Introduction
With experience, working with ASP.NET, I noticed some important XHTML tags that are rarely used by web developers, even the experienced ones, so I thought of writing this article to promote them.
Most of the mentioned elements are HTML compatible, but all of them are XHTML compatible. I've tested these elements on Internet Explorer 6 and Firefox 1.5. Also, I've validated the demo project against XHTML 1.1 and XHTML 1.0 Transitional on the W3C Validator.
The elements are optgroup, label, fieldset/legend, col/colgroup and acronym. In this article, I point out the differences in displaying each of these elements between Internet Explorer and Firefox, moreover, I show their relation with ASP.NET. What follows is a quick introduction for each element:
1. optgroup
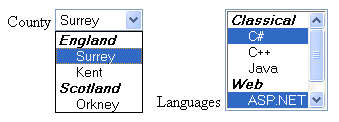
<label for="county">County</label>
<select id="county">
<optgroup label="England">
<option>Surrey</option>
<option>Kent</option>
</optgroup>
<optgroup label="Scotland">
<option>Orkney</option>
</optgroup>
</select>
<label for="languages">Languages</label>
<select size="6" multiple="multiple" id="languages">
<optgroup label="Classical">
<option>C#</option>
<option>C++</option>
<option>Java</option>
</optgroup>
<optgroup label="Web">
<option>ASP.NET</option>
<option>PHP</option>
</optgroup>
</select>
The optgroup, which stands for Option Group, is an element that groups a set of option elements, inside a select element, and labels them. It is perfect for showing states and cities, countries and states, and other similar categorized items.
Unfortunately, this element is not generated by any ASP.NET server controls, however, I believe you can easily inherit from the DropDownList, ListBox, or the Item controls and make the necessary modifications to generate it.
2. label

<label for="FirstName">Full Name</label>
<input id="FirstName" type="text" />
Gender:
<label for="male">Male</label>
<input id="male" type="radio" name="gender" />
<label for="female">Female</label>
<input id="female" type="radio" name="gender" />
The label element provides a caption for a form element. Its main attribute is the "for" attribute which will point to the element that you want to provide a caption for.
In addition to providing a caption for the element, label will make selecting the associated element easier; so by clicking on the caption, you will be setting focus to the associated element, as if it is making the caption text a part of the associated element. In the provided demo, try clicking on the word "Full Name" and the text box next to it will be selected; also, when you click on the word "Male", the radio button will be selected.
ASP.NET generates this element for the Text property of the RadioButton and CheckBox server controls (and other controls as well). This explains the secret of setting focus to the control whenever clicking the text next to it. In ASP.NET 2.0, the Label server control has a new attribute AssociatedControlID that will render the control as an HTML label associated to the specified element versus rendering it as a span element.
3. fieldset/legend

<fieldset>
CP is a good place to publish XHTML related articles.
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Information</legend>
<label for="FirstName">Full Name</label>
<input id="FirstName" type="text" />
Gender:
<label for="male">Male</label>
<input id="male" type="radio" name="gender" />
<label for="female">Female</label>
<input id="female" type="radio" name="gender" />
</fieldset>
The fieldset is an element that creates a frame, and legend is an optional element that creates a title for this frame.
In ASP.NET 2.0, there is a new attribute GroupingText for the Panel web control that will render it a legend and fieldset. However, ASP.NET 1.1 doesn't have any standard web control that could generate this element.
4. col/colgroup

<table border="1">
<colgroup>
<col width="150px" />
<col width="10px" />
<col width="220p" />
</colgroup>
<tr>
<td valign="top">1</td>
<td> </td>
<td>2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td>
<td> </td>
<td>4</td>
</tr>
</table>
The colgroup element is a table element. Its only child element is the col element. Each col element affects a column in the table. You can specify attributes that apply to all the columns in the colgroup element, and specific attributes for individual columns in the col element. You can also omit the colgroup element and keep the col elements.
The advantage of using the col element is that you only need to specify an attribute once rather than adding the same attribute across every td element in the column, and the result is less attributes and easier to manage code.
For cross-browser issues, use the width attribute only with the colgroup and col elements because I noticed that Firefox doesn't support all the attributes of the colgroup and col.
Sadly, the ASP.NET's Table and GridView server controls do not generate these elements.
5. acronym

<acronym title="Code Project">CP</acronym> is a good place to publish
<acronym title="Extensible HyperText Markup Language">XHTML</acronym>
related articles.
The acronym element provides a definition for a term via the title attribute. By using this element, you are helping readers who are not familiar with the term, better optimizing your page for search engines and supporting accessibility.
By default, IE 6 doesn't show any sign on the text surrounded by this element; however, Firefox displays a dashed line under it. Both browsers display a tool tip of the full meaning whenever you stop your cursor over it.
If you like this element, have a look at the abbr (abbreviation) element which has a similar role.
Conclusion
I have spotted some elements that I thought need to have extra light on; however, there are more hidden elements to spot like th, tf, base, address, bdo, blockquote, code, dl, dt, dd, and dfn elements.
This article served as a quick reference for each element; for a full list of the attributes and usage, try the W3 Schools, htmldog.com, and you can always go back to the official documentation at the World Wide Web Consortium.
If you found the contents of this article useful, then please remember to vote.
History
- 25th April, 2006 - First version
- 10th May, 2006 - Second version
- 13th May, 2006 - Third version
