay out of the way as much as possible and provide a super-duper-happy-path to all interactions". I would not add anything more on this as it is the best description of Nancy, I personally found the use of Nancy very handy and not very complicated.
Nancy is designed as a Domain-Specific Language (DSL) for handling, DELETEGET, HEAD, OPTIONS, POST, PUT and PATCH requests.
The next part of this article will discuss how to use NancyFx to build up a Microservice.
