Sadly, even with React and Redux, there is no one clear way how to handle asynchronous calls to the API (backend) or any other side effects. This article is going to show four ways of solving this problem and compare the pros and cons of each one.
Introduction
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Very often, using React means using React with Redux. Redux is another JavaScript library for managing global state. Sadly, even with these two libraries, there is no one clear way how to handle asynchronous calls to the API (backend) or any other side effects.
In this article, I’m trying to compare different approaches to solving this problem. Let’s define the problem first.
Component X is one of the many components of the web site (or mobile, or desktop application, it’s also possible). X queries and shows some data loaded from the API. X can be page or just part of the page. Important thing that X is a separate component which should be loosely coupled with the rest of the system (as much as possible). X should show loading indicator while data is retrieving and error if call fails.
This article assumes that you already have some experience with creating React/Redux applications.
This article is going to show 4 ways of solving this problem and compare pros and cons of each one. It isn’t a detailed manual of how to use thunk, saga, suspense or hooks.
Code of these examples is available on GitHub.
Initial Setup
Mock Server
For testing purposes, we are going to use json-server. It’s an amazing project that allows to build fake REST API very fast. For our example, it looks like this:
const jsonServer = require('json-server');
const server = jsonServer.create();
const router = jsonServer.router('db.json');
const middleware = jsonServer.defaults();
server.use((req, res, next) => {
setTimeout(() => next(), 2000);
});
server.use(middleware);
server.use(router);
server.listen(4000, () => {
console.log(`JSON Server is running...`);
});
db.json file contains test data in json format.
{
"users": [
{
"id": 1,
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Doe",
"active": true,
"posts": 10,
"messages": 50
},
...
{
"id": 8,
"firstName": "Clay",
"lastName": "Chung",
"active": true,
"posts": 8,
"messages": 5
}
]
}
After starting server, call to the http://localhost:4000/users returns the list of the users with imitation of delay about 2s.
Project and API Call
Now we are ready to start coding. I assume that you already have React project created using create-react-app with Redux configured and ready to use.
If you have any difficulties with it, you can check out this and this article.
The next thing is to create a function to call API (api.js)
const API_BASE_ADDRESS = 'http://localhost:4000';
export default class Api {
static getUsers() {
const uri = API_BASE_ADDRESS + "/users";
return fetch(uri, {
method: 'GET'
});
}
}
Redux-thunk
Redux-thunk is a recommended middleware for basic Redux side effects logic such as simple async logic like request to the API. Redux-thunk itself doesn’t do a lot. It’s just 14!!! Lines of the code. It just adds some “syntax sugar” and nothing more.
Flowchart below helps to understand what we are going to do.
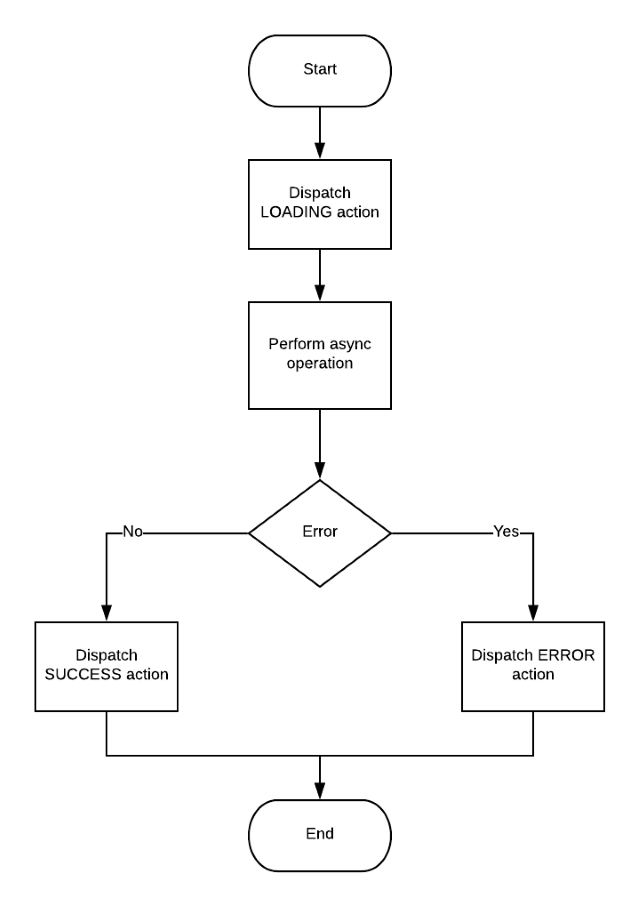
Every time action is performed reducer changes state accordingly. Component maps state to properties and use these properties in render() method to figure out what user should see: loading indicator, data or error message.
To make it work, we need to do 5 things.
1. Install tunk
npm install redux-thunk
2. Add thunk Middleware When Configuring Store (configureStore.js)
import { applyMiddleware, compose, createStore } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from './appReducers';
export function configureStore(initialState) {
const middleware = [thunk];
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ || compose;
const store = createStore(rootReducer, initialState,
composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(...middleware)));
return store;
}
In line 12-13, we also configure redux devtools. A bit later, it will help to show one of the problems with this solution.
3. Create Actions (redux-thunk/actions.js)
import Api from "../api"
export const LOAD_USERS_LOADING = 'REDUX_THUNK_LOAD_USERS_LOADING';
export const LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS = 'REDUX_THUNK_LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS';
export const LOAD_USERS_ERROR = 'REDUX_THUNK_LOAD_USERS_ERROR';
export const loadUsers = () => dispatch => {
dispatch({ type: LOAD_USERS_LOADING });
Api.getUsers()
.then(response => response.json())
.then(
data => dispatch({ type: LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS, data }),
error => dispatch
({ type: LOAD_USERS_ERROR, error: error.message || 'Unexpected Error!!!' })
)
};
It’s also recommended to have actions creators separated (it adds some additional coding), but for this simple case, I think it’s acceptable to create actions “on the fly”.
4. Create reduser (redux-thunk/reducer.js)
import {LOAD_USERS_ERROR, LOAD_USERS_LOADING, LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS} from "./actions";
const initialState = {
data: [],
loading: false,
error: ''
};
export default function reduxThunkReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case LOAD_USERS_LOADING: {
return {
...state,
loading: true,
error:''
};
}
case LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS: {
return {
...state,
data: action.data,
loading: false
}
}
case LOAD_USERS_ERROR: {
return {
...state,
loading: false,
error: action.error
};
}
default: {
return state;
}
}
}
5. Create Component Connected to redux (redux-thunk/UsersWithReduxThunk.js)
import * as React from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import {loadUsers} from "./actions";
class UsersWithReduxThunk extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.props.loadUsers();
};
render() {
if (this.props.loading) {
return <div>Loading</div>
}
if (this.props.error) {
return <div style={{ color: 'red' }}>ERROR: {this.props.error}</div>
}
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Active?</th>
<th>Posts</th>
<th>Messages</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.props.data.map(u =>
<tr key={u.id}>
<td>{u.firstName}</td>
<td>{u.lastName}</td>
<td>{u.active ? 'Yes' : 'No'}</td>
<td>{u.posts}</td>
<td>{u.messages}</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
data: state.reduxThunk.data,
loading: state.reduxThunk.loading,
error: state.reduxThunk.error,
});
const mapDispatchToProps = {
loadUsers
};
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(UsersWithReduxThunk);
I tried to make component as simple as possible. I understand that it looks awful. :)
Loading indicator:

Data:

Error

3 files, 109 line of code (13(actions) + 36(reducer) + 60(component)).
Pros
- “Recommended” approach for react/redux applications
- No additional dependencies. Almost, thunk is tiny :)
- No need to learn new things
Cons
- A lot of code in different places
- After navigation to another page, old data is still in the global state (see picture below). This data is outdated and useless information that consumes memory.
- In case of complex scenarios (multiple conditional calls in one action, etc.), code isn’t very readable

Redux-saga
Redux-saga is a redux middleware library designed to make handling side effects easy and in a readable way. It leverages an ES6 Generators which allows to write asynchronous code that looks synchronous. Also, this solution is easy to test.
From a high level perspective, this solution works the same as thunk. Flowchart from thunk example is still applicable.
To make it work, we need to do 6 things.
1. Install saga
npm install redux-saga
2. Add saga Middleware and Add All Sagas (configureStore.js)
import { applyMiddleware, compose, createStore } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga';
import rootReducer from './appReducers';
import usersSaga from "../redux-saga/sagas";
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware();
export function configureStore(initialState) {
const middleware = [sagaMiddleware];
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ || compose;
const store = createStore
(rootReducer, initialState, composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(...middleware)));
sagaMiddleware.run(usersSaga);
return store;
}
Sagas from line 4 will be added in step 4.
3. Create Action (redux-saga/actions.js)
export const LOAD_USERS_LOADING = 'REDUX_SAGA_LOAD_USERS_LOADING';
export const LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS = 'REDUX_SAGA_LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS';
export const LOAD_USERS_ERROR = 'REDUX_SAGA_LOAD_USERS_ERROR';
export const loadUsers = () => dispatch => {
dispatch({ type: LOAD_USERS_LOADING });
};
4. Create Sagas (redux-saga/sagas.js)
import { put, takeEvery, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects'
import {loadUsersSuccess, LOAD_USERS_ERROR, LOAD_USERS_LOADING, LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS}
from "./actions";
import Api from '../api'
async function fetchAsync(func) {
const response = await func();
if (response.ok) {
return await response.json();
}
throw new Error("Unexpected error!!!");
}
function* fetchUser() {
try {
const users = yield fetchAsync(Api.getUsers);
yield put({type: LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS, data: users});
} catch (e) {
yield put({type: LOAD_USERS_ERROR, error: e.message});
}
}
export function* usersSaga() {
yield takeEvery(LOAD_USERS_LOADING, fetchUser);
}
export default usersSaga;
Saga has quite a steep learning curve, so if you’ve never used and never read anything about this framework, it could be difficult to understand what’s going on here. Briefly, in userSaga function, we configure saga to listen to LOAD_USERS_LOADING action and trigger fetchUsers function. fetchUsers function calls API. If call is successful, then LOAD_USER_SUCCESS action is dispatched, otherwise LOAD_USER_ERROR action is dispatched.
5. Create reducer (redux-saga/reducer.js)
import {LOAD_USERS_ERROR, LOAD_USERS_LOADING, LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS} from "./actions";
const initialState = {
data: [],
loading: false,
error: ''
};
export default function reduxSagaReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case LOAD_USERS_LOADING: {
return {
...state,
loading: true,
error:''
};
}
case LOAD_USERS_SUCCESS: {
return {
...state,
data: action.data,
loading: false
}
}
case LOAD_USERS_ERROR: {
return {
...state,
loading: false,
error: action.error
};
}
default: {
return state;
}
}
}
Reducer is absolutely the same as in thunk example.
6. Create Component Connected to redux (redux-saga/UsersWithReduxSaga.js)
import * as React from 'react';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {loadUsers} from "./actions";
class UsersWithReduxSaga extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.props.loadUsers();
};
render() {
if (this.props.loading) {
return <div>Loading</div>
}
if (this.props.error) {
return <div style={{color: 'red'}}>ERROR: {this.props.error}</div>
}
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Active?</th>
<th>Posts</th>
<th>Messages</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.props.data.map(u =>
<tr key={u.id}>
<td>{u.firstName}</td>
<td>{u.lastName}</td>
<td>{u.active ? 'Yes' : 'No'}</td>
<td>{u.posts}</td>
<td>{u.messages}</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
data: state.reduxSaga.data,
loading: state.reduxSaga.loading,
error: state.reduxSaga.error,
});
const mapDispatchToProps = {
loadUsers
};
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(UsersWithReduxSaga);
Component is also almost the same as in thunk example.
4 files, 136 line of code (7(actions) + 36(reducer) + sagas(33) + 60(component)).
Pros
- More readable code (
async/await) - Good for handling complex scenarios (multiple conditional calls in one action, action can have multiple listeners, canceling actions, etc.)
- Easy to unit test
Cons
- A lot of code in different places
- After navigation to another page, old data is still in the global state. This data is outdated and useless information that consumes memory.
- Additional dependency
- A lot of concepts to learn
Suspense
Suspense is a new feature in React 16.6.0. It allows to defer rendering part of component until some condition is met (for example, data from API loaded).
To make it work, we need to do 4 things (it’s definitely getting better :)).
1. Create cache (suspense/cache.js)
For cache, we are going to use simple-cache-provider which is basic cache provider for react applications.
import {createCache} from 'simple-cache-provider';
export let cache;
function initCache() {
cache = createCache(initCache);
}
initCache();
2. Create Error Boundary (suspense/ErrorBoundary.js)
It’s an Error Boundary to catch errors thrown by Suspense.
import React from 'react';
export class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = {};
componentDidCatch(error) {
this.setState({ error: error.message || "Unexpected error" });
}
render() {
if (this.state.error) {
return <div style={{ color: 'red' }}>ERROR: {this.state.error || 'Unexpected Error'}</div>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;
3. Create Users Table (suspense/UsersTable.js)
For this example, we need to create an additional component which loads and shows data. Here, we are creating resource to get data from API.
import * as React from 'react';
import {createResource} from "simple-cache-provider";
import {cache} from "./cache";
import Api from "../api";
let UsersResource = createResource(async () => {
const response = await Api.getUsers();
const json = await response.json();
return json;
});
class UsersTable extends React.Component {
render() {
let users = UsersResource.read(cache);
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Active?</th>
<th>Posts</th>
<th>Messages</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{users.map(u =>
<tr key={u.id}>
<td>{u.firstName}</td>
<td>{u.lastName}</td>
<td>{u.active ? 'Yes' : 'No'}</td>
<td>{u.posts}</td>
<td>{u.messages}</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
);
}
}
export default UsersTable;
4. Create Component (suspense/UsersWithSuspense.js)
import * as React from 'react';
import UsersTable from "./UsersTable";
import ErrorBoundary from "./ErrorBoundary";
class UsersWithSuspense extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ErrorBoundary>
<React.Suspense fallback={<div>Loading</div>}>
<UsersTable/>
</React.Suspense>
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}
}
export default UsersWithSuspense;
4 files, 106 line of code (9(cache) + 19(ErrorBoundary) + UsersTable(33) + 45(component)).
3 files, 87 line of code (9(cache) + UsersTable(33) + 45(component)) if we assume that ErrorBoundary is a reusable component.
Pros
- No redux needed. This approach can be used without redux. Component is fully independent.
- No additional dependencies (simple-cache-provider is part of the React)
- Delay of showing Loading indicator by setting
dellayMs property - Less lines of code than in previous examples
Cons
Cache is needed even when we don’t really need caching.- Some new concepts need to be learnt (which is part of the React).
Hooks
At the time of writing, this article hooks are not officially released yet and available only in the “next” version. Hooks is indisputably one of the most revolutionary upcoming features which can change a lot in the React world in the nearest future. More details about hooks can be found here and here.
To make it work for our example, we need to do one!!!!!!! thing.
1 Create and Use Hooks (hooks/UsersWithHooks.js)
Here, we are creating 3 hooks (functions) to “hook into” React state.
import React, {useState, useEffect} from 'react';
import Api from "../api";
function UsersWithHooks() {
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState('');
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchData() {
try {
const response = await Api.getUsers();
const json = await response.json();
setData(json);
} catch (e) {
setError(e.message || 'Unexpected error');
}
setLoading(false);
}
fetchData();
}, []);
if (loading) {
return <div>Loading</div>
}
if (error) {
return <div style={{color:
'red'}}>ERROR: {error}</div>
}
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Active?</th>
<th>Posts</th>
<th>Messages</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{data.map(u =>
<tr key={u.id}>
<td>{u.firstName}</td>
<td>{u.lastName}</td>
<td>{u.active ? 'Yes' :
'No'}</td>
<td>{u.posts}</td>
<td>{u.messages}</td>
</tr>
)}
</tbody>
</table>
);
}
export default UsersWithHooks;
1 files, 60 line of code!!!!.
Pros
- No redux needed. This approach can be used without redux. Component is fully independent.
- No additional dependencies
- About 2 times less code than in other solutions
Cons
- For the first look, code looks weird and difficult to read and understand. It will take some time to get used to hooks.
- Some new concepts need to be learnt (which is part of the React)
- Not officially released yet
Conclusion
Let’s organize metrics as a table first.
| | Files | Lines of code | Dependencies | Redux needed? |
| Thunk | 3 | 109 | 0.001 | yes |
| Saga | 4 | 136 | 1 | yes |
| Suspense | 4/3 | 106/87 | 0 | no |
| Hooks | 1 | 60 | 0 | no |
- Redux is still a good option to manage global state (if you have it)
- Each option has pros and cons. Which approach is better depends on project: complexity, use cases, team knowledge, when project is going to production, etc.
- Saga can help with complex use cases
- Suspense and Hooks are worth considering (or at least learning), especially for new projects
That's it — enjoy and happy coding!
History
- 30th January, 2019: Initial version
