Tables can be defined as the structure which contains the data in the database. There can be many ways to create table and to insert data into the table. Some of the ways to create a table are given below.
1. Creation of a Table with the Help of a Create Statement
For example, suppose we want to create a table called tbl_student, then the syntax of creating this table is given below:
CREATE TABLE tbl_Students( [Studentid] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Firstname] [nvarchar](200) , [Lastname] [nvarchar](200) , [Email] [nvarchar](100) )
Let us suppose we want to insert data into the table tbl_students, then we can use the insert statements to insert data into the table.
The insert statement used for inserting the data is given below:
Insert into tbl_students(Firstname,lastname,email) select 'Vivek','Johari',
'Vivek@abc.com' union all select 'Pankaj','Kumar',
'Pankaj@abc.com' union all Select 'Amit','Singh','amit@abc.com'
Here, we can insert multiple rows into the table with the help of a single query mentioned above.
Another way to insert the values into the table tbl_students is:
insert into tbl_students(Firstname,lastname,
email) Values('Manish','Kumar',
'manish@abc.com') Insert into tbl_students(Firstname,
lastname,email) Values('Abhishek','Singh',
'abhishek@abc.com') Insert into tbl_students(Firstname,
lastname,email) Values ('Uma','Sharma','Uma@abc.com')
Here, whenever we need to insert a row into the table, we have to use a separate insert statement.
The result of the above SQL queries can be verified with the help of the following query:
SELECT * FROM tbl_students
Result:
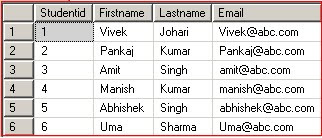
Note: We don't need to insert data into the column Studentid since it is defined as the Identity column and whenever a record is inserted into the table, SQL Server automatically inserts value into this column.
2. Creation of Table with the Help of Another Table
2.1. Suppose we want to create a table tbl_studentinfo which contains a subset of the columns (studentid, Firstname, Lastname) of the table tbl_student, then we can use the following query. Select studentid, Firstname, Lastname into tbl_studentinfo from tbl_students.
This query will create a table tbl_studentinfo having columns studentid, Firstname, Lastname and it contains data of these columns from the table tbl_students. This can be verified with the help of the query given below:
SELECT * FROM tbl_studentinfo
Result:
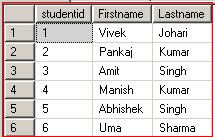
2.2. Suppose we want to create a table which is exactly the copy of a given table, then we can also use the following SQL query:
SELECT * INTO tbl_studentscopy FROM tbl_students
The table tbl_studentscopy created by the above SQL query will contain exactly the same data as tbl_students. This can be verified with the help of the query given below:
SELECT * FROM tbl_studentscopy
Result:
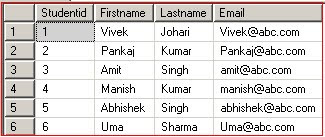
There is another interesting way to insert the values into a table with the help of another table. For example, suppose we have a table named as tbl_Studentsdemo whose structure is given below:
CREATE TABLE tbl_Studentsdemo( [Studentid] [int] IDENTITY(1,
1) NOT NULL, [Firstname] [nvarchar](200) , [Lastname] [nvarchar](200) ,
[Email] [nvarchar](100) )
Now if we want to insert values into the table from the table tbl_students, then we can use the following SQL query to insert the data into the table.
Insert into tbl_Studentsdemo(Firstname,lastname,
email) SELECT Firstname,lastname,email FROM tbl_students
The above query will insert all the data from the table tbl_students into the table tbl_Studentsdemo. Again we can verify it with the help of the given query:
SELECT * FROM tbl_Studentsdemo
Result:

